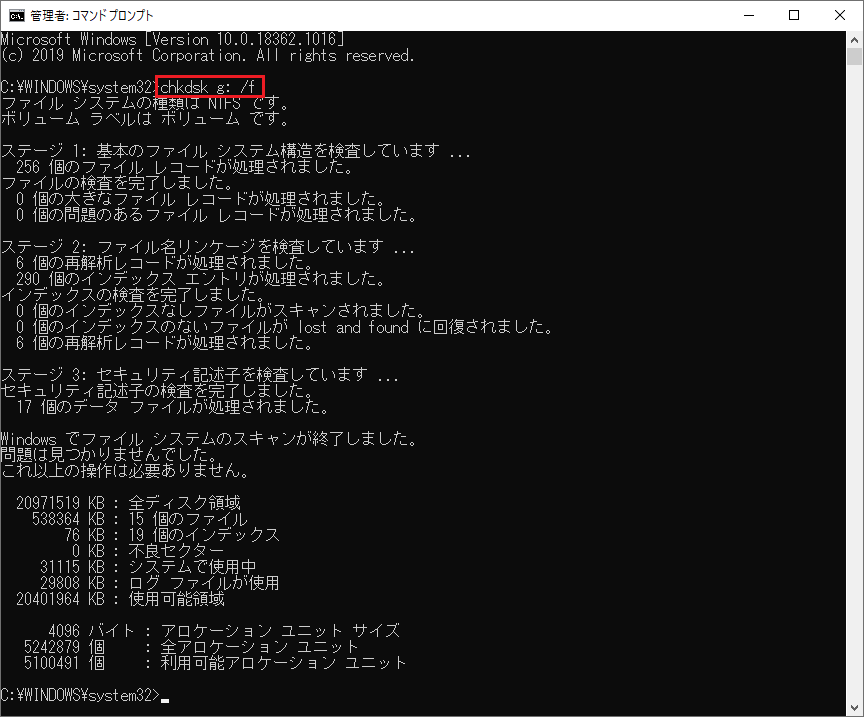
Run System File Checker Windows A Comprehensive Guide
Run System File Checker Windows to maintain your Windows system’s health and integrity. This guide delves into the ins and outs of using SFC, from initiating a scan to troubleshooting common issues and optimizing its usage. We’ll cover everything from basic GUI methods to advanced command-line techniques, plus explore alternative repair methods and crucial security considerations.
Understanding the System File Checker (SFC) is essential for anyone who wants to keep their Windows system running smoothly. This powerful tool can identify and repair corrupted system files, helping prevent unexpected crashes and maintain optimal performance. Whether you’re a seasoned tech user or a novice, this guide provides clear instructions and valuable insights to help you navigate the process effectively.
Introduction to System File Checker (SFC)
The System File Checker (SFC) is a built-in utility in Windows operating systems designed to scan and restore corrupted system files. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of Windows, ensuring that critical components function correctly. This tool is invaluable for troubleshooting issues that might arise from malware attacks, corrupted installations, or unexpected system shutdowns.SFC works by comparing the current versions of system files with their original, known-good versions stored in the Windows installation media.
If any discrepancies are found, SFC attempts to repair or replace the problematic files with the correct versions. This process can often resolve a variety of issues, including application crashes, startup problems, and general system instability.
Understanding the Purpose and Functionality of SFC
SFC’s primary purpose is to verify the integrity of critical system files. This verification process is vital because corrupted or damaged system files can lead to various issues, from minor inconveniences to significant system failures. The tool actively seeks out and repairs these corrupted files, restoring the system to a stable and functional state. By ensuring the correct versions of files are in place, SFC enhances system stability and prevents further issues from arising.
Common Scenarios Where SFC Might Be Used
SFC is a valuable tool for addressing a range of issues. One common scenario involves detecting and repairing corrupted system files that might arise after a malware attack or a system crash. Another scenario is when an application or driver exhibits unexpected behavior, which could be a symptom of corrupted system files. SFC can also be beneficial in cases where a user has recently performed a complex system configuration change, potentially causing file corruption.
