Mobile App Security Scanner A Deep Dive
Mobile app security scanner is crucial for protecting your applications from evolving threats. This guide delves into the intricacies of these vital tools, exploring various types of vulnerabilities they detect and the methods they use. We’ll also compare popular scanners, highlighting key features, pricing, and supported platforms. Understanding these scanners empowers developers to create more secure apps, ultimately protecting users’ data and privacy.
From the fundamental functionalities to advanced vulnerability analysis techniques, this in-depth look covers the full spectrum of mobile app security. We’ll explore how these scanners help detect vulnerabilities early in the development lifecycle, ultimately bolstering app security. The guide also examines different testing methods, integrations, report generation, and crucial selection criteria for developers to consider.
Introduction to Mobile App Security Scanners
Mobile applications are increasingly crucial for businesses and individuals, handling sensitive data and critical functions. Unfortunately, these apps can harbor vulnerabilities that expose this data to cyber threats. Mobile app security scanners play a vital role in identifying and mitigating these risks, protecting users and organizations from potential breaches.These scanners are automated tools that systematically analyze mobile applications for various security flaws.
Their purpose is not just to detect weaknesses but also to provide actionable insights and recommendations for remediation, thus significantly improving the overall security posture of the application.
Types of Security Vulnerabilities Detected
Mobile applications can be susceptible to a wide range of security vulnerabilities. Scanners are designed to identify common issues like insecure data storage, lack of authentication, and improper authorization. Furthermore, they can detect vulnerabilities related to network communication, such as insecure communication channels and potential man-in-the-middle attacks. They also scrutinize the application’s code for injection flaws, cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities, and potential issues with insecure libraries.
Methods Employed by Scanners
Mobile app security scanners employ various methods to assess applications. Static analysis involves examining the application’s codebase without executing it. This method helps identify vulnerabilities in the code structure. Dynamic analysis, on the other hand, involves executing the application in a controlled environment and observing its behavior. This approach uncovers runtime vulnerabilities and potential exploits.
Hybrid analysis combines both static and dynamic analysis to provide a comprehensive security assessment. Some scanners also use symbolic execution, which analyzes the application’s code in a symbolic representation, allowing for more comprehensive vulnerability detection.
Comparison of Popular Mobile App Security Scanners
The market offers a range of mobile app security scanners with varying features, pricing models, and supported platforms. Choosing the right scanner requires careful consideration of the specific needs and resources of the organization.
Scanner Comparison Table
| Scanner | Features | Pricing | Supported Platforms |
|---|---|---|---|
| AppScan | Robust static and dynamic analysis, comprehensive vulnerability detection, reporting and remediation assistance | Typically enterprise-level pricing, subscriptions | Android, iOS |
| Checkmarx | Strong static analysis capabilities, advanced vulnerability detection, integrations with CI/CD pipelines | Enterprise-level pricing, subscriptions | Android, iOS |
| OWASP ZAP | Open-source, versatile for both web and mobile applications, community support | Free | Android, iOS (through emulation or testing frameworks) |
| Fortify | Wide range of security analysis capabilities, strong integration with development tools | Enterprise-level pricing, subscriptions | Android, iOS |
Key Features and Functionality
Mobile app security scanners are essential tools for developers and security professionals alike. These automated systems play a critical role in identifying vulnerabilities within mobile applications before they can be exploited by malicious actors. By proactively uncovering potential weaknesses, these scanners contribute to the overall security posture of the application and mitigate the risk of data breaches or other security incidents.These scanners analyze various aspects of the app, including its code, libraries, and interactions with external systems.
This comprehensive analysis allows them to pinpoint potential vulnerabilities and provide detailed reports, enabling developers to address these issues before they impact users. Understanding the specific functionalities and the types of vulnerabilities targeted is crucial for leveraging these tools effectively.
