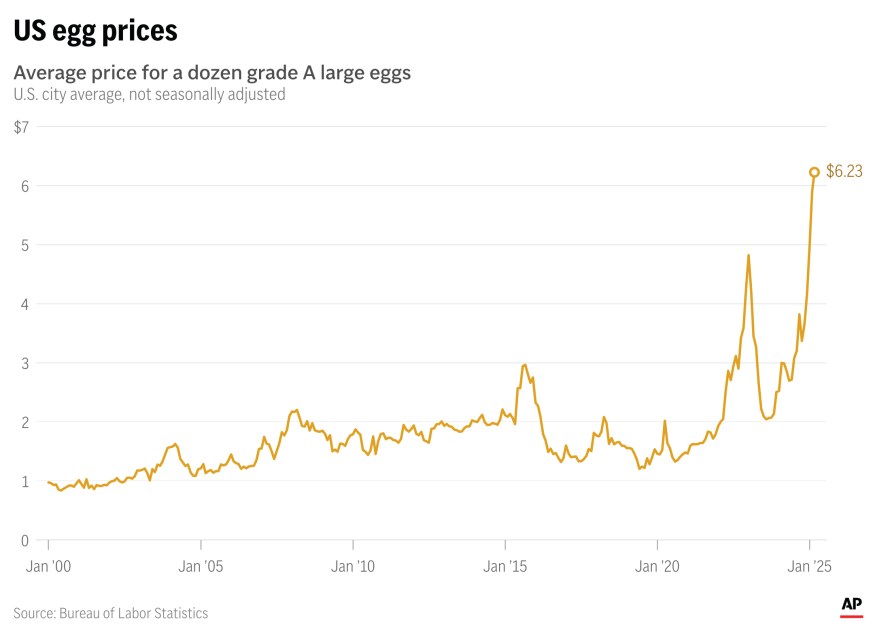
Egg Prices Increase to Record Highs
Egg prices increase to record highs, prompting a global scramble to understand the factors behind this dramatic shift. From avian flu outbreaks impacting production to escalating feed costs, the rise in egg prices is affecting consumers, industries, and the entire supply chain. This article delves into the complexities of this situation, examining the historical context, contributing factors, and potential long-term consequences.
This analysis explores the global egg market, highlighting the recent surge in prices. We’ll look at regional variations, the impact on consumer behavior, and the implications for various industries. We’ll also analyze the supply chain vulnerabilities, consider alternative protein sources, and offer a glimpse into potential future price predictions.
Global Egg Market Overview: Egg Prices Increase To Record
The global egg market, a crucial component of the protein industry, has experienced significant price fluctuations over the years. These price swings are often influenced by a complex interplay of supply-side factors and consumer demand. Understanding these trends is essential for assessing the current market situation and anticipating future price movements.
Egg prices have skyrocketed to record highs, leaving many of us scrambling for affordable protein sources. This economic pressure is forcing us to get creative, and consider alternatives like ms office 365 alternatives for our productivity needs, as well as our grocery budgets. While the price of eggs continues to be a concern, we’re all adapting to the changing market.
Historical Trends in Egg Prices
Egg prices have shown a tendency to fluctuate over time, often mirroring broader economic trends and seasonal variations. Historically, price spikes have been observed during periods of high demand or supply disruptions. Significant events like disease outbreaks, extreme weather, or changes in consumer preferences have all left their mark on the market, causing substantial price changes. This volatility necessitates a nuanced understanding of the factors contributing to these changes.
Factors Influencing Global Egg Prices
Several key factors contribute to the price fluctuations in the global egg market. Supply and demand dynamics play a critical role. Increased consumer demand for eggs often leads to higher prices, while an abundant supply can drive prices down. Weather patterns, particularly extreme temperatures or prolonged periods of drought, can significantly impact egg production. Disease outbreaks, affecting poultry flocks, can also drastically reduce supply and push prices upward.
Furthermore, government policies, import/export regulations, and the presence of significant players in the market, like large-scale egg producers and retailers, also have a substantial impact.
Current Global Egg Market Situation
The current global egg market is characterized by notable regional variations in prices. Supply chain disruptions, caused by various factors including the pandemic and geopolitical events, have created an uneven playing field. In some regions, prices have reached record highs due to reduced availability. Conversely, other regions have experienced relative stability or even slight price decreases, primarily due to different production levels, demand, and market conditions.
