Fluoride Treatment Dental Experts Your Guide
Fluoride treatment dental experts are crucial in maintaining optimal oral health. They offer a wide range of fluoride treatments, from topical applications to professional procedures, tailored to individual needs. Understanding these treatments, their benefits, and the experts who administer them is key to making informed decisions about your dental care.
This comprehensive guide explores the various types of fluoride treatments, highlighting their effectiveness, application methods, and the crucial role dental professionals play in delivering them. We’ll also delve into the specific needs of different patient groups and address any safety concerns.
Overview of Fluoride Treatment
Fluoride treatments are essential preventative dental procedures that fortify tooth enamel, reducing the risk of cavities and promoting oral health. These treatments work by incorporating fluoride ions into the tooth structure, making it more resistant to acid attacks from bacteria and sugars in the mouth. This strengthened enamel helps protect against the demineralization process, a crucial step in the cavity formation cycle.Fluoride treatments are tailored to specific needs and can be administered in various forms, ranging from simple daily fluoride rinses to professional applications.
They target different stages of oral health, from preventing cavities in children to restoring enamel strength in adults. The goal is to maximize the benefits of fluoride for optimal oral health.
Types of Fluoride Treatments
Fluoride treatments encompass a range of applications, each designed to address specific needs. These treatments are carefully chosen based on the patient’s individual risk factors, oral health status, and dentist’s assessment. This targeted approach ensures the most effective results.
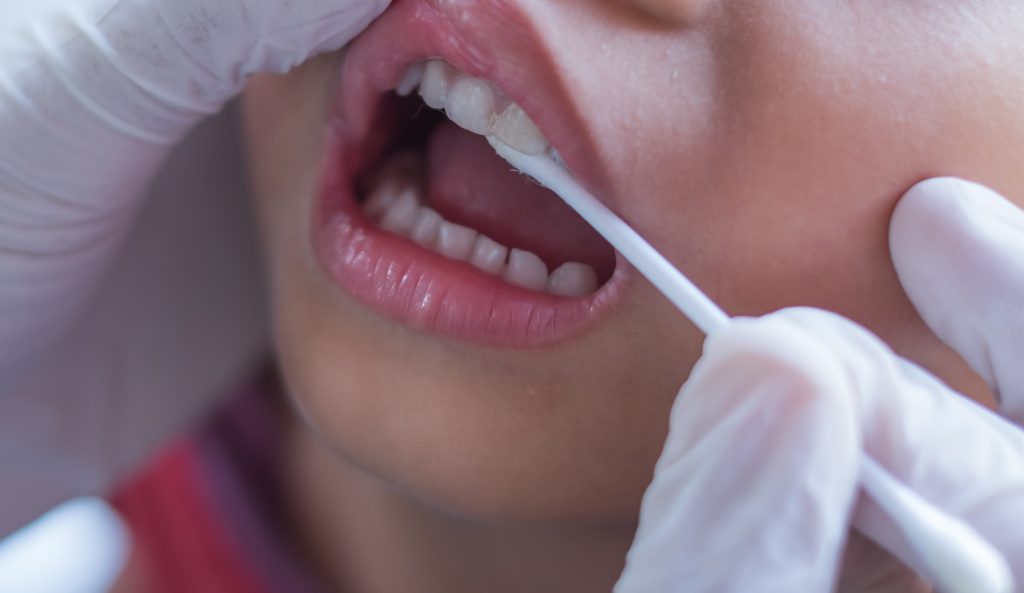
- Topical Fluoride: This involves applying fluoride solutions directly to the teeth, often via a rinse or a gel. These solutions are designed to increase fluoride concentration in the mouth, promoting remineralization and enamel strengthening. A simple daily fluoride rinse can be part of this, strengthening teeth through consistent exposure to fluoride.
- Fluoride Varnish: Fluoride varnish is a highly concentrated, viscous fluoride solution applied to the teeth. The thick consistency ensures a higher fluoride concentration remains in contact with the enamel for an extended period, leading to a more significant remineralization effect. It’s often used in preventative treatments, particularly for children, and in specific cases of enamel erosion.
- Professional Fluoride Treatments: These involve more concentrated fluoride applications, often performed by dental professionals. These treatments are typically scheduled during check-ups and are aimed at achieving a higher level of fluoride uptake in the teeth, improving their resistance to decay. Examples include professional fluoride gels or foams, delivered in a controlled and effective manner.