Moreover, a poorly executed installation of software or a hardware malfunction can sometimes lead to system file corruption, necessitating the use of SFC.
How to Initiate an SFC Scan
There are two primary methods to initiate an SFC scan: through the graphical user interface (GUI) or using command-line options. Each method offers unique advantages and disadvantages. Using the command-line provides greater control, but the GUI method is generally more user-friendly for novice users.
Different SFC Command-Line Options
Using the command prompt provides more granular control over the SFC scan. The `/scannow` option is the most common, initiating a scan of all protected system files. Other options are available, offering greater customization for specific scenarios. For instance, `sfc /scannow /offbootdir=C:\mount\winre\` allows running SFC from a different location, while `sfc /scannow /offwindir=C:\Winnt` would work on older versions of Windows.
Comparing GUI and Command-Line Methods
| Method | Steps | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| GUI | Open Command Prompt as administrator, type `sfc /scannow` and press Enter. | Easy to use, requires minimal technical knowledge. | Limited control over the scan process, cannot specify alternative locations. |
| Command Line | Open Command Prompt as administrator, type `sfc /scannow /offbootdir=C:\mount\winre\ /offwindir=C:\Winnt` (or other options) and press Enter. | Greater control over the scan, allows for alternative boot directories and Windows installations. | Requires more technical knowledge and understanding of the command-line options. |
Troubleshooting Common SFC Issues: Run System File Checker Windows
System File Checker (SFC) is a valuable tool for maintaining Windows system integrity, but it’s not immune to problems. Understanding potential pitfalls and how to address them can significantly improve your troubleshooting process. Knowing the reasons behind SFC scan failures and the various error messages can help you pinpoint the root cause and implement the appropriate fix.SFC scans, while often successful, can sometimes encounter roadblocks.
These roadblocks can stem from various sources, including temporary glitches in the system, hardware issues, or even conflicts with other applications. This section delves into the common obstacles you might encounter when running SFC, and provides practical solutions to overcome them.
Potential Reasons for SFC Scan Failure
SFC scans can fail due to several factors. A crucial factor is ensuring the system’s integrity before running the scan. Temporary issues, such as network connectivity problems or insufficient system resources, can also cause a scan to halt prematurely. Corrupted system files themselves can sometimes prevent the scan from completing. Furthermore, conflicting processes running concurrently can lead to errors.
Common SFC Error Messages
SFC scans can produce various error messages, each indicating a specific problem. Understanding these messages is key to determining the necessary steps to rectify the issue. Some common error messages include:
- Error 0x80070003: This error often arises from insufficient privileges or problems accessing the required system files. Addressing this requires ensuring that the user running the scan possesses the necessary administrator permissions.
- Error 0x80070057: This error frequently points to problems with the Windows installation itself or the integrity of system files. A clean boot or reinstallation might be needed to resolve this issue.
- Error 0x80070002: This message often signals a problem with accessing files or resources. Checking for any pending system updates or incompatible software can help.
- “The system cannot find the file specified.”: This message can indicate a problem with file paths, potentially due to a damaged hard drive or corrupt file system.
Solutions for Handling SFC Scan Errors
Addressing SFC scan errors requires a systematic approach. First, identify the specific error message to pinpoint the root cause. Then, apply the corresponding solution. These solutions often include checking system privileges, running SFC with elevated permissions, verifying system integrity, ensuring sufficient disk space, and resolving any conflicts with other applications.
Running the System File Checker in Windows can be a lifesaver for troubleshooting various issues. It’s like a digital doctor, checking for corrupted system files. But sometimes, when you’re deep in the trenches of computer problems, it’s easy to forget about the bigger picture, like the current drama surrounding Steph Curry and the Golden State Warriors. Are the NBA and their opponents deliberately trying to hamper the Warriors’ success?
The Warriors Mailbag delves into this fascinating topic in a recent piece exploring the tension surrounding the team, warriors mailbag is the nba out to get steph curry golden state. Thankfully, a quick SFC scan can often resolve many minor problems, restoring a healthy system without all the drama.
