Inequality American Life Expectancy A Deep Dive
Inequality American life expectancy is a stark reality, highlighting the significant disparities in health outcomes across various demographics. This exploration delves into the complex factors contributing to these differences, examining racial, socioeconomic, geographic, behavioral, healthcare access, environmental, and policy implications. Understanding these nuanced issues is crucial for developing effective strategies to promote health equity and improve the overall well-being of all Americans.
From the historical context of racial bias in healthcare to the present-day impact of socioeconomic factors, this analysis will explore how various elements intersect to shape life expectancy. We’ll also examine the roles of health behaviors, access to quality healthcare, environmental factors, and policies in perpetuating or mitigating these disparities.
Racial Disparities in Life Expectancy
Racial disparities in life expectancy remain a significant public health concern in the United States. While progress has been made in some areas, substantial gaps persist, highlighting systemic inequities that impact health outcomes. Understanding the historical context, contributing factors, and disparities in healthcare access is crucial to developing effective strategies for improvement.The persistent difference in life expectancy between racial groups in the US is a complex issue with deep roots in historical and contemporary societal factors.
These disparities are not simply a matter of individual choices; they reflect the cumulative impact of systemic disadvantages, including unequal access to quality healthcare, environmental factors, and socioeconomic conditions. Addressing these disparities requires a multifaceted approach that tackles the root causes and promotes equitable access to resources.
Comparative Analysis of Life Expectancy
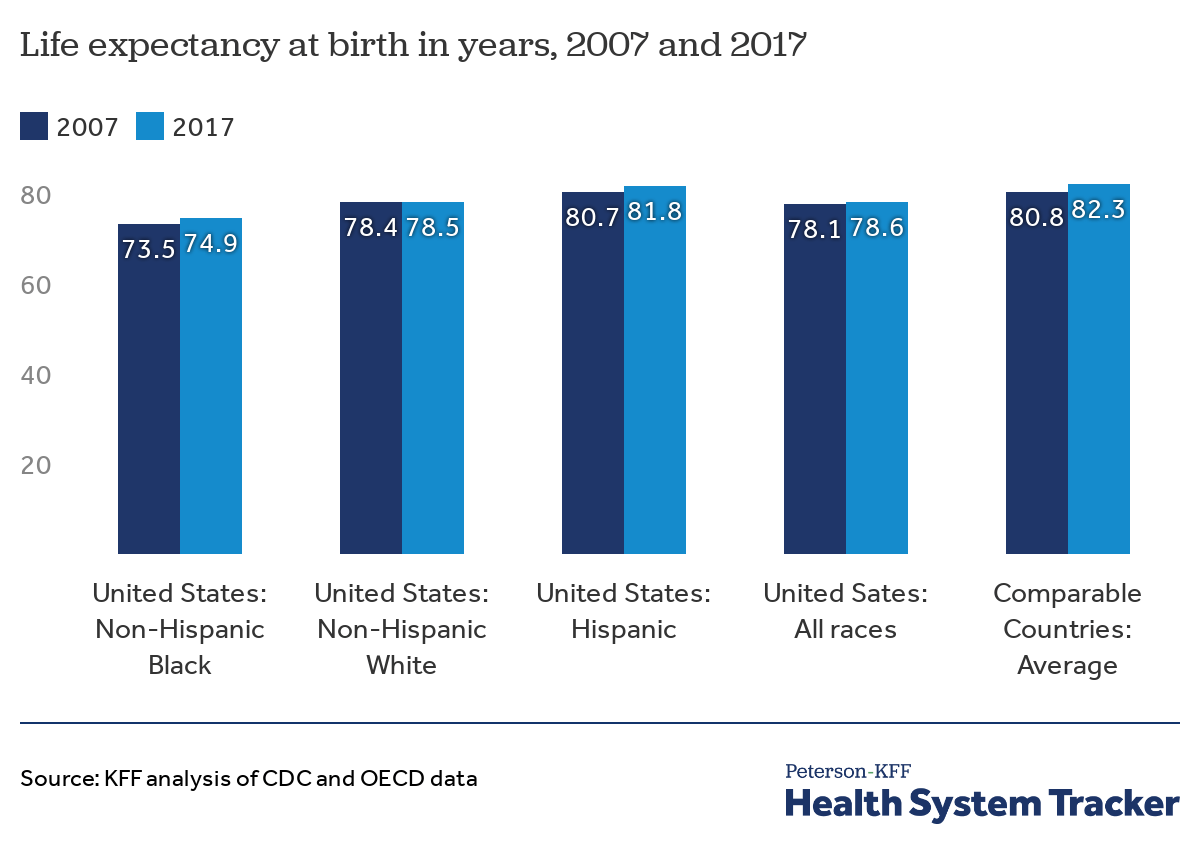
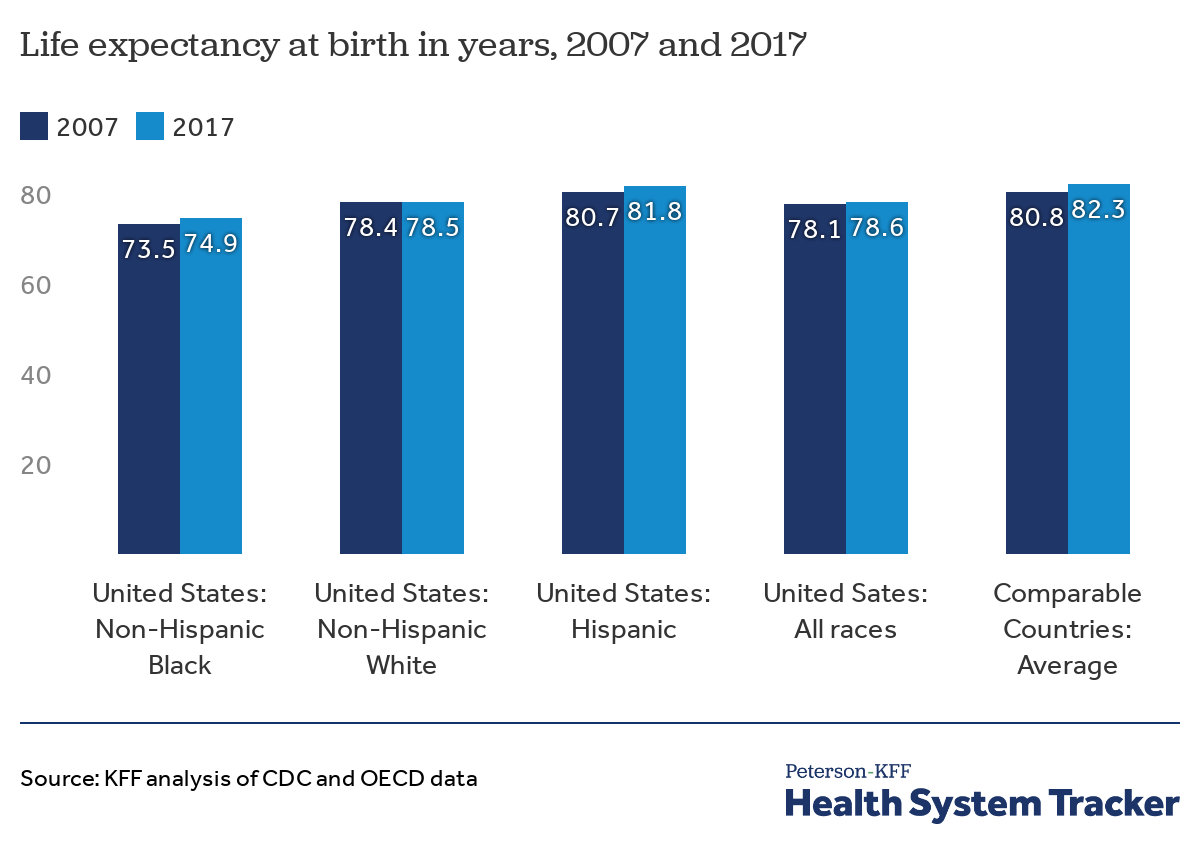
Life expectancy at birth varies significantly across racial groups in the US. Data consistently shows lower life expectancies for Black and Hispanic populations compared to their White counterparts. These differences are not only statistically significant but also represent a profound societal issue. This disparity underscores the need for a thorough examination of the contributing factors.
