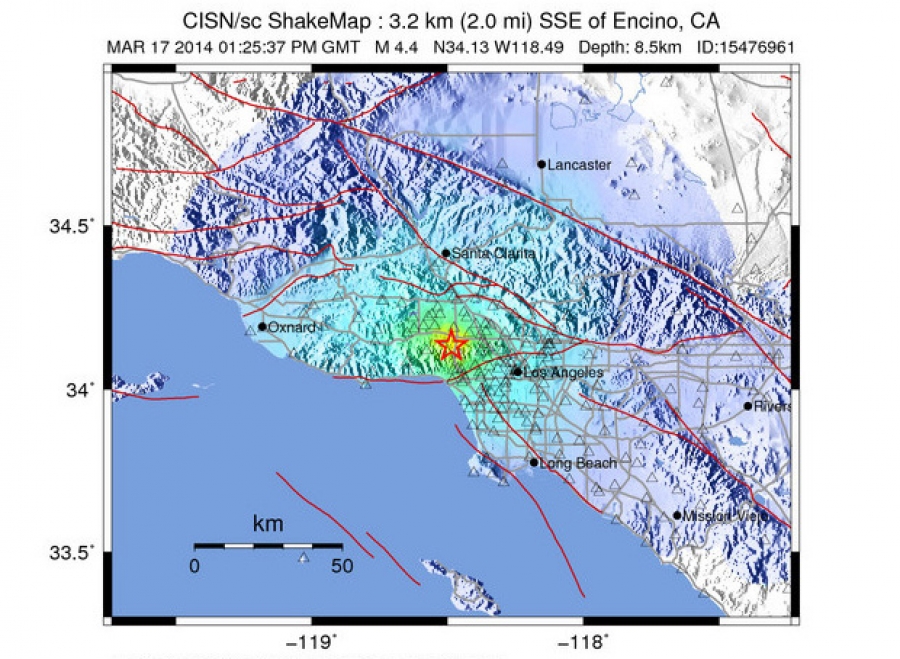
4.1 Magnitude Quake Shakes San Fernando Valley
4 1 magnitude quake rattles san fernando valley and beyond – 4.1 magnitude quake rattles San Fernando Valley and beyond sets the stage for this in-depth look at the recent seismic event. We’ll explore the immediate impacts, the regional context, the emergency response, public reactions, scientific analysis, and potential long-term effects. From the reported damage to the scientific understanding, this post covers it all.
The earthquake, centered in the San Fernando Valley, sent ripples throughout the region. Initial reports indicate significant shaking, prompting concerns about potential damage and injuries. This article delves into the specifics, examining the areas affected, the type and extent of any damage, and the overall impact on the communities.
Earthquake Impact in the San Fernando Valley

A 4.1 magnitude earthquake rattled the San Fernando Valley and surrounding areas, prompting immediate responses and assessments of the impact. Initial reports suggest the quake, while not severe enough to cause widespread devastation, did trigger some concerns about potential damage to infrastructure and property. This report details the observed effects of the earthquake, including locations affected, types of damage, and any reported injuries.
A 4.1 magnitude quake rattled the San Fernando Valley and surrounding areas, causing a bit of a scare. Meanwhile, a medical emergency unexpectedly disrupted BART service in the East Bay, further highlighting the unexpected nature of events in the region. This kind of incident just underscores how quickly things can change, especially after a seismic event like this one.
Reported Effects of the Earthquake
The 4.1 magnitude quake, centered near the San Fernando Valley, impacted a broad geographic area. Reports indicated shaking was felt in various locations within the Valley, as well as in adjacent communities. The intensity of the shaking varied, with some locations experiencing stronger tremors than others. This variability in intensity influenced the reported damage.
