Enabling and Exiting Fastboot Mode Guide
Enabling and exiting fastboot mode guide provides a comprehensive walkthrough for navigating this crucial process. Understanding how to effectively use fastboot mode is essential for various device maintenance and troubleshooting tasks. This guide will walk you through the entire process, from initial setup to safe shutdown. We’ll cover prerequisites, step-by-step instructions, troubleshooting, and even advanced techniques. It’s a must-read for anyone working with devices that support fastboot.
This guide dives into the world of fastboot mode, a powerful tool for device optimization and repair. It’s like a secret key to your device’s inner workings, enabling you to perform actions that might not be possible through regular operating system interfaces. We’ll explore the various scenarios where fastboot mode is beneficial, providing a detailed breakdown of how it can be used for specific purposes.
We’ll also examine the potential pitfalls and offer solutions for common troubleshooting issues.
Introduction to Fastboot Mode
Fastboot mode is a special boot mode for Android devices, offering low-level access to the system. It’s primarily designed for advanced users and technicians to perform specialized tasks, like flashing custom ROMs, recovering from boot loops, or updating the system software. This mode bypasses the typical Android boot sequence, granting access to the device’s internal components in a controlled environment.Fastboot mode’s primary advantage is its ability to provide direct control over the device’s firmware.
This is invaluable for troubleshooting, recovery, and system modifications that are not possible through standard Android methods. It is a powerful tool, but its use requires caution, as incorrect actions can lead to data loss or permanent system damage.
Purpose and Benefits of Fastboot Mode
Fastboot mode is crucial for tasks that require a more direct interface with the device’s low-level components. This access is vital for flashing custom ROMs or kernels, which significantly alter the device’s operating system. Furthermore, fastboot mode is indispensable for performing critical repairs, such as recovering from a boot loop or restoring a device to a known working state.
Its direct access to the firmware allows for efficient and precise modifications, enabling users to optimize the device’s performance or install specific features not available through standard updates.
Figuring out how to enable and exit fastboot mode can be tricky, but thankfully there are helpful guides online. While I was researching this, I came across some interesting news about the Grammys wildfire relief changes, grammys wildfire relief changes. Hopefully, these changes will help those affected by the fires. Regardless, understanding how to enable and exit fastboot mode is a valuable skill for anyone working with mobile devices.
Typical Scenarios for Fastboot Mode Usage
Fastboot mode is a vital tool in various situations, allowing users to manipulate their device’s firmware beyond standard Android capabilities. Here’s a breakdown of common scenarios where fastboot mode is commonly used.
| Situation | Fastboot Usefulness | Alternative Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Flashing a custom ROM | Fastboot allows direct flashing of custom ROMs, which can provide enhanced performance, features, or aesthetics not found in stock ROMs. | Attempting a standard ROM update, which might not accommodate the desired modifications. |
| Recovering from a boot loop | Fastboot can often fix boot loops by restoring the system to a known good state. | Performing a factory reset through the standard Android recovery menu. |
| Installing a custom kernel | Fastboot allows the installation of a custom kernel for enhanced performance and stability. | Utilizing a standard operating system update, which might not include the necessary kernel changes. |
| Troubleshooting system issues | Fastboot allows for checking device hardware, which may reveal underlying issues. | Using diagnostic tools within the standard Android operating system. |
| Updating system software (in some cases) | Fastboot provides a way to update the device’s firmware through a specific process. | Using the standard Android operating system update mechanism. |
Enabling Fastboot Mode
Enabling fastboot mode is a crucial step for advanced device troubleshooting and custom firmware installations. It grants access to a special boot mode that allows direct interaction with the device’s low-level software. Understanding the prerequisites and steps for enabling fastboot mode is vital for anyone working with Android devices at a deeper level.
Prerequisites for Enabling Fastboot Mode
Before attempting to enable fastboot mode, ensure the necessary conditions are met. This typically involves charging the device to a sufficient level to prevent unexpected shutdowns during the process. It’s also recommended to back up any critical data, as some actions in fastboot mode can potentially erase user data. Further, having the correct USB drivers installed on your computer is essential for communication.
