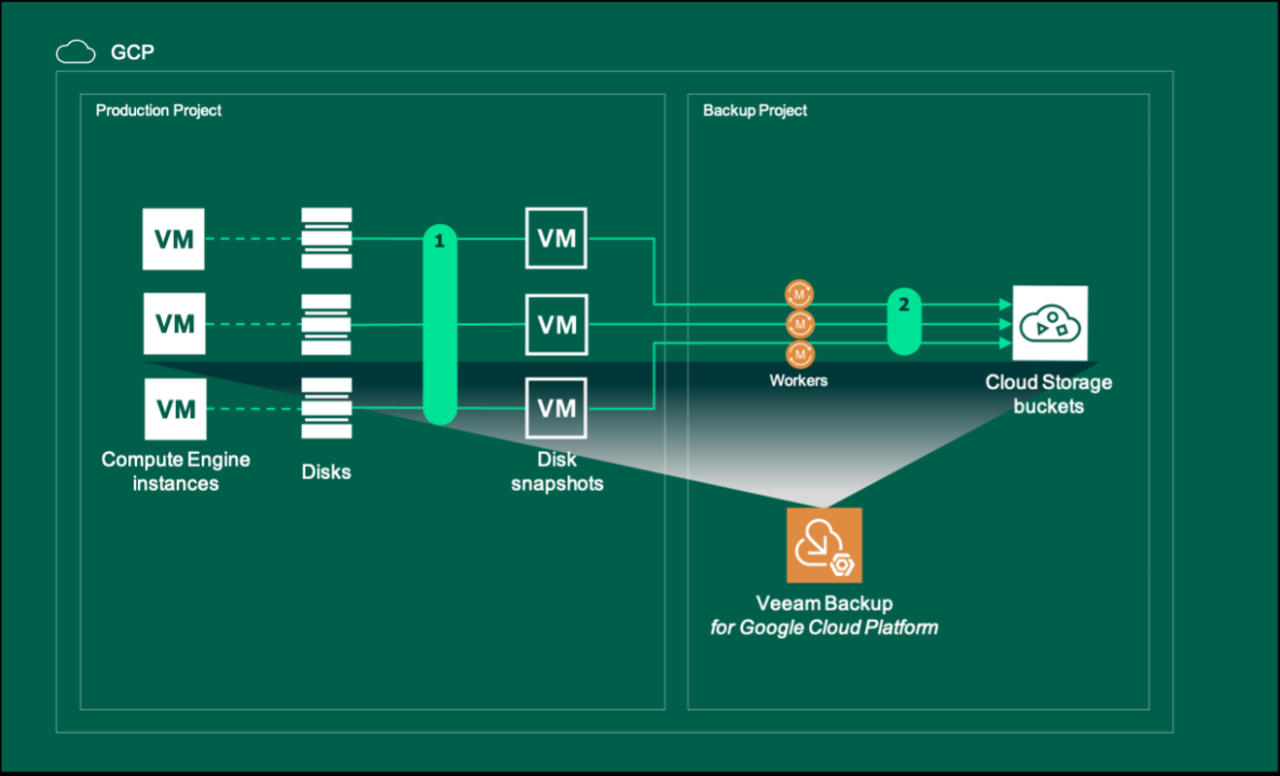
Google Cloud VM Backup A Comprehensive Guide
Google Cloud VM backup sets the stage for a deep dive into securing your virtual machines. This guide explores the various backup options available within Google Cloud Platform, from basic strategies to advanced configurations. We’ll cover everything from understanding different backup types to ensuring your backups are secure and compliant with industry standards.
This in-depth look at Google Cloud VM backups covers essential topics like choosing the right backup strategy, implementing effective configurations, and recovering your data in the event of a failure. We’ll examine how to manage backup retention, optimize performance, and ensure compliance. A table comparing backup solutions and a breakdown of security considerations are also included.
Introduction to Google Cloud VM Backup
Protecting your virtual machines (VMs) on Google Cloud Platform (GCP) is crucial for business continuity and disaster recovery. Regular backups ensure data availability and minimize downtime in case of unforeseen events. This article explores the concept of VM backups within GCP, outlining the available options and emphasizing their importance.Google Cloud offers various backup solutions tailored to different needs and budgets.
These solutions range from simple snapshots to comprehensive replication strategies, providing flexibility for managing VM backups. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each option is key to choosing the best approach for your specific environment.