Causes of Corruption Detected by SFC
SFC identifies corrupted files by comparing them to their original versions stored in the Windows image. Potential causes of corruption include:
- Software Conflicts: Incompatible or conflicting software installations can lead to system file corruption.
- Hardware Failures: Failing hard drives, memory issues, or other hardware problems can cause file system damage.
- Power Outages: Unexpected power loss during system operation can lead to data corruption in memory or on the hard drive.
- Virus or Malware Infections: Malicious software can directly alter or delete system files, leading to corruption.
- Operating System Errors: Occasionally, errors within the operating system itself can cause corruption.
Verifying System Integrity Before Running SFC
Verifying system integrity before running SFC scans is crucial. This ensures that the system is stable and that any pre-existing issues won’t complicate the scan. Actions like running a disk check or verifying that all system drivers are up-to-date can contribute to a more accurate and reliable scan.
Running the System File Checker in Windows is a pretty straightforward way to fix corrupted system files. It’s a handy tool, but sometimes, you might need a little extra help, like figuring out what’s going on with a property like a local business. For example, if you’re looking into properties of a local business in San Jose, like Glenna Glee Avilla glenna glee avilla san jose ca , you might discover interesting insights into the area’s business climate.
Ultimately, the System File Checker can be a powerful tool for keeping your Windows system running smoothly.
Error Code Table
| Error Code | Description | Possible Causes | Solutions ||—|—|—|—|| 0x80070003 | Insufficient privileges or access problems. | User lacks administrator privileges, or system files are inaccessible. | Run SFC as administrator. || 0x80070057 | Problems with Windows installation or system file integrity. | Damaged installation, corrupted system files.
| Reinstall Windows or perform a repair installation. || 0x80070002 | Problems accessing files or resources. | Pending system updates, incompatible software, or insufficient disk space. | Update drivers, install pending updates, or free up disk space. || 0x80070490 | Insufficient disk space.
| Not enough space on the hard drive to complete the scan. | Free up disk space by deleting unnecessary files. |
Optimizing SFC Usage
System File Checker (SFC) is a valuable tool for maintaining the integrity of your Windows system files. However, maximizing its effectiveness involves more than just running it once. Proper planning and execution can significantly improve the scan’s efficiency and minimize disruptions to your workflow. This section delves into best practices for utilizing SFC to ensure your system remains robust and reliable.Understanding the intricacies of SFC usage allows for a more strategic approach.
By optimizing scan times and preparing the system beforehand, users can leverage the tool’s capabilities to address corrupted files effectively and with minimal impact.
Best Practices for Running SFC Scans
A well-executed SFC scan involves careful planning and execution. The following practices contribute to a smoother and more effective process.
- Scheduling SFC Scans: Scheduling SFC scans during periods of low system activity is crucial. Avoid running the scan during peak usage times, such as when you’re actively working or gaming, to minimize performance degradation. This proactive scheduling ensures that the integrity checks don’t interfere with your ongoing tasks.
- Choosing the Right Scan Type: Different scan types address various scenarios. A quick scan focuses on commonly used files, offering a faster but less comprehensive check. A full scan, on the other hand, scrutinizes all system files, ensuring a more thorough examination. The optimal scan type depends on the suspected issue. A full scan is suitable for identifying widespread corruption or after major system updates, while a quick scan can suffice for routine checks.
- Preparing the System: Before initiating an SFC scan, it’s advisable to close all unnecessary programs. Minimizing background processes frees up system resources, allowing the scan to run more efficiently. This proactive step ensures the scan has the optimal environment for accurate and thorough analysis.
Optimal Time to Run SFC Scans
Running SFC scans at optimal times is critical to minimize performance impact. Avoid periods of heavy system usage.
- Off-Peak Hours: Scheduling SFC scans during off-peak hours, such as overnight or when the system is not in active use, is a best practice. This approach minimizes disruption to ongoing tasks.
- Low System Load: Monitoring system load is vital. Running the scan when system resources are less constrained prevents significant slowdowns and ensures a smoother execution.
