IDS vs IPS Network Security Solutions
IDS vs IPS network security solutions are crucial in today’s digital world. Understanding the nuances between Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) is key to fortifying your network. This exploration dives deep into the core differences, mechanisms, deployment considerations, and performance aspects of these vital security tools.
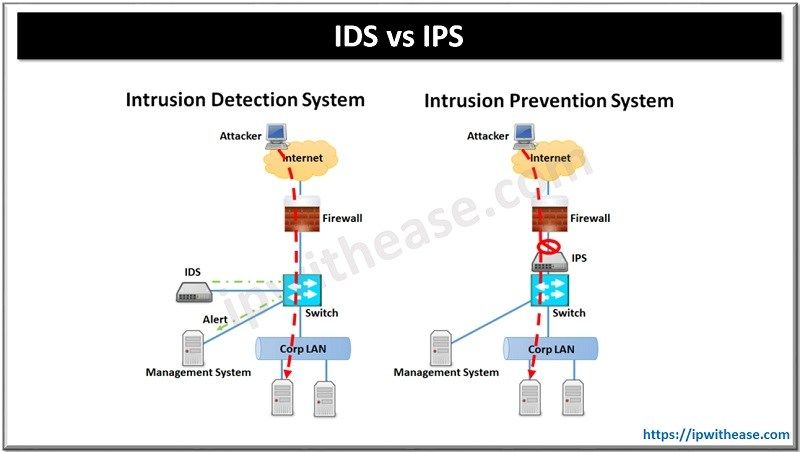
IDS, acting as a vigilant watchman, monitors network traffic for malicious activity. IPS, on the other hand, takes a proactive stance, actively blocking potential threats. Choosing the right solution hinges on a thorough understanding of their individual strengths and weaknesses.
Introduction to Network Security Solutions: Ids Vs Ips Network Security Solutions
Network security is paramount in today’s interconnected digital world. The increasing reliance on online services and the proliferation of data breaches highlight the critical need for robust security measures to protect sensitive information and maintain the integrity of networks. Protecting against unauthorized access, malicious attacks, and data breaches is no longer a luxury but a fundamental requirement for organizations and individuals alike.Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) are crucial components in safeguarding networks.
They act as vigilant guardians, constantly monitoring network traffic for suspicious activities and reacting accordingly. Understanding the intricacies of IDS and IPS technologies is essential for effective network security implementation.
Fundamental Concepts of IDS and IPS
IDS and IPS technologies are designed to detect and, in the case of IPS, prevent malicious activities targeting a network. IDS systems monitor network traffic for known attack patterns and security anomalies, generating alerts when suspicious behavior is detected. IPS systems, building upon IDS capabilities, actively intervene to block or mitigate identified threats, thereby preventing attacks from succeeding.
Core Differences Between IDS and IPS
The primary distinction between IDS and IPS lies in their response mechanisms. IDS systems primarily act as early warning systems, identifying potential threats and alerting administrators to take corrective actions. IPS systems, on the other hand, actively prevent intrusions by blocking malicious traffic or taking other preventative measures. This proactive approach distinguishes IPS from IDS, offering a more robust layer of security.
Comparison of IDS and IPS
| Feature | IDS | IPS |
|---|---|---|
| Detection Method | Passive monitoring of network traffic for known attack signatures and anomalies. It analyzes network packets and system logs to identify malicious activities. | Active monitoring of network traffic and real-time analysis for suspicious patterns and known attack signatures. It dynamically analyzes the packets and logs. |
| Response | Alerts administrators of detected threats. The administrator then decides how to respond (e.g., blocking, investigation). | Prevents intrusions by blocking malicious traffic, dropping packets, or initiating other countermeasures. It acts as an immediate response. |
| Deployment Location | Can be deployed in various locations, including inline or out-of-band, to monitor network traffic. | Typically deployed inline in the network path, allowing it to inspect and potentially block malicious traffic in real-time. |
IDS Mechanisms
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) are crucial components of a robust network security strategy. They act as vigilant sentinels, constantly monitoring network traffic for suspicious patterns and activities that might indicate malicious intent. Effective IDS deployments require a deep understanding of the diverse methods used to identify and respond to threats. This section delves into the mechanisms employed by IDS to detect malicious activity, including the strengths and weaknesses of each method.IDS mechanisms can be broadly categorized into signature-based and anomaly-based detection.
