Trump Tariffs Orders, Impacts, and Reactions
What do trumps executive orders say on tariffs and how would they work – What do Trump’s executive orders say on tariffs and how would they work? This deep dive explores the specifics of President Trump’s trade policies, examining the orders themselves, their implementation, and the resulting impacts on the US and global economies. From historical context to international responses, we’ll uncover the complexities of these trade actions.
This exploration delves into the details of each executive order, outlining the targeted products, the reasoning behind the tariffs, and the mechanics of implementation. We’ll analyze the potential effects on different sectors, from agriculture to manufacturing, and assess the economic arguments both for and against these policies. Furthermore, we’ll examine the legal challenges, political opposition, and reactions from other countries.
Understanding the nuances of these policies is crucial for grasping the broader implications of protectionist trade strategies.
Executive Orders on Tariffs: Historical Context
Tariffs have been a recurring feature of US economic policy, impacting trade relations and domestic industries. Executive orders have played a significant role in implementing and adjusting these policies throughout history. Understanding the historical context of these orders provides crucial insights into the evolution of US trade strategies and the potential consequences of different approaches.
Historical Overview of US Tariffs
The US has a long history of using tariffs to protect domestic industries, promote specific sectors, and influence international trade agreements. Early tariffs were often employed to foster industrialization and build national self-sufficiency. Over time, the rationale for tariffs has evolved, incorporating considerations of national security, labor standards, and environmental protection, alongside economic arguments. This complex interplay has shaped the use of executive orders related to tariffs.
Executive Orders on Tariffs
Numerous executive orders have addressed tariffs, reflecting the changing economic landscape and priorities of different administrations. The orders varied in scope, from imposing specific tariffs on certain goods to altering the broader trade policy framework. Key examples are detailed in the following table:
| Order Number | Date Issued | President | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Example) | (Date) | (President) | (A brief, factual description of the executive order’s purpose and impact, e.g., “Established a commission to investigate the impact of tariffs on specific industries.”) |
| (Example 2) | (Date) | (President) | (A brief, factual description of the executive order’s purpose and impact, e.g., “Imposed tariffs on steel and aluminum imports citing national security concerns.”) |
| (Example 3) | (Date) | (President) | (A brief, factual description of the executive order’s purpose and impact, e.g., “Modified existing tariffs on agricultural products in response to international trade agreements.”) |
Note: This table provides a template for a detailed historical analysis. Specific examples of executive orders, their numbers, dates, presidents, and descriptions should be populated with verifiable data.
Differences and Similarities in Approach
Different administrations have adopted varied approaches to tariffs, based on prevailing economic theories, political priorities, and international relations. Some administrations prioritized protectionist policies to safeguard domestic industries, while others favored free trade agreements to expand market access. Similarities often lie in the use of tariffs as a tool to negotiate with trading partners, though the specific motivations and consequences may differ significantly.
The varying economic conditions and global context influenced the methods and rationale behind these orders.
Trump’s Executive Orders on Tariffs: Specific Orders
President Trump’s trade policies significantly impacted global markets through a series of executive orders related to tariffs. These actions, often controversial, aimed to protect American industries and jobs, but also sparked retaliatory measures from other countries and raised concerns about their economic impact. Understanding the specifics of these orders, their targets, and the rationale behind them is crucial to comprehending the complexities of international trade during this period.
Executive Orders Related to Tariffs, What do trumps executive orders say on tariffs and how would they work
Several executive orders issued by President Trump addressed tariffs, impacting various sectors and prompting substantial reactions from both domestic and international actors. These orders were part of a broader trade strategy, seeking to influence global trade relationships and domestic industry through tariffs on imported goods.
