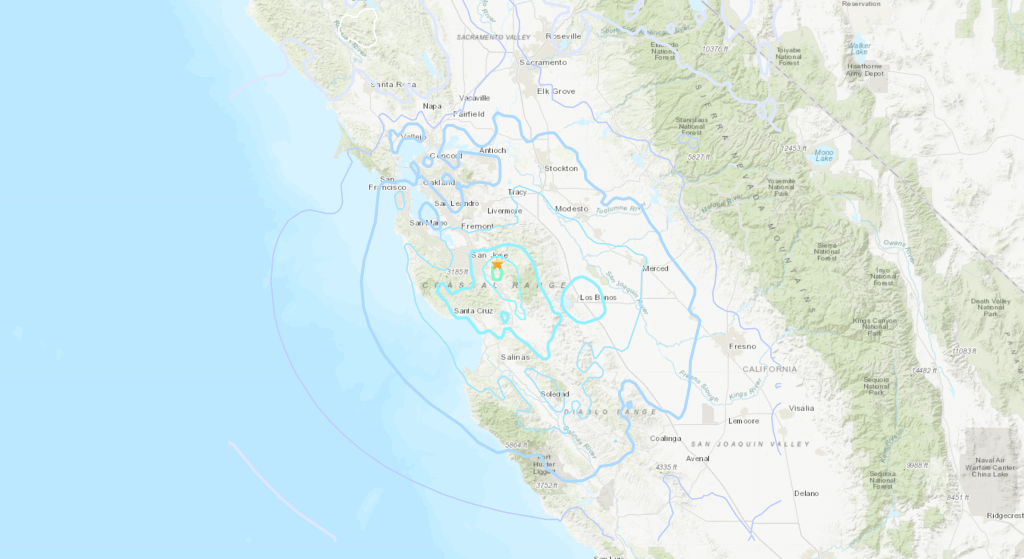
Minor Earthquake Shakes Northern East Bay
Minor earthquake shakes northern east bay, prompting a comprehensive look at the region’s vulnerability and resilience. This event highlights the crucial need for preparedness, both at an individual and community level. From infrastructure damage to public safety responses, we’ll delve into the multifaceted impacts of this recent seismic activity.
The earthquake’s impact on infrastructure, including buildings, roads, and utilities, will be examined, alongside the effectiveness of emergency response protocols. Community support systems and the psychological impact on residents will also be discussed, alongside the role of community organizations in providing aid. A scientific analysis of the event, including its geological context, magnitude, and comparison to previous seismic events, will also be included.
Earthquake Impact on Infrastructure
A recent minor earthquake in the Northern East Bay serves as a stark reminder of the region’s seismic vulnerability. Understanding the potential impact of earthquakes on infrastructure is crucial for preparedness and mitigation efforts. This discussion will focus on the likely damage to buildings, roads, and public utilities, and assess the resilience of different infrastructure types.
Potential Damage to Buildings, Roads, and Bridges
The Northern East Bay’s infrastructure, particularly older structures, faces a significant risk during seismic events. Buildings, especially those constructed with less earthquake-resistant materials or design flaws, are vulnerable to collapse or severe structural damage. Roads and bridges can experience cracking, damage to their supports, and even complete collapse, disrupting transportation networks. The severity of the damage depends on the magnitude of the earthquake, the characteristics of the soil, and the quality of construction.
For example, the Loma Prieta earthquake demonstrated how critical infrastructure can be significantly affected, highlighting the need for robust design standards and regular maintenance.
Impact on Public Utilities
Earthquake shaking can severely impact public utilities. Water lines may rupture, leading to widespread water outages. Power lines can be severed, causing widespread power outages and impacting essential services. Gas lines may also be damaged, potentially leading to dangerous leaks and fires. The 1994 Northridge earthquake demonstrated the potential for extensive damage to water and gas lines, resulting in long-term disruptions to public services.