Steps to Enable Fastboot Mode
Enabling fastboot mode generally involves a specific sequence of actions, depending on the device model. A consistent approach for most devices is to power off the device completely and then initiate the fastboot mode activation sequence.
Fastboot Mode Activation Procedure
- Power off the device completely. Waiting for the device to fully power down before initiating the fastboot sequence is crucial to avoid errors.
- Press and hold the designated hardware button(s) for fastboot mode activation. This varies between different device models. For example, some devices require holding the volume down and power buttons simultaneously, while others use a combination of volume up and power. Consult your device’s user manual for the precise button combination.
- Release the button(s) once the fastboot mode screen appears on the device’s display. This indicates the device has successfully entered fastboot mode.
Verification of Fastboot Mode
After completing the steps, verify that fastboot mode is enabled. Connecting the device to a computer via a USB cable is essential for this process. Most devices will display a confirmation message on the device’s screen. Additionally, the computer’s command-line interface (CLI) can be used to verify fastboot mode by checking if the device is recognized by the system’s fastboot tools.
Figuring out how to enable and exit fastboot mode can be tricky, but it’s crucial for some device maintenance. Thankfully, there are helpful guides available online. Meanwhile, San Pablo’s leaders are laying out a multi-year plan for the city’s future, as detailed in this article san pablo leaders set multi year vision for city. Once you’ve got the fastboot mode sorted, you’ll be ready for any future device upgrades or troubleshooting!
| Step | Action | Expected Result |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Power off the device | Device powers off completely |
| 2 | Press and hold the designated fastboot buttons | Fastboot mode screen appears on the device’s display |
| 3 | Release the fastboot buttons | Fastboot mode is enabled. The device should be recognized by the computer’s fastboot tools. |
| 4 | Connect the device to the computer using a USB cable | Device is recognized by the computer and appears as a fastboot device in the command prompt. |
Exiting Fastboot Mode
Exiting fastboot mode is a crucial step to return your device to normal operation after performing various tasks, such as flashing ROMs or recovery images. Incorrectly exiting fastboot mode can lead to boot loops, bricked devices, or other unpredictable issues. Therefore, understanding the proper procedures is vital for maintaining the health and functionality of your device.
Methods for Exiting Fastboot Mode
Various methods exist for exiting fastboot mode, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. The most common approaches are power cycling and using the fastboot commands. Understanding these methods is essential for ensuring a smooth transition back to normal operation.
Power Cycling
Power cycling, a simple yet effective method, involves physically turning off the device and then turning it back on. This method is generally reliable but may not always be the fastest. The process is straightforward and accessible to most users.
- Locate the power button on your device.
- Press and hold the power button for a few seconds until the device turns off.
- Wait for a few seconds to ensure the device is completely powered down.
- Press and hold the power button again to turn the device back on.
Fastboot Commands
Using fastboot commands offers a more precise and controlled method of exiting fastboot mode. This approach allows for specific actions and provides a way to return the device to normal boot sequence. It is particularly useful for advanced users or situations where the power cycle might not be sufficient.
- Ensure your device is connected to the computer via a USB cable.
- Open a command prompt or terminal window.
- Navigate to the fastboot directory on your computer.
- Type the command “fastboot reboot” and press Enter.
Comparison of Exit Methods
The following table compares the different methods for exiting fastboot mode, highlighting their steps and potential advantages and disadvantages.