Each approach has its own advantages and disadvantages, and a hybrid approach often proves most effective in contemporary network security.
Signature-Based Detection
This method relies on predefined patterns or signatures of known malicious activities. IDS systems are pre-programmed with a database of attack signatures, which represent the characteristics of various malicious code, exploits, and malicious network behaviors. When network traffic matches a stored signature, the IDS raises an alert.This approach is highly effective against known threats. Its strength lies in its ability to quickly identify and block attacks for which the signature is already in the database.
However, it suffers from a significant limitation: it is ineffective against previously unknown or zero-day attacks. New malware frequently evolves, making it difficult to maintain a comprehensive signature database.
IDS vs. IPS network security solutions are crucial for protecting systems, but sometimes seemingly unrelated events can highlight the importance of these technologies. For example, a recent incident involving a report of cat food milk being reported to the Los Gatos Police Department, as detailed in this news story cat food milk called in to los gatos police , reminds us that even seemingly bizarre situations can mask a vulnerability or malicious activity.
Ultimately, robust IDS and IPS systems are vital for identifying and preventing more serious security threats.
Anomaly-Based Detection
This method focuses on identifying deviations from normal network behavior. Anomaly-based IDS monitors network traffic for unusual patterns, creating a baseline of normal activity. Any significant departure from this baseline triggers an alert. This method is particularly valuable in detecting zero-day attacks or novel forms of malicious activity, as it doesn’t rely on prior knowledge of the threat.While effective in detecting previously unseen threats, anomaly-based detection is prone to generating false positives.
This means it might raise alerts for legitimate network activity that simply deviates from the established norm. This can lead to a high volume of alerts that need careful analysis, impacting network performance and potentially causing unnecessary disruptions.
Common IDS Attack Signatures
- Port Scanning: A series of connection attempts to various ports on a target system.
- Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks: Overwhelming a target system with traffic, making it unavailable.
- SQL Injection: Malicious code injected into SQL queries to compromise databases.
- Brute-Force Attacks: Repeated attempts to guess passwords or other authentication credentials.
- Malware Downloads: Identifying malicious code being downloaded from malicious websites or sources.
These examples represent a small fraction of the vast number of attack signatures used by IDS systems. Regular updates to the signature database are essential to maintain effectiveness.
IDS Sensors and Functionalities
Different types of sensors are deployed to monitor various network segments and traffic. This provides a comprehensive view of the network’s security posture.
| Sensor Type | Functionality |
|---|---|
| Network-based Sensors | Monitor network traffic flowing through the network infrastructure, such as routers and switches. They analyze network packets for malicious activity. |
| Host-based Sensors | Monitor activities on individual computers or servers, detecting malicious behavior originating from within a system. |
| Wireless Sensors | Monitor wireless network traffic, identifying malicious activity on Wi-Fi networks. |
| Application-based Sensors | Monitor specific applications and services for malicious activity, like unauthorized access or attempts to manipulate application data. |
These sensors work in conjunction to provide a comprehensive security solution. The choice of sensor type depends on the specific needs and architecture of the network being protected.
IPS Mechanisms
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) take network security a step further than Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS). While IDS primarily monitors network traffic for malicious activity, IPS actively intervenes to prevent attacks. This proactive approach is crucial in today’s threat landscape, where swift action is often the difference between a successful attack and a secure network. Understanding the mechanisms used by IPS is essential for implementing effective security strategies.
IPS Prevention Methods
IPS employs various methods to prevent malicious activity. Two primary approaches are signature-based prevention and anomaly-based prevention. Each method has its own strengths and weaknesses, and a robust IPS deployment often combines both for comprehensive protection.
Signature-Based Prevention
This method relies on pre-defined signatures or patterns that match known malicious code or attack sequences. When the IPS detects a match, it takes action to block or mitigate the threat.
- Effectiveness: Signature-based prevention is highly effective against known threats, as it can identify and block attacks that have already been documented.
- Limitations: Its effectiveness is limited to known threats. New or unknown attacks, polymorphic malware, or zero-day exploits will not be recognized.
