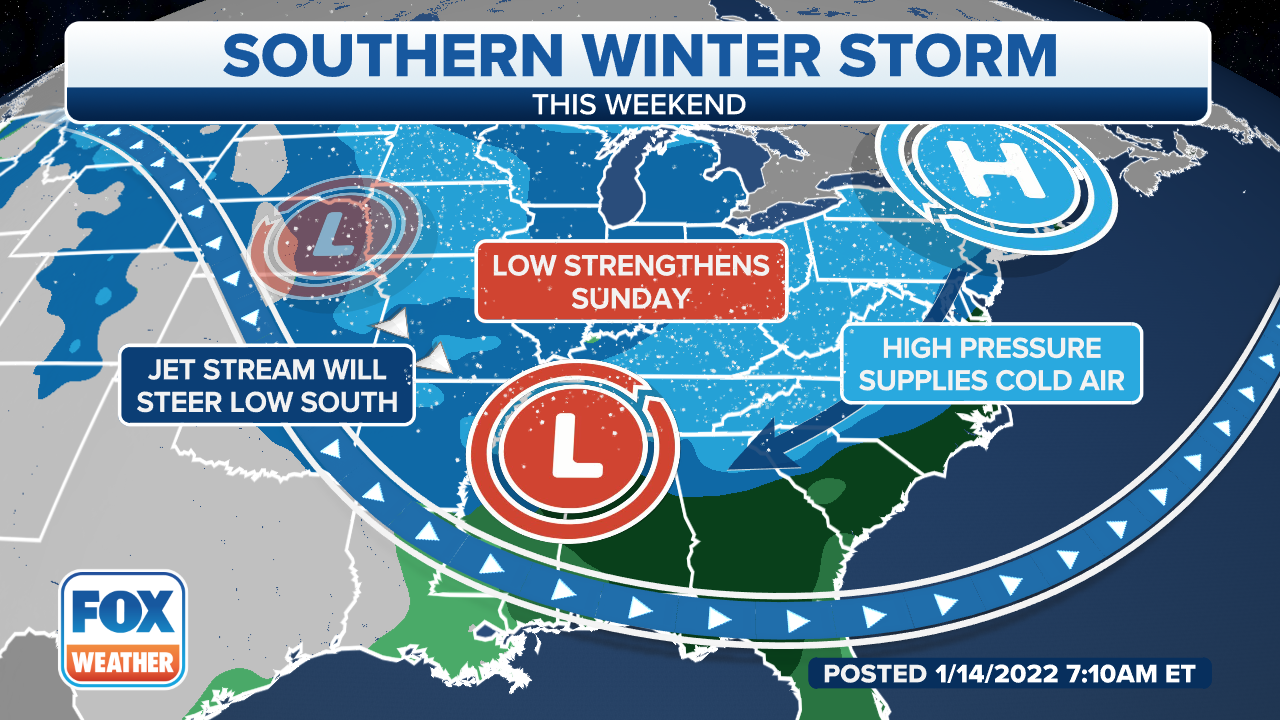
Winter Storm Deep South US A Comprehensive Guide
Winter storm deep south us poses significant challenges to infrastructure, communities, and the economy. This guide delves into the potential impacts, from power outages and transportation disruptions to health risks and economic losses. We’ll explore preparedness strategies, historical context, and the crucial role of community support in navigating these challenging winter weather events.
The Deep South US, while accustomed to warm weather, is vulnerable to severe winter storms. This guide examines the wide-ranging consequences of such storms, providing valuable insights into the various facets of such an event.
Impact on Infrastructure: Winter Storm Deep South Us
Winter storms in the Deep South US, while not as severe as those in the northern states, can still cause significant disruptions to infrastructure. Freezing temperatures, heavy snowfall, and ice accumulation can overwhelm existing systems, leading to widespread outages and hindering essential services. Understanding the potential impacts is crucial for preparedness and effective response.
Power Outages
Power grids in the Deep South, while generally robust, are susceptible to winter storm damage. Ice accumulation on power lines can cause them to break, leading to widespread outages. Trees falling onto power lines are another common cause. The extent of outages depends on factors like the intensity and duration of the storm, the age of the infrastructure, and the effectiveness of preventative measures.
For example, the 2021 winter storm in Texas demonstrated the vulnerability of power grids even in areas considered well-prepared.