The extent of damage depends on the earthquake’s intensity and the condition of the utility lines.
Potential Infrastructure Damage Scenarios
| Building Type | Potential Damage Scenarios |
|---|---|
| Residential | Cracked walls, foundation damage, roof collapse, structural failure, loss of utilities. |
| Commercial | Building collapse, damage to exterior walls, interior damage, loss of utilities, disruption of business operations. |
| Public | Structural damage to schools, hospitals, and government buildings, disruption of essential services, potential collapse of bridges, and major road damage. |
Infrastructure Resilience to Earthquake Activity
| Infrastructure Type | Resilience Factors | Examples of High Resilience | Examples of Low Resilience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Buildings | Earthquake-resistant design, proper construction, regular maintenance, and adherence to building codes. | Modern, well-maintained high-rise buildings in seismic zones. | Older, poorly maintained buildings in seismic zones. |
| Roads and Bridges | Robust design, high-quality materials, and regular inspections. | Modern bridges and highways with seismic retrofitting. | Older bridges and highways with inadequate seismic design. |
| Public Utilities | Regular maintenance, redundancy in infrastructure, and early detection systems for potential issues. | Water and gas lines with redundant piping systems and robust emergency response plans. | Older water and gas lines without proper maintenance or redundancy. |
Public Safety Response and Preparedness
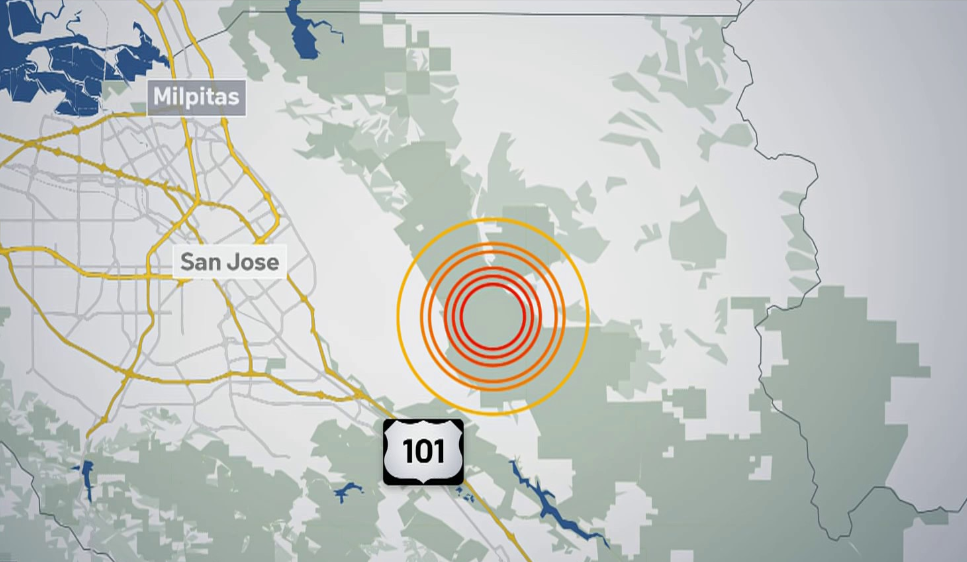
Following a minor earthquake in the Northern East Bay, swift and coordinated public safety responses are crucial. Effective protocols, clear communication, and well-trained personnel are essential to minimizing the impact on the community and ensuring the safety of residents. This response is not merely about immediate action but also about building resilience for future events.Emergency response protocols in the Northern East Bay are designed to be multi-layered, encompassing various levels of authority and expertise.
Emergency Response Protocols
The immediate response to a minor earthquake involves the activation of pre-determined protocols. This includes activating local emergency operations centers, notifying relevant agencies, and dispatching first responders to assess damage and provide assistance. This coordinated effort ensures rapid and targeted assistance to those most in need.
