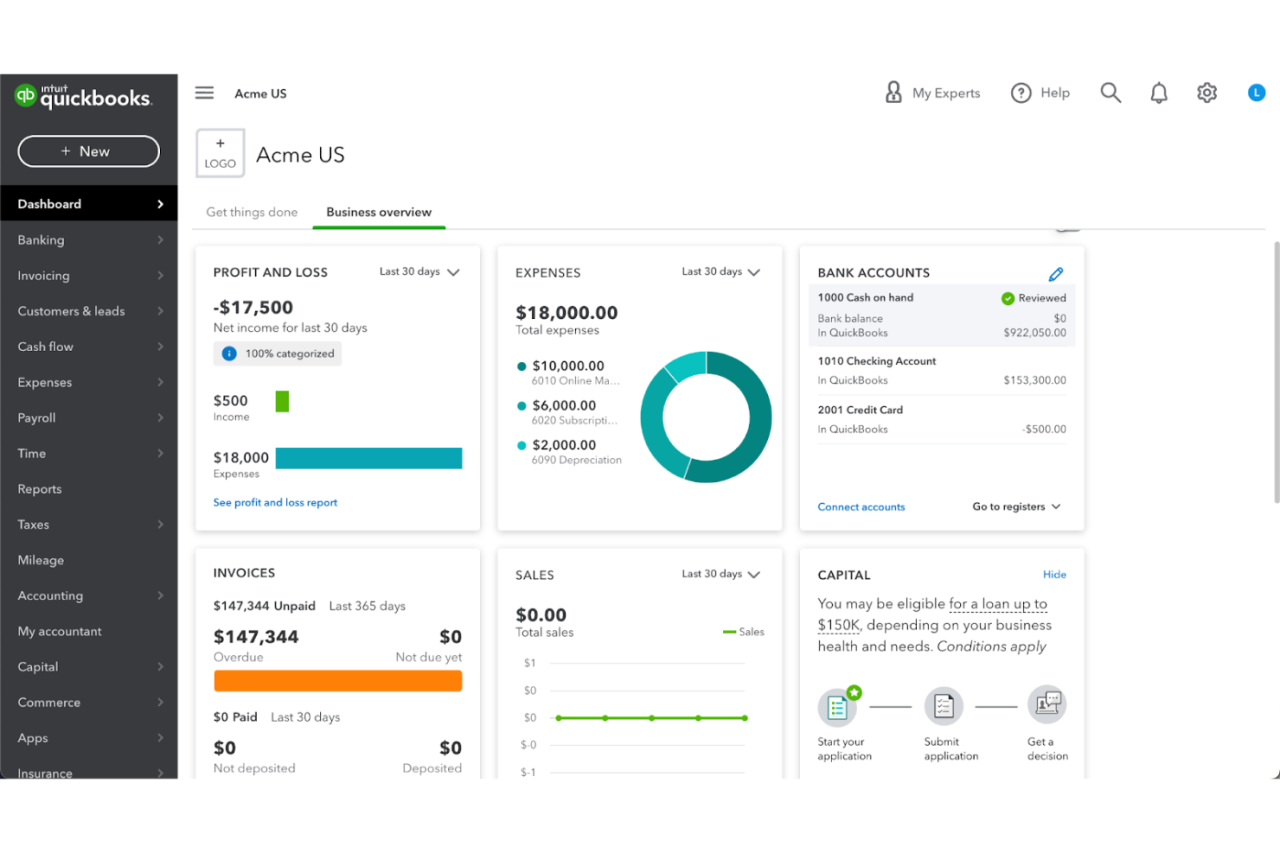
Best Financial Management Software Your Ultimate Guide
Best financial management software is crucial for anyone managing finances, whether a small business owner or a seasoned investor. This guide dives deep into the world of financial management tools, exploring various types, features, and how to choose the right one for your needs. From budgeting and accounting to investment tracking, we’ll cover everything you need to know to make informed decisions and optimize your financial well-being.