Mechanisms of Fluoride Strengthening
Fluoride ions, when incorporated into tooth enamel, replace hydroxyl ions in the hydroxyapatite crystals that form the tooth’s structure. This substitution results in a more stable and resistant form of apatite, making the enamel less susceptible to acid attacks and decay.
The process is akin to strengthening a material by incorporating a more resilient component into its structure.
The resulting fluorapatite is more resistant to dissolution by acids, acting as a shield against cavity-causing bacteria.
Forms of Fluoride Delivery
Fluoride is delivered in various forms to ensure optimal absorption and effectiveness. The chosen delivery method depends on the desired outcome and the patient’s specific needs.
- Gels: Fluoride gels are highly concentrated fluoride solutions that are applied directly to the teeth. They are often used in professional dental settings to achieve targeted fluoride treatments.
- Foams: Fluoride foams are another form of concentrated fluoride solution, applied in a similar manner to gels. The foam consistency ensures even distribution on the tooth surfaces.
- Varnishes: Fluoride varnishes are viscous, concentrated solutions that form a protective coating on the teeth. This coating ensures prolonged fluoride exposure, maximizing remineralization effects.
Comparison of Fluoride Treatment Types
| Treatment Type | Application Method | Effectiveness | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topical Fluoride Rinse | Daily rinsing with a fluoride solution | Moderate, but continuous use is key | Ongoing, daily |
| Fluoride Varnish | Professional application by a dentist | High, due to prolonged fluoride contact | Several months (depending on frequency) |
| Professional Fluoride Gel/Foam | Professional application by a dentist | Very High, due to high concentration | Several months (depending on frequency) |
Benefits of Fluoride Treatments
Fluoride treatments are a cornerstone of preventive dentistry, offering significant advantages in combating tooth decay and enhancing oral health. These treatments work by strengthening tooth enamel and making teeth more resistant to the acids that cause cavities. This process is particularly important for children and adolescents whose teeth are still developing, as well as adults at risk for cavities.
Preventing Dental Cavities
Fluoride treatments significantly reduce the risk of developing cavities. By incorporating fluoride into tooth enamel, the enamel becomes more resistant to the acids produced by bacteria in the mouth. This enhanced resistance directly translates to a lower likelihood of cavities forming. Studies have consistently demonstrated a strong correlation between fluoride use and a decrease in the incidence of dental caries.
Fluoride treatment from dental experts is crucial for preventing cavities, and it’s a topic I’ve been passionate about for a while now. Seeing how professional athletes like Jimmy Butler, ready to pick up slack for an exhausted Stephen Curry after a streak-snapping loss here , really highlights the importance of proactive health measures. It’s a similar principle in oral care: regular checkups and fluoride treatments are essential for long-term dental well-being.
Remineralizing Tooth Enamel
Fluoride plays a crucial role in remineralizing tooth enamel. When acids attack the enamel, tiny mineral crystals are lost. Fluoride ions, actively incorporated into the enamel structure, help to replenish these lost minerals. This process, called remineralization, strengthens the enamel, making it more resilient against future acid attacks. This restorative effect helps to halt the early stages of decay, preventing further damage.
Long-Term Benefits of Consistent Fluoride Use
Consistent fluoride use yields long-term benefits, contributing to a healthier, more resilient smile. Individuals who incorporate fluoride treatments into their oral hygiene routine experience reduced risk of cavities throughout their lives. This consistent protection, especially when initiated early in life, sets the stage for a lifetime of improved oral health. The benefits of early intervention are often more significant as it affects the development of teeth, improving the overall quality of oral health.
For example, children who receive regular fluoride treatments are more likely to maintain healthy teeth as adults.
Comparison with Other Preventive Measures
Fluoride treatments are highly effective preventive measures. While other methods like regular brushing and flossing are essential, fluoride treatments provide an additional layer of protection. Fluoride treatments act as a shield, strengthening the enamel against the harmful effects of bacteria and acids. The effectiveness of fluoride treatments often complements other preventive measures, creating a comprehensive approach to oral health.
For example, a patient who meticulously brushes and flosses but still has a tendency to develop cavities might see a significant reduction in cavities with fluoride treatments.
Examples of Improved Oral Health
Fluoride treatments demonstrably enhance oral health. For instance, individuals with a history of cavities might experience a notable decrease in future cavities after consistent fluoride treatments. This prevention is crucial, as cavities can lead to pain, infection, and even the need for extensive dental work. Additionally, fluoride treatments contribute to a more comfortable and confident smile, allowing individuals to maintain a healthy lifestyle without the constant threat of tooth decay.