Core Functionalities of Scanners
Mobile app security scanners employ a variety of techniques to identify potential security flaws. They examine the application’s source code, analyze dependencies, and simulate real-world attack scenarios. These scans often incorporate static and dynamic analysis methods, providing a more comprehensive assessment of the app’s security posture.
Types of Vulnerabilities Targeted
Mobile applications are susceptible to a wide range of vulnerabilities. These scanners are designed to detect common issues such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), insecure data storage, and authentication flaws. They also often look for vulnerabilities in third-party libraries and dependencies, which can introduce significant security risks if not properly vetted. These scanners provide a vital early warning system for potential weaknesses in the application.
Security Checks Performed by Scanners
Mobile app security scanners perform a range of security checks to identify vulnerabilities. These checks typically include analyzing code for common patterns indicative of vulnerabilities, verifying the integrity of libraries and dependencies, simulating user interactions to identify potential vulnerabilities in the application’s logic, and scrutinizing the application’s data handling practices. These scans can be customized based on the specific vulnerabilities a developer or security team wishes to address.
Examples of Detected Vulnerabilities, Mobile app security scanner
Scanners can identify vulnerabilities like insecure storage of sensitive data, such as user credentials or financial information. They can also detect SQL injection vulnerabilities, where malicious SQL code is injected into the application’s queries, potentially allowing attackers to gain unauthorized access to the database. Another common vulnerability is cross-site scripting (XSS), where attackers can inject malicious scripts into the application, which can be executed by other users.
Early Detection of Vulnerabilities
Early detection of vulnerabilities is paramount in minimizing the impact of security breaches. Mobile app security scanners provide an automated way to identify potential security issues during the development process, allowing developers to address them before the application is deployed to end-users. This proactive approach saves significant resources and prevents potential security incidents.
Security Checks Performed by Scanners (Table)
| Security Check | Description |
|---|---|
| Code Analysis | Examines the application’s source code for patterns indicative of vulnerabilities like SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and insecure data handling. |
| Dependency Analysis | Evaluates the integrity and security of third-party libraries and frameworks used in the application. |
| Dynamic Analysis | Simulates user interactions and executes the application to identify vulnerabilities in its logic and behavior. |
| Data Handling Analysis | Checks the application’s handling of sensitive data, such as user credentials and financial information, for insecure storage and transmission. |
| Authentication and Authorization Analysis | Assesses the application’s authentication and authorization mechanisms to identify vulnerabilities that could allow unauthorized access. |
Vulnerability Detection and Analysis
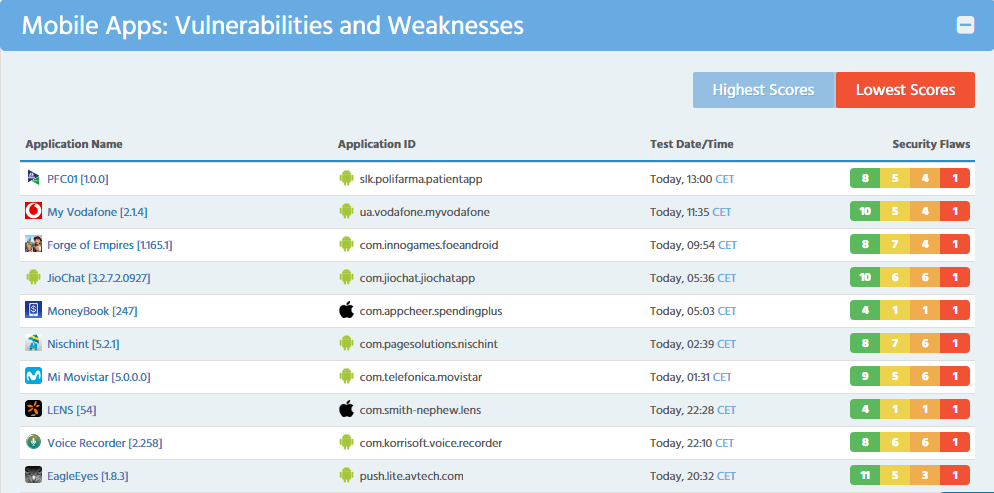
Mobile app security scanners are crucial tools for identifying potential weaknesses in applications. These vulnerabilities, if left unaddressed, can expose sensitive data, compromise user accounts, and lead to significant financial and reputational damage. Thorough vulnerability detection and analysis is the cornerstone of a robust security posture.Understanding the methods used by these scanners to pinpoint and categorize vulnerabilities is key to effective remediation.