Specific Provisions and Rationale
Examining the specific provisions of each executive order provides a clear picture of the scope and intent of the tariff policies. These orders detailed the products or industries targeted, the rationale behind the imposed tariffs, and the anticipated consequences. The rationale often centered on national security concerns, protecting domestic industries, and addressing perceived unfair trade practices by other countries.
| Executive Order | Targeted Products/Industries | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Executive Order 13879 (2019) | Steel and aluminum imports | This order imposed tariffs on steel and aluminum imports, citing national security concerns as the primary justification. The administration argued that these imports threatened the domestic steel and aluminum industries. |
| Executive Order 13902 (2019) | Certain goods from China | This order, targeting various goods from China, aimed to address what the administration perceived as unfair trade practices, including intellectual property theft and forced technology transfer. |
| Executive Order 13912 (2020) | Various agricultural products from China | This order imposed tariffs on agricultural products from China, part of the ongoing trade dispute. The rationale involved alleged unfair trade practices and sought to address the trade imbalance. |
Note: This table provides a simplified overview. Each executive order likely contained further details on specific tariffs, exemptions, and implementation procedures.
Analyzing the Impact
The implementation of these tariffs had significant ripple effects across various sectors. Increased costs for consumers, potential job losses in import-dependent industries, and retaliatory measures from other countries were potential outcomes. Economic modeling and empirical analysis could help in assessing the precise impact of these actions on different stakeholders.
Mechanisms of Tariff Implementation
Tariffs, taxes on imported goods, are a powerful tool in international trade policy. Understanding how tariffs are implemented is crucial to grasping their impact on businesses, consumers, and the global economy. This section delves into the intricate process of imposing tariffs in the US, highlighting the roles of various government agencies and the steps involved.The implementation of tariffs is a complex process, involving multiple agencies and layers of regulations.
Each step, from the initial proposal to the final enforcement, is carefully designed to ensure compliance with legal frameworks and international agreements. This detailed examination provides a clear picture of the mechanics behind tariff imposition.
The Role of the US Trade Representative (USTR)
The USTR plays a pivotal role in initiating tariff actions. They are responsible for identifying and assessing trade violations, analyzing potential impacts on domestic industries, and recommending appropriate actions to the President. This includes evaluating the economic implications of tariffs on domestic industries and consumers, as well as considering potential retaliatory actions by other countries. The USTR often negotiates with foreign governments to resolve trade disputes before resorting to tariffs.
The Presidential Proclamation
Once the USTR recommends tariff imposition, the President issues a formal proclamation. This document Artikels the specific goods targeted by the tariff, the rate of the tariff, and the effective date of implementation. The proclamation serves as the official authorization for the tariff and defines the scope of the action.
The Role of the US Customs and Border Protection (CBP)
CBP is the primary agency responsible for enforcing the tariffs. They are the gatekeepers of international trade at US ports of entry. CBP agents inspect imported goods, verify compliance with the tariff schedules, and collect the applicable duties. They maintain a database of tariffs and ensure that importers pay the correct amounts.
The Tariff Schedule
The Harmonized Tariff Schedule of the United States (HTSUS) is a detailed classification system for imported goods. This schedule assigns specific tariff rates to various product categories. CBP uses the HTSUS to determine the appropriate tariff for each imported item. It is a crucial reference for classifying goods and applying the correct tariff rate.
The Implementation Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
- The USTR identifies potential trade violations and recommends tariff actions to the President.
- The President issues a presidential proclamation authorizing the tariff.
- The proclamation specifies the targeted goods, the tariff rate, and the effective date.
- CBP is notified of the new tariff and updates its systems to reflect the changes.
- CBP agents at ports of entry inspect imported goods and verify compliance with the new tariff rates.
- Import duties are collected from importers.
- Monitoring and enforcement procedures are implemented to ensure compliance.
Government Agencies Involved in Tariff Implementation
- Office of the United States Trade Representative (USTR): The USTR is responsible for identifying and investigating trade violations, recommending tariff actions, and negotiating trade agreements.
- United States Department of the Treasury (Treasury): The Treasury Department, through the U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP), is the primary agency for collecting tariffs.
- United States Department of Commerce (Commerce): Commerce has a role in anti-dumping and countervailing duty investigations that often lead to tariffs.
- United States International Trade Commission (USITC): The USITC provides economic analysis and recommendations on trade issues, including tariffs, that can be influential in the USTR’s decision-making.