This comprehensive guide examines the key aspects of choosing the right financial management software. We’ll explore essential features, compare popular options, and highlight the benefits of adopting such software for improved accuracy and efficiency. We’ll also touch upon crucial implementation steps and real-world case studies to provide practical insights.
Introduction to Financial Management Software
Financial management software is a powerful tool for individuals and businesses to organize, track, and analyze their financial data. It streamlines the process of managing finances, allowing users to make informed decisions and achieve their financial goals. This software can automate tasks, provide insights, and ultimately improve overall financial well-being.This software encompasses a wide range of functionalities, from basic budgeting and accounting to complex investment strategies.
Understanding the different types of software and their specific capabilities is crucial for choosing the right solution to meet your needs.
Types of Financial Management Software
Financial management software comes in various forms, each catering to different aspects of financial administration. These range from basic budgeting tools to sophisticated investment platforms, each with its own set of strengths. Understanding these different types helps in selecting the most suitable option for individual or business needs.
- Budgeting Software: These programs help users create and track budgets, monitor expenses, and identify areas where spending can be reduced. They typically include features for income tracking, expense categorization, and visualization of spending patterns. Examples include Mint and Personal Capital.
- Accounting Software: Designed for businesses and organizations, these tools manage transactions, generate financial reports, and handle payroll. More sophisticated versions offer features for inventory management and accounts receivable/payable. Popular examples include QuickBooks and Xero.
- Investment Tracking Software: This category focuses on managing investment portfolios, tracking performance, and generating reports on investment returns. Tools often include features for portfolio diversification, risk assessment, and comparison of different investment options. Examples include Fidelity Go and Vanguard Personal Advisor.
Common Features of Financial Management Software
Most financial management software shares core functionalities to facilitate financial planning and analysis. These common features contribute to the overall effectiveness of the software in handling financial tasks.
- Data Entry and Management: The ability to input financial transactions, including income and expenses, is fundamental. Effective data management ensures accuracy and allows for detailed analysis.
- Reporting and Analysis: Generating reports on financial performance is a key feature. These reports can include income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements, providing insights into the financial health of the user.
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Creating and managing budgets is a common feature, helping users plan for future expenses and income. Sophisticated software also allows for forecasting based on historical data and projected trends.
- Automated Reminders and Notifications: These features help users stay organized by sending reminders for payments, upcoming bills, and other financial obligations.
Comparison of Financial Management Software Types
The table below compares and contrasts the key features of three different types of financial management software: budgeting, accounting, and investment tracking. This comparison highlights the specific functionalities each type offers and can assist in selecting the appropriate software for particular needs.
| Feature | Budgeting Software | Accounting Software | Investment Tracking Software |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Entry | Income and expense tracking, simple transactions | Complex transactions, invoices, bills, payroll | Investment transactions, stock trades, mutual fund activity |
| Reporting | Spending summaries, expense categorization, visualizations | Financial statements (income statement, balance sheet, cash flow), detailed transaction reports | Portfolio value, performance tracking, investment return analysis |
| Budgeting | Core function, creating and tracking budgets | Limited budgeting features, often integrated with other modules | Limited budgeting features, focuses on investment strategies |
| Investment Tracking | Limited investment tracking (if any) | No investment tracking | Core function, portfolio management, investment analysis |
Choosing the Right Software
Finding the perfect financial management software is crucial for any business, regardless of size. It’s not just about tracking expenses; it’s about streamlining operations, making informed decisions, and ultimately, achieving financial success. Choosing the wrong software can lead to wasted time, inaccurate data, and lost opportunities. This section delves into the key factors to consider when making this important decision.Selecting the right financial management software requires careful consideration of various factors.
Finding the best financial management software can be tricky, but it’s crucial for any business. Thinking about recent events, like the Utah Utes firing Craig Smith, highlights the importance of careful resource allocation, which is something that good financial management software can help with. Understanding the strategic implications of such decisions, as detailed in this article about utah fires craig smith on the curious timing the resource commitment and what comes next for the utes , shows how effective financial management is essential for making informed decisions.