Ultimately, a healthier smile is directly correlated with a more positive self-image.
Fluoride treatment from dental experts is crucial for preventing cavities, but sometimes, even the most routine dental procedures can have unexpected outcomes. For example, recent news reports highlight a disturbing incident in a Starbucks drive-thru, where a fight escalated to a stabbing. This shocking story reminds us of the importance of maintaining calm and seeking peaceful resolutions, even in the most stressful situations.
Regardless of these unfortunate events, fluoride treatment remains a vital part of maintaining oral health.
Dental Experts and Fluoride Treatments
Fluoride treatments are a valuable tool in preventative dentistry, and their successful application hinges heavily on the expertise of the dental professionals administering them. Proper training and understanding of fluoride chemistry, application techniques, and patient needs are crucial for maximizing the benefits and minimizing risks. This section delves into the qualifications, roles, and procedures involved in fluoride treatments.Dental professionals specializing in fluoride treatments possess a deep understanding of oral health and the specific needs of different patient populations.
Their expertise goes beyond simply applying fluoride; it encompasses patient assessment, treatment planning, and ongoing monitoring.
Qualifications and Training of Dental Professionals
Dental hygienists and dentists are the primary professionals trained to administer fluoride treatments. Dental hygienists typically receive extensive training in preventive care, including fluoride application techniques, during their formal education. They undergo supervised clinical practice to refine their skills and gain experience in diverse patient scenarios. Dentists, on the other hand, receive a comprehensive education encompassing all aspects of oral health, including diagnosis, treatment planning, and preventative measures.
Their training includes the advanced knowledge and skills necessary to integrate fluoride treatments into a broader patient care strategy.
Roles of Dental Experts in Fluoride Treatment Plans
Dental experts play multifaceted roles in fluoride treatment plans. Their duties include patient assessment, identifying appropriate treatment methods, and educating patients on the benefits and proper use of fluoride. A thorough evaluation of each patient’s oral health, including existing dental conditions, is essential to tailor the fluoride treatment to their specific needs. Dental professionals also advise patients on maintaining good oral hygiene practices to maximize the effectiveness of fluoride treatments.
Fluoride Treatment Procedures
The procedures involved in administering various fluoride treatments vary based on the specific treatment type and the patient’s needs. Some common methods include varnish applications, tray treatments, and professional fluoride rinses. Each method has unique application steps and considerations for patient comfort and safety. Proper application techniques are crucial for optimal fluoride uptake and prevention of potential side effects.
Importance of Proper Fluoride Application Techniques
Precise and controlled application techniques are vital for maximizing the effectiveness of fluoride treatments. Overapplication can lead to fluorosis, while underapplication negates the desired preventative benefits. Dentists and hygienists are trained to ensure accurate application, considering factors such as the patient’s age, existing dental conditions, and sensitivity levels. Consistent adherence to proper technique minimizes risks and maximizes positive outcomes.
Typical Fluoride Treatment Steps
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Patient assessment and medical history review, including any allergies or sensitivities. |
| 2 | Oral examination to identify areas requiring fluoride treatment and assess overall oral health. |
| 3 | Selection of appropriate fluoride treatment based on patient needs and oral conditions. |
| 4 | Thorough cleaning of the affected tooth surfaces. |
| 5 | Careful application of fluoride treatment, following recommended protocols for duration and technique. |
| 6 | Patient education on proper oral hygiene practices and fluoride use. |
| 7 | Follow-up appointment scheduling to monitor treatment progress and effectiveness. |
Fluoride Treatment and Specific Patient Groups

Fluoride treatments are a crucial part of preventive dentistry, offering significant benefits across various age groups and health conditions. Understanding the unique fluoride needs of different patient populations is essential for tailoring treatment plans to maximize effectiveness and minimize risks. This section will delve into the specific fluoride requirements for children, pregnant women, the elderly, and patients with particular medical conditions.
Fluoride Needs of Children and Adolescents
Children and adolescents are at a critical stage of oral development. Their growing teeth are particularly susceptible to decay, making fluoride supplementation vital. Optimal fluoride exposure during this period strengthens enamel, reducing the risk of cavities and promoting healthy tooth development. Fluoride varnish applications and daily fluoride supplements are often recommended by dentists to address the unique needs of children and adolescents.
Early intervention with fluoride treatments can significantly reduce the likelihood of dental problems later in life.