VM Backup Concepts in GCP
Virtual Machine (VM) backups in GCP are crucial for safeguarding data stored within the VM’s disk. These backups allow you to restore the VM to a previous state in case of data loss or system failure. Different backup strategies address varying needs, enabling granular control over data protection.
Backup Options within Google Cloud
Google Cloud provides a spectrum of backup solutions, each with its own set of features and capabilities. This variety allows organizations to select the approach best suited to their specific needs and budget.
- Snapshots: These are point-in-time copies of your VM disks. They are efficient for quick recovery and can be used to create backups for specific instances.
- Automated Backups: Google Cloud provides automated backup solutions, which are configured to regularly create backups of your VMs. These solutions are particularly useful for maintaining a consistent backup schedule and are well-suited for recurring backups.
- Replication: This approach involves creating a copy of the VM in a different location. This is a robust solution, offering high availability and data protection. This replication process is valuable for disaster recovery scenarios, ensuring business continuity.
Benefits of Regular VM Backups
Regular VM backups are critical for maintaining data integrity and ensuring business continuity. Implementing a robust backup strategy reduces the risk of data loss and minimizes potential disruptions.
- Data Protection: Backups safeguard data from various threats, such as accidental deletion, hardware failure, or malicious attacks.
- Disaster Recovery: Regular backups allow for quick and easy restoration of VMs in case of a disaster. This minimizes downtime and data loss during recovery.
- Compliance: In many industries, data backup is a regulatory requirement. Regular backups ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
Comparison of VM Backup Solutions
The table below compares different VM backup solutions offered by Google Cloud.
| Backup Solution | Features | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Snapshots | Point-in-time copies of disks; easy to restore; low cost. | Fast recovery; simple setup; cost-effective for frequent recovery points. | Limited recovery options for complex scenarios; may not meet stringent recovery needs. |
| Automated Backups | Scheduled backups; configurable retention policies; integration with other GCP services. | Automated management; predictable recovery; enhanced compliance. | May not be ideal for very large VMs or high-frequency recovery requirements. |
| Replication | Creating copies of VMs in a different location; high availability. | Robust disaster recovery; high availability; minimal data loss in outages. | Higher cost than other options; setup can be more complex. |
Backup Strategies and Methods
Choosing the right backup strategy for your Google Cloud VMs is crucial for data protection and business continuity. A well-defined strategy ensures your data is safeguarded against various threats, ranging from accidental deletion to catastrophic hardware failures. This section delves into different backup strategies, their effectiveness, and how to select the best approach for your specific needs.Different backup strategies offer varying levels of efficiency and data recovery speed.
Understanding these nuances allows you to tailor your backup plan to your unique requirements, ensuring optimal protection without unnecessary overhead.
Setting up Google Cloud VM backups is crucial for data safety, especially when dealing with sensitive information. Recent issues like the realpage rent algorithm berkeley lawsuit highlight the importance of robust systems for safeguarding data. Proper VM backups ensure business continuity and help prevent costly data loss, a lesson that applies equally to both personal and professional settings.
Backup Strategy Types
Various backup strategies cater to different needs and priorities. Understanding the characteristics of each strategy is key to selecting the most appropriate one.
- Full Backup: A full backup copies the entire VM’s data. It’s comprehensive but can be time-consuming, especially for large VMs. Its advantage lies in its ability to restore the entire system quickly in the event of a complete loss. This method is useful for initial backups or when complete data recovery is needed immediately. A common use case would be backing up a new VM or a VM that has undergone significant changes.
- Incremental Backup: An incremental backup only copies the data that has changed since the last backup. This significantly reduces backup time and storage requirements compared to a full backup, especially for VMs with frequent minor changes. However, it requires the previous incremental backup to restore the data, potentially making the restoration process slightly more complex. This strategy is ideal for VMs with consistent, smaller updates, such as development environments or databases.
Keeping my Google Cloud VM backups safe is crucial, but sometimes, the most important backups are the ones for your furry friend! Rainy days call for a good waterproof dog raincoat, and finding the best ones can be a challenge. Thankfully, the best waterproof dog raincoats for rainy day walks provides a great resource for choosing the perfect gear for your pup.
No matter the weather, having reliable backup solutions is key, whether it’s for your data or your dog’s comfort. Backups are essential, and so are the best raincoats.
