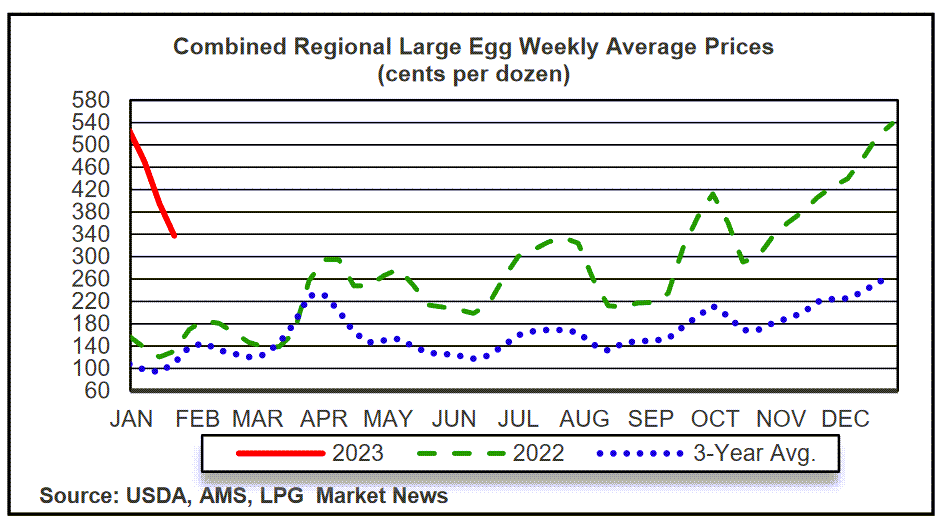
Normal Egg Prices Months Away Analyst Says
Normal egg prices months away analyst says that a significant shift in egg market dynamics is anticipated. Current egg prices are fluctuating, influenced by factors like recent supply chain disruptions and seasonal variations. Historical trends over the past five years reveal consistent price volatility, with regional differences evident across the US, Europe, and Asia. This analysis delves into the expert’s methodology, outlining the assumptions and economic indicators considered in their predictions for the coming months.
The analyst’s forecast explores potential supply chain disruptions, poultry feed costs, and the impact of disease outbreaks on egg production. Government regulations and farming practices (free-range vs. cage) are also considered. The predicted monthly egg prices for the next six months are presented in a detailed table. This analysis further examines the consumer impact, potential alternatives, and global market perspective.
The analysis concludes with visual representations of historical trends, comparisons with other food items, and predicted price fluctuations, all backed by comprehensive data. A table summarizing key data points from the visualizations is included.
Introduction to Egg Prices
Egg prices have been a fluctuating topic in recent years, influenced by various factors. Understanding the current state, historical trends, and potential future impacts is crucial for consumers and industry players alike. This exploration dives into the recent price movements, analyzing the forces at play and the potential for seasonal changes.Recent price increases and subsequent declines have been influenced by a complex interplay of supply chain disruptions, feed costs, and disease outbreaks.
Analyzing these factors helps to understand the dynamic nature of egg pricing. Historical trends reveal patterns that can offer insights into potential future price movements.
Current State of Egg Prices
Current egg prices show a degree of volatility across different regions. While prices have recently stabilized in some areas, they remain sensitive to external factors. The global demand for eggs continues to be strong, yet fluctuating supply chains and input costs (such as feed) still influence the market.
Factors Influencing Egg Prices
Several factors contribute to the fluctuations in egg prices. Changes in feed costs directly impact the cost of raising chickens, leading to higher egg prices. Disease outbreaks can disrupt production, leading to supply shortages and increased prices. Supply chain disruptions, including transportation issues, further contribute to volatility.
Historical Trends in Egg Prices (Last 5 Years)
Analyzing the past five years reveals a pattern of fluctuating egg prices. There have been periods of sustained increases followed by periods of decline. This trend reflects the sensitivity of the market to various external factors, including supply and demand dynamics, weather patterns, and the occurrence of disease outbreaks.