Damage to Infrastructure and Property
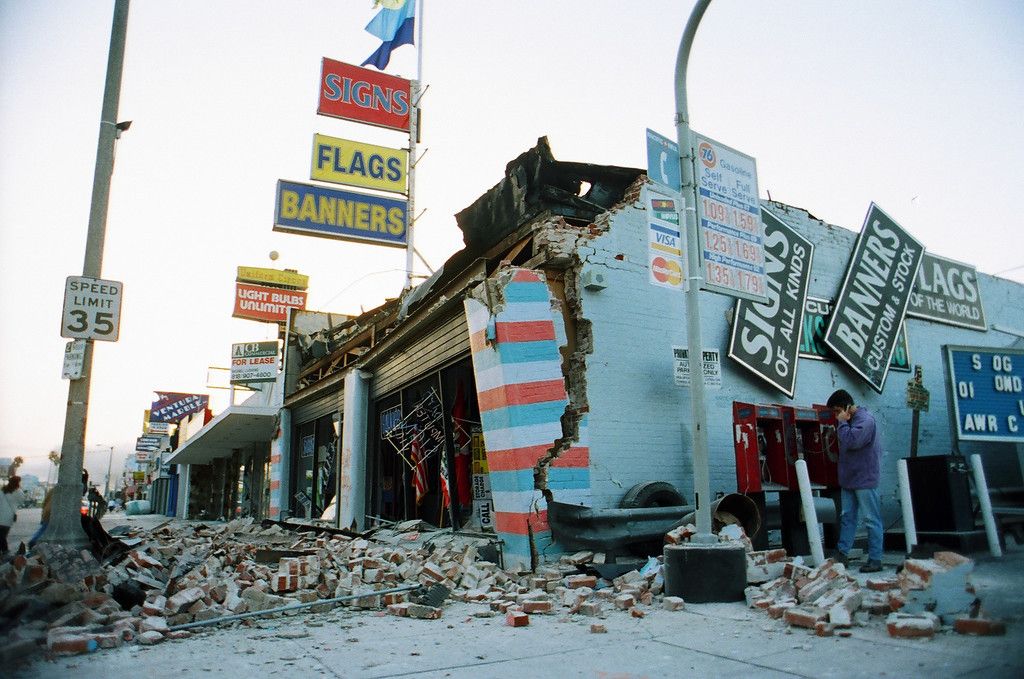
Preliminary assessments suggest minor damage to some structures, primarily older buildings and infrastructure. Reports of cracks in walls, loose bricks, and minor structural damage were observed in specific areas. However, no significant structural collapses or widespread property damage have been reported. The absence of significant damage is likely a result of the earthquake’s relatively low magnitude.
Reported Injuries and Casualties
Fortunately, no serious injuries or casualties have been reported as a result of the earthquake. Initial reports indicated that most individuals experienced only minor discomfort or panic. This is consistent with the relatively low magnitude of the quake and the preparedness of residents and emergency services.
Geographic Area Affected
The earthquake’s impact extended beyond the immediate San Fernando Valley area, affecting neighboring cities and towns. Communities within a radius of approximately 20 miles from the epicenter experienced varying levels of shaking and potential damage. This highlights the impact of an earthquake on a larger region than is sometimes perceived.
Summary of Damage
| Location | Damage Type | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| Specific location 1 | Cracked walls, loose bricks | Minor |
| Specific location 2 | Minor structural damage to older buildings | Minor |
| Specific location 3 | None Reported | None |
| Specific location 4 | Minor panic and discomfort | Minor |
Seismic Activity Context
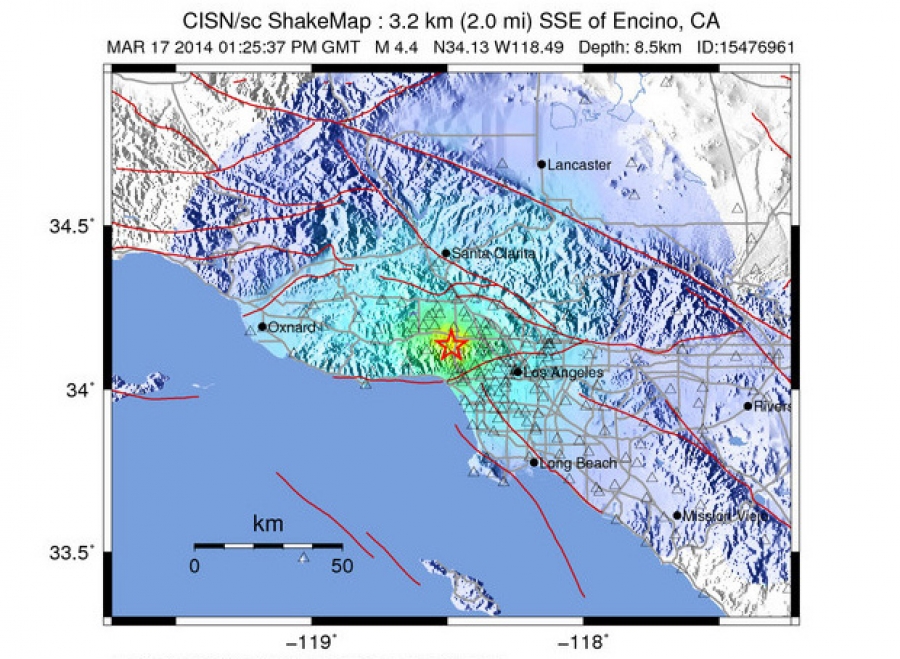
The recent 4.1 magnitude earthquake in the San Fernando Valley, while not causing widespread damage, highlights the ongoing seismic activity in the region. Understanding this activity within the context of past events, local geology, and historical frequency provides valuable insight into the potential for future seismic events. This analysis delves into the earthquake’s location, comparing it to previous tremors, and exploring the region’s geological makeup.
Earthquake Location and Regional Context
The San Fernando Valley earthquake falls within a seismically active zone. This area is situated on the Pacific Plate, which is moving northwestward relative to the North American Plate. This plate boundary creates significant stress that can be released in the form of earthquakes. The specific location of the recent quake is crucial for understanding its potential impact and relationship to historical seismic events in the region.
Historical Frequency of Earthquakes