Importance of Fluoride for Pregnant Women
Pregnant women require adequate fluoride intake to support the developing teeth of their unborn child. Fluoride is essential for the formation of strong, healthy enamel in the fetus’s teeth. Insufficient fluoride intake during pregnancy can increase the risk of dental problems in the child, potentially leading to cavities and other issues. Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fluoride-containing foods and consulting a dentist about fluoride supplements is vital for the oral health of both mother and child.
Fluoride Needs of Elderly Patients
Elderly individuals often experience a decline in saliva production, increasing their risk of tooth decay. Maintaining adequate fluoride levels is crucial for protecting their teeth from cavities and maintaining oral health. Fluoride treatments, such as prescription fluoride rinses, can help address this issue, offering protection against the risk of tooth decay in this age group. The elderly are often more prone to dry mouth, making fluoride treatments even more important.
Fluoride Needs of Patients with Specific Medical Conditions, Fluoride treatment dental experts
Certain medical conditions can influence a patient’s fluoride needs. For instance, individuals with conditions that affect saliva production, such as Sjogren’s syndrome, require careful consideration of fluoride treatments. Also, patients with gastrointestinal issues might have difficulty absorbing fluoride from dietary sources, necessitating adjustments to their treatment plan. Regular communication with the patient’s dentist and other healthcare providers is essential for developing a tailored approach.
Recommended Fluoride Treatment Approaches by Patient Group
| Patient Group | Fluoride Needs | Treatment Recommendations |
|---|---|---|
| Children (0-18 years) | Developing teeth are highly susceptible to decay. Optimal fluoride exposure during this period strengthens enamel. | Fluoride varnish applications, daily fluoride supplements (as advised by dentist), and ensuring adequate fluoride in the diet. |
| Pregnant Women | Fluoride is crucial for the development of strong teeth in the fetus. | Maintaining a balanced diet with sufficient fluoride intake, consulting a dentist about supplements, and regular dental checkups. |
| Elderly Patients (65+) | Reduced saliva production increases the risk of tooth decay. | Prescription fluoride rinses, fluoride toothpaste, and regular dental checkups to monitor oral health. |
| Patients with Medical Conditions (e.g., Sjogren’s, Gastrointestinal issues) | Specific medical conditions can affect fluoride absorption and saliva production. | Individualized treatment plans based on the specific condition, possibly including prescription fluoride rinses, and close monitoring with the dentist and other healthcare providers. |
Safety and Considerations Regarding Fluoride Treatments
Fluoride treatments, while generally safe and beneficial for dental health, require careful consideration of potential side effects, proper application, and individual circumstances. Understanding the nuances of fluoride usage is crucial for maximizing its benefits and minimizing any risks. This section will explore the safety protocols and precautions surrounding fluoride treatments, highlighting important factors to consider before initiating these procedures.
Potential Side Effects of Fluoride Treatments
Fluoride, when used appropriately, poses minimal risk. However, some individuals might experience mild side effects, such as temporary tooth discoloration or a slight tingling sensation in the mouth. These effects are usually temporary and resolve on their own. In rare cases, more significant side effects may occur. It is vital to be aware of these potential reactions and to report any unusual or persistent symptoms to your dentist.
Importance of Proper Dosage and Application
The effectiveness and safety of fluoride treatments hinge heavily on proper dosage and application. Dentists carefully calibrate the concentration and duration of fluoride application to achieve optimal results without exceeding safe limits. Overexposure to fluoride can lead to fluorosis, a condition characterized by staining of the teeth, especially in children. Dentists are trained to minimize these risks.
Precautions to Take During Fluoride Treatment
Taking precautions before, during, and after a fluoride treatment is crucial for ensuring a safe and positive experience. Patients should inform their dentist of any existing medical conditions, allergies, or sensitivities, as these factors may influence treatment protocols. Patients should follow their dentist’s instructions meticulously, such as avoiding eating or drinking for a specified time after the treatment.
Contraindications for Fluoride Treatments
Certain conditions can make fluoride treatments unsuitable for specific patients. Individuals with hypersensitivity to fluoride, certain underlying medical conditions (like kidney problems), or a history of adverse reactions to previous fluoride treatments should discuss these factors with their dentist before undergoing the treatment. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also consult their healthcare providers to determine if fluoride treatments are safe for them.
Important Factors to Consider Before Initiating Fluoride Treatments
Before deciding on fluoride treatment, careful consideration of several factors is essential. Age is a significant factor, as children and adolescents require different fluoride application methods and dosages compared to adults. Patients should discuss their individual needs and oral health history with their dentist to determine the most suitable treatment approach. The dentist’s expertise and experience are key factors in ensuring the safety and effectiveness of the treatment.