Different types of vulnerabilities require different detection strategies. Analysis techniques are vital for understanding the root causes of flaws and crafting targeted fixes.
Vulnerability Detection Process
The process of vulnerability detection involves automated and manual techniques to scrutinize the application’s code, structure, and behavior. Automated scanners use predefined rules and patterns to identify known vulnerabilities, while manual analysis employs deeper inspection to uncover complex or novel issues. This layered approach increases the chances of detecting a wide spectrum of vulnerabilities. Static analysis, for example, examines the code without executing it, while dynamic analysis observes the app’s behavior during runtime.
This combination helps provide a comprehensive view of the application’s security.
Mobile app security scanners are crucial these days, especially considering how much sensitive data we store on our phones. Just think about the recent incident involving cat food milk being called in to the Los Gatos Police department cat food milk called in to los gatos police. While seemingly bizarre, it highlights the importance of robust security measures in preventing similar issues from affecting apps we use daily.
A good security scanner can identify potential vulnerabilities before they become major problems.
Examples of Vulnerability Detection
Scanners identify vulnerabilities by examining code for common patterns. For instance, a SQL injection vulnerability might be detected by recognizing suspicious SQL queries within the application’s code. Similarly, cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities are often identified by analyzing user input handling routines. A missing authentication mechanism might be detected by scanning for the absence of critical security controls.
Each vulnerability type has unique detection signatures and patterns that scanners are trained to recognize.
Vulnerability Analysis Techniques
Various techniques are employed for analyzing vulnerabilities. Static analysis examines the application’s codebase without executing it. This method identifies vulnerabilities based on code structure and syntax. Dynamic analysis, conversely, executes the application under controlled conditions, observing its behavior and identifying vulnerabilities during runtime. Hybrid analysis combines both static and dynamic approaches to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the application’s security.
Fuzzing, a technique that injects invalid or unexpected data into the application, is also used to uncover vulnerabilities.
Analysis Report Generation
The analysis report summarizes the detected vulnerabilities, providing details on their severity, potential impact, and suggested remediation strategies. Reports typically include the location of the vulnerability within the code, the vulnerability type, and a description of how the vulnerability could be exploited. Detailed explanations and actionable advice for fixing the vulnerabilities are crucial. The report helps developers understand the nature of the issue and implement effective solutions.
Comparison of Vulnerability Analysis Methods
Static analysis is typically faster and cheaper than dynamic analysis, but it might miss vulnerabilities that only appear during runtime. Dynamic analysis provides a more accurate picture of vulnerabilities that manifest during execution, but it is often more resource-intensive and time-consuming. Hybrid analysis attempts to combine the strengths of both approaches, providing a more complete security assessment.
Mobile app security scanners are crucial these days, especially with the rise of app-based services. Thinking about how much effort goes into crafting a great app, like the dedication of the three filmmakers striving to make it to Cinequest, three filmmakers strive to make it to Cinequest , it’s important to ensure those apps are safe and secure.
A robust scanner can help identify vulnerabilities before they become major problems.
