WiFi Repeater vs Extender Your Ultimate Guide
Wi fi repeater vs extender – WiFi repeater vs extender sets the stage for this in-depth comparison, exploring the nuances of these often-confused network devices. Understanding their differences is key to boosting your home Wi-Fi signal and getting the most out of your internet connection. We’ll dive into their functionalities, setup, performance, and more, helping you decide which device best suits your needs.
This comprehensive guide explores the technical aspects, practical considerations, and real-world scenarios surrounding repeaters and extenders. From the fundamental differences in their operating principles to their impact on your existing network, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to make an informed decision.
Introduction to Wi-Fi Repeaters and Extenders
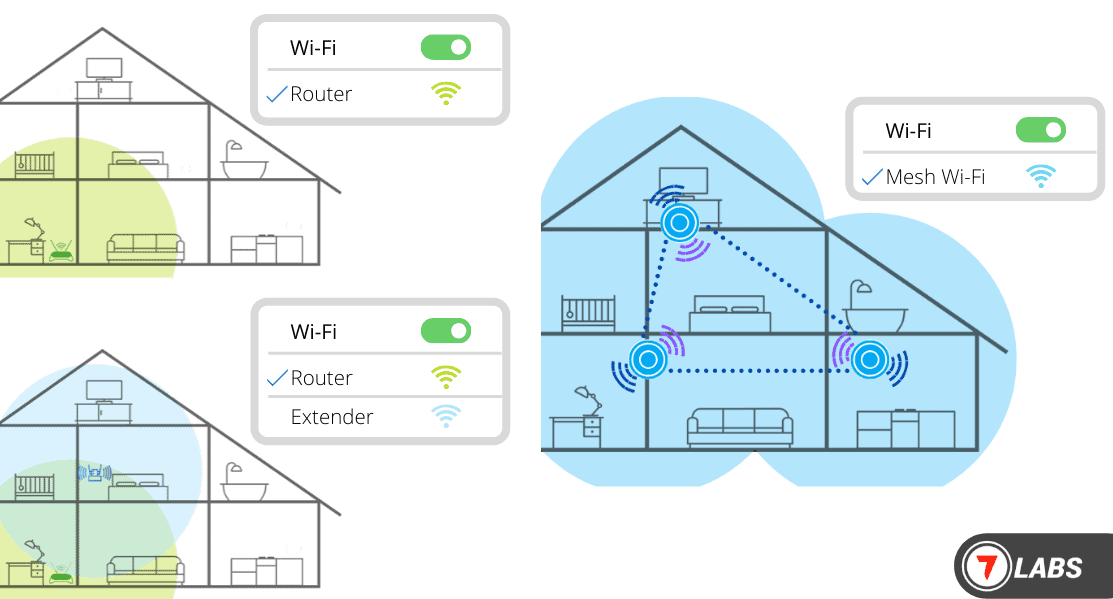
Wi-Fi repeaters and extenders are both crucial devices for boosting your Wi-Fi signal, but they work in slightly different ways. Understanding their distinctions can help you choose the right device for your specific needs. They’re often used interchangeably, but knowing their differences is key to getting the best Wi-Fi performance possible.These devices are designed to increase the coverage area of your existing Wi-Fi network.
A repeater essentially copies the signal, while an extender enhances the existing signal, extending it to areas where the original signal is weak. The choice depends on the specifics of your home or office setup and your Wi-Fi router’s capabilities.
Core Functionalities of Wi-Fi Repeaters
Wi-Fi repeaters act as a secondary access point, receiving and retransmitting the signal from your router. This effectively doubles the reach of your Wi-Fi network, particularly useful in large homes or offices with multiple floors or walls that interfere with the signal. They are excellent for expanding coverage to areas where the original signal is weak or non-existent. Think of a repeater as a relay station for your Wi-Fi signal.
Core Functionalities of Wi-Fi Extenders
Wi-Fi extenders, on the other hand, work by strengthening the existing signal from your router. They essentially create a new Wi-Fi network, but operate as an extension of your primary network, not a completely independent one. They’re ideal for bridging the gap in areas where the signal is weak but not completely non-existent. They improve the signal quality in those areas by increasing the strength of the signal.
Think of an extender as a signal amplifier.
Situations Where Each Device is Most Beneficial
Repeaters are better suited for extending coverage to areas with no or very weak Wi-Fi signal, such as basements or the back yard. A scenario where a repeater shines is a house with a large, open floor plan. By placing a repeater in the center of the area, the signal is more evenly distributed. Extenders are more helpful when your existing Wi-Fi signal is already present but is weak.
This might be the case in a small house where a wall is blocking the signal, but you don’t want to completely lose connection. Imagine a guest room in a house with an already existing signal.