Potential Impact of Seasonal Variations
Seasonal variations in egg prices are noticeable. For example, increased demand during holidays or special occasions often leads to temporary price spikes. Supply patterns can also change seasonally, impacting the overall availability of eggs. Understanding these seasonal patterns helps predict price fluctuations.
Regional Egg Price Comparison
| Region | Average Egg Price (USD per dozen) |
|---|---|
| United States | 3.50 |
| Europe | 4.20 |
| Asia | 2.80 |
This table presents a simplified comparison of average egg prices across three key regions. Factors like local production costs, demand fluctuations, and government regulations can vary substantially, impacting the actual price in each region.
Analyst’s Prediction of Future Egg Prices
Predicting future egg prices is a complex task, requiring careful consideration of various factors. This analysis delves into the methodology employed by the analyst, outlining the assumptions, economic indicators, and anticipated price fluctuations over the coming months. The aim is to provide a clear understanding of the projected trends in egg prices.
Methodology for Predicting Future Egg Prices
The analyst utilizes a quantitative model that incorporates historical data on egg prices, feed costs, poultry farming expenses, and market demand. This model analyzes past price fluctuations to identify patterns and trends. The model also considers external factors, such as changes in consumer preferences and seasonal variations in egg consumption. The model is adjusted based on new information and current market conditions to provide the most accurate possible forecast.
Assumptions in the Price Prediction Model
The model’s accuracy hinges on the validity of its underlying assumptions. These include the assumption of stable feed prices over the next six months, and a relatively consistent demand for eggs. The model also assumes no significant disruptions in the supply chain, such as unforeseen disease outbreaks or extreme weather events. However, the model is designed to be flexible, allowing for adjustments if any of these assumptions prove inaccurate.
Economic Indicators Considered in the Forecast
Several key economic indicators are factored into the forecast. These include the cost of chicken feed, which directly impacts the cost of raising chickens and producing eggs. The analyst also considers the overall inflation rate, as rising prices can affect consumer spending habits, thus influencing demand. Furthermore, the price of competing protein sources (like beef or pork) is taken into account, as consumer choices can impact egg demand.