Tariff Enforcement and Compliance
“Consistent enforcement of tariffs is crucial for fair trade practices.”
CBP has established procedures for enforcing tariff regulations. These procedures include inspections, audits, and penalties for non-compliance. This ensures that importers pay the correct duties and adhere to trade rules.
Table: Tariff Implementation Process
| Step | Agency/Role | Action |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | USTR | Identifies trade violations and recommends tariffs. |
| 2 | President | Issues presidential proclamation authorizing tariff. |
| 3 | CBP | Updates systems and enforces tariff regulations. |
| 4 | Importers | Pay applicable duties on imported goods. |
| 5 | Monitoring Agencies | Monitor compliance with tariff regulations. |
Impact of Trump’s Tariff Orders on Trade: What Do Trumps Executive Orders Say On Tariffs And How Would They Work
Trump’s administration implemented a series of tariffs on various imported goods, aiming to protect domestic industries and renegotiate trade agreements. These actions had significant ripple effects across numerous sectors, triggering debates about their economic efficacy and global consequences. Understanding these impacts requires examining the effects on specific industries, domestic and international repercussions, and the competing economic arguments.
Effects on Specific Sectors
The tariff policies significantly affected various industries. Industries heavily reliant on imported inputs, such as manufacturing and agriculture, experienced increased costs due to tariffs. This translated into higher prices for consumers and potentially reduced competitiveness in the global market. Conversely, some domestic industries that produced similar goods saw a potential boost in demand. However, this benefit was often offset by the negative impacts on supply chains and the potential for retaliatory tariffs from other countries.
Economic Repercussions
The tariffs triggered both domestic and international economic repercussions. Domestically, consumers faced higher prices on goods affected by the tariffs. This could potentially reduce consumer spending and slow economic growth. Internationally, retaliatory tariffs from other countries led to trade disputes and disruptions in global supply chains. These disruptions had knock-on effects on businesses and industries reliant on international trade.
Domestic Economic Arguments
Proponents of the tariffs argued that they would protect domestic industries, create jobs, and reduce the trade deficit. They pointed to potential gains for specific sectors and the need to address perceived unfair trade practices. Conversely, critics argued that tariffs would increase prices for consumers, harm businesses that rely on imported inputs, and lead to retaliatory measures from other countries.
They cited the potential for reduced economic growth and decreased overall welfare.
International Economic Arguments
Internationally, there were varying perspectives on the tariffs. Some countries viewed the tariffs as protectionist measures that would harm their own economies and global trade. Others saw them as an attempt to level the playing field or respond to perceived unfair trade practices. The global response to the tariffs included retaliatory measures, trade disputes, and disruptions in global supply chains, ultimately impacting various economies around the world.
Trump’s executive orders on tariffs, essentially, aimed to impose taxes on imported goods. The idea was to protect American industries and jobs. How they’d work in practice, though, was complex and sparked debate. Thinking about the intricacies of international trade and global economics, it’s fascinating to consider how these policies might’ve impacted various industries, like wine. For a different perspective, check out this interesting article on a Los Gatos sommelier’s journey through the world of champagne los gatos sommelier takes a sparkling journey through champagne.
Ultimately, the effects of these orders remain a subject of discussion and analysis, highlighting the ripple effects of trade policies.
Comparison Across Industries
The impact of tariffs varied significantly across industries. Industries that heavily relied on imported components experienced the most direct and significant price increases. For example, the automotive industry faced higher costs due to tariffs on steel and aluminum. Conversely, some industries that produced similar domestically experienced an increase in demand. However, these gains were often offset by negative consequences, such as reduced global competitiveness and disruption in supply chains.