Impact of System Performance During an SFC Scan
The performance of your system during an SFC scan directly correlates to the scan’s duration and effectiveness. High resource consumption during the scan can lead to slower system response times.
- Resource Allocation: The SFC scan requires significant system resources, potentially impacting other applications. Understanding this resource demand helps users make informed choices about when to perform the scan.
- Performance Degradation: A full system scan can lead to noticeable performance degradation. Anticipating this slowdown allows users to plan accordingly and schedule the scan during periods of low activity.
Strategies to Minimize Disruption During an SFC Scan
Strategies to minimize disruption during an SFC scan are important for maintaining productivity.
- Prioritization: Prioritize the SFC scan when system demands are low. This proactive approach minimizes the impact on other applications and ensures a more efficient process.
- Background Execution: If possible, initiate the scan in the background, allowing users to continue their work while the integrity checks are performed.
Preparing the System for an SFC Scan
Adequate preparation enhances the efficiency and accuracy of the SFC scan.
- Closing Unnecessary Programs: Closing unnecessary programs releases system resources, allowing the scan to operate more smoothly and accurately.
- Disconnecting Unnecessary Devices: Disconnecting unnecessary external devices can reduce potential conflicts and ensure a more efficient scan.
Comparing Different Scan Types
Understanding the nuances of different scan types empowers users to choose the most appropriate method for their needs.
| Scan Type | Description | Suitability |
|---|---|---|
| Quick Scan | Checks only frequently accessed files. | Routine checks, suspected minor corruption. |
| Full Scan | Checks all system files. | Suspected widespread corruption, after major updates. |
Best Practices Summary
This table summarizes best practices for utilizing SFC effectively.
| Practice | Description | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Schedule Scans | Perform scans during low system activity. | Minimizes disruption to ongoing tasks. |
| Choose Appropriate Scan Type | Select quick scan for routine checks, full scan for major issues. | Ensures efficiency and thoroughness. |
| Prepare the System | Close unnecessary programs and disconnect unused devices. | Optimizes system resources for the scan. |
Advanced SFC Techniques
System File Checker (SFC) is a powerful tool for repairing corrupted system files. While basic scans can identify and fix many issues, advanced techniques allow for more precise and targeted repairs. These techniques provide a deeper understanding of how SFC operates and enables users to troubleshoot complex problems more effectively.Advanced SFC techniques leverage specific command-line parameters to refine the scanning process.
Understanding these parameters allows for more controlled and efficient repairs, saving time and resources. Furthermore, knowing how to target specific file types or individual files enables users to diagnose and resolve specific corruption issues with greater precision.
Advanced Command-Line Parameters
Understanding and utilizing the command-line parameters of SFC is crucial for advanced users. These parameters allow for greater control over the scanning and repair process.
- The `/scannow` parameter is the most common and fundamental command. It initiates a system-wide scan for corrupted files and attempts to repair them. However, parameters like `/scan` and `/scanonce` can be used to control scan intervals and frequency. For example, `/scanonce` will only scan once, while `/scan` can initiate a scheduled scan.
- The `/offbootdir` parameter allows specifying a different directory for the scan, which is useful for situations where the primary boot directory might be inaccessible or corrupted. This parameter is particularly useful for troubleshooting situations involving boot sector corruption.
- The `/offwindir` parameter is similar to `/offbootdir` but focuses on the Windows installation directory. This is crucial if the system files within the Windows directory are corrupted but the boot directory is functional.
- The `/c` parameter forces SFC to replace the corrupted files without prompting for confirmation. This is useful for automated scripts and situations where a prompt could cause delays. This option is generally advised for users with some technical proficiency and the ability to quickly evaluate the integrity of the files to be replaced.
Targeting Specific File Types
SFC is not limited to a system-wide scan. It can be directed to scan specific file types or locations, enabling targeted repairs. This targeted approach is particularly helpful in situations where a specific application or component is malfunctioning.
- Using the `/scanfile` parameter, SFC can be directed to examine specific files or groups of files. This allows the scan to focus on the suspected area of corruption. This parameter allows for a more precise diagnosis and repair of corrupted files.