Common Vulnerabilities and Their Impact
| Vulnerability | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| SQL Injection | Unauthorized data access, modification, or deletion; database compromise. |
| Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) | User session hijacking, data theft, and malicious code execution on vulnerable user accounts. |
| Improper Authentication | Unauthorized access to sensitive information and application functionality. |
| Missing Authorization | Unauthorized access to sensitive resources or functionality. |
| Sensitive Data Exposure | Exposure of sensitive data, potentially leading to identity theft or financial loss. |
Mobile App Security Testing Methods
Mobile application security scanners utilize a variety of testing methods to identify vulnerabilities. These methods vary in their scope and depth, enabling security analysts to systematically assess different aspects of an application’s security posture. Understanding these diverse approaches is crucial for effectively utilizing security scanners and mitigating potential risks.Mobile app security testing methods are not monolithic. They range from automated scans that look for known vulnerabilities to more manual techniques that probe for unexpected behaviors.
The choice of method depends heavily on the specific context of the application, its functionality, and the potential threat landscape. Selecting appropriate testing methods helps ensure comprehensive coverage and accurate identification of weaknesses.
Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
SAST tools analyze the source code of an application without executing it. This approach helps identify vulnerabilities in the code’s design, logic, and implementation. SAST methods are effective at catching coding errors, insecure configurations, and vulnerabilities like SQL injection or cross-site scripting (XSS) that are inherent in the code.SAST tools typically use a variety of techniques including:
- Code analysis to detect coding flaws.
- Rule-based approaches to identify known vulnerabilities.
- Pattern recognition to find potentially insecure patterns in the code.
The data collected during SAST includes the identified vulnerabilities, their severity ratings, and the lines of code where the vulnerabilities reside. Limitations include the inability to assess vulnerabilities arising from runtime configurations or interactions with external systems. A scenario for SAST would be scanning the Android Java code of a mobile banking application for potential SQL injection flaws during development.
Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)
DAST methods analyze an application’s behavior during runtime. This approach involves simulating user interactions and observing the application’s responses to detect vulnerabilities like insecure API usage, authentication bypasses, and session management flaws. DAST tools can identify vulnerabilities that static analysis might miss.DAST tools typically employ techniques such as:
- Automated attack simulations against the application’s API.
- Input validation testing to check for vulnerabilities in handling user input.
- Testing different user roles and functionalities to identify access control flaws.
Data collected includes detailed logs of application behavior, error messages, and responses to different inputs. Limitations include the inability to analyze the internal code structure and difficulty in identifying complex vulnerabilities that are not triggered during the testing phase. A DAST scenario involves simulating a user login to a social media app to check for potential session hijacking vulnerabilities.
Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST)
IAST methods combine elements of SAST and DAST. They analyze the application’s code while it is running, allowing for a more comprehensive assessment. IAST tools often insert probes into the application’s runtime environment to monitor and detect suspicious activities. This approach provides a more comprehensive security assessment by identifying vulnerabilities in both the code and its execution.
- Monitoring of code execution to detect runtime vulnerabilities.
- Use of probes and agents to intercept and analyze network traffic.
- Real-time feedback and identification of vulnerabilities.
Collected data includes details of the execution path, runtime errors, and identified vulnerabilities. IAST limitations include the need for specialized tools and potentially higher resource consumption. A scenario for IAST involves monitoring the execution of a mobile payment application’s backend API during a transaction to catch vulnerabilities in data handling.
Penetration Testing
Penetration testing involves simulating real-world attacks against an application to identify vulnerabilities. This is a manual process where security professionals use various techniques to exploit potential weaknesses in the application’s security mechanisms. The goal is to gain unauthorized access, extract sensitive data, or disrupt service.
- Manual testing using techniques like social engineering or exploiting known vulnerabilities.
- Automated tools are often used to aid in the reconnaissance phase.
- Deep dive analysis of application behavior and security controls.
The collected data includes detailed reports on identified vulnerabilities, their exploitability, and the impact on the application. Penetration testing limitations include the potential for high costs, difficulty in simulating all possible attack scenarios, and the requirement for skilled security professionals. A scenario for penetration testing involves mimicking a malicious actor attempting to gain access to sensitive user data in a mobile banking application.