Disruptions to Water and Sewage Systems
Freezing temperatures can severely impact water and sewage systems. Frozen pipes can burst, leading to water main breaks and flooding. Heavy snowfall can also overwhelm sewer systems, leading to overflows and contamination. This is particularly problematic in areas with aging infrastructure. Proper insulation and preventative measures are vital for minimizing these disruptions.
Transportation Network Impacts
Winter storms significantly impact transportation networks. Heavy snowfall and icy conditions can make roads impassable, disrupting traffic flow and causing delays. Railways may be forced to halt operations due to hazardous conditions, impacting the movement of goods and people. Airports may close due to poor visibility or runway conditions. This leads to cancellations and significant delays for travelers.
The 2014 winter storm in the Eastern US, which caused widespread transportation disruptions, illustrates the severity of these impacts.
Infrastructure Resilience Comparison
| Infrastructure System | Resilience Factors | Vulnerabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Power Grids | Modernization efforts, advanced weather forecasting, and robust maintenance schedules. | Ice accumulation on lines, tree damage, and aging infrastructure. |
| Roads | Regular maintenance, de-icing procedures, and well-maintained road surfaces. | Heavy snowfall, freezing temperatures, and limited de-icing resources. |
| Water and Sewage Systems | Regular pipe inspections, insulation, and leak detection systems. | Frozen pipes, inadequate insulation, and aging infrastructure. |
| Communication Networks | Redundant systems and backup power sources. | Power outages, severe weather conditions, and potential damage to communication towers. |
Communication Network Impacts
Communication networks, including cell towers and internet infrastructure, can be severely affected by power outages and storm damage. These disruptions can hinder emergency response efforts and create difficulties for individuals to communicate with family and friends. In areas with limited alternative communication methods, the impact is magnified. Power outages directly affect the ability of these systems to function.
Preparedness and Response

Winter storms in the Deep South US, though less severe than those in the northern US, still pose significant threats to infrastructure and personal safety. Understanding how to prepare and respond effectively is crucial to minimizing damage and disruption. This discussion will cover essential steps individuals and local governments can take to ensure a smooth and safe passage through these events.Local preparedness efforts, combined with individual precautions, significantly reduce the impact of winter storms.
This involves a multifaceted approach, including robust emergency communication systems, readily available supplies, and community-wide collaboration.
Home Preparedness for Winter Storms
Preparing your home for a winter storm involves several key steps. Prioritizing these measures will enhance your safety and minimize potential damage.
- Stock up on essential supplies. Having a well-stocked emergency kit with food, water, batteries, flashlights, first-aid supplies, and medications is paramount. Consider items specific to the Deep South, such as extra blankets and warm clothing, as temperatures can still drop significantly. Remember, the need for supplies can extend beyond a few hours.
- Secure your home. Protect your windows and doors from damage. Clear gutters and downspouts to prevent water damage. Take steps to protect exterior pipes from freezing.
- Prepare for power outages. Charge all electronic devices and keep a portable power source handy. Have a plan for cooking and heating if power is lost. Having a backup heating source, such as a fireplace or portable heater, is vital for maintaining warmth.
Role of Local Governments in Response
Local governments play a critical role in managing winter storm response. Their preparedness strategies are crucial for the safety and well-being of their constituents.
The winter storm battering the deep south US is really wreaking havoc, and it’s a stark reminder of the power of nature. Tragically, this severe weather comes on the heels of a horrific DUI accident in Gilroy, where a driver was charged with murder after a crash that claimed the life of a pregnant woman. This tragic incident highlights the devastating consequences of irresponsible driving, and sadly underscores the need for responsible decision-making, especially during challenging weather conditions like the one impacting the south.
The sheer force of the winter storm continues to cause disruption across the region.
- Establish clear communication channels. Local governments should have well-defined communication plans to disseminate information about road closures, power outages, and other potential hazards. These communication channels must be accessible to everyone, including those without reliable internet access.
- Ensure adequate emergency resources. Having sufficient personnel, equipment, and supplies readily available is essential. This includes snow removal equipment, emergency shelters, and personnel trained in disaster response.
- Implement and enforce safety regulations. Local governments must ensure compliance with safety guidelines. This might include enforcing building codes or issuing warnings about dangerous road conditions.
Emergency Communication Plans
Effective emergency communication is vital during winter storms. These plans should be developed and practiced beforehand.
- Establish a family communication plan. Designate a meeting place in case family members are separated. Ensure everyone knows how to contact each other. Have a secondary contact person outside of the immediate area.