Specific File Recovery
The ability to recover specific files damaged by SFC is possible. However, this typically requires manual intervention using other recovery tools.
- SFC primarily focuses on system files and cannot directly recover individual files. It is important to note that, if a critical file is damaged, other repair mechanisms or recovery tools may be required.
Advanced Troubleshooting Scenarios
SFC encounters various issues during scans and repairs. Troubleshooting these scenarios requires careful analysis and potentially other tools.
- SFC often encounters errors or fails to repair certain files. Troubleshooting involves reviewing error messages, verifying system integrity, and potentially using other diagnostic tools to identify the root cause. In certain cases, the error messages might be cryptic, so it is important to refer to the error message’s specific context and try other troubleshooting methods.
- SFC might report that no errors were found even when the system exhibits malfunctioning behavior. This scenario requires a deeper investigation, considering factors such as registry corruption, missing or damaged drivers, or incompatibility issues. Comprehensive checks across various system components should be performed in this situation.
Specialized SFC Tools
Various specialized tools offer enhanced functionality compared to the standard SFC command.
| Tool | Function |
|---|---|
| Windows Resource Kit Tools | Includes advanced utilities for repairing system files and troubleshooting issues, potentially offering more options than the standard SFC. |
| Third-party repair tools | Third-party software may provide additional features and options for repairing system files, beyond the standard SFC capabilities. Care should be taken when using third-party software. |
Alternative Repair Methods
System File Checker (SFC) is a powerful tool, but it’s not the only way to repair corrupted system files in Windows. Understanding alternative methods and their strengths and weaknesses is crucial for effective troubleshooting. Different approaches may be better suited for specific scenarios, and knowing when to use each method can save significant time and frustration.Alternative repair methods provide a wider range of options for resolving file system issues beyond the capabilities of SFC.
By examining these methods, you can better diagnose and rectify problems in your Windows installation.
Alternative Repair Tools
Various tools can help repair corrupted system files. These tools often employ different techniques, leading to varying degrees of effectiveness. Consider the specific characteristics of each tool before deciding on a course of action.
- Windows System Restore: This feature allows reverting your system to a previous state, effectively undoing changes that might have introduced corrupted files. It’s an excellent solution for restoring the system to a known good state, especially after installing problematic software or drivers. This method can be useful for rolling back to a stable configuration. However, it requires a previous restore point to be effective.
- DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management): DISM is a command-line tool used to repair Windows image files. It’s often more powerful than SFC for handling more complex image corruption, such as system files integral to Windows’ boot process. This command-line utility can address deeper-level issues and is a critical tool for advanced system administrators. It should be used with caution, as incorrect commands can further damage the system.
- Third-Party Repair Tools: Several third-party applications offer advanced system repair functionalities, potentially including the ability to scan for and fix various file corruption issues. Carefully evaluate the reputation and reliability of these tools before deploying them on your system. These tools should be used with caution, as their efficacy and impact on the system can vary.
Comparison of Repair Methods, Run system file checker windows
A clear comparison of different methods can guide you in choosing the appropriate approach.
| Method | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| SFC | Scans and repairs corrupted system files. | Relatively simple to use, often resolves basic issues. | Limited in addressing severe corruption, may not work on all issues. |
| System Restore | Reverts the system to a previous state. | Useful for recovering from recent changes, often effective for software conflicts. | Requires a valid restore point, can’t address problems beyond the restore point. |
| DISM | Repairs Windows image files. | More comprehensive than SFC, addresses deeper-level issues. | Requires technical knowledge, potentially more complex to use. |
| Third-Party Tools | Offers advanced system repair capabilities. | Potentially comprehensive, various tools available. | Potential for compatibility issues, requires careful evaluation of the tool’s reliability. |
Data Backup and Recovery Options
Before attempting any repair, backing up your data is crucial. Unforeseen issues during the repair process can lead to data loss.