| Method | Steps | Pros/Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Power Cycling | Turn off, wait, turn on | Pros: Simple, widely accessible; Cons: Potentially slower, less precise. |
| Fastboot Commands | Connect, navigate, type “fastboot reboot” | Pros: Precise, controlled; Cons: Requires computer access, potentially more complex. |
Troubleshooting Enabling/Exiting Fastboot Mode
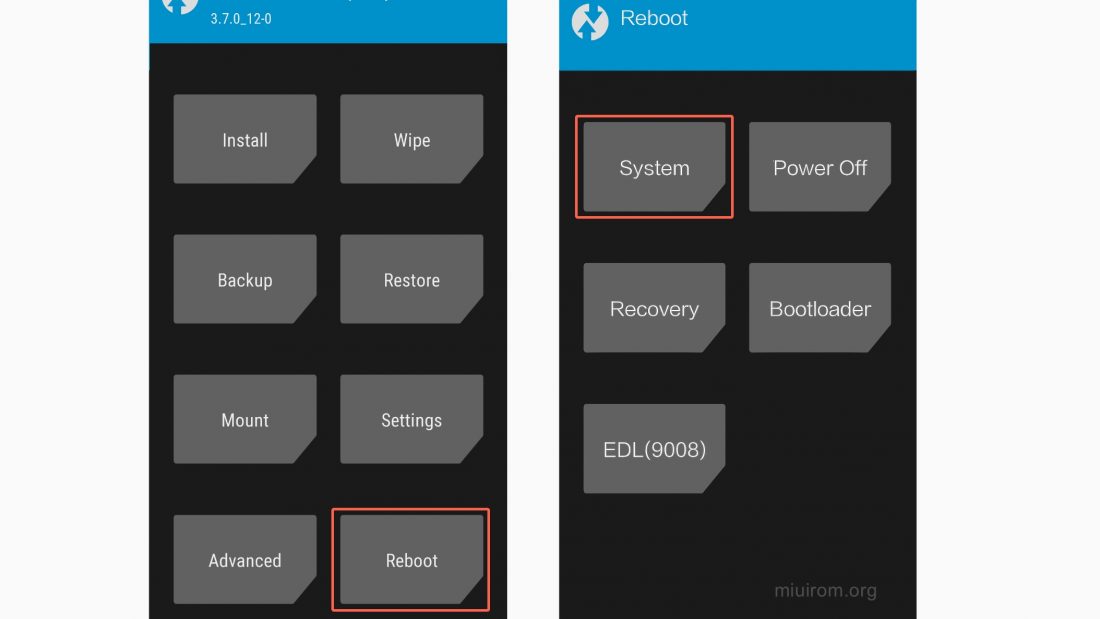
Fastboot mode, a crucial component for device maintenance and troubleshooting, sometimes presents challenges during its activation or deactivation. This section delves into common issues encountered while enabling or exiting fastboot mode and provides detailed solutions for each. Understanding these problems is vital for a smooth and successful fastboot experience.
Common Fastboot Mode Enabling Issues
A variety of factors can hinder the successful entry into fastboot mode. These issues often stem from incorrect procedures, device configurations, or software glitches. Troubleshooting these problems requires a methodical approach.
- Incorrect Button Combination: Improper button combinations during the fastboot entry process can prevent the device from entering the desired mode. This might involve pressing the wrong buttons, not holding them for the required duration, or not following the precise sequence of button presses. To resolve this, carefully review the device’s manufacturer documentation for the correct button sequence and hold each button for the specified duration.
Verify that all buttons are pressed simultaneously or in the correct sequence. For example, if the instructions indicate pressing the volume down button and the power button together, ensure both buttons are pressed at the same time.
- Device Not Responding: The device might not respond to the button combination, leading to a failure to enter fastboot mode. This issue can be caused by various factors, such as a device being in a deep sleep state, a faulty power supply, or software glitches. To resolve this, ensure the device is fully powered on. Try restarting the device and then attempting to enter fastboot mode again.
If the issue persists, try a different USB cable or charging port.
- Incompatible USB Cable/Port: A faulty or incompatible USB cable or charging port can interrupt the communication between the device and the computer, hindering fastboot mode activation. The device might not be recognized by the computer, or the fastboot command might fail to execute. Using a different USB cable or port, preferably a known good one, might solve the problem. If using a specific USB port known to have issues with charging, try a different port.
Common Fastboot Mode Exiting Issues
Exiting fastboot mode, while often straightforward, can also present challenges. These issues frequently involve incorrect commands or software glitches.