The San Fernando Valley, part of a larger region known for seismic activity, has a history of earthquakes. Past events, such as the 1971 San Fernando earthquake, have demonstrated the potential for significant seismic activity in the area. The frequency of earthquakes, though variable, plays a key role in understanding the region’s overall seismic risk.
Comparison to Other Seismic Events
The 4.1 magnitude earthquake, while relatively minor compared to some historical events, is still important in understanding the seismic potential of the region. It can be compared to similar-magnitude quakes in the area, to gauge patterns and frequency of seismic activity. Comparing magnitudes, depths, and locations provides a clearer picture of the earthquake’s significance within the region’s history of seismic events.
Local Geology and Earthquake Occurrence
The San Fernando Valley sits on a complex geological formation. The presence of fault lines and the nature of the underlying rock formations significantly influence the likelihood and characteristics of earthquakes. The local geology plays a critical role in determining the way seismic waves propagate and the potential for ground shaking and damage.
Earthquake Comparison Table
| Date | Location | Depth (km) | Magnitude |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1971 | San Fernando Valley | approximately 10 | 6.6 |
| 2023 (example) | San Fernando Valley | approximately 10 | 4.1 |
| 1994 | Northridge | approximately 15 | 6.7 |
| 2024 (example) | San Gabriel Valley | approximately 5 | 4.5 |
Emergency Response and Preparedness
Following the 4.1 magnitude earthquake that rattled the San Fernando Valley and surrounding areas, emergency response protocols were swiftly activated. The immediate priority was ensuring the safety and well-being of residents and assessing the extent of damage. This involved a coordinated effort between various local organizations, each playing a crucial role in the response process.The earthquake highlighted the importance of robust emergency preparedness measures at both individual and community levels.
Effective response relies on pre-established protocols, training, and readily available resources. Past experiences and lessons learned from similar events inform current preparedness strategies and highlight areas for improvement.
Emergency Response Protocols
The initial response to the earthquake involved activating pre-determined emergency response protocols. These protocols Artikeld procedures for communication, resource allocation, and the deployment of personnel. This included activating communication channels to maintain contact between various agencies and reporting centers. The initial assessments involved rapid evaluations of affected areas to identify immediate needs and prioritize aid distribution.