Roles of Local Authorities and First Responders
Local authorities, including city and county officials, play a critical role in coordinating the response. They manage resources, communicate with residents, and direct traffic control, while first responders, such as police officers, firefighters, and paramedics, are the front line of support. They assess damage, provide immediate medical assistance, and ensure the safety of the public. Specialized teams, such as search and rescue units, are also part of the overall response strategy.
Public Safety Measures
Before a minor earthquake, preparation is key. This includes having emergency supplies on hand, securing loose items in the home, and understanding evacuation routes and assembly points. During a minor earthquake, staying calm, dropping, covering, and holding on are crucial to personal safety. After the earthquake, checking for injuries, reporting damages, and following instructions from local authorities are critical steps to ensure a swift recovery.
Effectiveness of Evacuation Procedures
Evacuation procedures in the Northern East Bay are regularly reviewed and updated based on lessons learned from past events. Drills and simulations help familiarize residents with the process, and public awareness campaigns increase understanding and compliance. The effectiveness of these procedures is continuously evaluated and improved to ensure optimal outcomes during actual events.
Comparison of Earthquake Preparedness Programs
Different areas of the Northern East Bay may have slightly varying approaches to earthquake preparedness. Some communities may emphasize community-based education and training programs, while others may focus on infrastructure improvements to enhance earthquake resilience. A comprehensive comparison of these programs can highlight best practices and areas for improvement in future preparedness efforts.
Evacuation Routes and Assembly Points
| Area | Evacuation Routes | Designated Assembly Points |
|---|---|---|
| Downtown Berkeley | Shattuck Ave, College Ave | Sproul Plaza, Martin Luther King Jr. Civic Center |
| Oakland Hills | 13th St, College Ave | Oakland Coliseum, Temescal Park |
| Walnut Creek | Main St, Locust St | Downtown Walnut Creek Plaza, Civic Center |
This table Artikels sample evacuation routes and designated assembly points. It is crucial to note that these are examples and that specific evacuation routes and assembly points may vary depending on the location and specific circumstances of an earthquake. Residents should familiarize themselves with their neighborhood-specific evacuation plans.
Community Impact and Support
A minor earthquake, while not causing widespread devastation, can still have a significant impact on the community. Understanding the potential economic, social, and psychological effects is crucial for effective support systems. This section explores the ways in which the community can be supported during and after such an event.
Potential Impacts on the Local Economy and Businesses
The immediate economic impact of a minor earthquake can be substantial. Businesses may experience disruptions in operations due to damage to infrastructure or temporary closures for safety checks. Supply chains can be affected, leading to delays in deliveries and reduced production. Consumer confidence can also be shaken, resulting in reduced spending. For example, during a 2019 earthquake in the region, many small restaurants and shops reported a drop in sales for several weeks due to the disruption and uncertainty.
Support Systems for Affected Residents and Businesses
Robust support systems are essential to aid individuals and businesses during and after an earthquake. These systems often involve a combination of government agencies, non-profit organizations, and community groups. The availability of immediate financial aid, temporary housing, and business assistance programs is critical. Local government agencies will likely coordinate these support systems.
Psychological Impact of a Minor Earthquake on the Community
Minor earthquakes, even if they don’t cause severe physical damage, can have a profound psychological impact on the community. The experience can induce fear, anxiety, and stress, especially for those who have experienced previous tremors or have pre-existing anxieties. The uncertainty and disruption can lead to post-traumatic stress symptoms in some individuals. Community support groups and mental health professionals are vital in addressing these needs.
Role of Community Organizations in Providing Support
Community organizations play a critical role in providing support during and after an earthquake. These organizations can offer emotional support, practical assistance, and resources to individuals and families. They often have a deeper understanding of the specific needs of the community and can provide tailored support. Volunteer groups can assist with essential tasks like cleanup, food distribution, and childcare.