Table of Mobile App Security Testing Methods
| Method | Description | Data Collected | Limitations | Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAST | Analyzes source code | Vulnerabilities, severity, code location | Doesn’t cover runtime issues | Finding SQL injection flaws in Java code |
| DAST | Analyzes application during runtime | Application behavior, error messages | Can’t analyze internal code structure | Simulating a user login to detect session hijacking |
| IAST | Combines SAST and DAST | Execution path, runtime errors | Needs specialized tools | Monitoring API calls during a payment transaction |
| Penetration Testing | Simulates real-world attacks | Vulnerability details, exploitability | High cost, limited attack scenarios | Attempting to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data |
Scanner Integrations and Deployment: Mobile App Security Scanner
Integrating mobile app security scanners seamlessly into development workflows is crucial for proactive security. This integration process ensures that security checks are performed consistently throughout the development lifecycle, reducing vulnerabilities and enhancing the overall security posture of the application. Effective deployment across different environments, whether testing, staging, or production, is equally important to maintain a consistent level of security scrutiny.Deployment strategies need to be tailored to specific development platforms and environments.
The choice of integration methods and infrastructure plays a significant role in the efficiency and effectiveness of the security scanning process. This allows developers to focus on building features rather than constantly addressing security vulnerabilities.
Integration into Development Workflows
Efficient integration into the development workflow is essential for continuous security checks. This reduces the risk of introducing vulnerabilities during the coding process. Integrating scanners into CI/CD pipelines ensures that security testing is performed automatically and frequently, which is vital for maintaining a high level of security throughout the development cycle. This automated process can be set up to run scans on every code commit or on a scheduled basis, ensuring consistent security checks.
Deployment in Different Environments
Deployment in various environments, including development, testing, staging, and production, requires careful consideration. The infrastructure for each environment needs to be optimized to handle the specific security scanning requirements. The infrastructure requirements vary based on the environment and the scale of the application. The approach to deployment will differ based on the size of the application and the resources available.
Infrastructure Requirements
Effective scanner deployment requires suitable infrastructure. This includes robust servers with adequate processing power, storage capacity, and network bandwidth to handle large-scale scans and analysis. Scalability is a crucial factor, as the volume of data processed by the scanner can vary greatly depending on the application size. This infrastructure should be able to accommodate growth and changes in the development process.
Integration Options for Various Development Platforms
Different development platforms require tailored integration strategies. The choice of integration method will depend on the specific development platform being used. Choosing the right integration method is essential for streamlining the security scanning process and ensuring its effectiveness.
| Development Platform | Integration Options |
|---|---|
| React Native | Integration via npm packages or custom scripts |
| Flutter | Integration using Dart packages and custom scripts |
| Ionic | Integration via npm packages or custom scripts |
| Native Android/iOS | Integration via command-line tools or SDKs |
Deployment Scenarios
Different deployment scenarios demand distinct approaches. For example, a small-scale project might utilize a single server, whereas a large-scale enterprise application might require a distributed system of servers to handle the volume of data and the scalability needs.
- Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD): Integration into CI/CD pipelines allows automated security scans at each stage of the development process. This ensures that vulnerabilities are detected early, minimizing the impact on the project.
- Dedicated Security Testing Environments: Creating separate testing environments allows for comprehensive security testing without impacting the development or production environments. This isolated testing environment ensures that the scanner does not interfere with the normal operation of the application.
- Automated Scheduled Scans: Implementing automated scheduled scans can monitor the application for vulnerabilities and ensure that security measures are consistently enforced. This routine checking helps prevent unexpected breaches.
Report Generation and Remediation
Mobile app security scanners generate detailed reports outlining vulnerabilities found during the testing process. These reports are crucial for developers to understand the weaknesses in their applications and take corrective actions. Thorough reporting and remediation are vital steps to enhancing app security and protecting user data.The process of remediation involves more than just fixing the identified vulnerabilities; it often requires a broader security strategy to prevent future issues.
This includes updating security protocols, employing robust code review processes, and regularly testing for new vulnerabilities. A proactive approach to security, supported by detailed reports, is key to building resilient and trustworthy mobile applications.