Regional Variations in Egg Prices (2020-2023)
| Year | Region | Average Egg Price (USD per dozen) |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | North America | 2.50 |
| 2020 | Europe | 2.80 |
| 2020 | Asia | 1.80 |
| 2021 | North America | 2.80 |
| 2021 | Europe | 3.20 |
| 2021 | Asia | 2.00 |
| 2022 | North America | 3.50 |
| 2022 | Europe | 4.00 |
| 2022 | Asia | 2.50 |
| 2023 | North America | 3.80 |
| 2023 | Europe | 4.50 |
| 2023 | Asia | 2.80 |
Note: Average egg prices are estimates and may vary based on specific market conditions and local factors.
Factors Contributing to Price Increase

Record egg prices have sent ripples through kitchens and grocery stores worldwide. This surge isn’t a fleeting phenomenon; it’s a complex issue with multiple contributing factors, each playing a crucial role in pushing up the cost of this essential food item. Understanding these factors is key to comprehending the current market dynamics and potential future trends.
Avian Influenza Outbreaks
Avian influenza, or bird flu, has had a devastating impact on global egg production. These outbreaks, often concentrated in specific regions, lead to the culling of large numbers of laying hens. This drastic reduction in the available laying flock directly translates into a decreased supply of eggs. The reduced supply, combined with the consistent demand for eggs, inevitably drives up prices.
The economic losses and disruption to poultry farms caused by the outbreaks exacerbate the price increase.
Feed Costs
The cost of feed, primarily grains like corn and soy, has been a significant driver in the recent surge in egg prices. Higher grain prices, influenced by various factors such as drought conditions, global market fluctuations, and increased demand, translate directly into increased feed costs for poultry farms. This, in turn, pushes up the production cost of eggs, making them more expensive to produce and sell.
The correlation between grain prices and egg prices is undeniable and reflects the direct link in the supply chain.
Geopolitical Events and Economic Factors
Geopolitical instability and economic uncertainties can also significantly impact egg prices. International trade disruptions, sanctions, and fluctuating currency exchange rates can affect the availability and cost of feed ingredients. For instance, if a major grain-producing nation faces political instability, the ripple effect on the global market can lead to shortages and price increases, which in turn affect the cost of feed and, ultimately, eggs.
This demonstrates the complex interconnectedness of global markets.
Comparison of Egg Prices
| Egg Type | Average Price (USD per dozen) during Price Increase Period |
|---|---|
| Organic | $5.50 – $7.00 |
| Free-Range | $4.00 – $5.50 |
| Conventional | $3.00 – $4.00 |
The table above provides a general overview of the price range for different egg types during the recent period of heightened prices. Note that these are approximate figures and actual prices may vary based on location and retailer. The significant price difference between organic and conventional eggs reflects the higher production costs associated with organic farming practices.
Consumer Impact and Implications
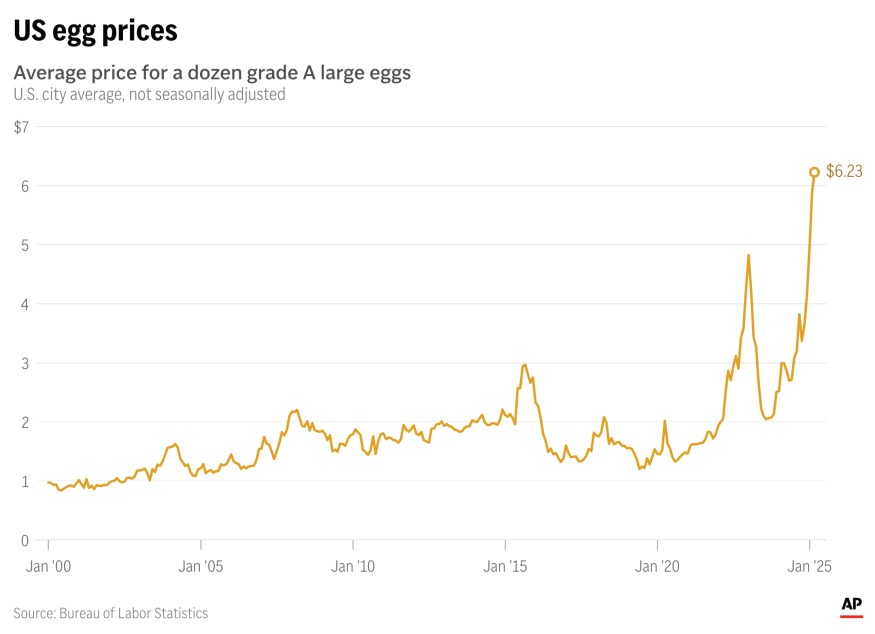
Record-high egg prices are significantly impacting consumers, forcing adjustments in purchasing habits and potentially altering dietary choices. This ripple effect extends beyond individual wallets, affecting related industries like bakeries and restaurants, and demanding a careful look at the broader economic implications. The increasing cost of eggs highlights the vulnerability of food security and the cascading consequences of supply chain disruptions.