Running the System File Checker in Windows can sometimes help with odd issues, like those pesky JavaScript errors. For instance, if you’re encountering a “JavaScript heap out of memory” error, trying to resolve the underlying issue by running SFC (System File Checker) might be a good starting point. You might also find that addressing the core issue, like optimizing your code to avoid memory leaks, is vital.
Fixing the JavaScript errors with solutions like fix javascript heap out of memory error can also help, though running SFC might be a necessary step alongside these other troubleshooting techniques.
“Data backup is an essential step before any system repair to prevent data loss.”
Utilize Windows’ built-in backup tools or reliable third-party solutions to create a complete backup of your important files and folders. Restoring from a backup provides a safe fallback option in case the repair process fails. Recovery options like creating a Windows installation media can also help in handling more complex situations.
Security Considerations
Running System File Checker (SFC) can be a powerful tool for maintaining system health, but it’s crucial to understand the potential security risks and best practices to mitigate them. A compromised system can lead to corrupted files, which SFC aims to repair, but the process itself needs careful management to prevent further complications. Understanding the security implications of SFC use is vital for a secure and stable computing environment.Security is paramount when working with system files.
Incorrectly executed SFC scans can introduce vulnerabilities or potentially exacerbate existing issues. Proper precautions and awareness of potential pitfalls are essential for responsible use.
Potential Security Risks of SFC
SFC scans, while intended to restore system integrity, can pose risks if not performed under secure conditions. Unauthorized access to the system during an SFC scan could allow malicious actors to manipulate or alter files, potentially introducing malware or hindering the scan’s effectiveness. Malicious software might also interfere with SFC, either preventing it from running correctly or manipulating its results.
This highlights the need for robust security measures when performing SFC scans.
Best Practices for Securing the System During an SFC Scan
Maintaining system security during an SFC scan requires proactive measures. These steps are critical for preventing unauthorized access and ensuring the integrity of the process.
- System Integrity Protection (SIP): Ensuring SIP is enabled can prevent unauthorized changes to critical system files during an SFC scan. Disabling SIP for an SFC scan should only be done when absolutely necessary and only by trusted administrators. Regular system backups before any significant system modification are essential to restore to a known good state if issues arise.
- Firewall Configuration: Verify the firewall’s configuration to ensure that the SFC process has the necessary permissions to access and modify system files. Open necessary ports or allow the SFC process to communicate if needed, while maintaining robust firewall protection to prevent unwanted network access.
- User Account Control (UAC): UAC should be enabled to restrict access to system files and resources. If a malicious program gains access, UAC can help prevent its propagation throughout the system.
- Antivirus and Antimalware Software: Maintain up-to-date antivirus and antimalware software. These tools can detect and prevent malicious activity during the SFC scan or before it begins. Regular scans can help to mitigate potential risks and keep your system secure.
Impact of Malware on System Files and SFC’s Role
Malware can corrupt or replace legitimate system files, leading to instability and security vulnerabilities. SFC can help detect and restore these corrupted files, thus mitigating the damage caused by malware. Identifying the malware and removing it are critical steps after using SFC to restore system files.
Ensuring SFC Does Not Interfere with Other System Processes
SFC, as a system utility, can interact with other running processes. Careful planning is essential to prevent conflicts or unintended consequences. Monitoring resource usage during an SFC scan can help prevent conflicts and ensure smooth operation.
Role of System Integrity Checks in Overall Security
System integrity checks, including SFC, are crucial components of a robust security strategy. Regular checks can detect and rectify corrupted files, preventing potential vulnerabilities and maintaining the system’s overall health. They provide a vital line of defense against malicious attacks.
“System integrity checks are vital to maintaining a secure and stable computing environment. Regular checks can help detect and mitigate threats to system stability and security.”
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, running System File Checker (SFC) is a vital step in maintaining a healthy Windows system. This guide provided a comprehensive overview, from fundamental usage to advanced troubleshooting and security best practices. By understanding the different methods, common issues, and optimization strategies, you can confidently use SFC to ensure your system’s integrity. Remember to always back up your data before initiating any repair process.
Now you’re equipped with the knowledge to keep your Windows system running like a well-oiled machine!