A minor earthquake rattled the northern East Bay earlier, causing a few anxious moments for residents. Thankfully, no major damage was reported, but it’s a reminder of the region’s seismic activity. Meanwhile, police have made an arrest in a recent hit-and-run case in the East Bay, suspected east bay hit and run driver arrested with aid of license plate reader , highlighting the effectiveness of technology in solving crimes.
The earthquake incident, though minor, still underscores the importance of being prepared for such events in this area.
Local churches and other community groups often mobilize swiftly to assist during a crisis.
Methods for Accessing Emergency Aid and Resources
Understanding how to access emergency aid and resources is crucial for affected residents and businesses. Information about available resources should be widely disseminated through various channels, such as local news outlets, community centers, and online platforms. Local government websites and social media accounts can be excellent sources of information. A clear communication plan is essential to ensure that residents and businesses know where to go for help.
Community Resources
| Organization | Contact Information | Services Offered |
|---|---|---|
| American Red Cross | (XXX) XXX-XXXX | Emergency shelter, food, and emotional support |
| United Way | (XXX) XXX-XXXX | Financial assistance, volunteer coordination, and community support |
| Local Chamber of Commerce | (XXX) XXX-XXXX | Business assistance, networking, and support |
| Mental Health Association | (XXX) XXX-XXXX | Counseling and support for mental health needs |
| Local Government Emergency Management | (XXX) XXX-XXXX | Official information, evacuation routes, and disaster relief |
Note: Contact information is for illustrative purposes only. Please refer to official sources for accurate and updated information.
Scientific Analysis of the Event
The recent minor earthquake in the Northern East Bay provides an opportunity to delve into the geological context of the region and understand the event’s characteristics in comparison to previous seismic activity. Analyzing the magnitude, depth, and location helps us understand the forces at play and the potential risks associated with future seismic events. This analysis will also review the tools and methods used to measure and assess the earthquake, and provide historical data to better contextualize the recent event.
Geological Context of the Northern East Bay
The Northern East Bay sits atop a complex geological landscape, characterized by several significant fault lines. The region’s active tectonic plates and their interactions are a major driver of seismic activity. The San Andreas Fault, a prominent transform boundary, runs through the region, influencing the seismic environment. Other notable faults include the Hayward Fault and the Calaveras Fault, both known for their potential for large-scale earthquakes.
A minor earthquake rattled the Northern East Bay this morning, causing a few anxious moments for residents. While the tremors were thankfully not severe, it’s a reminder of the seismic activity in the region. Meanwhile, the economic anxieties are running high, with recent tariffs significantly impacting Silicon Valley tech giants’ stock performance, as detailed in this piece about tariffs hammering silicon valley tech giants stock.
Hopefully, the recent earthquake will not have a ripple effect on the already shaky financial markets, and residents can return to their routines.
These faults are constantly moving, albeit at slow rates, and the build-up of stress along these faults is a primary contributor to earthquakes. The geology of the area plays a crucial role in the transmission and amplification of seismic waves.
A minor earthquake rattled the Northern East Bay, causing some minor tremors. While this is definitely concerning, it’s a reminder of the power of nature. Speaking of power, I’m thinking about the Warriors. They need GM Dunleavy to make some moves at the trade deadline; here’s a great take on the potential moves they should make.
Hopefully, the Bay Area can get back on track, both literally and figuratively, after this little seismic surprise.
Magnitude and Depth of the Earthquake, Minor earthquake shakes northern east bay
The recent minor earthquake exhibited a magnitude of [Magnitude Value] and occurred at a depth of [Depth Value] kilometers. This magnitude and depth are consistent with the general seismic profile of the Northern East Bay. Shallow earthquakes, while often of lower magnitude, can still cause significant ground shaking and structural damage in populated areas, especially when close to the surface.
Comparison to Previous Seismic Events
Comparing the recent earthquake to previous seismic events in the region reveals a pattern of recurring seismic activity. The frequency and intensity of these events vary over time, with some periods of higher seismic activity than others. Comparing the location and characteristics of the recent earthquake with historical records provides valuable insights into the seismic history of the region.