Ultimately, the right software streamlines processes and ensures optimal use of resources, which is key for long-term success.
These factors extend beyond just the initial cost, encompassing the long-term benefits and potential for growth. Understanding your business’s specific needs, size, and budget is paramount in choosing a solution that aligns with your present and future goals.
Factors to Consider When Selecting Software
Different businesses have unique needs. A small startup will have different requirements from a large corporation. Understanding your business’s size and specific needs is critical. Consider factors such as the number of employees, the complexity of transactions, and the types of financial data you need to track.
- Budget: Software costs vary significantly. Free options exist, but they often come with limited features. Mid-range solutions offer a balance of features and cost, while enterprise-level software can be tailored to the most complex financial needs. A clear budget will help narrow down the search.
- Business Size: Small businesses might benefit from cloud-based software with user-friendly interfaces, while larger organizations may require more advanced features, such as multi-user access and detailed reporting.
- Specific Needs: Some businesses need specialized features, like inventory management, while others may focus on invoicing and customer relationship management. Identify the essential features that are vital for your business’s operations.
Importance of User-Friendliness
A user-friendly interface is essential for efficient financial management. Software that is intuitive and easy to navigate will save time and reduce errors. Employees will be more likely to use the system consistently, leading to more accurate data and better financial insights.Ease of use translates to faster data entry, less frustration, and increased adoption rates among employees. This translates to fewer errors, greater accuracy, and improved data quality.
It allows staff to focus on higher-level tasks instead of struggling with complex software.
Robust Reporting Capabilities
Financial management software should provide comprehensive reporting capabilities. Reports should be customizable and easily generated to provide insights into various aspects of your finances. Key performance indicators (KPIs) should be easily trackable. This allows for informed decision-making, trend analysis, and proactive adjustments to strategies.Detailed and insightful reports are crucial for understanding the financial health of your business.
The ability to generate reports on various aspects of your finances, such as revenue, expenses, and profitability, is essential for strategic decision-making. Customized reports can offer granular details, allowing for more accurate analyses.
Pricing Models
Software pricing models vary significantly. Some software uses a subscription model, where you pay a recurring fee based on the features and users. Other solutions may have one-time purchase options or tiered pricing structures based on the level of features required.Understanding the different pricing models is crucial. Factors such as the number of users, features included, and support services all influence the final cost.
Compare pricing options carefully to determine the most cost-effective solution for your needs. Be sure to factor in any additional costs such as training or implementation fees.
Comparison of Popular Software
This table compares three popular financial management software options, highlighting their pros and cons.
| Software | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Software A | User-friendly interface, robust reporting, affordable pricing | Limited customization options, fewer advanced features |
| Software B | Extensive features, highly customizable, strong support | Steep learning curve, higher price point |
| Software C | Excellent for small businesses, free tier available | Limited features, less robust reporting capabilities |
Benefits of Using Financial Management Software
Financial management software is no longer a luxury but a necessity for businesses of all sizes. From streamlining accounting processes to empowering better financial decision-making, these tools offer significant advantages over manual methods. By automating tasks and providing insightful data, software empowers businesses to optimize their financial performance.
Improved Accuracy and Efficiency
Financial management software drastically improves the accuracy of financial data by eliminating manual data entry errors. This is particularly crucial for large volumes of transactions. Automated calculations ensure consistency and reduce the potential for human error, resulting in more reliable financial statements. Further, the automation of repetitive tasks frees up valuable time for financial professionals to focus on strategic analysis and decision-making.
This efficiency boost leads to quicker turnaround times for reports and faster response to financial fluctuations.
Enhanced Financial Decision-Making
Financial management software provides a comprehensive view of financial performance, enabling informed decision-making. Real-time data visualization tools allow users to quickly analyze trends, identify patterns, and make data-driven choices. This detailed insight into cash flow, profitability, and expenses empowers businesses to make proactive adjustments to strategies and achieve desired financial outcomes. By identifying potential problems early, software helps businesses react swiftly to changes in the market and optimize resources for maximum impact.