- Incorrect Command Usage: The wrong command might be used to exit fastboot mode, causing it to fail or remain in fastboot mode. This might stem from typos, improper syntax, or using a command incompatible with the device. To resolve this, double-check the correct command syntax. Consult the device’s documentation for the precise command required to exit fastboot mode. Ensure the command is executed in the correct directory.
For example, `fastboot reboot` might be used in a specific command-line environment.
- Device Not Responding to Commands: The device might not respond to the exit command, preventing it from exiting fastboot mode. This issue could stem from a communication failure between the computer and the device or a software glitch on the device. Verify the connection between the computer and the device is stable. If the device doesn’t respond, try restarting the device and then attempting to exit fastboot mode again.
If the issue persists, consult the device’s manufacturer documentation.
- Software Errors: Software errors or glitches on the computer or device might interfere with the command execution, preventing a smooth exit from fastboot mode. These errors might manifest as unexpected behavior or error messages. Ensure the device’s software is up-to-date. If possible, try restarting the computer and then executing the command to exit fastboot mode.
Troubleshooting Table
| Issue | Explanation | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect Button Combination | Improper button sequence during fastboot entry. | Refer to device documentation for correct button sequence. |
| Device Not Responding | Device doesn’t respond to button combination. | Ensure device is fully powered, restart device, try different USB cable/port. |
| Incompatible USB Cable/Port | Faulty or incompatible cable/port. | Use a different USB cable or port. |
| Incorrect Command Usage | Wrong command used to exit fastboot. | Double-check command syntax and device documentation. |
| Device Not Responding to Commands | Device doesn’t respond to exit command. | Verify stable connection, restart device, check software updates. |
| Software Errors | Software glitches interfering with command execution. | Ensure device and computer software is up-to-date. |
Device Compatibility and Variations
Fastboot mode, while a powerful tool for device maintenance, isn’t universally implemented or identically executed across all Android devices. Different manufacturers and models often have unique requirements and procedures for entering and exiting fastboot. Understanding these variations is crucial to avoid damaging your device during troubleshooting or customization.Different Android device manufacturers may implement fastboot mode in slightly different ways, even with similar operating systems.
These variations can range from minor differences in the key combinations needed to initiate fastboot mode to more significant variations in the commands required for specific actions within the fastboot environment.
Device-Specific Fastboot Procedures
Understanding device-specific fastboot procedures is essential for successful execution. Different devices might require unique key combinations or power button sequences to enter fastboot mode. This section details the possible variations.
- Some devices might require a combination of power and volume buttons to initiate fastboot mode. For instance, pressing and holding the power button while simultaneously pressing the volume down button could initiate fastboot mode on a particular device.
- Other devices might require a specific power-off sequence followed by a specific button combination to enter fastboot mode. This could involve a prolonged power button press followed by the volume up button, or a combination of the power button and volume buttons pressed in a certain sequence.
- There are instances where holding a specific button combination, while the device is being powered on, might initiate fastboot mode. For example, holding the power button, volume down button, and a specific function button simultaneously, could initiate fastboot mode.
Operating System Influences, Enabling and exiting fastboot mode guide
Operating system versions can also influence the fastboot mode procedure. While the core functionality remains similar, the exact sequence for initiating or exiting fastboot might differ slightly between various Android versions.
- Older Android versions might have slightly different fastboot commands or procedures compared to newer versions.
- Some devices running specific Android versions might require additional steps or configurations to enable or disable fastboot mode, which may not be necessary for other versions.
Fastboot Mode Procedures by Device
The table below provides a concise overview of fastboot mode procedures for specific device types. Keep in mind that this is not an exhaustive list, and specific models may have unique instructions. Consult your device’s user manual for the most accurate information.
Figuring out how to enable and exit fastboot mode can be tricky, but thankfully there are guides available. While you’re tackling that techy stuff, remember to pamper yourself too! For example, to revitalize your dry locks, check out some fantastic nourishing hair masks. Revive dry hair with the best nourishing hair masks offer a range of options to suit various needs.