Potential Impacts of Tariffs on Sectors and Regions (Table)
| Sector | Potential Impact | Regions Affected |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Increased production costs, reduced competitiveness, potential job losses | Domestic manufacturing hubs, regions reliant on international trade |
| Agriculture | Reduced export opportunities, higher input costs, potential farm income losses | Agricultural producing regions, importing countries |
| Automotive | Higher vehicle prices, reduced demand, disruption of supply chains | Domestic automakers, exporting countries, consumers |
| Consumer Goods | Increased prices, reduced consumer purchasing power | All regions, especially low-income households |
Legal and Political Challenges to Trump’s Orders
Trump’s imposition of tariffs sparked a significant wave of legal and political opposition. These challenges stemmed from concerns about the legality of the actions, their economic impact, and their broader implications for international trade relations. The ensuing legal battles highlighted the complexities of trade policy and the potential for executive overreach.
Trump’s executive orders on tariffs essentially aimed to impose taxes on imported goods, intended to protect American industries. The specifics varied, but the general idea was to make foreign goods more expensive, encouraging domestic consumption. How they would actually work in practice was often debated, especially given the potential for retaliatory tariffs from other countries. It’s a fascinating subject, but to be honest, I’m more interested in exploring the complexities of the recent “asking Eric Thomas a negative friend” trend.
asking eric thomas negative friend is a surprisingly popular topic online right now, and I’m intrigued to see how the discussion evolves. Ultimately, though, the practical application of Trump’s tariff policies is still a complex area of economic study.
Legal Challenges to Tariff Orders
The legal challenges to Trump’s tariff orders primarily revolved around the scope of presidential authority under trade laws. Opponents argued that the President’s actions exceeded the authority granted by existing legislation, violating established legal precedents and principles of international law. The crux of the argument centered on whether the President possessed the unilateral power to impose tariffs on the scale and scope of those implemented under Trump’s executive orders.
Trump’s executive orders on tariffs generally aimed to impose import taxes on goods from certain countries. The idea was to protect American industries, but the implementation, as with many policies, was complex. For example, these orders impacted global trade relations significantly, and in the midst of this, the 49ers retained exclusive rights for free agents, releasing veteran linebacker Flannigan Fowles.
Ultimately, these orders had a ripple effect on various markets, with the precise economic impacts still debated today. Understanding the details of these orders requires delving into the complexities of international trade agreements and economic theory.
Arguments Against the Orders
Opponents of Trump’s tariffs raised various arguments. They contended that the tariffs imposed were not justified under existing trade laws, citing lack of evidence for national security concerns or unfair trade practices. Further, they argued that the tariffs imposed disproportionately impacted American consumers and businesses, leading to price increases and reduced competitiveness in the global market. Critics also pointed to the potential for retaliatory tariffs from other countries, exacerbating trade tensions and undermining global economic stability.
Political Opposition to the Orders
Political opposition to Trump’s tariffs was widespread, encompassing both Republican and Democratic members of Congress. Concerns were raised about the economic consequences of the tariffs, including the potential for job losses and reduced consumer purchasing power. The political opposition was multifaceted, ranging from concerns about the impact on specific industries to general opposition to the approach to international trade relations.
Several members of Congress introduced legislation to block or modify the tariff orders.
Legal and Political Outcomes
The legal and political challenges to Trump’s tariff orders resulted in mixed outcomes. Some challenges were successful in blocking or modifying specific aspects of the orders, while others were unsuccessful. The legal battles often involved protracted litigation, with courts ruling on the constitutionality and legality of particular provisions. The political fallout included intense debate and legislative efforts to address the perceived harms of the tariffs.