- Monitor official sources for information. Keep updated on weather conditions and advisories from local authorities and national weather services. Pay close attention to any warnings or advisories regarding hazardous conditions.
- Use multiple communication methods. Have backup plans in case one method of communication is unavailable. This might include phone calls, text messages, social media, or a combination of these.
Preparedness Strategies Across Deep South States
Different states in the Deep South US adopt varying approaches to winter storm preparedness.
| State | Key Preparedness Strategies |
|---|---|
| Alabama | Focus on infrastructure maintenance, community alerts, and emergency shelter availability. |
| Louisiana | Emphasis on coastal protection, evacuation planning, and community resilience programs. |
| Mississippi | Prioritize road maintenance, timely warnings, and cooperation with neighboring states. |
| Texas | Emphasis on energy infrastructure preparedness, evacuation routes, and severe weather forecasting. |
Comprehensive Community Preparedness Plan
A comprehensive community preparedness plan should incorporate elements of home preparedness, local government response, and emergency communication.
The deep freeze gripping the southern US during the winter storm has highlighted the urgent need for infrastructure improvements. Pittsburg, for example, has unveiled a comprehensive road pavement plan, but securing the necessary funding remains a significant hurdle. This plan could be a crucial step towards better resilience, but the winter storm underscores how vulnerable our systems are when resources are lacking.
Hopefully, solutions for these infrastructure issues can be found quickly, before the next major weather event hits.
“A strong community plan is built on a foundation of collaboration, clear communication, and a shared understanding of risks.”
- Establish a community coordination center. This central location will serve as a hub for communication, resource distribution, and coordination among different agencies and community members.
- Develop a detailed inventory of resources. Identify and catalog available supplies, equipment, and personnel. This ensures that resources are readily accessible during a crisis.
- Conduct regular drills and exercises. Practice response procedures to ensure everyone is prepared and can work effectively together.
Economic Consequences

Winter storms in the Deep South US, while often disruptive, have significant economic repercussions. Beyond the immediate damage to infrastructure and the inconvenience to residents, these storms create cascading effects that impact various sectors, from tourism to agriculture, and ultimately affect the region’s overall financial well-being. The financial losses associated with such events can be substantial, requiring careful planning and mitigation strategies.
Financial Losses for Businesses
The financial toll on businesses in the Deep South during a winter storm can be substantial. Direct losses include damage to property, equipment, and inventory. Businesses may also incur costs associated with temporary closures, lost sales, and expenses related to restoring operations. For example, a restaurant forced to close for several days due to power outages will lose revenue and incur costs for staffing and potential food spoilage.
Indirect losses can be even more impactful, such as disruptions to supply chains and reduced consumer spending in the aftermath of the storm.
Impact on Tourism and Hospitality
The Deep South’s tourism and hospitality industries are highly vulnerable to winter storms. Closures of attractions, roads, and airports lead to cancellations and lost revenue for hotels, restaurants, and other businesses reliant on visitor spending. For example, a ski resort in the region, normally open year-round, may be forced to close for an extended period due to severe weather conditions.
This leads to significant lost revenue for the business and job losses for employees.
Disruptions to Supply Chains
Winter storms can severely disrupt supply chains, particularly for perishable goods. Road closures, power outages, and logistical challenges can halt the movement of goods, resulting in delays and increased costs. For instance, produce from farms in the region may be unable to reach markets due to blocked roads or damaged infrastructure, leading to losses for farmers and wholesalers.
Impact on Agricultural Production
Agricultural production in the Deep South is vulnerable to the effects of winter storms. Damage to crops, livestock, and infrastructure can have substantial economic consequences. Heavy snow and ice can damage fruit trees and other agricultural products. For instance, citrus groves in Florida and other parts of the region can suffer significant damage during winter storms, leading to substantial losses in the following months.
Furthermore, livestock can be affected by cold temperatures and a lack of access to food and water.
Potential Measures to Mitigate Economic Losses
Several measures can help mitigate the economic losses associated with winter storms. These include:
- Investing in resilient infrastructure that can withstand severe weather events.
- Developing comprehensive emergency preparedness plans that include contingency strategies for businesses and communities.
- Implementing robust supply chain management systems that can adapt to disruptions.
- Supporting agricultural practices that enhance resilience to weather-related damage, such as crop diversification and improved livestock management.
These strategies can help to lessen the economic impact of winter storms, ensuring a quicker recovery for affected businesses and communities.