Historical Context of Disparities
Historical factors, including slavery and its enduring legacy, have significantly shaped racial health disparities. Policies and practices that historically marginalized certain racial groups have created and perpetuated systemic inequalities. These inequalities continue to manifest in contemporary healthcare access, environmental factors, and socioeconomic conditions. The cumulative effect of these historical injustices creates lasting consequences for health outcomes.
Contributing Factors, Inequality american life expectancy
Several interconnected factors contribute to racial disparities in life expectancy. These include socioeconomic status, access to quality healthcare, environmental factors, and cultural factors. Addressing these factors in a holistic manner is critical to bridging the gaps in life expectancy.
Healthcare Access and Quality
Differences in healthcare access and quality are key contributors to racial disparities. This encompasses factors such as insurance coverage, geographic location, and cultural competency of healthcare providers. Unequal access to preventive care, timely diagnosis, and appropriate treatment can exacerbate health conditions and lead to poorer outcomes. These disparities in healthcare are often interwoven with other systemic factors.
Table: Life Expectancy by Race
| Race | Average Life Expectancy (approximate) | Potential Contributing Factors |
|---|---|---|
| White | 77-80 years | Historically better access to resources, higher socioeconomic status in many cases, lower exposure to certain environmental hazards. |
| Black | 72-75 years | Historical trauma (slavery), ongoing systemic racism, lower socioeconomic status, limited access to quality healthcare, higher exposure to environmental hazards. |
| Hispanic | 78-80 years (varies significantly by country of origin) | Varying socioeconomic status based on country of origin, varying access to healthcare and resources, cultural factors, potential language barriers, and unique environmental challenges. |
Socioeconomic Disparities in Life Expectancy
A significant disparity exists in life expectancy across different socioeconomic groups in the United States. Factors such as income, access to quality healthcare, and educational opportunities play a crucial role in shaping health outcomes and life spans. This disparity highlights the need for comprehensive policies and interventions aimed at reducing health inequities.The relationship between socioeconomic status and life expectancy is deeply intertwined.
Lower socioeconomic status is consistently associated with a shorter lifespan. This correlation is evident in various metrics, including access to healthcare, nutrition, and safe living environments. Individuals with lower incomes often face greater challenges in accessing essential resources, leading to poorer health outcomes and a decreased life expectancy.
Income Brackets and Life Expectancy
Differences in life expectancy are stark across income brackets. Individuals in higher income groups generally experience longer life spans compared to those in lower income groups. This difference isn’t simply about access to healthcare; it reflects a broader spectrum of factors that influence health and well-being.
Factors Influencing Life Expectancy
A multitude of socioeconomic factors contribute to the disparity in life expectancy. Access to nutritious food, stable housing, and quality education are vital determinants of health and longevity. Lack of access to these basic needs can significantly impact health outcomes, leading to higher rates of chronic diseases and premature mortality.
Access to Nutritious Food
A consistent lack of access to nutritious food, especially in lower-income communities, contributes significantly to health disparities. Limited access to fresh produce, coupled with reliance on cheaper, less nutritious options, can lead to higher rates of diet-related diseases. This can have a substantial impact on life expectancy, as these diseases can lead to premature death.
Housing Stability
Stable housing is crucial for overall well-being. Individuals facing housing instability often experience higher levels of stress, which can negatively impact their health. Poor housing conditions, such as inadequate sanitation and lack of ventilation, can also contribute to the spread of infectious diseases. These factors can lead to a reduction in life expectancy in vulnerable populations.