Streamlined Accounting Process
Financial management software streamlines the entire accounting process, from recording transactions to generating reports. Automated data entry, reconciliation, and reporting capabilities reduce manual effort significantly. Software often integrates with other business systems, further automating processes like invoicing and expense tracking. This integration ensures data consistency and reduces the likelihood of errors arising from manual data transfer between systems.
An example of this streamlined process is automating invoice processing, allowing for quicker payments and improved cash flow.
Reduced Errors and Improved Financial Control
By automating various financial tasks, software minimizes the potential for human error, leading to greater accuracy and reliability in financial reporting. This is particularly important for compliance with accounting standards and regulations. Furthermore, the centralized data storage facilitated by financial management software improves financial control by providing a single source of truth for all financial information. This ensures everyone involved has access to the same accurate data, preventing discrepancies and enhancing accountability.
Robust audit trails are often built into the software, making it easier to track changes and identify any irregularities.
Time Saved with Financial Management Software
| Accounting Task | Time Saved (Estimated, Manual vs. Software) |
|---|---|
| Data Entry | Up to 80% |
| Report Generation | Up to 75% |
| Reconciliation | Up to 90% |
| Invoice Processing | Up to 60% |
| Expense Tracking | Up to 70% |
The table above illustrates the substantial time savings achievable through the use of financial management software. These estimations highlight the significant efficiency gains that businesses can experience by transitioning from manual processes to automated systems. The figures vary based on the complexity of the task and the specific software used.
Features and Capabilities: Best Financial Management Software
Choosing the right financial management software hinges on understanding its core functionalities. Beyond the basic accounting capabilities, robust software offers a suite of features designed to streamline financial processes, improve decision-making, and ultimately, drive business success. These features range from budgeting tools to advanced forecasting capabilities, all contributing to a more comprehensive financial picture.
Budgeting Tools
Effective financial management relies heavily on accurate budgeting. Financial management software with robust budgeting tools empowers users to create, track, and monitor budgets across various departments or projects. These tools facilitate the setting of realistic financial targets and allow for continuous monitoring of progress against those targets. Real-time updates provide a clear picture of variances, allowing for proactive adjustments and informed decision-making.
This feature is invaluable for businesses of all sizes, from startups to established corporations, helping them stay on track financially and avoid unexpected issues.
Finding the perfect financial management software can be a game-changer for your finances. But sometimes, you need a sharp tool to really get into the nitty-gritty, like the best steak knife sets for a perfectly sliced cut. Ultimately, the right financial management software is key to a well-organized budget and future financial freedom.
Reporting and Analysis Features
Comprehensive reporting and analysis are critical components of any effective financial management system. Software with robust reporting features allows for the generation of insightful reports tailored to specific needs. These reports can encompass everything from income statements and balance sheets to detailed performance metrics. Furthermore, advanced analytical tools provide in-depth insights into financial trends, allowing for data-driven decision-making and strategic planning.
These features allow users to identify patterns, pinpoint areas of improvement, and forecast future performance.
Advanced Features
Premium financial management software often includes advanced features designed to provide deeper insights and support more complex financial strategies. These include sophisticated forecasting capabilities that extrapolate current trends to predict future financial performance. Financial modeling tools allow for “what-if” scenarios, enabling users to assess the impact of different strategic decisions on their financial position. This level of detail is particularly valuable for companies looking to plan for expansion, mergers, or acquisitions.
For instance, a company considering a new product line could use financial modeling to project potential sales, costs, and profitability, making more informed decisions.
Finding the best financial management software can be tricky, but it’s crucial for anyone managing their finances. Thinking about the impact of climate change, especially extreme cold events, is equally important. Recent polls, like this one on the effects of extreme cold climate change, extreme cold climate change poll , highlight the need for careful financial planning in the face of unpredictable weather.
Ultimately, a robust financial management system will help you adapt and overcome these challenges, whether you’re tracking personal budgets or running a business.