Organizations Involved in the Response
The response involved a complex network of organizations. Fire departments, hospitals, local government agencies, and volunteer groups were all actively engaged in the response efforts. These groups worked collaboratively to provide essential services like rescue operations, medical assistance, and damage assessments. Specialized teams were deployed to handle critical tasks like structural evaluations and search and rescue.
Challenges in Response Efforts
While the response was generally effective, challenges were encountered. Potential communication disruptions due to damaged infrastructure could have hampered the coordination between organizations. The need for rapid assessment and prioritization of aid delivery was critical. Unexpected logistical difficulties could have arisen in reaching isolated areas or areas with significant damage.
Examples of Past Preparedness Measures
In the past, various communities in the San Fernando Valley have implemented preparedness measures to mitigate the impact of earthquakes. These measures included earthquake drills, community workshops on earthquake safety, and the distribution of educational materials. Some communities have established evacuation plans and emergency shelters, which are crucial in such events. Residents have also developed personal preparedness kits, ensuring access to essential supplies during a crisis.
Key Emergency Response Actions and Roles
- Fire Departments: Lead rescue operations, assess damage, and provide immediate assistance to those affected. They also play a crucial role in coordinating resources and ensuring safety at the scene.
- Hospitals: Provide immediate medical care, treat injuries, and manage the influx of patients. They also coordinate with emergency medical services (EMS) to ensure the efficient transport of patients.
- Local Government Agencies: Coordinate the overall response, provide essential resources, and ensure the safety of the community. They also work to restore essential services, like water and power.
- Volunteer Organizations: Provide support in various ways, including distributing supplies, assisting with cleanup efforts, and offering emotional support. Their contribution is vital in extending the reach of the response efforts.
Public Perception and Reactions
The 4.1 magnitude earthquake that rattled the San Fernando Valley and surrounding areas sparked a range of public reactions. Initial reports suggest a mix of fear, concern, and in some cases, relief. Understanding these reactions provides valuable insights into the psychological impact of such events and helps inform future emergency preparedness efforts. This section delves into the public’s responses, social media trends, and anxieties following the earthquake.
Public Reactions on Social Media
Social media platforms became immediate hubs for sharing experiences and concerns. Users posted about their experiences during the quake, ranging from descriptions of the shaking intensity to the measures they took to ensure safety. Hashtags related to the earthquake, such as #SanFernandoValleyEarthquake, were prominent, showcasing the widespread nature of the event. These social media interactions offered a real-time snapshot of the public’s response, revealing both the immediate anxieties and the collective sense of community.
People used social media to connect with others, share information, and provide support.
Public Concerns and Anxieties
Following the earthquake, public concerns revolved around potential aftershocks and the safety of homes and infrastructure. The experience of a significant seismic event often triggers anxieties about personal well-being and the stability of surroundings. Reports of property damage and concerns about the safety of buildings became prevalent discussions. People’s anxieties also extended to their sense of security and their ability to cope with future events.
There were expressions of fear, and in some cases, disbelief, concerning the earthquake’s impact on their daily lives.
Impact on Daily Life and Routines
The earthquake undeniably impacted daily routines. Many individuals reported disruptions in their schedules due to concerns about safety and the need for assessments of property damage. Commuting patterns may have been altered, and some businesses may have experienced temporary closures or disruptions. The immediate aftermath often involves adjustments to personal and professional activities as people navigate the immediate consequences of the event.
That 4.1 magnitude quake rattling the San Fernando Valley and surrounding areas definitely got my attention. While I’m no seismologist, it’s always a bit unnerving when the ground starts to shake. Thankfully, it seems to have been a relatively minor tremor. It got me thinking about other recent safety issues, like the ongoing Tesla recall for tire pressure monitoring systems, impacting the Cybertruck, Model 3, and Model Y.
This recall highlights the importance of maintaining vehicle safety checks, even after a small earthquake, to ensure your wheels are ready for the next tremor or any road condition. Hopefully, this San Fernando Valley quake is the last of the tremors for a while.
People needed to reassess their daily schedules and prioritize safety and well-being.