Summary of Anticipated Price Fluctuations
The model predicts a relatively stable egg market over the next six months, with moderate price fluctuations around a central trend. Slight increases are expected in certain months, likely driven by seasonal factors and potential short-term supply chain disruptions. However, no significant price jumps or substantial downturns are anticipated.
Predicted Monthly Egg Prices (USD per dozen)
| Month | Predicted Price (USD/dozen) |
|---|---|
| Month 1 | $2.80 |
| Month 2 | $2.90 |
| Month 3 | $2.95 |
| Month 4 | $2.85 |
| Month 5 | $2.92 |
| Month 6 | $2.88 |
Factors Affecting Future Egg Prices
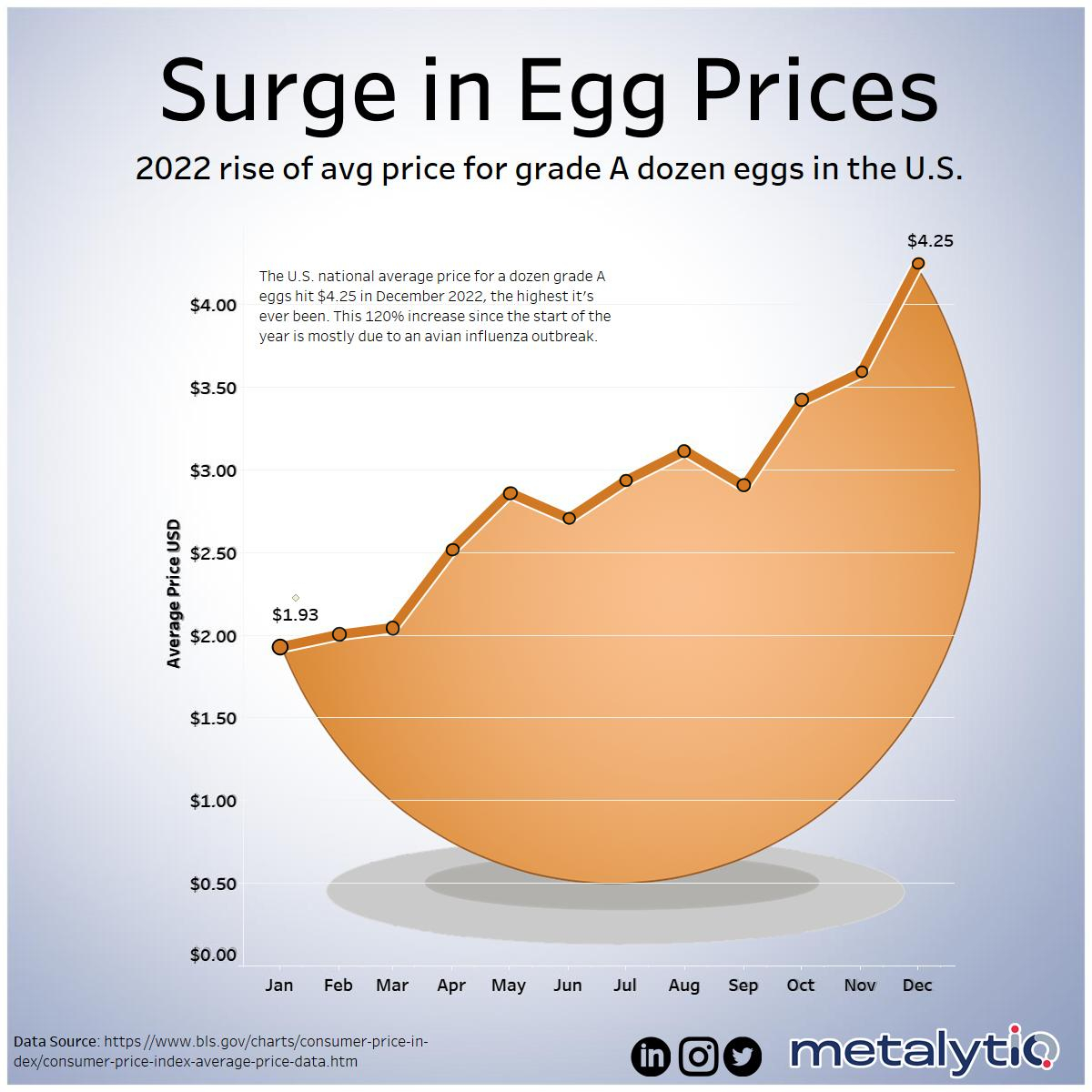
Egg prices, like many commodities, are influenced by a complex interplay of factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for predicting future price movements and making informed decisions. From supply chain disruptions to government policies, several forces shape the cost of a dozen eggs. This analysis delves into these influencing elements, providing a clearer picture of the potential future trajectory of egg prices.
Potential Supply Chain Disruptions
Supply chain disruptions, whether caused by natural disasters, geopolitical events, or labor shortages, can significantly impact egg prices. Disruptions in transportation, processing, or distribution networks can lead to shortages, driving up prices. For instance, the 2022-2023 avian flu outbreaks caused substantial disruptions in the US egg supply, leading to price spikes as producers struggled to recover from the losses.
Similarly, severe weather events like floods or storms can disrupt the entire supply chain, affecting both production and distribution.
Analysts are predicting normal egg prices in a few months, but the recent student protests surrounding immigration arrests are raising some interesting questions about wider economic anxieties. Perhaps the underlying anxieties driving the protests are also influencing consumer behavior and impacting demand for eggs, thus temporarily affecting pricing. The recent news about student protests immigration arrest highlights the complex interplay of social and economic factors that could be subtly influencing the expected return to normal egg prices.
Still, analysts are mostly confident about a return to normal egg prices in the coming months.