Education
Education plays a significant role in shaping health outcomes. Individuals with higher levels of education often have better access to information about healthy lifestyles, which can translate into healthier choices. Higher levels of education can also translate into better-paying jobs, providing increased access to resources that promote health and well-being.
Correlation Between Income and Life Expectancy
| Income Bracket | Average Life Expectancy | Associated Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Low-income | Shorter | Limited access to nutritious food, unstable housing, lower education levels, higher stress levels, limited access to healthcare |
| Middle-income | Moderate | Moderate access to nutritious food, stable housing, moderate education levels, moderate stress levels, moderate access to healthcare |
| High-income | Longer | Greater access to nutritious food, stable housing, higher education levels, lower stress levels, better access to healthcare |
“Socioeconomic disparities in life expectancy are a complex issue, requiring multifaceted solutions. Interventions targeting access to nutritious food, stable housing, and quality education are crucial for reducing health inequities and promoting overall well-being.”
The stark reality of inequality in American life expectancy is a pressing issue. While some enjoy seemingly endless opportunities, others face significant barriers. A potential factor influencing this disparity is access to technology. Imagine the difference a more affordable smartphone, like the upcoming apple iphone 16e cheaper , could make in connecting people to vital resources.
This disparity ultimately impacts overall health outcomes and underscores the need for a more equitable society.
Geographic Disparities in Life Expectancy

The United States, despite its economic strength, faces significant health disparities across different states and regions. These variations in life expectancy highlight the complex interplay of socioeconomic factors, healthcare access, environmental conditions, and lifestyle choices. Understanding these geographic differences is crucial for developing targeted interventions to improve public health and reduce health inequities.Geographic location plays a substantial role in shaping health outcomes.
Factors like access to quality healthcare, environmental exposures, and prevalent lifestyle choices contribute to variations in life expectancy. This analysis delves into these geographic disparities, examining potential contributing factors, and underscores the need for region-specific strategies to address these complex health challenges.
Comparative Analysis of Life Expectancy Across US Regions
Life expectancy varies considerably across US states and regions. Factors like access to quality healthcare, environmental conditions, and lifestyle choices influence these differences. For example, states with robust healthcare systems and lower rates of chronic diseases generally exhibit higher life expectancies. Conversely, states facing socioeconomic challenges, environmental risks, or limited access to healthcare tend to show lower life expectancy figures.
A thorough analysis requires a comprehensive evaluation of multiple contributing factors.
Potential Explanations for Variations in Life Expectancy
Several factors contribute to the disparities in life expectancy across different US regions. Access to quality healthcare, including preventative care, timely diagnosis, and treatment, significantly impacts health outcomes. Environmental factors, such as air and water quality, exposure to pollutants, and access to healthy food options, also influence health status. Lifestyle choices, encompassing diet, physical activity, smoking rates, and substance abuse, are crucial determinants of individual health and longevity.
Role of Access to Healthcare in Geographic Disparities
Access to quality healthcare services is a key determinant of life expectancy variations. States with better-funded healthcare systems, more primary care physicians, and robust public health infrastructure generally show higher life expectancy rates. Conversely, regions with limited access to healthcare providers, long wait times for appointments, and inadequate insurance coverage face significant challenges in improving health outcomes. Lack of access to essential medical services directly contributes to higher mortality rates and lower life expectancy in underserved communities.
Role of Environmental Factors in Geographic Disparities
Environmental factors significantly influence life expectancy. Regions with poor air and water quality, exposure to hazardous substances, and limited access to healthy food options often experience higher rates of chronic diseases and lower life expectancies. For example, areas with high levels of industrial pollution may see higher rates of respiratory illnesses, impacting life expectancy. Conversely, states with cleaner air and water, and better access to nutritious food, often have better health outcomes and higher life expectancy.
Role of Lifestyle Choices in Geographic Disparities
Lifestyle choices play a critical role in shaping health outcomes and life expectancy. Factors like diet, physical activity, smoking rates, and substance abuse have significant impacts on overall health. For example, states with higher rates of obesity and smoking may experience higher rates of cardiovascular disease and lower life expectancy. Conversely, regions with healthier lifestyle choices, including higher rates of physical activity and healthier diets, tend to have improved health indicators and increased life expectancy.