- Differential Backup: A differential backup copies the data that has changed since the last full backup. It combines the speed of incremental backups with the completeness of full backups. This method is faster than a full backup and uses less storage than incremental backups, but still requires the full backup for restoration. Differential backups are suitable for situations where a full backup is performed regularly, and subsequent changes are relatively frequent.
Backup Strategy Comparison
The choice of backup strategy depends on factors such as data volume, update frequency, and recovery time objectives. Each strategy offers a trade-off between speed, storage space, and restoration complexity.
| Backup Strategy | Efficiency | Effectiveness | Storage Usage | Restoration Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full | Low | High | High | Fast |
| Incremental | High | Moderate | Low | Moderate |
| Differential | High | High | Moderate | Moderate |
Selecting the Optimal Strategy
Consider the following factors when choosing the best backup strategy:
- Data Volume: For large VMs, incremental or differential backups are more efficient than full backups.
- Update Frequency: If the VM data changes frequently, incremental or differential backups are preferred for reduced backup time.
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): If rapid recovery is essential, a full backup might be necessary, even if it’s less efficient.
- Storage Capacity: Incremental and differential backups use less storage space than full backups.
Backup Scheduling
Regular backup scheduling is essential for data protection. A well-defined schedule ensures consistent backups and minimizes data loss risk.
| Schedule Type | Frequency | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Daily | Once per day | Suitable for VMs with frequent but not constant changes. |
| Weekly | Once per week | Suitable for VMs with less frequent changes, like production servers. |
| Monthly | Once per month | Suitable for archival purposes or less-critical VMs. |
| Custom | Variable | Allows for customized scheduling based on specific needs. |
Backup Configuration and Implementation: Google Cloud Vm Backup
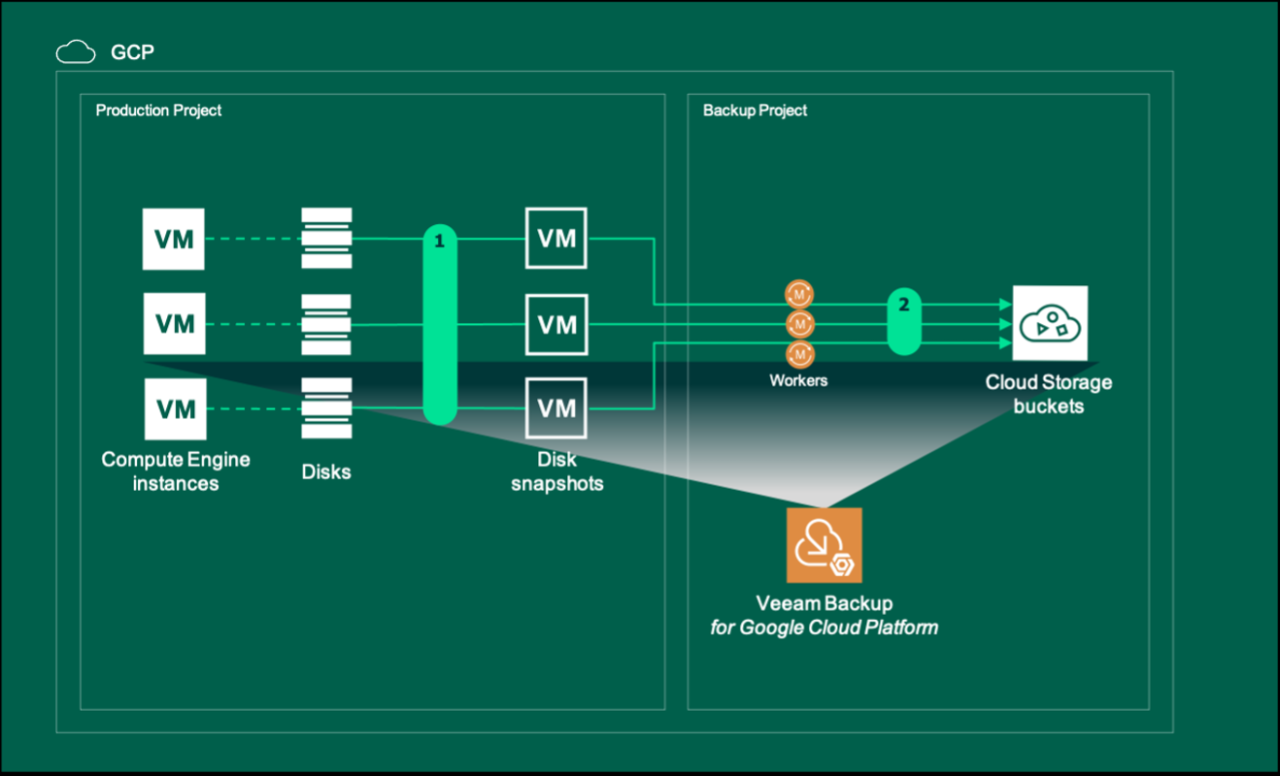
Setting up reliable backups for your Google Cloud Virtual Machines (VMs) is crucial for data protection and business continuity. This process involves careful configuration choices to ensure backups are effective and meet your specific needs. Choosing the right strategy and implementing it correctly can save you significant time and effort in the event of data loss.Implementing robust backup strategies involves more than just selecting a tool.