Integration with Other Business Tools
Modern businesses rely on various tools to manage different aspects of their operations. A key benefit of modern financial management software is its ability to integrate with other business applications. This integration allows for seamless data flow between systems, reducing manual data entry and enhancing data accuracy. For example, integration with CRM systems allows for the linking of customer data with financial transactions, providing a holistic view of customer profitability and purchasing patterns.
This interconnectedness can streamline workflows, automate processes, and ultimately improve overall business efficiency.
Security and Data Protection
In today’s digital landscape, security and data protection are paramount. Financial management software must prioritize the security of sensitive financial data. Robust security features, including encryption, access controls, and regular security audits, are essential to safeguard against unauthorized access and data breaches. This is not just a matter of compliance but also of protecting the financial well-being of the business and maintaining the trust of stakeholders.
Key Features Summary
| Feature | Functionality |
|---|---|
| Budgeting | Creating, tracking, and monitoring budgets across departments or projects; identifying variances and making adjustments. |
| Reporting & Analysis | Generating insightful reports (e.g., income statements, balance sheets); providing in-depth financial trend analysis. |
| Forecasting | Extrapolating current trends to predict future financial performance. |
| Financial Modeling | Assessing the impact of different strategic decisions on financial position through “what-if” scenarios. |
| Integration | Seamless data flow between financial management software and other business applications (e.g., CRM, ERP). |
| Security | Protecting sensitive financial data through encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. |
Implementation and Integration
Choosing the right financial management software is only half the battle. Successful implementation hinges on a smooth transition, effective staff training, and meticulous data management. A well-executed implementation ensures the software seamlessly integrates into your existing workflow, maximizing its benefits and minimizing disruptions.Implementing financial management software is a multi-faceted process requiring careful planning and execution. This involves not only the technical aspects of installation and integration but also the crucial element of user training to ensure everyone is proficient in utilizing the new system.
Data migration is another critical step, requiring meticulous planning to avoid errors and ensure the integrity of your financial records.
Typical Implementation Process
A typical implementation process follows a structured approach, involving several key phases. These phases are crucial for a successful transition and minimize disruptions to daily operations. A well-defined implementation plan ensures that the project is completed on time and within budget. This also helps avoid potential pitfalls, ensuring a smooth integration.
- Needs Assessment and Planning: This phase involves a thorough evaluation of your current financial processes and identifying areas where the software can improve efficiency. The software selection should align with the specific requirements of the business. This stage involves detailed documentation of the current processes and identification of the desired outcomes of the software implementation.
- Software Configuration and Setup: This stage focuses on installing the software and configuring it to meet the specific needs of the organization. Customizations and configurations should be meticulously documented. The process includes creating user accounts, setting up security protocols, and configuring data import options.
- Data Migration: The process of transferring existing financial data into the new system is crucial. Data integrity is paramount, requiring careful validation and cleansing of the data before import. The process should be tested thoroughly to ensure accuracy and minimize potential errors.
- User Training and Support: Comprehensive training is essential for users to effectively utilize the software. Training programs should be tailored to the specific needs and roles of different staff members. Ongoing support is vital for addressing questions and concerns.
- Testing and Validation: Rigorous testing is crucial to ensure the accuracy and functionality of the software. This phase involves running various scenarios and tests, including data entry and reporting functions. Identifying and rectifying any errors in this stage will prevent major problems later on.
- Deployment and Go-Live: The final phase involves deploying the software to all users and transitioning operations to the new system. This stage needs a smooth plan for data transfer, ensuring minimal disruption to normal business activities.
Integrating with Existing Systems
Integrating financial management software with existing systems is a critical step for seamless data flow and improved efficiency. This integration should be planned meticulously to ensure that data flows correctly between systems.
- API Integration: Many financial management software solutions offer Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) to facilitate data exchange with other systems. These APIs enable seamless communication and data transfer between different applications, eliminating manual data entry and reducing errors.
- Data Mapping: Proper data mapping is essential to ensure that data from different systems aligns correctly. This involves establishing a clear mapping between fields in the existing systems and the new financial management software. This ensures that data is transferred accurately.