Anomaly-Based Prevention
This method works by establishing a baseline of normal network activity. Any deviations from this baseline are flagged as potential threats. The IPS can be configured to either block or alert on these anomalies.
- Effectiveness: Anomaly-based prevention is valuable in detecting zero-day exploits or unknown attacks that do not match known signatures. It can also detect unusual patterns of behavior that could indicate malicious activity.
- Limitations: It can generate a high volume of false positives. This can lead to network disruptions if not properly configured. Establishing an accurate baseline for normal activity can be challenging and requires careful monitoring.
IPS Prevention Mechanisms
An IPS employs a variety of prevention mechanisms, which can be categorized as follows:
- Packet Filtering: Examining network packets for malicious content or patterns, and discarding those deemed harmful.
- Connection Filtering: Controlling network connections by identifying and rejecting suspicious connections or those exhibiting abnormal behavior.
- Application Control: Preventing specific applications or services from initiating or receiving connections that could be exploited.
- Protocol Enforcement: Ensuring compliance with defined network protocols and rejecting connections that violate these protocols.
- Stateful Inspection: Examining the context of network connections to detect malicious activity more effectively.
IPS Attack Blocking and Mitigation
The IPS process for blocking and mitigating attacks can be described as follows:
- Detection: The IPS monitors network traffic for malicious activity based on pre-defined signatures or deviations from normal activity.
- Analysis: The detected activity is analyzed to determine its nature and potential impact.
- Response: Based on the analysis, the IPS can take action to block the attack, such as dropping malicious packets, disconnecting malicious connections, or quarantining infected systems.
- Logging: The entire process, including detection, analysis, and response, is logged for auditing and future analysis.
Deployment and Implementation Considerations
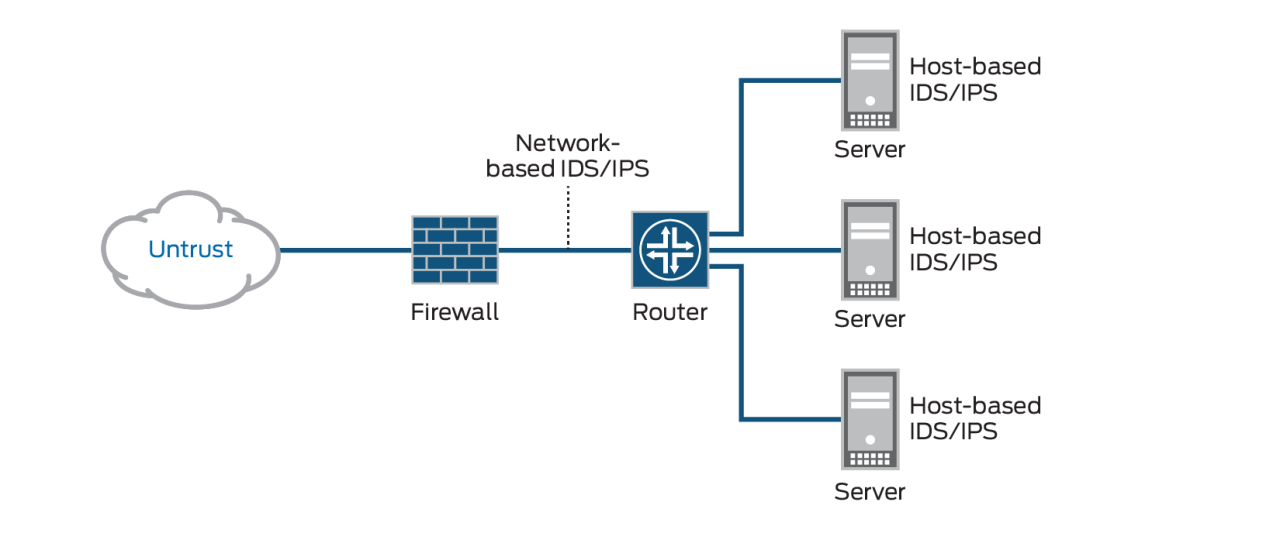
Deploying Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) effectively is crucial for robust network security. Proper deployment considers various factors, including the network’s architecture, security policies, and available resources. A well-implemented IDS/IPS can significantly reduce vulnerabilities and enhance overall security posture.Choosing the right deployment strategy and configuration is critical to the success of an IDS/IPS solution. This involves understanding the different deployment options, evaluating your specific needs, and carefully configuring the system for optimal performance and efficiency.