Consumer Purchasing Behavior Changes
Consumers are responding to the escalating egg prices by making conscious choices about their purchases. Many are opting for less frequent consumption of eggs, substituting them with alternative protein sources, or reducing portions. This shift in purchasing behavior is a direct result of the increased cost, impacting both individual and family budgets. Some are exploring ways to stretch their egg budget, such as buying smaller quantities more frequently or looking for sales and deals.
Dietary Habit Shifts
The rising egg prices are likely to lead to a noticeable shift in dietary habits. Consumers might reduce the frequency of egg-based meals, particularly those that are more expensive to prepare, such as elaborate breakfasts or dishes that heavily rely on eggs. This could lead to a decrease in the consumption of omelets, frittatas, and other egg-centric dishes.
Instead, they might favor alternatives like breakfast cereals, pancakes, or even simply toast and fruit.
Impact on Food Budgets
The impact on average consumer food budgets is substantial. Eggs are a staple ingredient in many households, and their price increase directly affects the overall cost of meals. Families may experience a significant strain on their grocery budgets, especially if eggs are a substantial part of their regular diet. For instance, a family of four consuming eggs three times a week might see a noticeable increase in their weekly food expenses.
Impact on Related Industries
The rising cost of eggs is undeniably impacting related industries. Bakeries, for example, may experience a reduction in demand for egg-based products, like cakes and pastries. Restaurants might adjust their menus to include less egg-heavy dishes or implement strategies to reduce egg costs in their recipes. They may also face the challenge of passing on the increased egg prices to consumers, potentially affecting their profitability.
Breakfast Options Price Comparison
The following table illustrates the potential price differences between various breakfast options incorporating eggs, showcasing the impact of the egg price increase. This data is an illustrative example and may vary based on location and specific ingredients.
| Breakfast Option | Estimated Price (USD) |
|---|---|
| Scrambled Eggs with Toast | $5.00 |
| Oatmeal with Berries and Eggs | $6.50 |
| Breakfast Burrito with Eggs | $7.50 |
| Yogurt Parfait with Berries and a Fried Egg | $4.00 |
| Pancakes with Eggs and Syrup | $6.00 |
Supply Chain Analysis
The soaring egg prices have exposed vulnerabilities in the global egg supply chain. Understanding these bottlenecks, the differences in production methods, and the role of intermediaries is crucial to predicting future price fluctuations and potential solutions. This analysis delves into the intricacies of the egg market, highlighting potential points of disruption and strategies for strengthening the chain.
Bottlenecks in the Egg Supply Chain
The egg supply chain is complex, involving multiple stages from farm to consumer. Several factors can disrupt this process, leading to shortages and price increases. These bottlenecks can include issues with feed availability, transportation challenges, and unexpected outbreaks of avian influenza. A significant factor is the unpredictability of disease outbreaks, as they can decimate flocks and cause substantial delays in production recovery.
Also, extreme weather events, like floods or droughts, can disrupt feed production and overall farm operations.
Efficiency of Different Egg Production Methods
Different egg production methods have varying levels of efficiency, influencing their contribution to overall supply. Industrial egg production, often criticized for its intensive practices, prioritizes large-scale output and cost-effectiveness. This model, while efficient in maximizing production, often sacrifices animal welfare considerations. Free-range egg production, on the other hand, prioritizes animal welfare and a more natural environment. However, the lower density and variable production conditions can lead to lower overall efficiency compared to industrial methods.
Hybrid models, which combine aspects of both approaches, attempt to find a balance between efficiency and welfare, though the optimal balance is still a subject of debate.
Role of Intermediaries and Distributors
Intermediaries and distributors play a crucial role in connecting egg producers with consumers. They facilitate the movement of eggs through various channels, from farms to retail stores. Their efficiency directly impacts the price consumers pay, as high transaction costs and inefficiencies can result in increased final prices. Large-scale distributors often leverage economies of scale, while smaller, localized distributors may have limited purchasing power, potentially increasing their costs and affecting pricing.
A complex web of relationships and contracts between various entities, from producers to wholesalers to retailers, affects the final price of eggs.
Egg Supply Chain Diagram
The egg supply chain begins with feed production and farm operations. The diagram illustrates potential disruption points.