- Data Validation: Implementing validation checks throughout the integration process is crucial to ensure data accuracy. These checks should identify inconsistencies or errors in the data before it’s transferred to the new system.
Staff Training
Effective staff training is essential for maximizing the benefits of the new financial management software.
- Tailored Training Programs: Training programs should be tailored to the specific needs and roles of each staff member. This approach ensures that employees understand the features relevant to their jobs. This reduces confusion and enhances efficiency.
- Hands-on Workshops: Hands-on workshops and practical exercises are beneficial for enhancing understanding. These allow users to interact directly with the software and develop practical skills.
- Ongoing Support: Providing ongoing support and access to resources after the initial training is essential. This allows staff to address questions and concerns as they arise. A dedicated support team is invaluable in this regard.
Importing Existing Data
Importing existing data into the new financial management software requires careful planning and execution.
- Data Extraction: Extract data from the current system in a structured format. This involves defining the specific data fields to be imported and using the appropriate tools for extraction.
- Data Cleaning and Transformation: Clean and transform the extracted data to align with the new software’s format. This may involve handling missing values, correcting errors, and converting data types. Data cleaning is crucial for preventing errors in the new system.
- Data Validation: Validate the imported data to ensure accuracy and completeness. This step involves comparing the imported data with the original data and resolving any discrepancies. This is an essential step in preventing errors.
- Data Loading: Import the cleaned and validated data into the new financial management software. This step involves using the software’s import features and ensuring the data is loaded correctly.
Data Backup and Recovery
Robust data backup and recovery procedures are critical to protect financial records from loss.
- Regular Backups: Implement a regular backup schedule for the financial data to safeguard against data loss. The backup should be stored in a secure location, separate from the primary system. Frequency of backups should be established according to the organization’s needs.
- Testing Recovery Procedures: Regularly test the recovery procedures to ensure they function as expected. This will help identify and resolve any issues before they impact operations. Testing recovery procedures is essential to minimize downtime.
- Data Security Measures: Employ appropriate security measures to protect the backups from unauthorized access. This includes encryption and access controls. Ensuring data security is paramount for any financial data.
Implementation Stages
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Needs Assessment | Evaluating current processes, identifying software requirements |
| Configuration & Setup | Installing and configuring the software |
| Data Migration | Transferring existing data to the new system |
| Training | Providing comprehensive training to staff |
| Testing | Testing the software and data integrity |
| Deployment | Transitioning to the new system |
Case Studies and Examples
Financial management software is no longer a luxury; it’s a necessity for businesses of all sizes. Seeing how real businesses have leveraged these tools to streamline operations, improve profitability, and achieve specific goals is invaluable. This section explores real-world examples and highlights the positive impacts of effective financial management software implementations.
Successful Implementations Across Industries
Diverse businesses have successfully integrated financial management software to enhance their financial health. These examples demonstrate the software’s versatility and applicability across various sectors. For instance, a small bakery using software to manage inventory, track sales, and monitor expenses can quickly identify areas for improvement and adjust their pricing strategy. Likewise, a non-profit organization can use software to manage donations, track expenses, and generate financial reports, allowing them to demonstrate accountability and secure future funding.
Improving Cash Flow Management
Financial management software excels at streamlining cash flow management. One example is a retail clothing store that utilizes software to automate invoice processing, payment reminders, and reconciliation. This automation frees up staff time and reduces errors, allowing the store to collect payments more efficiently and predict future cash needs. The improved visibility into cash flow enables the business to make informed decisions about inventory purchases and staffing levels, leading to more efficient operations.
Aiding in Tax Preparation
Financial management software significantly simplifies tax preparation. Consider a restaurant owner who uses software to automatically categorize expenses, track receipts, and generate reports. This streamlined process not only ensures accurate tax reporting but also allows the business owner to identify deductions and credits, optimizing their tax position. The software often integrates with tax preparation software, providing a seamless workflow for accurate and timely filing.