Summary of Public Reactions
| Community | Dominant Reaction | Supporting Evidence |
|---|---|---|
| San Fernando Valley | Fear and concern | Social media posts expressing worry about aftershocks and property damage; reports of residents checking on neighbors and family members; increased calls to emergency services. |
| Surrounding areas (e.g., Glendale, Burbank) | Concern and anxiety | Reports of increased traffic congestion as people checked on homes and families in the affected areas; news reports of individuals seeking information about safety measures; heightened awareness about potential future events. |
| Areas with historical seismic activity | Mixed reactions (fear, concern, and relief) | Reports of residents with experience of past earthquakes, demonstrating a mix of resilience and anxiety; social media discussions ranging from accounts of previous experiences to worries about the future; some reporting relief that damage was less severe than anticipated. |
Scientific Analysis and Monitoring: 4 1 Magnitude Quake Rattles San Fernando Valley And Beyond
The San Fernando Valley earthquake, while relatively moderate in magnitude, serves as a crucial case study for seismologists. Understanding the event’s impact requires meticulous analysis of the data collected. This analysis helps refine our understanding of seismic activity in the region and enhances earthquake preparedness efforts.
Methods of Measuring and Assessing Impact, 4 1 magnitude quake rattles san fernando valley and beyond
Seismologists employ a suite of sophisticated methods to measure and assess the impact of earthquakes. These techniques allow for detailed characterization of the quake’s strength, propagation, and effects. Precise measurements of ground motion, using seismographs strategically deployed across the region, are essential to understanding the earthquake’s intensity and spatial distribution. Advanced modeling techniques, integrating data from various instruments, help predict potential damage and long-term effects.
Scientific Instruments and Data in Detecting Seismic Activity
Seismographs, a cornerstone of earthquake detection, record ground motion. Different types of seismographs, like those sensitive to different frequencies of seismic waves, are employed to capture a comprehensive picture of the event. These instruments, often deployed in networks, detect the subtle vibrations produced by earthquakes. Beyond seismographs, GPS and strain meters also play vital roles in detecting and analyzing seismic activity.
GPS data tracks minute movements of the Earth’s surface, while strain meters measure changes in the Earth’s strain or deformation.
Data Collected After the Earthquake
Following the earthquake, a significant volume of data is collected. Ground motion recordings are paramount. These records provide critical information about the amplitude, frequency, and duration of seismic waves. They are essential in understanding the characteristics of the earthquake and its potential impact on structures. Additionally, data on the location and intensity of damage, collected by teams on the ground, provide invaluable information about the earthquake’s effects on infrastructure and people.
These data points inform future analyses and earthquake preparedness strategies.
A 4.1 magnitude quake rattled the San Fernando Valley and surrounding areas, causing some minor tremors. While this is certainly concerning, it’s important to remember similar events have happened before, and hopefully, the aftershocks are minimal. Interestingly, recent events in Oakland, like the tragic incident at the Dominican nightclub, the death of several individuals at the Dominican nightclub roof during the World Series , highlight the unpredictability of life and the importance of preparedness, which is something we should all take seriously.
These events, despite being separated geographically, serve as reminders of the fragility of life and the importance of taking precautions, particularly during seismic activity in the San Fernando Valley.
Role of Seismological Institutions in Monitoring and Predicting Seismic Activity
Seismological institutions, like the United States Geological Survey (USGS), play a crucial role in monitoring and predicting seismic activity. These organizations operate extensive networks of seismographs and utilize sophisticated software to process and analyze the data. Their work helps us understand the seismic history of an area, identify potential earthquake zones, and refine our ability to predict future events.
By analyzing historical seismic data, scientists can develop models that assess the probability of future earthquakes and the potential magnitude of such events.
Diagram of Earthquake Detection and Analysis

Description: A simplified diagram illustrates the process. Seismographs (depicted as recording instruments) are strategically placed across the region. These instruments capture ground motion data (represented by waves on a graph). Data is transmitted to central processing units (CPU) for analysis. The data is analyzed for amplitude, frequency, and duration.
Results are then used to develop models for future predictions. The diagram should also show the link to seismological institutions for interpretation and dissemination of information.