Comparison of Wi-Fi Repeaters and Extenders
| Feature | Repeater | Extender |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Type | Receives and retransmits the signal | Amplifies and strengthens the signal |
| Coverage Area | Extends the existing network’s range | Increases the strength of the existing network in a specific area |
| Performance | Might slightly reduce speed if the signal is too weak | Increases signal strength without affecting speed |
| Setup | Often requires configuration on both the router and the repeater | Usually simpler to set up, working directly with the router |
| Cost | Generally comparable in price to extenders | Usually less expensive than repeaters |
Factors Affecting Choice: Wi Fi Repeater Vs Extender
Choosing between a Wi-Fi repeater and an extender depends on several crucial factors. Understanding these nuances allows you to select the device best suited to your specific needs, ensuring optimal Wi-Fi performance and seamless connectivity throughout your home or office. A poorly chosen device can lead to frustrating performance issues, so careful consideration is key.Factors like your existing network setup, desired coverage, budget, and the number of connected devices significantly influence the appropriate choice.
Furthermore, signal strength and interference are crucial considerations that can impact your decision.
Figuring out Wi-Fi repeaters versus extenders can be tricky, but it’s not as mind-bending as crafting obsidian in Minecraft. You need to understand that while both aim to boost your signal, they achieve it in different ways. To get the best Wi-Fi range in your house, understanding the nuances of each device is key, like knowing how to make obsidian in Minecraft requires specific materials.
For a more detailed comparison of Wi-Fi repeaters vs. extenders, check out this guide on make obsidian in minecraft – it’s surprisingly helpful. Ultimately, the best choice depends on your specific needs and the layout of your home.
Existing Network Setup
Understanding your current Wi-Fi network architecture is essential. If your router is centrally located and the signal strength is weak in specific areas, a repeater might be the solution. Repeaters amplify the existing signal, effectively extending its reach. Conversely, if the router is located in a room with significant obstacles, a Wi-Fi extender, designed to overcome obstacles and create a new access point, may be more suitable.
A key distinction is the repeater’s role in amplifying the existing signal, whereas an extender creates a new access point, sometimes with a different SSID.
Coverage Needs
The area you need to cover plays a vital role. If you need to extend the signal throughout a large house or a multi-story building, a repeater might not be sufficient. A Wi-Fi extender, with its ability to establish a new access point, can provide broader coverage, but might require more than one extender for very large areas.
The physical layout of your home, the presence of walls and other obstructions, and the location of the router itself all contribute to the overall coverage challenge.
Budget
The price range of Wi-Fi repeaters and extenders varies significantly. Entry-level models are often more affordable, but they might not offer the same performance or features as higher-end devices. Consider your budget and prioritize features that align with your specific needs, such as multiple bands (2.4GHz and 5GHz), advanced security protocols, or faster speeds.
Number of Devices Connected
The number of devices connected to your network is another critical factor. A high number of devices often leads to a higher demand for bandwidth. If you have many devices consistently demanding high bandwidth (e.g., multiple streaming devices, gaming consoles, and smart home devices), a repeater or extender that supports higher speeds might be necessary to avoid performance bottlenecks.
A higher number of connected devices, particularly with demanding applications, may necessitate a device capable of handling that increased bandwidth load.
Signal Strength and Interference, Wi fi repeater vs extender
Weak signal strength and interference from other devices or appliances can significantly impact Wi-Fi performance. A repeater or extender can help overcome weak signal strength by amplifying the existing signal. However, interference can affect both repeaters and extenders. If interference is a primary concern, an extender might be a more robust solution as it can create a new access point that minimizes the impact of interference from other sources.
Identifying and mitigating the sources of interference is a crucial step.
Common Pitfalls
Avoid choosing a device based solely on price. Consider the features and performance specifications of various models. Another pitfall is failing to assess the current network setup, as this can hinder the choice of the optimal device. Do not underestimate the importance of signal strength and interference; these factors significantly influence the effectiveness of any Wi-Fi repeater or extender.
Choosing between a Wi-Fi repeater and extender can be tricky. A repeater essentially boosts the existing signal, while an extender creates a new network. For example, if you’re trying to get better Wi-Fi coverage for a San Jose State Spartan basketball game watch party, knowing the difference between a repeater and an extender could significantly improve your streaming experience.
Fortunately, checking out the San Jose State NCAA basketball Mountain West schedule and game times could be an insightful way to plan your home network upgrades for the upcoming season, and ultimately help you decide which option is best for your needs. Ultimately, the best choice depends on your specific setup.
Lastly, remember that the most advanced features might not always be necessary for your needs.