It requires understanding the nuances of backup configuration options, the parameters that influence backup performance, and how to manage retention policies for optimal data protection. This section dives into the specifics of configuring VM backups, outlining the steps and options available within Google Cloud.
Configuring Backup Schedules
Backup schedules determine when backups are taken. Regular backups are essential to maintain data integrity and minimize data loss. Setting a schedule ensures that backups occur consistently, minimizing the risk of missing critical data updates. A well-defined schedule ensures that you have frequent snapshots of your data for recovery purposes. It is crucial to establish a schedule that aligns with your organization’s operational needs.
For instance, backups can be scheduled hourly, daily, or weekly.
Selecting Backup Storage Locations
Choosing the right storage location is important for optimal backup performance and cost-effectiveness. Different storage options provide varying levels of performance and durability, impacting backup speed and cost. Google Cloud Storage provides a range of storage classes, including standard, nearline, and coldline, each with different pricing models and access speeds. Choosing the correct storage class balances your needs for recovery speed and cost-effectiveness.
Consider factors like the frequency of recovery needs and your budget when selecting a storage location.
Defining Backup Retention Policies
Backup retention policies dictate how long backups are stored. Setting appropriate retention periods balances the need for long-term data preservation with storage costs. For instance, you might want to keep backups for 7 days for immediate recovery needs and 30 days for compliance purposes. This policy allows for efficient management of your backup storage space while ensuring access to historical data as required.
Carefully consider the regulatory requirements and business continuity needs when establishing retention policies.
Essential Parameters for Configuration
A variety of parameters influence the effectiveness and efficiency of VM backups. These parameters should be carefully considered to ensure optimal backup performance.
| Configuration Setting | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Backup Schedule | Frequency and time of backups. | Impacts backup frequency and data coverage. |
| Storage Location | Cloud Storage location for backups. | Affects backup speed and cost. |
| Retention Policy | How long backups are kept. | Balances data preservation with storage costs. |
| Backup Type | Incremental or full backups. | Impacts backup size and speed. |
| Backup Source | The specific VM to be backed up. | Ensures the correct VM is targeted for backup. |
Step-by-Step Procedure for Configuring Backups
This procedure Artikels the steps to configure and implement backups for a specific VM instance.
1. Access Google Cloud Console
Navigate to the Google Cloud Console.
2. Select the VM Instance
Identify the specific VM you want to back up.
3. Enable the Backup Service
Ensure the Backup service is enabled in your project.
4. Configure Backup Schedule
Set the desired backup frequency and time.
5. Select Storage Location
Choose the appropriate storage location.
6. Define Retention Policy
Determine the duration backups will be retained.
7. Verify Backup Settings
Review all settings to ensure they meet your requirements.
Keeping your Google Cloud VM backups up to date is crucial, especially when considering the recent avian flu outbreak. The spread of the virus, particularly in agricultural settings, is raising some interesting questions. For example, why is Finland proactively vaccinating farmers while California isn’t? This Q&A article dives deep into the specifics: qa why finland is vaccinating farmers against bird flu but california isnt and more info about the spreading virus.
Understanding these preventative measures can inform better backup strategies for your own digital assets. Robust backup solutions are key to protecting your virtual machine data, no matter the global circumstances.
8. Initiate the Backup
Trigger the backup process.
Managing Backup Retention Policies
Modifying or deleting backup retention policies can be done within the Google Cloud Console. This process allows you to adjust retention periods based on evolving business needs. Regularly reviewing and updating retention policies is crucial for maintaining a balance between data protection and storage costs.