Once you’ve got your hair looking amazing, you can get back to mastering that fastboot mode guide!
| Device Type | Fastboot Mode Entry | Fastboot Mode Exit |
|---|---|---|
| Samsung Galaxy S22 | Simultaneously press and hold the power and volume down buttons until the fastboot screen appears. | Power off the device, and then power it on normally. |
| Google Pixel 7 | Press and hold the power button, then press and hold the volume down button. | Power off the device completely, and then turn it on in the normal startup sequence. |
| Xiaomi Redmi Note 11 | Press and hold the power button for a few seconds until the device vibrates, then quickly press and hold the volume down button. | Power off the device normally, and then turn it back on. |
Advanced Fastboot Commands (Optional): Enabling And Exiting Fastboot Mode Guide
Fastboot mode provides a powerful interface for interacting with your Android device at a low level. While basic commands like booting into recovery or wiping data are essential, advanced commands offer more granular control. This section delves into some useful advanced fastboot commands, providing detailed explanations, syntax, and illustrative examples. Understanding these commands can be beneficial for more complex tasks such as custom ROM installations or system modifications.Advanced fastboot commands allow for specific actions, like flashing partitions or configuring hardware settings, beyond the standard functions.
Proper usage is crucial to avoid potential damage to your device. Carefully review the commands and their potential implications before executing them.
Flashing a Specific Partition
Flashing a specific partition involves writing new data to a particular section of the device’s storage. This is often used for installing updates or modifying system components. The `flash` command, with specific partition names, is the primary tool.
fastboot flash
For instance, to flash a boot image named `boot.img` located in the current directory:
fastboot flash boot boot.img
Replace `
Retrieving Device Information
Gathering information about your device’s state can be vital for troubleshooting or understanding the current configuration. The `getvar` command is useful for retrieving various device parameters.
fastboot getvar
For example, to obtain the value of the `ro.build.version.release` variable, which holds the Android version:
fastboot getvar ro.build.version.release
This command is valuable for checking device specifications, build information, and various other parameters stored in the device’s system variables.
Using the `printenv` Command
The `printenv` command provides a comprehensive list of all current environment variables. This command is essential for debugging and understanding the current state of the device’s configuration.
fastboot printenv
The output will display a detailed listing of the environment variables and their corresponding values. This allows examination of crucial parameters, such as the boot mode, build properties, and more.
Summary Table of Advanced Fastboot Commands
| Command | Purpose | Syntax |
|---|---|---|
| `flash` | Flashes a specific partition with the provided image file. | fastboot flash <partition_name> <file_path> |
| `getvar` | Retrieves the value of a specific system variable. | fastboot getvar <variable_name> |
| `printenv` | Displays all current environment variables. | fastboot printenv |
Security Considerations
Fastboot mode, while offering powerful tools for device modification and troubleshooting, presents potential security risks if not handled carefully. Understanding these risks and implementing appropriate security measures is crucial for maintaining the integrity and safety of your Android device. Improperly used fastboot commands can lead to significant data loss or even compromise the device’s overall security.
Risks of Enabling Fastboot Mode
Fastboot mode grants elevated privileges, allowing access to the low-level operating system components. This expanded access significantly increases the possibility of unintended consequences, such as malware infection or unauthorized access to sensitive data. Unauthorized modifications to the system can lead to a variety of issues, from rendering the device unusable to allowing malicious actors to control it remotely.