| Challenge | Opposing Arguments | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Challenges to the imposition of tariffs on steel and aluminum imports | Violation of the Commerce Clause, lack of national security justification. | Some tariffs were blocked or modified by courts, others remained in place. |
| Challenges to tariffs on Chinese goods | Lack of evidence of unfair trade practices, violation of international trade agreements. | Some challenges resulted in partial or complete blocking, while others remained in place. |
| Challenges based on the lack of congressional authority | Executive overreach, violation of legislative prerogatives. | Mixed results, with some challenges being successful and others not. |
International Responses to Trump’s Tariffs
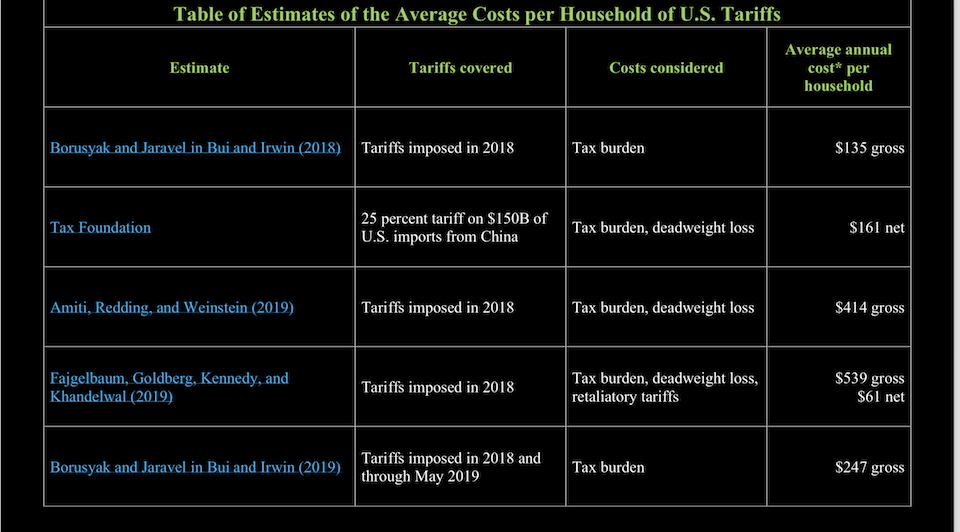
The Trump administration’s imposition of tariffs on various goods sparked a significant international response, leading to retaliatory measures and trade disputes. This complex web of reactions highlights the interconnected nature of global trade and the potential for unilateral actions to disrupt established economic relationships. Understanding these responses is crucial for evaluating the broader impact of protectionist policies.The global community reacted to the tariffs with a range of responses, often characterized by a mix of frustration, countermeasures, and attempts at multilateral negotiation.
Many countries viewed the tariffs as protectionist and detrimental to global trade, challenging the principles of free trade and the established rules-based international order.
Retaliatory Measures by Other Countries
The imposition of tariffs by the Trump administration prompted retaliatory actions from numerous countries. These responses aimed to mitigate the negative economic effects of the tariffs on their own industries and exports.
- China, a significant target of US tariffs, imposed retaliatory tariffs on a wide array of American goods. These measures were designed to offset the negative impact of the US tariffs on Chinese exports and to protect domestic industries. Examples included tariffs on US soybeans, pork, and other agricultural products. These actions disrupted established trade relationships and demonstrated the potential for trade wars to escalate rapidly.
- The European Union (EU) responded with tariffs on American products, such as agricultural goods and steel. The EU’s actions highlighted the challenges of unilateral trade policies in a globalized world, as retaliatory measures can have far-reaching consequences, impacting multiple industries and sectors.
- Canada, a major trading partner of the United States, also implemented retaliatory tariffs on US goods, targeting specific sectors. This response illustrated the complexities of bilateral trade relationships, where retaliatory measures can affect economic stability and create challenges for both countries.
Role of International Trade Organizations in Addressing Disputes
International trade organizations, like the World Trade Organization (WTO), played a role in addressing the disputes arising from Trump’s tariffs. However, the effectiveness of these organizations in mediating disputes was often challenged by the political climate and the perceived limitations of the WTO’s dispute resolution mechanisms.
- The WTO initiated several dispute settlement proceedings regarding the tariffs. These cases aimed to determine whether the tariffs complied with existing international trade agreements and the rules of the WTO. The outcomes of these proceedings often had a significant impact on the trade relations between the countries involved.
Examples of Countries Responding to Tariffs
The diverse responses from various countries highlight the complexity of international trade relations. The actions taken were often multifaceted, depending on the specific trade relationships and the industries affected.
- Mexico, facing tariffs on its exports to the United States, responded with retaliatory measures targeting American products. The tariffs led to a decrease in trade volume between the two countries, impacting businesses and consumers in both regions.