Patients should select a qualified dental professional with experience in administering fluoride treatments. Furthermore, the cost of the treatment and insurance coverage should be considered.
Alternatives and Comparisons to Fluoride Treatments
Beyond fluoride treatments, various preventive dental strategies aim to reduce cavities. Understanding these alternatives and their respective strengths and weaknesses helps patients and dentists make informed choices tailored to individual needs. This exploration delves into non-fluoride approaches to cavity prevention, providing a comprehensive overview of available options.
Fluoride treatment is a crucial aspect of dental care, and experts can help you understand the benefits and potential risks. However, the recent tragic news about the sugar bowl CFP quarterfinal between Georgia and Notre Dame, postponed after a deadly truck attack, highlights the importance of focusing on issues beyond sports. Thankfully, fluoride treatment experts can help you maintain a healthy smile, even during challenging times.
Alternative Preventive Measures
Numerous methods exist beyond fluoride to combat cavities. These strategies often target different aspects of oral health, ranging from dietary changes to specialized dental procedures. Effective cavity prevention relies on a multi-faceted approach that considers both systemic and local factors.
Dietary Modifications
Dietary changes play a crucial role in cavity prevention. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, coupled with limited consumption of sugary and acidic foods, can significantly impact oral health. Sugar is a major contributor to tooth decay, as bacteria in the mouth ferment it, producing acids that erode tooth enamel. Reducing sugar intake and opting for sugar-free alternatives can substantially lessen the risk of cavities.
For example, choosing xylitol-containing candies or chewing gums can actually inhibit bacterial growth.
Oral Hygiene Practices
Maintaining meticulous oral hygiene is paramount for cavity prevention. Regular brushing and flossing remove food particles and plaque, which are crucial for cavity development. Brushing twice daily for two minutes each time, using fluoride toothpaste, and flossing daily are essential for maintaining a healthy mouth. Using interdental brushes or other tools, particularly for hard-to-reach areas, can further enhance plaque removal.
Dental Sealants
Dental sealants are protective coatings applied to the chewing surfaces of teeth, particularly molars. These sealants fill in grooves and pits, preventing food particles and bacteria from accumulating. They create a barrier that inhibits plaque buildup, thereby reducing the risk of cavities. Dental sealants are often recommended for children and adolescents, particularly for vulnerable areas prone to cavities.
Professional Cleanings
Regular professional dental cleanings are vital for removing plaque and tartar buildup that brushing and flossing may miss. These cleanings remove hard deposits that can harbor bacteria, thereby improving oral hygiene and reducing the risk of cavities and gum disease. Professional cleanings also allow dentists to detect any potential issues early on.
Table of Cavity Prevention Methods
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Fluoride Treatment | Effective in strengthening enamel, reducing cavity risk, readily available, often affordable. | Potential for side effects (in high concentrations), some individuals may not respond as expected. |
| Dietary Modifications | Promotes overall health, reduces exposure to cavity-inducing substances. | Requires significant lifestyle changes, adherence can be challenging, may not be sufficient on its own. |
| Oral Hygiene Practices | Relatively inexpensive, easily accessible, can be performed at home. | Requires consistent effort, can be difficult to maintain thorough plaque removal in hard-to-reach areas. |
| Dental Sealants | Highly effective in preventing cavities in vulnerable areas, long-lasting protection. | Requires a dental visit, may not be suitable for all teeth, some individuals may experience sensitivity. |
| Professional Cleanings | Removes plaque and tartar buildup, detects potential issues early, improves overall oral hygiene. | Requires scheduling appointments, may not be a sufficient preventative measure alone. |