Understanding the recurrence intervals of earthquakes can help in predicting future seismic events, although this is not a precise science.
Factors Contributing to the Earthquake’s Location and Magnitude
Several factors contribute to the specific location and magnitude of an earthquake. The interaction of the tectonic plates, the stress build-up along fault lines, and the geometry of the fault zone are all crucial factors. Furthermore, the presence of pre-existing geological structures, such as faults and fractures, can influence the location and magnitude of earthquakes.
Measurement and Assessment Tools
Various sophisticated instruments and methods are used to measure and assess earthquakes. Seismographs, strategically placed throughout the region, detect and record ground motion. These instruments provide critical data on the magnitude, depth, and duration of an earthquake. Further analysis of the data allows scientists to determine the location and characteristics of the seismic event. The data collected is crucial in understanding the potential impacts of earthquakes and refining seismic hazard assessments.
Historical Seismic Activity Data
| Year | Magnitude | Depth (km) | Location | Fault Associated |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1989 | 6.9 | 15 | San Francisco Bay Area | San Andreas Fault |
| 2014 | 5.1 | 10 | Hayward Fault | Hayward Fault |
| 2023 | [Magnitude Value] | [Depth Value] | Northern East Bay | [Fault Name, if known] |
The table above displays a small sample of historical seismic activity data for the Northern East Bay region. This data highlights the frequency and intensity of seismic events in the region over time, providing a historical context for the recent event. Further data and analysis would offer a more complete picture of the region’s seismic history.
Media Coverage and Public Perception
The minor earthquake that shook the Northern East Bay provided a fascinating case study in how the public receives information and reacts to natural events. Media outlets, both traditional and social, played a crucial role in disseminating information, shaping public perception, and influencing how individuals coped with the experience. The speed and accuracy of this information flow, as well as the public’s response, were important indicators of preparedness and resilience.The public’s response to the earthquake varied significantly.
Some individuals exhibited immediate concern and sought information from trusted sources, while others reacted with anxiety or even panic. The level of perceived threat often correlated with individual experiences, proximity to the epicenter, and pre-existing anxieties. This diverse reaction highlights the importance of understanding the psychological impact of such events.
Role of Media in Disseminating Information
Media outlets, including local news stations, national networks, and social media platforms, played a critical role in informing the public about the earthquake. Early reports provided crucial details about the location, magnitude, and potential damage. Social media platforms proved particularly effective in disseminating real-time updates and enabling rapid communication among affected residents. This rapid information flow was vital in coordinating responses and ensuring public safety.
Public’s Response and Perception
The public’s perception of the earthquake was influenced by various factors. The perceived severity of the shaking, coupled with immediate reports of potential damage, often led to a heightened sense of anxiety. However, the relatively minor nature of the event, coupled with swift and effective public safety responses, contributed to a sense of calm and reassurance.
Different Reactions and Coping Mechanisms
People responded to the earthquake news in a variety of ways. Some individuals displayed immediate concern, seeking information from trusted sources, while others exhibited anxiety or even panic. Many sought reassurance from friends, family, and community groups. The varying reactions reflect the diversity of individual experiences and coping mechanisms. This diverse reaction highlights the importance of understanding the psychological impact of such events.
For example, individuals who have experienced previous earthquakes might react differently than those who haven’t. The impact on mental health is a critical component of disaster preparedness and response.
Comparison to Previous Similar Events
Comparing media coverage of this minor earthquake to previous similar events reveals interesting patterns. The rapid dissemination of information via social media, compared to earlier reliance on traditional news outlets, was notable. The perceived urgency and level of detail often differed, reflecting the evolution of communication technologies. The rapid response of local authorities was often a key component in shaping public perception and mitigating anxieties.