Illustrative Table of Geographic Disparities
| Geographical Location | Average Life Expectancy | Contributing Factors |
|---|---|---|
| State A (High Life Expectancy) | 80 years | High access to healthcare, low smoking rates, healthy diet |
| State B (Low Life Expectancy) | 75 years | Limited access to healthcare, high smoking rates, poor air quality, lower socioeconomic status |
| Rural Region C | 78 years | Limited access to specialists, lower healthcare provider density, lower socioeconomic status |
| Urban Region D | 79 years | High access to healthcare, high density of specialists, but higher prevalence of certain lifestyle choices |
Health Behaviors and Life Expectancy: Inequality American Life Expectancy
Our health behaviors significantly impact our life expectancy. From the food we eat to the amount of exercise we get, and even the habits we form around smoking and substance use, these choices have a direct correlation with the length and quality of our lives. Understanding these relationships and the demographic variations in these behaviors is crucial for developing effective public health strategies.The relationship between health behaviors and life expectancy is complex.
While genetic predisposition plays a role, modifiable lifestyle factors like diet, exercise, and avoiding harmful substances are powerful determinants of longevity. Disparities in access to resources, knowledge, and supportive environments can influence the adoption of healthy behaviors across different demographics, ultimately contributing to health inequities.
Relationship Between Health Behaviors and Life Expectancy
A multitude of health behaviors have measurable effects on life expectancy. These behaviors, ranging from dietary choices to physical activity levels, directly influence the risk of developing chronic diseases. Smoking, for example, significantly increases the risk of heart disease, lung cancer, and other life-threatening conditions. Conversely, a balanced diet and regular exercise reduce the risk of these conditions, leading to a longer and healthier life.
American life expectancy is significantly impacted by inequality, a deeply troubling issue. Factors like socioeconomic status and access to quality healthcare play a huge role. For instance, a recent case study on Steven Webb Gossett of Los Gatos, CA highlights the complex interplay of these factors and their influence on health outcomes. Ultimately, addressing these disparities is crucial to improving overall health and well-being across the nation.
Demographic Variations in Health Behaviors
Health behaviors vary significantly across different demographic groups. Socioeconomic status, race, ethnicity, and geographic location all influence the choices individuals make regarding diet, exercise, and substance use. For instance, individuals from lower socioeconomic backgrounds may have limited access to healthy food options or safe spaces for physical activity. Furthermore, cultural norms and traditions can shape dietary habits and attitudes toward exercise.
These disparities in access and knowledge are critical factors that must be considered when designing effective public health interventions.
Impact of Policy Interventions on Life Expectancy
Policy interventions can play a critical role in shaping health behaviors and, consequently, improving life expectancy. Government regulations on tobacco use, subsidies for healthy food, and public awareness campaigns can all contribute to positive changes in population health. For example, smoke-free policies in public spaces have demonstrably reduced smoking rates, leading to a decrease in related illnesses and increased life expectancy.
Similarly, community gardens and walking trails promote physical activity, contributing to improved cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
Table: Influence of Health Behaviors on Life Expectancy
| Behavior | Impact on Life Expectancy | Possible Interventions |
|---|---|---|
| Smoking | Significant reduction in life expectancy due to increased risk of various diseases. | Increased taxes on tobacco products, public awareness campaigns, smoke-free policies. |
| Poor Diet | Increased risk of obesity, heart disease, and type 2 diabetes, potentially reducing life expectancy. | Food subsidies for healthy foods, nutrition education programs, community gardens. |
| Lack of Exercise | Increased risk of heart disease, stroke, and other chronic illnesses, contributing to lower life expectancy. | Promoting access to safe parks and recreational facilities, creating community walking trails, workplace wellness programs. |
| Excessive Alcohol Consumption | Increased risk of liver disease, certain cancers, and accidents, potentially reducing life expectancy. | Public awareness campaigns, restrictions on alcohol advertising, treatment programs. |
Access to Healthcare and Life Expectancy
Access to quality healthcare is a fundamental determinant of health outcomes, and life expectancy is significantly impacted by the availability and affordability of medical services. The US, despite its economic strength, faces substantial disparities in healthcare access, leading to varying life expectancies across different demographic groups. This unequal access underscores the critical role healthcare policies play in shaping health equity.The relationship between access to healthcare and life expectancy is complex and multifaceted.