Future Trends in Fluoride Treatments: Fluoride Treatment Dental Experts
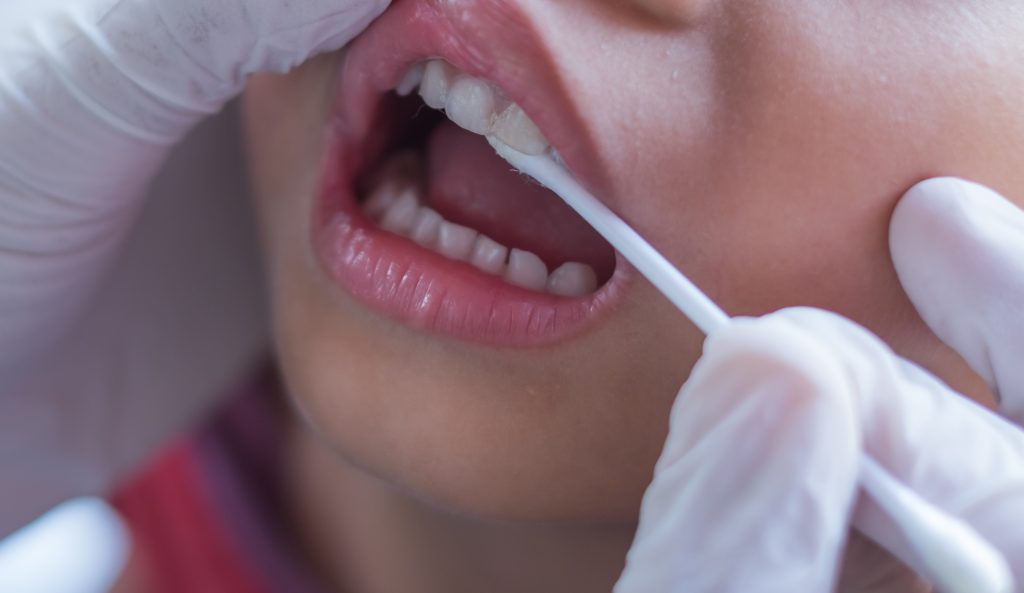
Fluoride, a crucial element in preventing dental caries, continues to be a cornerstone of preventive dentistry. While current fluoride treatments are highly effective, ongoing research and technological advancements are constantly pushing the boundaries of fluoride application, leading to improved efficacy and patient experience. This exploration delves into the exciting future of fluoride-based preventive care, examining emerging trends and potential breakthroughs.Fluoride treatments are evolving beyond traditional topical applications.
Researchers are investigating novel methods to deliver fluoride more effectively and precisely, targeting specific areas of the tooth and potentially enhancing its protective effects. This innovative approach promises to yield more predictable and lasting results in the fight against dental decay.
Novel Fluoride Delivery Systems
The current standard of fluoride application, like varnishes and gels, has limitations in terms of prolonged effect and targeted delivery. New technologies are addressing these limitations by exploring alternative delivery methods. These innovative methods aim to enhance the retention and efficacy of fluoride within the tooth enamel.
- Nanotechnology-based fluoride delivery systems are under development. These systems leverage the tiny size of nanoparticles to improve fluoride penetration and retention within tooth enamel, potentially leading to sustained release and enhanced protection against decay.
- Laser-assisted fluoride application is another area of active research. Lasers could be used to precisely target specific areas, maximizing fluoride concentration and improving treatment efficacy. This technique offers potential benefits for patients with complex dental structures.
- Fluoride-infused sealants represent a promising approach to prevent cavities in vulnerable areas like pits and fissures. These sealants would contain a controlled release of fluoride, providing continuous protection over time.
Personalized Fluoride Treatments
The future of fluoride treatments may involve tailoring treatments to individual patient needs. This approach recognizes that factors like age, oral hygiene habits, and the presence of specific dental conditions influence the effectiveness of fluoride treatment.
- Predictive modeling using patient-specific data could allow dentists to recommend optimal fluoride treatments, ensuring that the chosen treatment strategy aligns with the individual’s risk profile.
- Fluoride therapies adjusted for specific conditions, like dental erosion or hypersensitivity, are also under consideration. This personalized approach aims to enhance the effectiveness of fluoride in addressing the unique needs of diverse patient populations.
- Genetic factors impacting fluoride uptake and metabolism are being investigated. Understanding these factors could further refine personalized fluoride strategies.
Emerging Trends in Fluoride-Based Preventive Care
The integration of fluoride with other preventive strategies is a key emerging trend. Combining fluoride treatments with other preventative measures, like sealants or improved oral hygiene recommendations, could create a synergistic effect, maximizing the protection against dental caries.
- Fluoride-containing mouthwashes with extended release formulations are being developed to provide continuous fluoride exposure throughout the day.
- Fluoride-enriched toothpaste with targeted delivery mechanisms could enhance the effectiveness of daily oral hygiene practices. This approach would increase the patient’s active role in their oral health maintenance.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, fluoride treatments are a valuable tool in preventive dentistry, offering significant benefits for maintaining healthy teeth. By understanding the different types of treatments, the expertise of dental professionals, and the individual needs of various patient groups, you can make informed choices to protect your oral health. The future of fluoride treatments holds promising advancements, further enhancing their effectiveness and accessibility.