Understanding the nuances of network-based, host-based, and cloud-based deployments will allow you to tailor the solution to your specific network topology.
IDS vs. IPS network security solutions are crucial for protecting systems, but understanding their differences is key. San Jose’s PGE accountability regarding its energy utility, like san jose pge accountability energy utility , highlights the need for robust security measures. Ultimately, choosing the right IDS or IPS solution depends on the specific threats and vulnerabilities a company faces, ensuring comprehensive protection.
Deployment Scenarios
Different deployment scenarios cater to varying network needs. Network-based IDS/IPS solutions monitor and analyze network traffic flowing through the network infrastructure. Host-based systems, conversely, focus on monitoring and analyzing activity on individual hosts within the network. Cloud-based deployments offer scalability and flexibility, often using cloud-native security tools. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Factors to Consider
Several key factors influence the choice between network-based, host-based, and cloud-based IDS/IPS solutions. Network traffic volume significantly impacts the suitability of different approaches. A high-volume network might benefit from a network-based solution, while a low-volume network could effectively utilize a host-based system. Security policies should align with the chosen solution. A strict security policy often necessitates more comprehensive and granular monitoring.
Budget constraints can also play a significant role, as cloud-based solutions might have varying costs based on usage.
Configuration and Management
Effective configuration and ongoing management are vital for IDS/IPS systems. Configuration involves setting up the system’s rules and policies to match your security requirements. This includes defining which types of traffic are considered malicious and how the system should respond. Regular monitoring and updates are essential for ensuring the system remains effective against emerging threats. Implementing robust logging and reporting capabilities will facilitate incident response and provide crucial insights into potential vulnerabilities.
Deployment Strategies for Various Network Topologies
The choice of deployment strategy depends heavily on the specific network topology. For a star topology, a network-based IDS/IPS placed at the central hub can monitor all traffic. In a ring topology, strategically placed IDS/IPS devices can provide comprehensive monitoring of traffic flow. A hybrid network topology might benefit from a combination of network-based and host-based solutions for optimal coverage.
Example Deployment Strategies
| Network Topology | Deployment Strategy | Justification |
|---|---|---|
| Star Topology | Centralized network-based IDS/IPS at the hub | Ensures comprehensive monitoring of all traffic within the network. |
| Ring Topology | Distributed network-based IDS/IPS devices placed strategically along the ring | Provides comprehensive monitoring of traffic traversing the ring, enhancing detection of threats. |
| Hybrid Topology | Combination of network-based and host-based IDS/IPS solutions | Offers comprehensive coverage, utilizing network-based for traffic analysis and host-based for individual host monitoring. |
Performance and Efficiency
IDS/IPS systems, while crucial for network security, can significantly impact network performance. Understanding these impacts and employing optimization techniques is essential for maintaining both security and operational efficiency. Balancing security needs with network throughput is a key challenge for network administrators.Optimizing IDS/IPS performance involves a multifaceted approach, considering both hardware and software aspects. The goal is to minimize latency and overhead without sacrificing security effectiveness.
This section delves into strategies for achieving this balance.
Performance Impact on Network Throughput
IDS/IPS systems analyze network traffic in real-time, which inherently introduces overhead. This overhead can manifest as latency, potentially slowing down legitimate network communication. The impact is directly proportional to the volume of traffic analyzed and the complexity of the rulesets employed by the IDS/IPS. For instance, a high-volume network with stringent security rules will experience a greater performance impact compared to a low-volume network with fewer rules.
Methods to Optimize IDS/IPS Performance, Ids vs ips network security solutions
Several methods can mitigate the performance impact of IDS/IPS systems. Hardware optimization, including utilizing high-performance network cards and processing units, plays a vital role. Efficient rule sets and proper configuration are equally important. Employing lightweight signature databases and prioritizing rules can significantly reduce the processing load. Additionally, appropriate tuning parameters can streamline the analysis process.