Factors such as insurance coverage, provider availability, and the cost of care directly influence the ability of individuals to receive necessary medical services. These factors, in turn, contribute to variations in health outcomes and life expectancy. When individuals lack access to preventive care, timely diagnosis, and appropriate treatment, their health deteriorates, ultimately impacting their life expectancy. This is particularly pronounced for vulnerable populations who often face barriers to accessing quality healthcare.
Insurance Coverage and Life Expectancy
Insurance coverage is a cornerstone of healthcare access. Individuals with health insurance have a higher likelihood of receiving necessary medical care, including preventive services, which can significantly improve health outcomes. Conversely, individuals without insurance often face barriers to accessing care, potentially delaying treatment for chronic conditions or acute illnesses. This lack of coverage can contribute to poorer health outcomes and lower life expectancy.
For instance, studies have consistently shown a correlation between higher rates of uninsured individuals and lower life expectancies in specific geographic areas or demographic groups.
Provider Availability and Life Expectancy
The availability of healthcare providers, including doctors, specialists, and other medical personnel, is crucial for ensuring access to care. Rural communities often experience shortages of providers, leading to longer travel times to receive necessary medical services and potentially higher costs. Limited provider availability can result in delayed diagnoses, inadequate treatment, and ultimately, a reduction in life expectancy. This is particularly true for chronic conditions that require ongoing monitoring and management.
A shortage of specialists, such as cardiologists or oncologists, can severely impact the quality of care available in areas with limited access to these professionals.
Healthcare Affordability and Life Expectancy
The cost of healthcare is a significant barrier to access for many individuals and families. High medical bills can lead to financial hardship and limit the ability to seek necessary medical care. This is particularly true for low-income individuals and families, who may face significant challenges in affording routine checkups, preventative care, and treatment for chronic conditions. The cost of prescription medications, hospital stays, and specialized procedures can also be prohibitive for those without adequate financial resources.
This economic burden ultimately contributes to disparities in life expectancy.
Impact of Healthcare Policies on Disparities
Healthcare policies have a direct impact on disparities in life expectancy. Policies that promote access to affordable healthcare, increase provider availability, and address the cost of care can help to reduce these disparities. For example, expanding Medicaid coverage or implementing subsidies for health insurance can increase the number of insured individuals and reduce the financial burden of healthcare.
Policies focused on improving the distribution of healthcare providers in underserved areas can also improve access to care.
Correlation Between Healthcare Access and Life Expectancy
| Healthcare Access Measures | Life Expectancy | Corresponding Policies |
|---|---|---|
| Insurance Coverage Rate | Higher insurance coverage rates correlate with higher life expectancies. | Expanding Medicaid, subsidies for health insurance, and policies promoting affordability. |
| Provider Availability (per capita) | Higher provider availability per capita leads to higher life expectancy, particularly in underserved areas. | Incentivizing medical school graduates to practice in rural communities, support for healthcare training programs, and addressing provider shortages. |
| Healthcare Affordability Index | Lower healthcare affordability indices correlate with lower life expectancies. | Negotiating lower drug prices, controlling hospital costs, and providing financial assistance for healthcare services. |
Policies that address all these factors can contribute to a more equitable distribution of healthcare resources and improved life expectancy across different demographics.
Environmental Factors and Life Expectancy
Environmental factors play a significant role in shaping health outcomes and life expectancy. Exposure to pollutants, lack of access to green spaces, and other environmental hazards can negatively impact physical and mental well-being, contributing to a shorter lifespan. This influence is often amplified in vulnerable populations, further highlighting the intricate link between the environment and public health. Understanding these disparities is crucial for developing targeted interventions and promoting healthier communities.The connection between environmental factors and life expectancy is undeniable.