Mitigation Strategies
Careful planning and execution are paramount when using fastboot mode. This involves a comprehensive approach to security, encompassing both the actions taken and the environment in which they are performed. Following these measures can significantly reduce the risks associated with fastboot mode.
| Risk | Explanation | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Unauthorized Access | Malicious actors could potentially exploit vulnerabilities in fastboot mode to gain control of the device. | Ensure the device is connected to a trusted network or a secure environment. Use strong passwords and authentication methods to protect your device and its credentials. |
| Data Loss | Incorrect or malicious commands during fastboot operations can lead to irreversible data loss. | Always verify commands before execution. Back up crucial data before performing any fastboot actions. Use a reputable and trusted source for the commands. |
| Malware Infection | Fastboot mode provides a direct path to the low-level system, making it susceptible to malware infections. | Only use verified and trusted fastboot tools. Install security software on the device before entering fastboot mode, if possible. |
| System Instability | Unintentional or malicious modifications to the system files can lead to instability or malfunction. | Consult reliable documentation for proper commands and procedures. Test commands on a backup device or virtual machine first, if possible. |
Important Considerations
Always operate in a controlled environment, like a dedicated workstation or a network with robust security measures. A compromised device could allow attackers to access sensitive data or potentially control the device remotely, which can have serious consequences.
Additional Precautions
For sensitive devices or environments, consider using additional security layers, such as a virtual machine or a dedicated network segment, to isolate the device during fastboot operations. This adds an extra layer of protection against potential vulnerabilities and mitigates risks related to data breaches.
Illustrative Examples and Use Cases

Fastboot mode, a crucial intermediary state for Android devices, unlocks a powerful set of tools for system-level interventions. Understanding its practical applications is key to maximizing its utility. This section will delve into scenarios where enabling fastboot is necessary and demonstrate its use in practical applications.
Enabling fastboot mode is essential for tasks ranging from simple software updates to complex system repairs. Its unique capabilities allow for direct interaction with the device’s firmware without the need for a full operating system. This provides an avenue for tasks that would be otherwise impossible or significantly more complex through conventional means.
A Scenario Requiring Fastboot
A common scenario where fastboot mode is invaluable is during a device’s software update. A user might encounter a system-level bug that prevents a regular update from completing successfully. Instead of a full system reset, which can be time-consuming and potentially data-loss inducing, fastboot provides a means for installing the update directly onto the device’s firmware.
Practical Application: Updating a System Image
Imagine a user has a custom ROM they want to install on their Android device. The standard method through the operating system might fail due to incompatibility issues or system errors. Fastboot provides a direct path to install the new ROM image.
Detailed Walkthrough
- Device Preparation: Ensure the device is properly charged and connected to a computer with the appropriate USB drivers installed. The device must be in a state where it is recognized by the computer’s operating system as a device, not as an ordinary USB storage.
- Enabling Fastboot Mode: Follow the instructions Artikeld in the previous section for enabling fastboot mode on your device. This often involves specific hardware button combinations during boot-up. Carefully read your device’s manual for exact procedures. This step is crucial as incorrect procedure can result in unexpected consequences.
- Downloading and Preparing the ROM: Download the custom ROM file and place it in a readily accessible location on your computer. Ensure that the ROM is compatible with your device’s model and Android version. Incompatible ROMs can cause damage or render the device inoperable.
- Using Fastboot Commands: Open a command prompt or terminal window and navigate to the directory where you placed the downloaded ROM image. Then, use the appropriate fastboot command to flash the new ROM image. Examples of fastboot commands include flashing a system image: `fastboot flash system system.img`. A command prompt or terminal will be required for this process. A successful command execution will result in the display of messages confirming the process.
- Booting the Device: Once the flash process is complete, use the fastboot command to reboot the device into the new ROM. `fastboot reboot`. The device will restart and boot into the new system.
Benefits of Fastboot in this Context
The fastboot procedure is beneficial in this context because it allows for a targeted and controlled installation of the custom ROM, minimizing the risk of data loss or system corruption compared to a full system reset. It offers an efficient means to address potential compatibility issues with a new ROM. This targeted approach is essential for maintaining the device’s functionality and data integrity.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this enabling and exiting fastboot mode guide has equipped you with the knowledge to confidently navigate fastboot mode. We’ve covered everything from basic enabling and exiting procedures to advanced techniques and troubleshooting steps. By understanding the potential risks and benefits, you can now make informed decisions when working with your devices. Remember to always prioritize safety and follow the instructions carefully.
This comprehensive guide should serve as a valuable resource for any user needing to utilize fastboot mode.