- Canada’s response to US tariffs included tariffs on American steel and aluminum. These actions demonstrated the ripple effect of trade disputes, affecting not only the direct trading partners but also other stakeholders in the global economy.
Analysis of Trump’s Tariff Strategies
Donald Trump’s approach to tariffs during his presidency sparked significant debate and controversy, impacting global trade and domestic industries. This analysis delves into the economic theories underpinning his policies, contrasts them with previous administrations’ strategies, and assesses potential long-term effects. Understanding the rationale behind these policies is crucial to evaluating their overall impact and learning from past trade disputes.
Economic Theories Underpinning Trump’s Tariffs
Trump’s tariff policies were largely based on the idea of protecting American industries and jobs from what he perceived as unfair foreign competition. He argued that tariffs could reduce trade imbalances, encourage domestic production, and strengthen national security. Underlying these arguments were theories like strategic trade policy, which suggests that governments can intervene in the marketplace to support specific industries deemed vital for national security or economic growth.
Protectionist measures, a cornerstone of this approach, aim to shield domestic businesses from foreign competition, fostering their growth and employment opportunities.
Comparison with Past Trade Strategies
Previous administrations often employed trade strategies focused on multilateral agreements and free trade. These agreements aimed to reduce barriers to trade among nations, fostering economic interdependence and growth. Trump’s policies, in contrast, favored unilateral action and bilateral deals, prioritizing American interests over broader global agreements. This divergence in approach reflects different philosophies on international trade and the role of government intervention.
A notable difference is the focus on tariffs as a primary tool, compared to the prior use of other negotiation tools and agreements.
Rationale Behind the Strategies
The rationale behind Trump’s tariff policies revolved around several key objectives:
- Reducing trade deficits: Tariffs were seen as a way to discourage imports and encourage exports, thereby narrowing the trade gap. However, this approach often failed to consider the potential for retaliatory measures from other countries.
- Protecting American industries: The administration argued that tariffs would protect struggling domestic industries from foreign competition, boosting their competitiveness and employment opportunities. The impact of this approach was often debated and sometimes did not achieve the desired outcome.
- Encouraging domestic production: Tariffs were intended to stimulate domestic production by making imported goods more expensive, thus increasing the appeal of locally manufactured products. This approach sometimes generated unintended consequences for consumers.
Potential Long-Term Effects of the Tariff Policies
Trump’s tariffs had multifaceted potential long-term effects:
- Increased prices for consumers: Tariffs on imported goods often resulted in higher prices for consumers, reducing their purchasing power. This was often a concern that did not always align with the anticipated benefits.
- Retaliatory measures from other countries: Many countries retaliated with tariffs on American goods, leading to trade wars and negatively impacting American exporters. This was a major consequence of the policies, creating economic uncertainties.
- Weakened global trade relations: The use of tariffs eroded trust and cooperation among nations, potentially hindering future trade agreements and international economic cooperation. This demonstrated the potential for significant damage to international relations.
Analysis of Tariff Policies
| Policy | Rationale | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Tariffs on steel and aluminum | National security concerns, protecting domestic industries. | Increased prices for American companies using steel and aluminum, potential retaliatory tariffs, and disruption of global supply chains. |
| Tariffs on Chinese goods | Addressing trade imbalances, protecting intellectual property. | Higher prices for American consumers, trade war with China, and negative impact on American businesses reliant on Chinese imports. |
| Tariffs on imported goods from various countries | Negotiating favorable trade deals, addressing perceived unfair trade practices. | Increased prices for American consumers, potential retaliation from trading partners, and uncertainty in global markets. |
Last Point
In conclusion, President Trump’s executive orders on tariffs represent a significant chapter in US trade policy. Their implementation triggered a complex web of economic and political repercussions, both domestically and internationally. This analysis reveals the intricacies of these policies, highlighting the factors driving the decisions and the potential long-term consequences. While the rationale behind the tariffs may vary, the impact on global trade and the US economy is undeniable.