Backup Recovery and Restoration
Restoring your Google Cloud Virtual Machines (VMs) from backups is a crucial aspect of disaster recovery planning. A well-defined recovery strategy ensures minimal downtime and data loss in case of unforeseen events like hardware failures, accidental deletions, or malicious attacks. Understanding the process and different scenarios is key to maintaining business continuity.Effective restoration strategies go beyond simply retrieving data; they involve careful planning, clear procedures, and thorough testing to ensure a smooth and efficient recovery process.
Restoring VMs from Backups
Restoring a VM from a backup involves retrieving the entire VM state, including the operating system, applications, and data, to a new or existing instance. The restoration process is guided by the chosen backup strategy and the specific recovery point in time. The process often involves deploying a new VM instance and then restoring the necessary data and configuration from the backup.
Recovery Scenarios and Implications
Different recovery scenarios necessitate tailored restoration approaches. A hardware failure requires a complete VM restoration to a new instance. Accidental data deletion might necessitate a point-in-time restoration to a specific version. A ransomware attack might require a complete restore from a known good backup, excluding potentially infected data. Understanding these scenarios and their implications is critical for formulating a comprehensive disaster recovery plan.
Restoring to a Specific Point in Time
Google Cloud offers the ability to restore a VM to a specific point in time. This capability is vital for recovering from accidental modifications or data corruption. The specific point in time chosen is dependent on the backup strategy and the identified recovery point. This granular control allows for targeted recovery, minimizing the impact of data loss.
Careful planning is required to identify the correct recovery point and to ensure the restoration process is executed accurately.
Recovering Data from a Failed VM Instance
In the event of a failed VM instance, the recovery process may differ depending on the cause of the failure and the data’s importance. Complete restoration from a backup is often necessary. The restoration process typically involves creating a new VM instance and then transferring the backed-up data and configurations. Properly implemented backup strategies significantly ease the burden of recovering from a failed instance.
Restoration Options
| Restoration Method | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full VM Restore | Restores the entire VM state from a backup to a new or existing instance. | Preserves the entire VM configuration, including OS, applications, and data. | Can be time-consuming, especially for large VMs. |
| Point-in-Time Restore | Restores the VM to a specific point in time, preserving a snapshot of the data as it existed at that moment. | Allows recovery from accidental modifications or data corruption. | Requires careful selection of the recovery point and might not preserve recent changes. |
| Incremental Restore | Restores only the changes made since the last full backup. | Faster than full restores for recent data recovery. | Requires access to both full and incremental backups. |
| Data-Only Restore | Restores only specific data files or directories from a backup. | Useful for targeted data recovery. | Does not restore the entire VM configuration, potentially requiring additional setup. |
Backup Security and Compliance
Protecting your Google Cloud Virtual Machine (VM) backups is crucial for maintaining data integrity and adhering to regulatory requirements. Robust security measures ensure that sensitive information remains confidential and accessible only to authorized personnel. This section delves into the security considerations, best practices, and compliance aspects related to Google Cloud VM backups.Google Cloud provides a robust framework for securing backups, but proactive measures are essential to maintain a strong security posture.
Implementing encryption, access controls, and monitoring are key elements of a comprehensive backup security strategy. Furthermore, understanding industry regulations and tailoring backup practices to meet these requirements is paramount.
Security Considerations for Google Cloud VM Backups
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offers inherent security features for protecting backups, but implementing best practices further strengthens the overall security posture. Understanding the potential threats and vulnerabilities is crucial to developing a proactive security strategy.Data breaches, unauthorized access, and accidental data loss are significant risks. These risks are mitigated by employing strong authentication, encryption, and access controls. By implementing robust security measures, organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data compromise and ensure business continuity.
Security Best Practices for Google Cloud VM Backups
Implementing strong security practices is essential for safeguarding backups. These practices go beyond the inherent security of the platform, focusing on proactive measures to protect sensitive data.
- Strong Authentication: Utilizing multi-factor authentication (MFA) is critical to verify user identity and prevent unauthorized access. This adds an extra layer of security beyond simple passwords.
- Access Control Policies: Implementing strict access control policies limits who can access and modify backups. Granular permissions allow only authorized personnel to perform specific actions, such as restoring or deleting backups.
- Regular Security Audits: Regular security audits are essential to identify and address potential vulnerabilities. This helps to proactively address any weaknesses in the backup security infrastructure.