Health and Safety Concerns
A deep south winter storm presents unique health risks, particularly when extreme cold weather conditions persist. Understanding these risks, especially for vulnerable populations, is crucial for proactive safety measures. Protecting yourself and loved ones involves more than just stocking up on supplies; it’s about understanding the potential dangers and taking the necessary precautions.The cold can be especially dangerous in the Deep South, where people might not be as accustomed to extreme temperatures.
Even brief exposure to these conditions can lead to serious health problems, especially for those with pre-existing health conditions or limited mobility.
The winter storm slamming the deep south US is wreaking havoc, but sadly, other tragedies are also unfolding. A man was tragically shot and killed in East Oakland, a concerning development amidst the current weather crisis. Reports indicate this violent incident happened nearby, highlighting the complex challenges facing the region beyond the harsh winter conditions. Thankfully, the focus can return to the devastating winter storm affecting the deep south US, and the ongoing relief efforts needed.
man fatally shot in east oakland 65
Health Risks Associated with Extreme Cold
Exposure to extreme cold can lead to a range of health problems, from minor discomfort to life-threatening conditions. Hypothermia and frostbite are two of the most serious dangers. Shivering, confusion, and loss of coordination are early signs of hypothermia, while frostbite manifests as numbness and a bluish or pale appearance of affected skin. Early detection and intervention are vital for preventing severe complications.
Risks to Vulnerable Populations, Winter storm deep south us
Elderly individuals, children, and those with underlying health conditions are particularly susceptible to the negative impacts of cold weather. Elderly individuals may have decreased sensitivity to cold and difficulty regulating their body temperature. Children, with their smaller body mass, lose heat more quickly than adults. Those with pre-existing conditions may have reduced capacity to withstand the cold, exacerbating the risk of serious health problems.
Importance of Proper Winter Clothing and Shelter
Appropriate clothing is crucial for protecting against the cold. Layering clothing, including a waterproof outer layer, thermal underwear, and warm socks, is essential. Choosing appropriate footwear with good insulation is equally important. Seeking shelter from the elements, whether in a home, car, or designated warming center, is critical for preventing heat loss.
Potential Health Hazards and Preventive Measures
| Potential Health Hazard | Preventive Measures ||—|—|| Hypothermia | Dress in layers, seek shelter immediately, monitor body temperature, and watch for signs like shivering and confusion. || Frostbite | Wear warm, waterproof clothing, cover exposed skin, and avoid prolonged exposure to cold. || Dehydration | Drink plenty of fluids, especially warm beverages, to maintain hydration. || Respiratory problems | Limit exposure to cold air, use a humidifier or other methods to maintain indoor air quality.
|| Heart problems | Take extra precautions during cold weather, avoid strenuous activity, and consult with a doctor if you have any concerns. || Other pre-existing conditions | Be aware of how cold weather may exacerbate any existing medical conditions, and consult with a healthcare provider if necessary. |
Identifying and Responding to Hypothermia and Frostbite
Hypothermia is a life-threatening condition where the body loses heat faster than it can produce it. Early symptoms include shivering, confusion, and slurred speech. If you suspect hypothermia, get the person to a warm environment, remove wet clothing, and wrap them in blankets. Frostbite occurs when body tissue freezes. Symptoms include numbness, pain, and a bluish or pale appearance of the affected area.
Get the person to a warm environment and seek immediate medical attention. Seek medical attention promptly for both conditions.
Immediate action is critical when dealing with hypothermia or frostbite.
Historical Context
Winter storms have long plagued the Deep South US, impacting communities and infrastructure. Understanding past events offers valuable insights into potential future threats and the evolving nature of these storms. This examination considers historical storms, forecasting advancements, and the role of climate change in shaping these events. It also presents historical snowfall and temperature records to provide context.
Significant Winter Storms of the Past
The Deep South, while not typically associated with severe winter weather, has experienced impactful storms throughout history. These storms often manifest as ice storms, heavy snowfall, or strong winds, causing widespread power outages, transportation disruptions, and damage to infrastructure. Examples include the 1982 ice storm, the 1993 “Blizzard of the Century,” and the 2014 Winter Storm. Each event highlighted the vulnerability of the region’s infrastructure and preparedness levels to these severe winter weather events.
Evolution of Weather Forecasting and Prediction Models
Weather forecasting has undergone significant evolution since the early days of rudimentary observations. From simple weather maps to sophisticated computer models, advancements in technology have dramatically improved the accuracy and lead time of predictions. Early predictions relied heavily on visual observations and rudimentary mathematical models. Modern forecasts utilize complex atmospheric models and vast datasets, including satellite imagery and radar, resulting in much more accurate predictions and improved storm preparedness.