Factors Influencing Detection Accuracy and False Positives
Detection accuracy and the frequency of false positives are directly linked to the quality and relevance of the rules and signatures. A comprehensive set of rules, encompassing a wide range of attack patterns, increases the likelihood of identifying malicious activities. However, an overly broad or poorly written rule set can lead to numerous false positives, misclassifying legitimate traffic as malicious.
The IDS/IPS system’s ability to distinguish between normal and malicious traffic is crucial in minimizing false positives.
Role of Tuning Parameters in Achieving Optimal Performance
Tuning parameters, such as the sensitivity level of the intrusion detection system, significantly influence performance. A higher sensitivity setting may increase the detection rate of threats, but also raise the likelihood of false positives. Conversely, a lower sensitivity setting might miss some threats but significantly reduce false positives. Careful tuning of these parameters is crucial to strike the right balance between security and performance.
This process often involves iterative testing and adjustments based on observed network behavior. For instance, adjusting thresholds for suspicious activity levels can significantly refine the system’s effectiveness without sacrificing throughput. Network administrators should regularly monitor system performance metrics to fine-tune parameters and maintain optimal security.
IDS and IPS systems are crucial for network security, but the recent news about the Musk team seeking access to sensitive taxpayer data at the IRS ( musk team seeks access to sensitive taxpayer data at irs ) highlights a critical vulnerability in data protection. While IDS (Intrusion Detection Systems) alert on potential threats, IPS (Intrusion Prevention Systems) actively block them.
This whole situation underscores the need for robust security measures, including not just IDS/IPS solutions, but also comprehensive oversight of sensitive data handling by organizations and government agencies.
Security Challenges and Trends
IDS/IPS solutions are constantly evolving to keep pace with the ever-changing threat landscape. New and sophisticated attacks require robust defenses capable of adapting to emerging vulnerabilities and attack vectors. This necessitates a deep understanding of current and future security challenges, alongside the continuous development of innovative technologies.Emerging threats and vulnerabilities demand that IDS/IPS solutions adapt and evolve to address them effectively.
The increasing sophistication of malware and the rise of targeted attacks, like ransomware and advanced persistent threats (APTs), pose significant challenges. Exploits of zero-day vulnerabilities and the use of polymorphic malware further complicate the detection process. Moreover, the expanding attack surface created by the proliferation of IoT devices and cloud-based services creates new entry points for malicious actors.
Emerging Threats and Vulnerabilities
The threat landscape is constantly evolving, demanding that IDS/IPS solutions be proactive and adaptable. Advanced persistent threats (APTs) and ransomware attacks are becoming more sophisticated, requiring advanced detection and mitigation capabilities. The rise of automated attacks, often orchestrated by botnets, requires systems that can rapidly identify and respond to these automated patterns. Moreover, the exploitation of vulnerabilities in less-secure applications and systems, including IoT devices, continues to be a major concern.
New Trends in IDS/IPS Technologies
Cloud-based IDS/IPS solutions are gaining significant traction. These solutions offer scalability and flexibility, enabling organizations to adapt their security posture to changing needs. They can also leverage the collective intelligence of multiple data sources, offering a wider range of threat detection capabilities. Machine learning (ML) is also being integrated into IDS/IPS, enabling more sophisticated threat detection and prevention capabilities.
ML algorithms can identify patterns and anomalies that traditional signature-based systems may miss. This allows for faster detection and response to emerging threats.
Common Security Challenges in IDS/IPS Implementation
Implementing IDS/IPS solutions effectively can present numerous challenges. False positives, where legitimate activity is misclassified as malicious, can lead to performance issues and security disruptions. The sheer volume of network traffic can overwhelm IDS/IPS systems, leading to performance bottlenecks and potential missed threats. Balancing the need for comprehensive coverage with system performance and efficiency is crucial. Additionally, the continuous updates required to keep signatures and algorithms up-to-date pose a challenge.
Adapting to new threats and ensuring continued effectiveness demands constant monitoring and tuning.
Framework for Adapting to Evolving Security Threats
A robust framework for adapting to evolving security threats requires a multi-faceted approach. Regularly reviewing and updating threat intelligence feeds is paramount. This ensures the IDS/IPS solutions have the latest threat signatures and indicators. Implementing a proactive security posture that includes vulnerability assessments and penetration testing can help identify and mitigate weaknesses in the system. Continuous monitoring and evaluation of the IDS/IPS system’s performance are vital to identify and address potential issues.