Report Generation Methods
Security scanners employ various methods to generate vulnerability reports. Static analysis tools examine the app’s codebase without running it, identifying potential vulnerabilities based on coding patterns. Dynamic analysis tools, on the other hand, run the application in a controlled environment to detect vulnerabilities during runtime. Hybrid approaches combine both static and dynamic analysis techniques for a more comprehensive assessment.
These different methods contribute to a holistic understanding of the app’s security posture.
Vulnerability Report Format
A well-structured vulnerability report is essential for effective remediation. Reports typically include details such as the vulnerability type, affected code section, severity level, potential impact, and recommended remediation steps. The format often utilizes tables and clear descriptions to present the findings in a user-friendly manner.
Steps for Addressing Vulnerabilities
Remediation involves a systematic approach to address identified vulnerabilities. This usually includes:
- Understanding the Vulnerability: Carefully analyze the description of the vulnerability to understand its potential impact and how it could be exploited.
- Prioritization: Assign a severity level to each vulnerability based on its potential impact. Prioritize high-severity vulnerabilities for immediate remediation.
- Code Modification: Implement the recommended remediation steps to fix the vulnerability. This may involve updating code, adding security controls, or modifying configurations.
- Testing and Validation: Thoroughly test the modified code to ensure the vulnerability is resolved and that no new vulnerabilities have been introduced. Use various testing methods to validate the fix.
- Documentation: Document the remediation process, including the changes made, the vulnerability fixed, and the testing performed.
This methodical approach is crucial to ensure that vulnerabilities are addressed effectively and efficiently.
Effective Remediation Strategies
Effective remediation strategies go beyond simply fixing the identified vulnerabilities. They encompass a holistic approach that includes:
- Input Validation: Implement robust input validation mechanisms to prevent malicious data from affecting the application.
- Security Frameworks: Utilize established security frameworks and standards to guide the development process.
- Regular Updates: Regularly update libraries and dependencies to address known vulnerabilities.
- Security Training: Provide security training to developers to enhance their understanding of security best practices.
- Code Reviews: Conduct regular code reviews to identify potential vulnerabilities early in the development cycle.
Adopting these strategies strengthens the overall security posture of the application and reduces the risk of future attacks.
Vulnerability Report Template
A template for a comprehensive vulnerability report can include the following sections:
- Summary: A concise overview of the report’s findings and recommendations.
- Vulnerability Details: A detailed description of each identified vulnerability, including its type, severity, and location in the application.
- Remediation Steps: Specific instructions on how to address each vulnerability, including code changes and configuration adjustments.
- Impact Assessment: An evaluation of the potential impact of each vulnerability, including potential financial or reputational damage.
- Severity Levels: A table displaying the severity of each vulnerability.
This detailed template ensures a complete and structured approach to vulnerability reporting.
Vulnerability Severity Table
The following table illustrates a possible format for organizing vulnerability severity:
| Severity Level | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Critical | High risk of significant damage | System-wide compromise, data loss |
| High | Significant risk of damage | Data breaches, system outages |
| Medium | Moderate risk of damage | Partial data exposure, limited system disruption |
| Low | Minimal risk of damage | Minor data exposure, negligible system disruption |
This table provides a standardized way to categorize vulnerability severity and prioritize remediation efforts.
Scanner Selection and Evaluation Criteria

Choosing the right mobile application security scanner is crucial for effective security testing. A poorly selected tool can lead to missed vulnerabilities, wasted resources, and a false sense of security. Careful evaluation based on specific needs and priorities is essential to ensure the chosen scanner aligns with the application’s complexity and the organization’s security posture.Selecting a mobile app security scanner requires a methodical approach, considering various factors that go beyond just the advertised features.