Climate Change and Intensifying Winter Storms
Climate change is a complex issue that affects various weather phenomena. While the Deep South doesn’t experience the same levels of snowfall as more northern regions, the impact of winter storms is undeniable. Warmer temperatures can lead to more intense precipitation events, including heavy snow or freezing rain. This is because warmer air holds more moisture, potentially resulting in heavier snowfall or more widespread freezing rain.
Historical Snowfall and Temperature Records
Data on historical snowfall and temperature records for the Deep South US provide crucial context for assessing the potential impacts of future storms. Such records highlight trends and extremes, which can be compared with expected changes in the future. The records can help identify areas most vulnerable to extreme weather events and inform the development of strategies to mitigate their effects.
These records are crucial for understanding the potential impacts of future winter storms, which might deviate significantly from the norms. A detailed analysis of historical records is needed to understand these potential deviations.
| Year | Event | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 1982 | Ice Storm | Widespread power outages, significant damage to trees and infrastructure |
| 1993 | “Blizzard of the Century” | Heavy snowfall, transportation disruptions, significant power outages |
| 2014 | Winter Storm | Heavy snowfall, significant transportation disruptions, infrastructure damage |
Community Support and Relief
Winter storms, especially in the deep South, can leave communities reeling. Beyond the immediate dangers and infrastructure damage, the human cost requires a robust and well-coordinated response. Community support plays a critical role in ensuring the well-being of affected individuals and families during and after the storm’s aftermath.
Role of Non-profit Organizations
Non-profit organizations are often the first responders in the wake of a winter storm, providing vital support that government agencies may not immediately be able to deploy. They operate independently or alongside government initiatives, delivering food, shelter, and essential supplies. These organizations often have established networks and expertise in disaster relief, allowing them to quickly mobilize resources and target assistance to those most in need.
Their involvement is crucial for bridging the gap between immediate needs and longer-term recovery.
Importance of Community Volunteering
Community volunteers are indispensable during and after winter storms. Their efforts, whether offering a helping hand or donating time, provide an essential supplement to professional disaster relief teams. Volunteering can encompass a range of activities, from shoveling snow to providing emotional support. This collective effort strengthens community bonds and ensures a more comprehensive response to the storm’s effects.
The combined strength of individuals and organizations is often the key to a swift and effective recovery.
Accessing Government Assistance Programs
Navigating government assistance programs can be complex, especially during a crisis. Clear communication channels and readily available information are vital for affected individuals to understand the various programs available. Government websites and local emergency management offices are critical resources for accessing these programs. A streamlined application process and accessible information ensure that eligible individuals can receive the necessary aid.
Resources for Individuals and Families
| Category | Resource | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Emergency Supplies | Local Red Cross | Provides basic necessities like food, water, blankets, and first aid supplies |
| Financial Assistance | Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) | Offers financial aid for individuals and families suffering losses due to natural disasters. |
| Shelter | Local shelters, churches, and community centers | Provides temporary housing and support services for displaced individuals |
| Mental Health Services | Crisis hotlines, mental health providers | Offers support for those experiencing stress, anxiety, or trauma related to the storm. |
This table provides a starting point for individuals and families seeking resources after a winter storm. The specific resources available may vary based on the location and severity of the storm.
Effective Community Support Strategies in Previous Winter Storms
Successful community support strategies in previous winter storms highlight the importance of coordinated efforts. For example, during the 2018 winter storm in the Southeast, effective strategies included establishing centralized collection points for donations, establishing clear communication channels between residents and relief organizations, and providing training to volunteers on how to best assist those in need. Effective coordination among community leaders, government agencies, and non-profits is essential for maximizing the impact of relief efforts.
Illustrative Examples of Impacts
A severe winter storm, particularly in the Deep South, can have a devastating impact on daily life, infrastructure, and communities. The region, often unprepared for such extreme weather, faces unique challenges during these events. This section provides a hypothetical scenario illustrating the wide-ranging effects of a severe winter storm in a Deep South city, highlighting the challenges faced and the community’s response.
Hypothetical Storm Scenario: “Winter Fury” in Mobile, Alabama
The Deep South city of Mobile, Alabama, experiences a severe winter storm dubbed “Winter Fury.” The storm brings heavy snowfall, plunging temperatures well below freezing, and high winds. This is unusual for the region, as typical winter weather is mild.