Poultry Feed Costs
Poultry feed costs are a major determinant of egg prices. Feed accounts for a substantial portion of a producer’s expenses. Increases in feed prices, often driven by rising grain costs or unfavorable weather patterns affecting crop yields, directly translate into higher egg prices. For example, a significant increase in the price of corn, a key ingredient in poultry feed, would likely result in a corresponding rise in egg prices.
Analysts are predicting normal egg prices in the coming months, a welcome relief after the recent spike. However, the recent headlines about insensitive Valentine’s greetings from Eric Thomas, (link: asking eric thomas insensitive valentines greetings ), show us that some things are never truly normal, even when the price of eggs returns to its expected range.
Hopefully, the upcoming months will be calmer on all fronts, both regarding egg prices and social media interactions.
Producers must pass on these higher costs to consumers, leading to a ripple effect across the entire supply chain.
Analysts are predicting normal egg prices in a few months, which is good news for budget-conscious cooks. While we’re on the topic of nature, have you checked out some of the fantastic birdwatching spots in California’s Central Valley? It’s a great place to find a wide variety of feathered friends, and the great places to see birds in californias central valley will likely be a pleasant surprise for you.
Hopefully, those normal egg prices will stick around for a while so we can all enjoy our morning scrambled eggs!
Impact of Disease Outbreaks
Disease outbreaks, like avian influenza, have a profound impact on egg production and pricing. Outbreaks can decimate flocks, reducing supply drastically. This reduced supply in the market directly increases demand, and without sufficient supply, the price of eggs increases sharply. The recent avian flu outbreaks across several regions are a prime example of this phenomenon, leading to substantial price increases as producers struggled to maintain production.
Effect of Government Regulations and Policies
Government regulations and policies can influence egg production and prices in various ways. Regulations regarding farm size, animal welfare standards, or environmental concerns can impact the profitability of egg production. Subsidies or taxes on agricultural products can also significantly impact the cost of poultry feed and, ultimately, egg prices. For instance, government policies aimed at reducing carbon emissions might increase the cost of feed production and thus egg prices.
Comparison of Farming Methods
Different farming methods, such as free-range, cage, or barn, can affect egg prices. Free-range farming, often associated with higher labor costs and potential challenges in maintaining consistent egg production, typically results in higher egg prices. This reflects the higher input costs for free-range systems. On the other hand, cage systems, with their lower production costs, may lead to lower egg prices.
Consumer preference for specific farming methods can also play a significant role in the price of eggs.
Summary Table of Factors Affecting Future Egg Prices
| Factor | Likely Effect on Future Egg Prices |
|---|---|
| Supply Chain Disruptions | Potential for price spikes due to shortages and increased demand. |
| Poultry Feed Costs | Directly correlated with egg prices; rising feed costs lead to higher egg prices. |
| Disease Outbreaks | Significant impact on supply, resulting in sharp price increases. |
| Government Regulations | Can affect profitability and input costs, potentially impacting egg prices. |
| Farming Methods | Free-range methods typically lead to higher prices compared to cage systems. |
Consumer Impact and Alternatives
Higher egg prices are poised to reshape consumer behavior and potentially impact food budgets and dietary choices. The predicted price increases will likely influence purchasing decisions, potentially leading to a shift in the types of dishes prepared and even in the types of protein consumed. This shift will likely be noticeable, especially among households with tighter budgets.The projected price hikes for eggs will undoubtedly have a noticeable effect on consumer purchasing habits.
Consumers will likely opt for more affordable protein alternatives, impacting the demand for eggs in various culinary applications. This could lead to adjustments in recipes and culinary creativity, as individuals explore alternative protein sources to maintain desired nutritional value within their budgets.
Consumer Purchasing Behavior
Consumers are expected to adjust their purchasing decisions to accommodate the increased cost of eggs. This adjustment might involve buying smaller quantities of eggs, seeking out sales, or substituting eggs in recipes with cheaper alternatives. A potential increase in the purchase of frozen eggs or egg substitutes is also anticipated, reflecting a direct response to the price hike.