Exposure to air and water pollution, inadequate sanitation, and lack of access to green spaces can exacerbate existing health conditions and increase the risk of developing new ones. This effect is often seen disproportionately in communities with limited resources and political power.
Environmental Pollution and Life Expectancy
Air and water pollution are significant environmental hazards linked to reduced life expectancy. Exposure to particulate matter, heavy metals, and other pollutants can trigger respiratory illnesses, cardiovascular problems, and even cancer. Studies consistently demonstrate a correlation between high pollution levels and lower life expectancy rates in affected regions. For example, urban areas with heavy industrial activity often exhibit lower life expectancies compared to rural areas with cleaner environments.
Access to Green Spaces and Life Expectancy
The presence of green spaces has a demonstrably positive impact on health and well-being. Access to parks, gardens, and other natural areas provides opportunities for physical activity, stress reduction, and improved mental health. Research consistently shows a correlation between increased green space access and improved life expectancy. Studies in various cities have indicated that communities with greater access to green spaces tend to exhibit higher life expectancy rates.
The stark inequality in American life expectancy is a serious issue. While some communities face devastating consequences from climate change, like the devastating effects seen in California’s recent climate disasters, opinion california climate disasters highlighting the urgent need for equitable disaster relief and infrastructure, the disparity in access to healthcare and resources ultimately plays a huge role in these grim statistics.
Ultimately, these factors contribute to the significant gap in life expectancy across different demographics.
Disparities in Environmental Exposure and Life Expectancy
Environmental hazards often disproportionately affect certain communities. Low-income neighborhoods and communities of color frequently bear the brunt of pollution from industrial facilities, highways, and other sources. This unequal distribution of environmental hazards can exacerbate existing health disparities and contribute to significant differences in life expectancy across various populations. For instance, a study in a specific metropolitan area found that life expectancy was significantly lower in neighborhoods with higher levels of air pollution, and these neighborhoods were often characterized by lower socioeconomic status and a higher concentration of minority residents.
Vulnerable Populations and Environmental Factors
| Environmental Factor | Life Expectancy Impact | Vulnerable Population | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air pollution | Increased risk of respiratory illnesses, cardiovascular disease, and premature death. | Children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions. Low-income communities and communities of color. | Exposure to industrial emissions near residential areas. |
| Water contamination | Increased risk of waterborne diseases, developmental issues, and other health problems. | Children, pregnant women, and those with weakened immune systems. | Contaminated drinking water sources in underserved communities. |
| Lack of green spaces | Reduced physical activity, increased stress levels, and potential mental health issues. | Low-income communities, children, and individuals with limited mobility. | Areas with limited access to parks and recreational spaces. |
| Exposure to toxic chemicals | Increased risk of various cancers, developmental disorders, and other health problems. | Workers in manufacturing and other hazardous industries, nearby residents. | Communities near chemical plants or landfills. |
This table highlights the interplay between environmental factors, life expectancy, and vulnerable populations. The correlation between environmental exposure and health outcomes is clear. Targeted interventions to mitigate environmental hazards and promote access to healthy environments are critical for reducing health disparities and improving overall life expectancy.
Policy Implications
Addressing the persistent disparities in life expectancy requires a multifaceted approach encompassing policy interventions targeting various contributing factors. Effective policies must consider the complex interplay of socioeconomic status, geographic location, health behaviors, and access to healthcare. Successful interventions will need to be tailored to the specific needs of different communities and populations to achieve meaningful and sustainable improvements in health outcomes.A comprehensive strategy necessitates the development and implementation of evidence-based policies that address the root causes of these disparities.
These policies must not only aim to improve health outcomes but also to create more equitable systems that ensure all members of society have the opportunity to live long, healthy lives. Furthermore, evaluation of existing policies is crucial to determine their effectiveness and to identify areas for improvement.