Egg prices are soaring to record highs, making breakfast a luxury for many. It’s a stark contrast to the devastation unfolding across Southern California, where recent wildfires have left a trail of destruction. Images from the photos fatal southern california firestorm highlight the scale of the crisis, further emphasizing the interconnectedness of global events and their impact on everyday costs.
The rising egg prices, unfortunately, seem to be just another example of this reality.
Feed Production
/ \
/ \
/ \
/ \
/ \
Farm Operations -> Processing/Packaging
/ \
/ \
/ \
/ \
/ \
/ \
Transportation -> Distribution Centers
/ \
/ \
/ \
/ \
/ \
Retail Outlets -> Consumers
Potential disruption points include:
- Feed shortages: Disruptions in feed production can impact egg production significantly.
- Transportation issues: Delays in transportation, due to weather or infrastructure problems, can lead to delays in egg delivery.
- Disease outbreaks: Avian influenza or other outbreaks can cause significant production losses and disruptions.
- Pricing fluctuations: Changes in commodity prices (e.g., feed costs) can influence the price of eggs at different stages of the supply chain.
Strategies for Addressing Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
Strategies to enhance supply chain resilience in the egg industry include:
- Diversification of feed sources: Reducing reliance on single feed suppliers to mitigate risk of shortages.
- Improved disease surveillance and prevention: Implementing robust biosecurity measures and rapid response protocols for disease outbreaks.
- Strengthening logistics and transportation networks: Investing in reliable and resilient transportation infrastructure to ensure efficient egg movement.
- Developing alternative egg production methods: Exploring and supporting innovative egg production methods that can potentially mitigate the impact of disruptions in other methods.
Alternative Protein Sources
The escalating cost of eggs, coupled with growing health concerns and environmental considerations, has sparked a surge in interest in alternative protein sources. Consumers are actively seeking diverse protein options, and this shift is impacting the global food market significantly. Beyond eggs, a range of plant-based and lab-grown proteins are vying for a larger share of the market.
This trend is not merely a fleeting fad; it reflects a fundamental change in consumer preferences and the need for sustainable and varied protein sources.
The nutritional value of alternative proteins varies greatly, and understanding these differences is crucial for informed consumer choices. While eggs offer a complete protein profile, alternative options may excel in certain aspects, like lower saturated fat content or reduced environmental impact. This comparison requires a nuanced examination of individual nutrients and their potential health implications. The impact on the egg market is undeniable.
The rise of alternative proteins poses a challenge, but also an opportunity for the egg industry to innovate and adapt. This involves exploring new market niches, developing novel egg substitutes, and highlighting the unique nutritional advantages of eggs.
Nutritional Comparison of Eggs and Alternative Proteins
A key aspect of this shift involves evaluating the nutritional value of various protein sources. Eggs are a rich source of high-quality protein, essential vitamins (like vitamin D and B12), and healthy fats. However, alternative protein sources may vary significantly in their nutritional profiles. Plant-based proteins, for example, often excel in fiber content and are lower in saturated fat, but might not contain the same balance of essential amino acids found in eggs.
Lab-grown proteins can be tailored to contain specific nutrients, but their long-term nutritional impact remains a subject of ongoing research.
Potential for Innovation in Alternative Egg Substitutes
The need for egg substitutes has accelerated the development of innovative products. These substitutes aim to mimic the functional properties of eggs, particularly in baking and cooking applications. For instance, some plant-based alternatives utilize ingredients like flaxseed meal, chia seeds, or silken tofu to mimic the binding and emulsification properties of eggs. These substitutes are often formulated with specific nutritional goals in mind, and the market is constantly evolving with new formulations and improved textures.
Egg prices are soaring to record highs, leaving many of us scrambling to find affordable alternatives. Meanwhile, Steph Curry’s performance in the recent Suns game was surprisingly quiet, a stark contrast to his usual dazzling displays, as seen in steph curry quiet in blowout loss to suns at home. This unfortunate trend of high egg prices is certainly putting a damper on breakfast plans for many families, and it’s a shame that even a star player like Steph Curry had a relatively quiet night.
It’s a crazy time for eggs, and that’s certainly not a great feeling for anyone’s budget.
Further research and development are needed to create substitutes that are as versatile and functional as eggs.
Table: Nutritional Profiles of Eggs and Common Alternative Protein Sources
| Nutrient | Egg | Soy Protein | Pea Protein | Plant-Based “Egg” Substitute |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein (g) | 6.3 | 6-8 | 5-7 | Variable, often lower |
| Fat (g) | 5 | 1-2 | 1-2 | Variable, often lower |
| Cholesterol (mg) | 186 | 0 | 0 | Variable, often lower |
| Vitamin D (mcg) | 1.5 | 0-1 | 0 | Variable, often lower |
| Vitamin B12 (mcg) | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | Variable, often lower or absent |
Note: Values are approximate and can vary depending on the specific product and preparation method.