- Regular Backup Testing: Regularly testing the recovery process for backups is vital to ensure the integrity and accessibility of the data. This includes verification of backup restore procedures.
Compliance with Industry Regulations and Standards
Adherence to industry regulations and standards is crucial for ensuring data protection and compliance. Various standards, such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR, dictate specific requirements for data security and privacy.Understanding the specific requirements of these regulations is essential to tailoring backup strategies for compliance. Organizations must demonstrate their commitment to data security and privacy by meeting the standards of these regulations.
Encryption Options for Protecting Backups
Data encryption is a fundamental security measure for protecting backups. Google Cloud Platform offers various encryption options to safeguard sensitive data.
- Customer-Managed Encryption Keys (CMEK): Organizations can use their own encryption keys to encrypt backups. This offers greater control over encryption keys and better aligns with specific regulatory requirements.
- Server-Side Encryption (SSE): Google Cloud automatically encrypts backups at rest using its own encryption keys. This option simplifies the encryption process while maintaining security.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Implementing DLP solutions can prevent sensitive data from being backed up unintentionally, which further enhances data security.
Summary of Security Features
| Security Feature | Description | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Strong Authentication | Verifies user identity with MFA | Enable MFA for all backup access |
| Access Control Policies | Limits access to authorized personnel | Define granular permissions for backup operations |
| Regular Security Audits | Identifies and addresses potential vulnerabilities | Conduct regular security assessments of backup infrastructure |
| Regular Backup Testing | Ensures integrity and accessibility of backups | Schedule and perform regular restore tests |
| Customer-Managed Encryption Keys (CMEK) | Organizations manage encryption keys | Use their own encryption keys for backups |
| Server-Side Encryption (SSE) | Google Cloud encrypts backups automatically | Leverage the built-in encryption capabilities |
| Data Loss Prevention (DLP) | Prevents sensitive data from being backed up | Implement DLP policies to identify and block sensitive data |
Monitoring and Management of Backups
Keeping your Google Cloud VMs backed up is crucial, but equally important is actively monitoring and managing those backups. Effective monitoring ensures that your backups are functioning correctly, identifying potential problems early, and enabling swift recovery in case of a disaster. This proactive approach prevents costly downtime and data loss.Regular monitoring allows you to catch issues before they escalate into major problems.
By tracking backup job status and performance, you can identify trends and take corrective actions, ensuring the integrity and reliability of your data protection strategy.
Backup Job Tracking and Issue Identification
Understanding the status of your backup jobs is paramount. Google Cloud provides detailed information on the progress and outcome of each backup operation. Reviewing these reports helps you identify any anomalies, such as failed backups, and pinpoint potential causes. For example, an intermittent network issue or insufficient storage space could cause backup failures. Thorough analysis of these reports allows for timely intervention and prevents data loss.
Tools for Backup Management and Troubleshooting
Google Cloud Platform offers a range of tools for managing and troubleshooting backups. The Cloud Console provides a central dashboard for monitoring backup jobs, visualizing their status, and facilitating the analysis of backup history. The Cloud Logging service logs backup events, which you can analyze to identify patterns or root causes of issues. Command-line tools, like the gcloud command-line interface, enable programmatic access and automation of backup management tasks.
These tools provide various levels of granularity, allowing you to address specific issues and enhance backup management.
Backup Failure Identification and Resolution Process
A well-defined process for identifying and resolving backup failures is critical. First, log any backup failures and document the timestamp, error messages, and any relevant context. Next, investigate the cause of the failure, considering factors like network connectivity, storage space, and VM configuration. Once the root cause is identified, implement the appropriate solution. This could involve adjusting resource allocation, addressing network connectivity problems, or updating VM configurations.
Finally, verify that the backup job is now functioning correctly. Regular testing and validation are crucial to maintaining backup integrity.
Monitoring Tools Overview
Effective backup management relies on the use of appropriate monitoring tools. A well-structured monitoring strategy will provide a comprehensive view of your backup infrastructure.
| Monitoring Tool | Functionality | Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Console | Provides a centralized dashboard for viewing backup job status, history, and performance metrics. Visualizations help identify trends and potential issues. | Directly integrated with Google Cloud Backup services. |
| Cloud Logging | Records backup events, including successful backups, failures, and warnings. Provides detailed logs for troubleshooting and root cause analysis. | Integrates with other Google Cloud services for comprehensive logging and monitoring. |
| gcloud command-line tool | Enables programmatic access and automation of backup management tasks. Provides a powerful way to automate backup monitoring and reporting. | Supports interacting with various Google Cloud services, including Backup. |
Advanced Backup Considerations
Taking VM backups to the next level involves more than just the basics. Advanced strategies are crucial for ensuring data availability and minimizing downtime in case of failures. This section dives into sophisticated techniques like automated scheduling, replication, and disaster recovery, along with optimizing performance for large-scale deployments.Effective backup strategies go beyond simply creating snapshots. Advanced considerations encompass techniques for ensuring rapid recovery, minimizing data loss, and protecting against various threats.