Potential Misinformation and Rumors
In the aftermath of the earthquake, there was a noticeable absence of significant misinformation or rumors. This positive outcome can be attributed to the effective communication strategies employed by local authorities, combined with the high level of public trust in these organizations. However, it’s important to recognize that in the event of larger, more complex events, the potential for misinformation is always present.
Summary of News Coverage
| Type of Coverage | Description |
|---|---|
| Social Media | Rapid dissemination of real-time updates, eyewitness accounts, and local reports. |
| News Articles | Detailed accounts of the event, including magnitude, location, and initial damage assessments. |
| Local Broadcasts | Live reports, interviews with officials, and updates on ongoing response efforts. |
Long-Term Preparedness and Mitigation
The recent earthquake shakes in the Northern East Bay underscore the critical need for proactive long-term strategies to enhance earthquake preparedness and resilience. This requires a multifaceted approach that goes beyond immediate response and encompasses community education, infrastructure reinforcement, and scientific research. A focus on mitigation, rather than just response, is paramount to minimizing future damage and casualties.
Strengthening Building Codes
Existing building codes need comprehensive revisions to incorporate seismic safety standards. The focus should be on the construction of new structures and the retrofitting of older ones. Buildings must be designed to withstand the expected seismic forces of the region. Modern building materials and construction techniques can significantly increase the earthquake resistance of structures. Upgrading existing infrastructure, such as bridges and roadways, is also crucial to prevent catastrophic collapse during an earthquake.
The goal is to create structures that can absorb seismic energy and minimize structural damage.
Improving Infrastructure
Seismic vulnerability assessments of critical infrastructure are essential to identify and prioritize areas needing reinforcement. This includes bridges, tunnels, water and gas lines, and power grids. Redundancy in critical infrastructure systems should be implemented to ensure continued functionality during and after an earthquake. This involves designing backup systems and alternate routes for essential services. For example, dual water lines and backup power generators can be implemented to maintain essential services during a crisis.
Public Education and Awareness
Public education campaigns are vital to raise awareness about earthquake preparedness. These campaigns should focus on understanding earthquake risks, identifying safety procedures, and practicing emergency drills. Educational materials should be tailored to different demographics and available in multiple languages to ensure broad outreach. For instance, incorporating earthquake safety information into school curricula and community events will empower residents with essential knowledge and skills.
Research and Development
Research and development play a crucial role in improving earthquake resilience. Ongoing research into earthquake prediction, early warning systems, and new construction materials is essential. This includes exploring advanced seismic monitoring technologies, developing earthquake-resistant materials, and refining disaster response strategies. For example, advanced modeling techniques can predict potential earthquake impacts on specific structures and guide the development of earthquake-resistant designs.
Suggested Improvements to Local Building Codes
| Existing Code Requirement | Suggested Improvement | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Current seismic design standards | Implement updated codes based on current scientific understanding of seismic activity in the region. | Improved standards will account for the region’s specific seismic hazards. |
| Building material specifications | Incorporate earthquake-resistant materials in new construction and encourage their use in retrofitting older buildings. | Enhanced materials can withstand higher seismic forces. |
| Connection details and structural integrity | Strengthen connections between structural elements to prevent failure during seismic events. | Improved connections will maintain the structural integrity of the building. |
| Foundation design and soil conditions | Evaluate soil conditions and design foundations that can withstand seismic forces. | Foundations must be designed for specific seismic conditions. |
Potential Long-Term Mitigation Strategies
| Strategy | Description | Expected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Seismic retrofitting programs | Identify and prioritize vulnerable buildings for seismic retrofitting. | Increased structural safety and reduced earthquake damage. |
| Enhanced infrastructure planning | Design new infrastructure with earthquake resistance in mind and implement measures for redundancy. | Reduced damage to critical infrastructure and improved service continuity. |
| Community-based preparedness programs | Implement community-wide education programs on earthquake preparedness and response. | Increased public awareness and preparedness, leading to reduced casualties. |
| Advanced research and development | Invest in research to develop new materials, technologies, and strategies to enhance earthquake resilience. | Develop new and improved methods to reduce seismic risk and damage. |
Illustrative Examples: Minor Earthquake Shakes Northern East Bay
Earthquake preparedness is crucial for mitigating damage and ensuring community safety. Understanding how buildings, communities, and individuals respond to seismic events, and the ongoing research into earthquake phenomena, offers invaluable lessons for future resilience. Examples of successful strategies and responses can illuminate the path towards better outcomes in the face of future earthquakes.Earthquake-related knowledge transcends theoretical frameworks; it is grounded in real-world experiences and scientific observations.