Impact on Daily Life
The storm disrupts daily routines significantly. Schools are closed for multiple days, impacting children and their parents’ work schedules. Essential services, like transportation and grocery stores, face closures due to hazardous conditions. People find it challenging to travel for work, appointments, or to simply get necessities. Power outages are widespread, affecting heating, lighting, and communication systems.
Basic needs like food, water, and medicine become difficult to access.
Community Coping Mechanisms
The community rallies together to cope with the aftermath. Neighbors help neighbors by sharing resources, providing support, and offering shelter. Local organizations and volunteers step in to provide meals, blankets, and essential supplies. Community centers become makeshift warming centers, offering a safe place to stay warm and get support. Local businesses open their doors to provide shelter and resources.
Local government agencies coordinate relief efforts, working with community groups to distribute supplies and ensure the safety of vulnerable populations.
Disruption of Daily Routines
The storm significantly disrupts the normal rhythm of daily life. Essential errands become impossible or dangerous to undertake due to hazardous road conditions. Travel is severely limited. Work schedules are affected, impacting businesses and employment. Many people experience isolation and anxiety as they struggle to maintain their normal routine.
Challenges Faced by First Responders
First responders face significant challenges during a severe winter storm. Hazardous road conditions hinder their ability to reach those in need. Extreme cold and potential injuries add to the risks they face. Limited visibility and communication difficulties can make rescue efforts complex. They often encounter a high volume of calls, stretching their resources thin.
Their dedication and resilience are crucial in navigating the crisis.
Predictive Modeling and Forecasting
Winter storms, especially those impacting the Deep South US, pose significant challenges due to their unpredictable nature. Accurate forecasting is crucial for effective preparedness and response. This section delves into the intricacies of generating winter storm predictions, examining the factors considered, and analyzing the historical accuracy of forecasts. Understanding these aspects is essential for mitigating the potential impacts of future events.
Methods of Winter Storm Prediction
Winter storm predictions rely on a combination of sophisticated models and observational data. These models simulate atmospheric conditions, including temperature, pressure, and wind patterns, to project the potential for precipitation, intensity, and duration. Initial forecasts are often based on global weather models, which provide a broad overview of the expected weather patterns. These models are then refined with regional data, incorporating localized factors such as terrain and surface features.
Factors Considered in Deep South Forecasts
Forecasting winter storms in the Deep South US necessitates a nuanced understanding of the region’s unique characteristics. Factors such as the proximity to water bodies, terrain variations, and the influence of fronts play a significant role in shaping the storm’s trajectory and intensity. Models also consider historical weather patterns for the region, including previous winter storms and their characteristics, which helps calibrate the predictive models.
Furthermore, the presence of specific atmospheric conditions, like jet streams and cold air masses, is meticulously analyzed.
Historical Accuracy of Forecasts
Evaluating the historical accuracy of winter storm forecasts is crucial for gauging the reliability of the predictive models. While significant advancements have been made in recent years, historical data reveals varying degrees of accuracy depending on the specific event and the sophistication of the models used. Forecasting the precise timing, location, and intensity of winter storms remains a challenge, especially in complex weather systems.
Nevertheless, the overall accuracy of forecasts has improved over time, thanks to increased computing power and better data collection methods.
Comparison of Forecasting Models
Several different models are used to predict winter storms, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Global models, such as the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) and the National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) models, provide a broad overview of atmospheric conditions. Regional models, such as those used by the National Weather Service, provide more localized detail and are crucial for refining the initial forecasts.
The choice of model often depends on the specific storm characteristics and the lead time available. Further improvements in model accuracy are continually being sought through ongoing research and development.
Analyzing Forecasting Model Accuracy
Analyzing the accuracy of forecasting models involves a multifaceted approach. Key performance indicators include comparing predicted precipitation amounts with observed values, examining the accuracy of timing predictions, and assessing the consistency of model outputs. Statistical metrics, such as the Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE) and the Mean Absolute Error (MAE), are commonly used to quantify the accuracy of forecasts.
The comparison of different models, using these metrics, provides valuable insights into the strengths and weaknesses of each approach. It is important to consider the specific characteristics of the winter storm event being analyzed when interpreting the results.
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, a winter storm deep south us can bring widespread devastation, impacting everything from infrastructure to individual well-being. Understanding the potential consequences, implementing proactive preparedness measures, and fostering strong community support are vital to mitigating the impact and ensuring resilience. This comprehensive guide equips readers with the knowledge to navigate such events effectively.