Potential Policy Interventions
Policies aimed at reducing inequality in life expectancy must tackle the multifaceted challenges that affect health outcomes. These interventions should focus on increasing access to quality healthcare, improving socioeconomic conditions, promoting healthy behaviors, and mitigating environmental risks. These are not mutually exclusive; effective interventions will often integrate elements of each strategy.
- Investing in Early Childhood Development Programs: Early childhood development programs can significantly impact health outcomes later in life. These programs often include nutrition support, educational opportunities, and access to healthcare, which can create a foundation for better health and well-being throughout life. Examples include Head Start programs in the United States, which have shown positive correlations with improved academic performance and reduced health disparities in children.
- Expanding Access to Affordable Healthcare: Ensuring all individuals have access to affordable and quality healthcare is crucial for improving health outcomes. Policies that expand health insurance coverage, lower out-of-pocket costs, and increase access to primary care services can significantly impact life expectancy, particularly for vulnerable populations. Universal healthcare systems, such as those in many European countries, demonstrate the positive impact of comprehensive coverage on health equity and life expectancy.
- Promoting Healthy Behaviors through Public Health Campaigns: Public health campaigns can play a vital role in promoting healthy behaviors. These campaigns should address issues such as smoking cessation, healthy eating, and regular physical activity. Effective campaigns often employ targeted messaging, community engagement, and partnerships with local organizations to reach diverse populations.
- Addressing Environmental Inequities: Policies that address environmental factors impacting health, such as air and water quality, exposure to hazardous waste, and access to green spaces, can improve life expectancy. Implementing regulations to control pollution and promote sustainable practices can significantly reduce health disparities among different communities. Studies have linked environmental factors to disparities in respiratory illnesses and other health problems, highlighting the importance of these interventions.
Economic and Social Impacts of Policy Implementation
Implementing policies to reduce life expectancy disparities can have both economic and social benefits. Improved health outcomes lead to a healthier workforce, reduced healthcare costs, and increased productivity. Moreover, these policies can foster greater social equity and cohesion by reducing disparities in health and well-being.
- Reduced Healthcare Costs: Preventive measures and early interventions can lead to a decrease in the overall cost of healthcare by reducing the need for expensive treatments and hospitalizations. Early detection and treatment of health problems can minimize long-term health issues, reducing overall costs. This can be particularly significant in populations with higher rates of chronic conditions.
- Increased Productivity and Economic Growth: A healthier population generally leads to a more productive workforce, resulting in increased economic output. Reduced absenteeism and presenteeism (reduced productivity while at work) due to illness can also contribute to economic growth.
- Improved Social Cohesion: Reducing disparities in life expectancy contributes to a more equitable and cohesive society. Policies promoting health equity foster social capital and reduce the burden of preventable illnesses on vulnerable populations. This leads to a more harmonious society with fewer disparities.
Potential Impacts of Policy Changes on Life Expectancy
The table below illustrates the potential impacts of specific policy changes on life expectancy.
| Policy | Potential Impact | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Expanding access to affordable healthcare | Increased access to preventative care, timely diagnosis, and treatment | Reduced mortality rates, improved health outcomes, particularly for vulnerable populations |
| Investing in early childhood development programs | Improved health and well-being in early years, reducing risk factors for chronic diseases | Improved health literacy, reduced disparities in childhood and adult health |
| Promoting healthy behaviors through public health campaigns | Increased awareness of risk factors, adoption of healthier lifestyles | Reduced prevalence of preventable diseases, decreased mortality rates |
| Addressing environmental inequities | Improved air and water quality, access to green spaces | Reduced exposure to pollutants, lower rates of respiratory and other environmental illnesses |
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the inequality in American life expectancy is a multifaceted problem with deep roots in history and present-day realities. Addressing this issue demands a comprehensive approach that tackles systemic inequalities, improves access to quality healthcare, and fosters healthier communities across the nation. By understanding the contributing factors and implementing effective policies, we can strive towards a future where all Americans have the opportunity to live long and healthy lives.