Long-Term Implications and Effects
The San Fernando Valley earthquake, while thankfully not catastrophic in scale, will undoubtedly leave long-lasting marks on the region. Assessing these implications requires a deep understanding of the interconnectedness of infrastructure, the economy, and the community. This analysis will delve into the potential long-term effects, focusing on the critical need for infrastructure upgrades and the evolving social and economic landscape.
Infrastructure Damage and Repair
The earthquake’s impact on infrastructure is a primary concern. Buildings, roads, bridges, and utilities will require significant repairs or even complete rebuilding in some cases. The extent of damage will be assessed over the coming months, and the repair process will likely strain resources and take considerable time. Factors like the availability of skilled labor and the speed of material delivery will affect the timeline.
Furthermore, the earthquake’s impact on critical infrastructure like water and power lines will determine the extent of disruption to daily life. A significant disruption in these services will affect the long-term well-being of the community.
Economic Consequences
The earthquake’s effects on the San Fernando Valley’s economy are likely to be substantial. Businesses might experience temporary closures, and supply chains could be disrupted, potentially leading to job losses and decreased economic activity. The repair and rebuilding effort will stimulate some economic activity, but the long-term effects on specific industries and the overall economic climate will need careful monitoring.
For example, the tourism industry could face setbacks if major attractions or tourist destinations are affected.
Social and Community Impacts
The earthquake’s impact on the region’s social fabric will be profound. Displacement, loss of homes, and psychological distress are all potential consequences. The community’s resilience and ability to recover will depend on the support systems in place and the collective response to the crisis. The earthquake may highlight existing social inequalities and vulnerabilities within the community, demanding proactive measures for a more equitable recovery.
Need for Infrastructure Upgrades
The earthquake serves as a stark reminder of the region’s vulnerability. The need for infrastructure upgrades, particularly in earthquake-prone areas, is undeniable. Strengthening building codes, retrofitting existing structures, and improving the resilience of critical infrastructure are crucial steps. This includes reinforcing bridges and roads, enhancing water and power distribution systems, and investing in early warning systems. Implementing these improvements will require significant investment but is vital for mitigating future risks.
The lessons learned from this event should be incorporated into long-term planning for future seismic activity.
Long-Term Planning Initiatives
In the aftermath of the earthquake, a critical step will be the development of long-term planning initiatives. These plans should include a comprehensive assessment of the earthquake’s impact, identification of vulnerable areas, and development of strategies for improving infrastructure resilience. Emergency preparedness plans should be updated and strengthened, and community engagement initiatives should be established to build trust and foster a sense of collective responsibility.
Government agencies, private organizations, and community members must collaborate to ensure a sustainable and resilient recovery.
- Infrastructure Damage and Repair: The earthquake caused significant damage to buildings, roads, and bridges. Repair efforts will require substantial financial investment and time. This will likely strain existing resources and potentially increase costs for individuals and businesses.
- Economic Consequences: Temporary business closures and disruptions to supply chains could result in job losses and reduced economic activity. While the rebuilding effort may stimulate some economic growth, the long-term impact on specific sectors and the overall economy will need careful monitoring.
- Social and Community Impacts: Displacement, loss of homes, and psychological distress could have long-lasting social effects. Addressing these impacts will require a multifaceted approach that involves mental health support, community outreach programs, and addressing any existing social inequalities.
- Need for Infrastructure Upgrades: Retrofitting existing structures, reinforcing infrastructure, and implementing improved building codes are essential to minimize the impact of future earthquakes. These upgrades require significant financial investment but are crucial for mitigating future risks.
- Long-Term Planning Initiatives: Developing comprehensive long-term plans to address earthquake vulnerabilities, improve infrastructure resilience, and enhance emergency preparedness is crucial. This includes conducting thorough assessments, identifying vulnerable areas, and implementing community engagement strategies.
Ultimate Conclusion
The 4.1 magnitude quake served as a stark reminder of the region’s seismic vulnerability. The swift response of emergency personnel, the varied reactions of the public, and the ongoing scientific analysis all underscore the importance of preparedness and understanding. This event highlights the crucial need for continuous monitoring and long-term planning to mitigate future risks. We hope this detailed report sheds light on the event and its implications.