Understanding these advanced approaches allows for more robust and reliable data protection in a dynamic cloud environment.
Backup Scheduling and Automation, Google cloud vm backup
Automated backup scheduling is essential for maintaining regular backups without manual intervention. This ensures consistent data protection, especially in large-scale deployments. A well-defined schedule, encompassing daily, weekly, or monthly backups, guarantees compliance with business continuity requirements and regulatory standards. Customizable schedules allow for flexibility based on varying workload demands. For example, a production database might require hourly backups during peak hours, while a development environment could be backed up on a less frequent schedule.
Replication Strategies for Enhanced Availability
Replication strategies are critical for creating copies of backups in geographically separate locations. This ensures business continuity in the event of a disaster in one region. The replication process creates a mirrored backup, allowing for instant recovery. This method is highly beneficial for organizations with stringent service level agreements (SLAs) and the need for rapid recovery in case of regional outages.
Examples include replicating a backup to a secondary region in another continent, enabling immediate access to data in case of a regional disaster.
Disaster Recovery Planning
Disaster recovery (DR) planning is a critical component of advanced backup considerations. This involves establishing a clear plan to restore data and systems in the event of a catastrophic event. DR plans should Artikel procedures for failing over to secondary locations, the required recovery time objectives (RTOs), and recovery point objectives (RPOs). This ensures minimal data loss and quick resumption of operations.
A well-defined DR plan can be the difference between business continuity and significant financial loss in the event of a natural disaster or major system failure. A real-world example would be a company replicating its critical application servers to a geographically separate region, allowing for rapid recovery in the event of a natural disaster affecting their primary location.
Optimizing Backup Performance
Optimizing backup performance is crucial, especially for large-scale deployments. This involves techniques like using faster storage types, leveraging compression algorithms, and implementing efficient backup tools. Backup performance directly impacts the speed of recovery. For example, a fast backup process might allow for daily full backups, reducing the recovery time objective (RTO) and the recovery point objective (RPO).
Using dedicated backup storage, optimizing the backup process, and leveraging compression techniques are essential to maintain the desired performance.
Managing Large-Scale VM Deployments
Managing large-scale VM deployments requires a centralized approach to backup management. This includes using a robust backup solution capable of handling numerous VMs and large datasets. A centralized management system streamlines the backup process, reduces operational overhead, and ensures consistent backup policies across the entire environment. A single pane of glass for backup management enables efficient monitoring, reporting, and control, especially in a dynamic environment.
The use of automation tools to manage large-scale VM backups is critical to efficiency and compliance.
Automated Backup Processes
Automated backup processes are vital for ensuring consistency and efficiency. They can include scheduling backups, initiating backups based on predefined criteria, and automating recovery procedures. These processes eliminate the need for manual intervention, reduce human error, and ensure that backups are performed regularly. Automated backup processes significantly reduce the risk of missed backups and contribute to improved data protection.
Using a dedicated backup solution that supports automation will significantly improve backup management.
Comparing Backup Methods for Large Data Volumes
Different backup methods offer varying performance characteristics. Consider comparing the performance of full backups, incremental backups, and differential backups for large data volumes. Full backups involve copying the entire dataset, which is time-consuming for large volumes. Incremental backups capture only changes since the last full or incremental backup, while differential backups capture changes since the last full backup.
Choosing the appropriate method depends on factors such as the frequency of data changes and the acceptable recovery time objective (RTO). Comparing the speed and efficiency of these methods helps determine the most suitable option for the specific data volume and recovery needs.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, securing your Google Cloud VMs is crucial, and this comprehensive guide provides a roadmap for effective backup strategies. By understanding the different backup methods, configurations, and security considerations, you can ensure your data is protected and readily available. Remember to tailor your backup approach to your specific needs and regularly review your configurations for optimal results.