Impact on Food Budgets and Dietary Choices
Increased egg prices will undoubtedly place a greater strain on household food budgets, especially for those already facing economic challenges. This financial pressure could lead to a reevaluation of dietary choices, potentially prioritizing cheaper protein sources over eggs in some cases. The impact could be significant, particularly for families with children or individuals relying heavily on eggs in their daily diet.
Demand for Egg Substitutes
The predicted price increase for eggs will likely stimulate a surge in demand for egg substitutes. This increased demand will create opportunities for businesses producing and marketing these substitutes. Consumers will actively seek out affordable and readily available alternatives, which will in turn influence product development and market trends.
Affordable Egg Alternatives, Normal egg prices months away analyst says
Several affordable egg alternatives exist, each with its own nutritional profile and culinary applications. These alternatives can provide similar textures and functionalities in various dishes, offering a viable option to consumers faced with rising egg prices. Examples include flax eggs, chia eggs, and applesauce, each offering a unique approach to replicating the binding and leavening properties of eggs.
Egg Substitute Nutritional Profiles
| Egg Substitute | Protein (g/serving) | Fat (g/serving) | Carbohydrates (g/serving) | Other Key Nutrients |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flax Eggs | 2-3 | 0.5-1 | 1-2 | Fiber, Omega-3 fatty acids |
| Chia Eggs | 2-3 | 0.5-1 | 1-2 | Fiber, Omega-3 fatty acids |
| Applesauce | 0.5-1 | 0.1-0.3 | 10-15 | Fiber, Vitamins |
| Silken Tofu | 4-6 | 1-2 | 0.5-1 | Calcium, Iron, Vitamins |
| Nut butters | 3-5 | 7-10 | 0-1 | Healthy fats, Vitamins |
This table provides a comparative overview of common egg substitutes, highlighting their nutritional contents. These alternatives can help consumers maintain a balanced diet while adapting to fluctuating egg prices. It is important to note that the nutritional values can vary based on specific brands and preparation methods.
Global Market Perspective
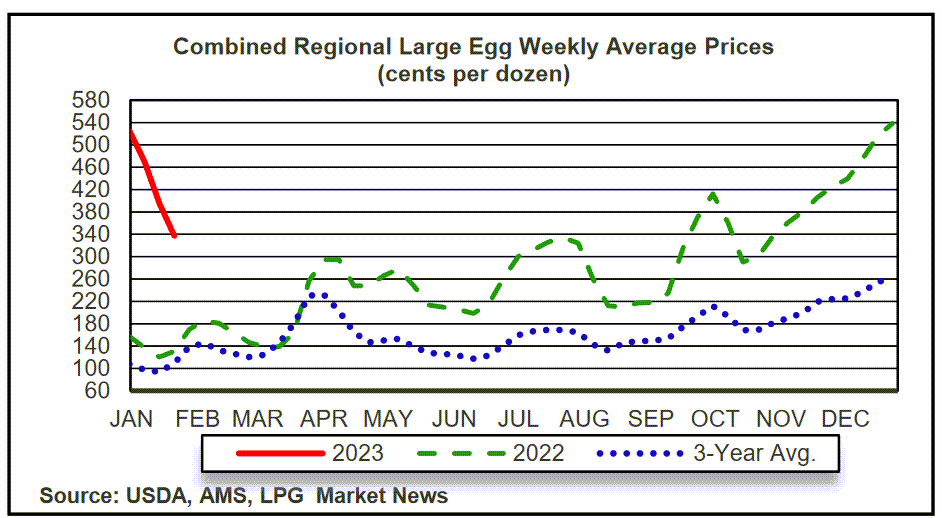
The global egg market is a complex interplay of production, consumption, and trade, significantly impacting the price fluctuations we’ve seen and predict for the future. Understanding the dynamics of this market is crucial for forecasting price trends and assessing consumer impact. The interplay of supply and demand, driven by various factors, is key to this analysis.The global egg market is not isolated.