Understanding the specific needs of your applications and the technical capabilities of different scanners is critical for successful implementation.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Scanner
The effectiveness of a security scanner relies heavily on factors beyond just its advertised features. Consideration should be given to factors such as the scanner’s ability to handle different mobile platforms (iOS, Android, hybrid), the depth and breadth of its vulnerability detection capabilities, and its integration with existing development workflows.
Mobile app security scanners are crucial these days, especially given the rise in cyber threats. Tragically, recent events like the Oakland fentanyl death of the husband of a California deputy attorney general highlight the importance of vigilance in all aspects of our lives. Understanding vulnerabilities in apps, like those used by law enforcement officials, is paramount, especially when considering the sensitive data they often handle.
Thorough security checks are a critical part of safeguarding sensitive information, much like ensuring safety protocols in high-risk situations. Strong security practices, like those used in mobile app security scanners, are just as important as personal vigilance. oakland fentanyl death husband california deputy attorney general is a sobering reminder of the need for comprehensive security measures in all applications.
- Platform Compatibility: Assess the scanner’s support for various mobile operating systems, including iOS, Android, and potentially hybrid frameworks. A scanner capable of analyzing different platforms ensures comprehensive coverage.
- Vulnerability Coverage: The scanner’s detection capabilities are paramount. Investigate the specific types of vulnerabilities it can identify, including common weaknesses like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and insecure data handling. Thorough coverage is vital.
- Integration Capabilities: A seamless integration with existing development pipelines is essential. The scanner should integrate with CI/CD tools and IDEs to streamline the testing process and automate security checks.
- Scalability and Performance: Consider the scanner’s ability to handle large and complex applications. Performance issues can significantly impact testing time, and scalability is essential for larger organizations.
- Reporting and Remediation Support: The scanner should provide clear and actionable reports, detailing identified vulnerabilities, their severity, and recommended remediation steps. Effective reporting facilitates faster resolution of issues.
Evaluation Criteria for Mobile App Security Scanners
Evaluating a mobile app security scanner requires a multi-faceted approach. Consider factors such as the scanner’s ease of use, the quality of its reporting, and its ability to integrate with existing security tools. These aspects determine the scanner’s overall effectiveness.
- Ease of Use: A user-friendly interface and clear documentation are essential. A scanner that is intuitive and easy to navigate streamlines the testing process and minimizes training time.
- Accuracy and Reliability: A scanner’s accuracy directly impacts the reliability of vulnerability detection. Reliable results ensure the organization’s security posture is correctly assessed.
- Reporting Quality: Reports should be comprehensive, detailed, and actionable. They should clearly identify vulnerabilities, provide remediation guidance, and categorize findings by severity.
- Customization Options: Flexibility is key. The scanner should offer customization options to tailor testing to specific application needs and security policies.
- Support and Maintenance: A reliable support system and regular updates are crucial for maintaining the scanner’s effectiveness and addressing evolving threats.
Successful Scanner Implementations
Numerous organizations have successfully implemented mobile app security scanners to enhance their security posture. For example, a large e-commerce company leveraged a scanner to identify and remediate several critical vulnerabilities in their mobile payment system, significantly reducing the risk of financial fraud. Another company successfully integrated the scanner into their CI/CD pipeline, enabling automated security checks during the development process, resulting in a more secure release cycle.
Scanner Capabilities Comparison
Different scanners offer varying levels of capabilities. Some focus on specific platforms, while others provide broader coverage. The specific capabilities of each scanner need to be carefully assessed against the needs of the application and the organization.
| Scanner | Platform Support | Vulnerability Coverage | Integration Capabilities |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scanner A | iOS, Android | High (covers OWASP Top 10) | Good (integrates with CI/CD) |
| Scanner B | Android | Medium (limited to common vulnerabilities) | Poor (limited integration) |
| Scanner C | iOS, Android, Hybrid | High (covers OWASP Top 10 + custom checks) | Excellent (deep integration with various tools) |
Key Questions to Ask When Evaluating Scanners
A comprehensive evaluation process should include several key questions. These questions ensure the scanner aligns with the organization’s specific needs and priorities.