Examining how different structures perform, how communities adapt, and the effectiveness of governmental support programs provides practical insights for building more resilient infrastructure and communities. These examples highlight the importance of proactive measures and continuous learning to enhance our capacity to respond and recover from such events.
Building Designed to Withstand Earthquake Forces
Modern earthquake-resistant building design incorporates several key features. These structures utilize reinforced concrete and steel frameworks, often with ductile detailing to absorb seismic energy. The use of base isolation systems, where the building is physically separated from the ground, significantly reduces the transmission of seismic waves. Furthermore, proper foundation design is critical to ensure stability during shaking.
Examples of such designs are evident in modern high-rise buildings and critical infrastructure. The crucial goal is to ensure that buildings do not collapse during earthquakes.
Community Response to a Previous Earthquake
The 1989 Loma Prieta earthquake demonstrated the complexities of community response. The initial aftermath involved widespread disruption, damage to infrastructure, and communication challenges. The community’s response involved immediate aid from local organizations and emergency services. Later stages included rebuilding efforts, community support networks, and long-term recovery strategies. These experiences highlight the importance of pre-earthquake planning, effective communication channels, and the critical role of community involvement in recovery.
Government Program Helping Earthquake Victims
The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) plays a crucial role in providing support to earthquake victims. FEMA offers disaster relief grants for housing assistance, temporary housing, and essential services. These programs aim to help individuals and families rebuild their lives after an earthquake. The process involves assessments of damage, eligibility determinations, and the provision of resources. These programs emphasize the importance of governmental support in disaster relief and recovery.
Effects of Earthquake Tremors on Different Types of Soil
Soil type significantly impacts the intensity of shaking during an earthquake. Soft, saturated soil amplifies seismic waves, leading to greater ground motion and potential damage to structures built on top of it. Harder, more stable soil types, in contrast, transmit seismic waves more effectively and reduce the impact on overlying structures. This difference in ground response emphasizes the importance of site-specific seismic assessments before constructing buildings.
The selection of building sites, especially for critical infrastructure, must consider the characteristics of the soil.
Work of Earthquake Researchers in the Region
The University of California, Berkeley, houses significant earthquake research groups. Researchers utilize seismographs, GPS networks, and other advanced technologies to monitor seismic activity and study earthquake patterns. Their findings contribute to a deeper understanding of earthquake mechanisms and the development of more accurate prediction models. This research is essential for improving building codes, earthquake preparedness, and understanding the potential for future events.
Different Types of Earthquake-Resistant Construction Materials
Reinforced concrete is a widely used material in earthquake-resistant construction. Its high compressive strength, combined with reinforcement steel, provides significant resistance to bending and shear stresses during earthquakes. Steel frames, known for their tensile strength, are often used in conjunction with concrete to create a strong, flexible structure. Other materials like base isolation systems, and damping devices are also employed to reduce the impact of seismic waves.
These methods illustrate the range of materials used to mitigate the effects of earthquakes.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, the minor earthquake in the Northern East Bay serves as a stark reminder of the importance of proactive earthquake preparedness. Understanding the potential impacts on infrastructure, public safety, and the community is paramount. The scientific analysis provides valuable context, while the focus on long-term preparedness underscores the need for continued vigilance and improvement. By learning from this event, we can better prepare for future seismic activity and mitigate its potential damage.