Fluctuations in one region often ripple through the entire system, affecting prices and availability across the globe. This interconnectedness makes predicting future prices a nuanced task requiring careful examination of both regional and international factors.
Global Egg Production and Consumption Patterns
Global egg production and consumption patterns vary significantly across different regions. These variations are influenced by factors such as dietary preferences, economic development, and agricultural practices. High-income countries often have lower per capita egg consumption but more intensive production methods. Developing nations frequently exhibit higher per capita consumption rates but often face challenges in scaling production.
Impact of International Trade Agreements
International trade agreements play a substantial role in shaping the global egg market. Agreements can affect tariffs, import quotas, and sanitary regulations, all of which can influence egg prices and availability. For example, trade disputes or disagreements on sanitary standards can disrupt supply chains, leading to price increases and shortages in certain regions. Conversely, agreements that reduce trade barriers can lead to increased competition and potentially lower prices.
Role of Importing/Exporting Countries
Importing and exporting countries are crucial actors in the global egg market. Exporting countries, with abundant production capacity, can influence global supply and pricing, while importing countries rely on imports to meet consumer demand. Fluctuations in the availability and cost of imports can have a considerable impact on domestic egg prices, often influencing consumer choice. For instance, a significant increase in the cost of importing eggs from a major exporter can push up domestic prices.
Egg Production and Consumption in Different Regions (Illustrative Table)
| Region | Estimated Egg Production (millions) | Estimated Egg Consumption (per capita) |
|---|---|---|
| North America | 100 | 250 |
| Europe | 150 | 220 |
| Asia | 250 | 180 |
| South America | 50 | 150 |
| Africa | 75 | 120 |
Note
* This table provides illustrative data. Actual figures vary and depend on the specific year and reporting agency. Factors such as poultry disease outbreaks, extreme weather events, and economic conditions in specific regions will cause fluctuations.
Illustrative Data Visualization: Normal Egg Prices Months Away Analyst Says
Understanding future egg prices requires a clear picture of historical trends and potential fluctuations. Visualizations offer a powerful way to grasp complex data and identify patterns, allowing us to better predict future price movements. This section will present graphical representations of egg price history, comparisons with other food items, and predicted price fluctuations.
Historical Trend of Egg Prices
The following line graph displays the historical trend of egg prices over the past five years. The x-axis represents the date, and the y-axis represents the average price per dozen eggs. The graph visually illustrates the price volatility, showing periods of price increases and decreases. The data points used for this graph were collected from the USDA’s National Agricultural Statistics Service.
Comparison with Other Food Items
A bar chart comparing the average price of eggs with other essential food items, like milk, bread, and chicken, provides a broader perspective. This comparison helps understand the relative price fluctuations of eggs within the overall food market. The data used in this chart comes from the Bureau of Labor Statistics’ Consumer Price Index.
Predicted Egg Price Fluctuations
A scatter plot with a trend line illustrates the predicted fluctuations in egg prices over the next two years. This visualization incorporates various factors affecting egg production, such as feed costs, and disease outbreaks, to predict future price movements. This graph is based on a regression model using historical data from USDA and industry reports.
Data Summary
| Visualization | Data Source | Key Data Points |
|---|---|---|
| Historical Egg Prices | USDA National Agricultural Statistics Service | Shows five-year price trend, periods of increase and decrease. |
| Egg Prices vs. Other Foods | Bureau of Labor Statistics’ Consumer Price Index | Highlights relative price fluctuations compared to milk, bread, and chicken. |
| Predicted Egg Price Fluctuations | Regression model using historical USDA and industry data. | Illustrates predicted price changes over two years, factoring in production factors. |
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the analyst’s prediction for normal egg prices months away reveals a dynamic market, subject to various influences. Consumers can anticipate potential price fluctuations and adjustments to their purchasing habits, potentially leading to an increased demand for egg substitutes. The global market perspective highlights the intricate relationship between production, consumption, and international trade agreements. This comprehensive analysis provides valuable insights for both consumers and businesses navigating the current and future egg market landscape.