- What specific vulnerabilities does the scanner detect?
- How does the scanner integrate with existing development workflows?
- What is the scanner’s accuracy and reliability rate?
- What is the support structure and maintenance policy for the scanner?
- How does the scanner handle different mobile platforms?
Future Trends in Mobile App Security Scanning
Mobile app security is constantly evolving, driven by the ever-increasing sophistication of malicious actors and the rapid advancement of mobile technology. This necessitates a dynamic approach to security scanning, adapting to new threats and vulnerabilities. Future trends in mobile app security scanning will prioritize proactive detection, automation, and integration with the broader development lifecycle.
Emerging Technologies and Their Impact
New technologies are reshaping the landscape of mobile app security scanning. Machine learning (ML) algorithms are becoming increasingly crucial for identifying complex patterns and anomalies indicative of potential vulnerabilities, often surpassing the capabilities of traditional rule-based systems. The rise of AI-powered analysis tools allows for faster, more accurate vulnerability detection, enabling quicker remediation cycles. Cloud-based platforms are also revolutionizing security scanning, providing scalability, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness for developers of all sizes.
This shift empowers businesses to integrate security scanning into their CI/CD pipelines, fostering a proactive approach to security.
Evolution of Security Scanning Methodologies
Traditional static and dynamic analysis methods are evolving to accommodate modern app architectures. Static analysis tools are now integrating with dynamic analysis techniques to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the application’s behavior. Fuzzing techniques are also being enhanced to handle the complexities of modern mobile platforms, leading to more effective vulnerability identification. This evolution focuses on identifying vulnerabilities earlier in the development lifecycle, enabling more cost-effective and efficient remediation.
Impact on Mobile App Development
These trends are fundamentally changing the mobile app development landscape. Security is no longer an afterthought but a core component of the development process, integrated seamlessly into the CI/CD pipeline. Developers are empowered with tools that allow them to identify and fix vulnerabilities early, reducing the risk of costly security breaches. This shift towards proactive security measures promotes the creation of more secure and reliable applications, ultimately building trust with users.
Examples of Future Trends and Their Potential Impact
One example of a future trend is the integration of blockchain technology for enhanced security auditing and provenance tracking. This would allow developers to trace the origin of code components and ensure their integrity, reducing the risk of malicious code insertion. Another trend is the use of behavioral analysis to identify unusual user activity that could indicate a potential attack.
This would allow for proactive detection of malicious activities before significant damage is caused. Finally, the rise of serverless architectures for mobile backends will require specialized scanning tools to assess the security of these distributed systems.
Predicted Future Trends in Mobile App Security Scanning
| Trend | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| AI-powered automated vulnerability detection | Leveraging machine learning to identify complex patterns and anomalies indicative of vulnerabilities | Faster, more accurate vulnerability detection, leading to quicker remediation cycles |
| Integration of static and dynamic analysis | Combining static analysis tools with dynamic analysis techniques to provide a comprehensive understanding of the application’s behavior | More comprehensive vulnerability identification and deeper understanding of the application |
| Cloud-based security scanning platforms | Providing scalable, accessible, and cost-effective security scanning solutions | Easier integration into CI/CD pipelines, fostering proactive security measures |
| Blockchain for security auditing | Using blockchain technology to enhance security auditing and provenance tracking | Reduced risk of malicious code insertion, enhanced code integrity |
| Behavioral analysis for proactive threat detection | Identifying unusual user activity indicative of potential attacks | Proactive detection of malicious activities, reducing damage potential |
Last Recap
In conclusion, mobile app security scanners are indispensable tools for building secure mobile applications. This comprehensive guide has explored the various aspects of these scanners, from their functionalities to selection criteria and future trends. By understanding the intricacies of these tools, developers can create robust and secure applications that protect user data and maintain a strong reputation. Ultimately, a secure app translates to a better user experience and stronger brand trust.