Table of Case Study Summaries
| Industry | Challenge | Software Solution | Positive Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Retail | Difficulty managing inventory, slow payment collection, inaccurate financial reporting | Financial management software with inventory tracking, automated invoice processing, and reporting capabilities | Improved inventory management, reduced operational costs, increased revenue, and more accurate financial reporting |
| Construction | Complex project accounting, difficulty tracking expenses and managing invoices, inefficient cash flow | Project-based financial management software with detailed cost tracking, expense categorization, and real-time cash flow monitoring | Reduced project costs, improved project profitability, enhanced cash flow prediction, and accurate reporting for clients |
| Non-profit | Maintaining accurate records of donations and expenses, ensuring transparency, securing future funding | Financial management software with donor management, expense tracking, and comprehensive reporting | Enhanced transparency, improved donor relations, and facilitated accurate financial reporting, attracting more donations and grant opportunities |
Future Trends
The financial management software landscape is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing user needs. Emerging trends are reshaping how businesses and individuals manage their finances, promising greater efficiency, accuracy, and insight. This evolution is crucial for staying competitive and adapting to the dynamic demands of the modern financial world.
Cloud-Based Solutions, Best financial management software
Cloud-based financial management software is rapidly gaining traction due to its accessibility, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. Businesses and individuals can access their financial data from anywhere with an internet connection, eliminating the need for expensive on-premises servers and complex installations. This flexibility allows for real-time collaboration and data sharing, which is particularly beneficial for businesses with remote teams or multiple locations.
Furthermore, cloud providers often handle maintenance and updates, freeing up internal IT resources to focus on core business functions.
AI Integration
Artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to revolutionize financial management software. AI-powered tools can automate tasks like data entry, report generation, and fraud detection. Sophisticated algorithms can identify patterns and anomalies in financial transactions, providing valuable insights for improved decision-making. AI can also personalize financial advice and recommendations, tailoring strategies to individual needs and circumstances. For example, AI-driven platforms can suggest optimal investment portfolios based on risk tolerance and financial goals.
Automation of Financial Tasks
Automation is transforming many aspects of financial management. Software can automate repetitive tasks such as invoice processing, expense tracking, and reconciliation. This automation leads to increased efficiency, reduced errors, and substantial time savings. By automating these processes, companies can allocate more resources to strategic initiatives and decision-making. Automated systems can also be programmed to adhere to compliance regulations, minimizing the risk of penalties and legal issues.
Mobile Accessibility
Mobile accessibility is becoming increasingly important in financial management software. Users expect to access and manage their finances on their smartphones and tablets. Mobile-friendly platforms provide convenient access to accounts, transactions, and reports anytime, anywhere. This accessibility is crucial for individuals who need to manage their finances on the go, such as freelancers or business owners. Moreover, real-time mobile updates ensure users always have the most current financial information available.
Predicted Advancements in Financial Management Software (Next 5 Years)
| Feature | Predicted Advancement | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Data Security | Enhanced encryption, multi-factor authentication, and advanced fraud detection algorithms will become standard. | Increased trust and confidence in using the software, leading to greater adoption. |
| AI-Driven Insights | Software will provide more sophisticated predictive analytics and personalized financial advice, offering proactive recommendations for better financial outcomes. | Improved decision-making and optimized resource allocation, especially for investment and budgeting. |
| Hyper-Personalization | Software will adapt to individual user behavior and preferences, delivering tailored financial strategies. | Increased user engagement and satisfaction, resulting in more effective financial management. |
| Integration Capabilities | Seamless integration with other business applications, such as accounting and CRM software, will become more prevalent. | Enhanced data flow and improved workflow efficiency across different business functions. |
| Natural Language Processing (NLP) | NLP will facilitate natural communication with the software, enabling users to query and receive financial information in a more conversational way. | Improved user experience and reduced learning curve for using the software. |
Last Point
In conclusion, selecting the best financial management software is a crucial step toward better financial control and informed decision-making. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview, covering everything from software types and features to implementation and future trends. By considering your specific needs and priorities, you can choose the ideal software to streamline your financial processes and achieve your goals.