Long-Term Price Prediction
The recent surge in egg prices has sent ripples through the food industry and consumer wallets. Understanding the potential trajectory of these prices over the coming years is crucial for both producers and consumers. Predicting the future is inherently complex, but analyzing current trends and potential factors can provide a clearer picture.
Predicting egg prices with certainty is difficult, but a careful analysis of current conditions and potential future developments suggests a multifaceted picture. The long-term price trend will likely be influenced by a combination of supply chain resilience, consumer demand shifts, and the emergence of alternative protein sources.
Factors Influencing Future Egg Prices
Several factors will influence the long-term price of eggs. These include the ongoing impact of avian influenza outbreaks, changes in consumer preferences, and the relative cost of alternative protein sources.
- Avian Influenza Outbreaks: Continued outbreaks of avian influenza pose a significant threat to egg production. The devastating impact of these outbreaks on poultry flocks necessitates a proactive approach to preventing future outbreaks. This includes biosecurity measures, vaccination programs, and monitoring of potential infection hotspots. For example, the 2022-2023 avian influenza outbreaks dramatically reduced the laying hen population, leading to a significant decrease in egg supply, which directly impacted egg prices.
- Consumer Demand Shifts: Consumer preferences for eggs are dynamic. Factors like health consciousness, dietary trends, and the increasing popularity of plant-based alternatives can all influence the demand for eggs. For example, the rise of veganism and vegetarianism has seen some consumers choose alternative protein sources, which can impact the demand for eggs.
- Alternative Protein Sources: The increasing availability and affordability of alternative protein sources like plant-based eggs and meat substitutes will likely impact the long-term demand for conventional eggs. These alternatives offer potential substitutes for eggs in many recipes, creating a more competitive market.
- Supply Chain Resilience: The resilience of the egg industry to long-term price pressures depends on the ability of producers to adapt to disruptions like avian influenza outbreaks and maintain consistent supply. Investing in sustainable farming practices, including disease prevention and efficient supply chain management, will be vital to maintaining a stable supply. For example, diversification of production methods and geographical locations of egg farms can mitigate the impact of regional outbreaks.
Long-Term Implications of the Current Price Increase
The current price increase has several long-term implications, affecting both consumers and the egg industry.
- Consumer Behavior: Consumers may adjust their purchasing habits to compensate for the higher prices, potentially shifting to cheaper alternatives or reducing their consumption of eggs.
- Industry Adaptation: The egg industry will need to adapt to the changing market landscape by exploring sustainable farming practices, implementing robust disease prevention strategies, and potentially investing in technologies to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Economic Impact: The price increase may have broader economic implications, impacting food budgets and the availability of eggs in different demographics.
Resilience of the Egg Industry, Egg prices increase to record
The resilience of the egg industry to long-term price pressures hinges on several key factors, including its ability to adapt to changing consumer preferences, improve efficiency, and mitigate risks associated with disease outbreaks.
- Industry Innovation: Continued innovation in egg production, such as improvements in feed efficiency and disease resistance, will help mitigate long-term price pressures. Investing in research and development can help reduce production costs and improve the overall sustainability of the industry.
- Supply Chain Diversification: Diversifying egg production across different regions can help reduce the impact of localized disruptions, such as disease outbreaks or extreme weather events. This diversification also helps to improve supply chain resilience.
- Consumer Education: Educating consumers about the nutritional benefits of eggs and highlighting sustainable farming practices can help maintain consumer demand.
Predicted Egg Price Trends (2024-2028)
Predicting the precise trajectory of egg prices over the next five years is inherently complex. However, considering current trends, a potential trajectory could look like this:
| Year | Estimated Egg Price (USD/dozen) |
|---|---|
| 2024 | 4.00-4.50 |
| 2025 | 4.25-4.75 |
| 2026 | 4.50-5.00 |
| 2027 | 4.75-5.25 |
| 2028 | 5.00-5.50 |
Note: This is a simplified illustration and does not account for all potential market fluctuations. The actual prices may vary based on unforeseen events and market dynamics.
Conclusive Thoughts
The recent surge in egg prices presents a multifaceted challenge, impacting everything from household budgets to industry practices. While the current crisis is significant, the resilience of the egg industry and the potential for innovation in alternative protein sources warrant further investigation. The long-term implications of this price increase remain to be seen, but this article provides a comprehensive overview of the situation, empowering readers to understand the complex forces at play.