Furthermore, fostering a culture of security awareness within the organization is essential to ensure that employees are aware of potential threats and how to avoid them.
Practical Examples
IDS/IPS solutions are more than just theoretical concepts; they’re vital components in today’s dynamic cybersecurity landscape. Real-world examples demonstrate their effectiveness in preventing attacks and mitigating risks. This section delves into practical applications, highlighting successful implementations and integrations with other security tools.
Real-World Attack Prevention Examples
IDS/IPS systems have proven their worth in numerous scenarios. For instance, a financial institution deployed an IDS solution that detected and blocked a sophisticated phishing campaign targeting customer accounts. The system flagged suspicious login attempts and email communications, preventing unauthorized access and potential financial losses. Another example involves a web hosting provider that leveraged an IPS to identify and mitigate a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack.
The IPS, in real-time, blocked malicious traffic, maintaining service availability for legitimate users.
Integration with Other Security Tools
IDS/IPS systems are not isolated entities. They often integrate seamlessly with other security tools, enhancing overall security posture. For example, an organization might integrate their SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) system with their IDS to provide a centralized view of security events. This consolidated approach allows for better threat detection, correlation, and response. Sophisticated solutions can also integrate with vulnerability scanners to proactively address potential weaknesses in the network.
By automating threat response and analysis, these combined tools improve efficiency and reduce response times.
Vendor Comparison Table
The market offers a variety of IDS/IPS solutions from different vendors. Here’s a simplified comparison table to illustrate key features and capabilities:
| Vendor | Solution Name | Key Features | Pricing Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vendor A | IDS-Pro | High accuracy in malware detection, real-time threat blocking, strong API integration | Subscription-based, tiered pricing |
| Vendor B | IPS-Shield | Robust DDoS protection, deep packet inspection, adaptable to various network topologies | Per-user/per-device licensing |
| Vendor C | NetworkFort | Advanced anomaly detection, customizable rules, automated incident response capabilities | Per-CPU/per-core licensing |
Note: This table is a simplified representation and does not include all vendors or features. Actual features and pricing models may vary. Thorough research is crucial before selecting an IDS/IPS solution.
Case Study: Successful IDS/IPS Implementation
“In 2022, a large telecommunications company implemented a next-generation IDS/IPS solution across its global network. The solution, incorporating advanced machine learning algorithms, significantly reduced the number of security incidents. The company observed a 40% decrease in unauthorized access attempts and a 25% reduction in malware infections. This success demonstrates the significant impact of a well-implemented IDS/IPS system in a complex environment.”
Ultimate Conclusion
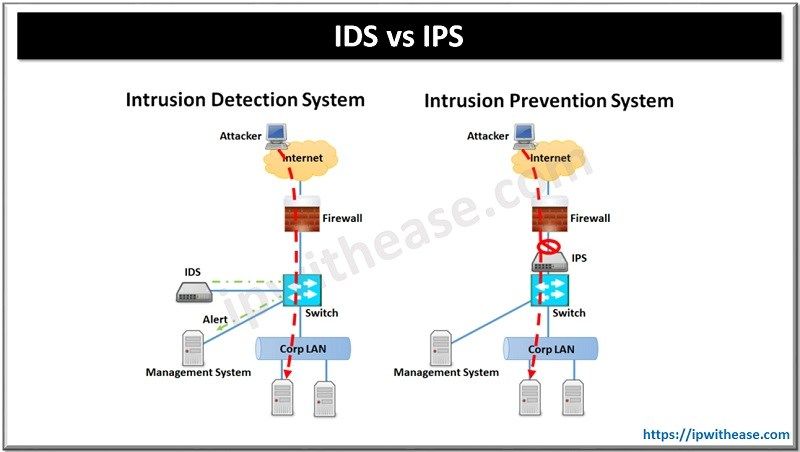
In conclusion, IDS and IPS are both essential components of a robust network security strategy. While IDS focuses on detecting intrusions, IPS steps in to prevent them. The optimal approach involves a blend of both, tailored to specific network needs and security policies. Considering factors like network traffic, budget, and evolving threats, organizations can deploy a layered security solution that minimizes vulnerabilities and maximizes protection.