Scenario-Based Recommendations
| Scenario | Recommendation | Justification |
|---|---|---|
| Small apartment with a centrally located router, weak signal in one corner. | Wi-Fi Repeater | Repeater will amplify the existing signal to reach the weak area. |
| Large house with significant obstacles, need coverage in multiple rooms and floors. | Wi-Fi Extender | Extender creates a new access point to overcome obstacles and provide broader coverage. |
| Home with many devices (smart home devices, streaming services, and gaming consoles), needing higher speeds and reduced congestion. | Wi-Fi Extender with high bandwidth capability. | An extender with higher bandwidth capability is ideal to handle the higher bandwidth demand. |
| Large office environment with multiple devices and potential interference from other electronic devices. | Wi-Fi Extender with advanced interference mitigation features. | Extender with interference mitigation capabilities is better suited to handle potential interference in a large environment. |
Technical Aspects
Understanding the technical differences between Wi-Fi repeaters and extenders is crucial for choosing the right device for your needs. These devices operate on different principles, leading to variations in performance and suitability for various network configurations. This section delves into the technical mechanisms, signal amplification, Wi-Fi standard impact, and environmental factors influencing their effectiveness.The key distinction lies in their network architecture.
Repeaters essentially create a new Wi-Fi network, while extenders simply expand the existing one. This fundamental difference affects their capabilities and limitations.
Network Architecture Differences
Repeaters operate by creating a new network with a new SSID (Service Set Identifier). This means devices must connect to the new network and reauthenticate, potentially leading to temporary disconnections. Extenders, on the other hand, expand the existing network. Devices remain connected to the original network and experience a seamless connection, eliminating the need for reauthentication. This difference impacts the complexity of network management and the overall user experience.
Signal Amplification Methods
Repeaters typically rely on signal amplification to boost the Wi-Fi signal. This often involves simply increasing the power of the transmitted signal. Extenders, however, often employ more sophisticated signal processing techniques, such as beamforming, which focuses the signal in the direction of the receiving device. Beamforming can significantly improve signal quality, especially in challenging environments with many obstacles.
Wi-Fi Standard Impact
The Wi-Fi standard (e.g., 802.11ac, 802.11ax) plays a vital role in determining the performance of both repeaters and extenders. Devices that support newer standards, such as 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6), typically offer faster speeds and better performance compared to those supporting older standards like 802.11n. The compatibility of the extender or repeater with the existing router’s Wi-Fi standard is critical.
A repeater supporting 802.11ax but connected to a router only supporting 802.11ac will experience performance limitations.
Impact of Wall Materials and Obstacles
Wall materials and obstacles, such as furniture and appliances, can significantly affect Wi-Fi signal quality. Concrete walls, for example, absorb and reflect Wi-Fi signals, reducing their strength. The effectiveness of repeaters and extenders in overcoming these obstacles depends on their signal amplification capabilities and the specific design of the device. Careful placement, considering the layout of the home or office, is essential for optimal performance.
Analyzing Existing Network Signals for Optimal Placement
Analyzing existing network signals using tools like Wi-Fi analyzers helps identify dead zones and areas with weak signal strength. These tools provide detailed information about the signal strength, interference levels, and channel utilization. This information allows for strategic placement of the repeater or extender to maximize coverage and minimize signal degradation. This involves understanding the layout of the building and identifying locations where the signal is weak.
Technical Specifications of Various Models
| Model | Wi-Fi Standard | Signal Amplification | Network Architecture | Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TP-Link RE605 | 802.11ac | Signal Boosting | Repeater | Easy Setup, Affordable |
| Netgear Orbi | 802.11ax | Beamforming | Extender | High-performance, Multi-room coverage |
| ASUS RT-AX88U | 802.11ax | Advanced Signal Processing | Router with Repeater Function | High-end, Versatile |
Note: This table provides a simplified comparison and does not include all available models. Always refer to the manufacturer’s specifications for detailed information.
Setup and Configuration
Setting up a Wi-Fi repeater or extender is a straightforward process that can significantly improve your home network’s coverage. Proper setup, including correct placement and configuration, is key to maximizing the device’s benefits and avoiding potential issues. Understanding the steps involved will allow you to quickly and effectively expand your Wi-Fi signal.Correct placement and optimal positioning of the repeater or extender are crucial for achieving the desired results.
The goal is to position the device in a location that maximizes signal strength and minimizes interference from walls, obstacles, and other electronic devices.
Step-by-Step Setup Procedure
The setup procedure generally involves these steps:
- Unpack the device and connect the power adapter.
- Locate a suitable placement for the repeater/extender, considering obstacles and signal strength.
- Connect the device to your existing network using the provided setup instructions. Typically, this involves selecting the appropriate SSID and entering the password.
- Configure the repeater/extender’s settings, including the channel and mode, if necessary. Some devices might offer advanced options for optimizing performance.
- Test the Wi-Fi connection to ensure proper coverage in the extended area.
Importance of Correct Placement
Proper placement is paramount for optimal performance. A repeater positioned near a router, while convenient, may not extend the signal effectively to all desired areas. Consider the physical layout of your home, identifying dead zones and areas with weak signal. Placing the repeater in a central location, away from walls and obstructions, is often a good starting point.
Testing signal strength in different locations is crucial to finding the best placement for the repeater.
Configuring the Device
The configuration process varies slightly depending on the specific device. Most devices will guide you through the process via a user-friendly interface. Look for settings related to the following:
- SSID (Service Set Identifier): Selecting the correct SSID of your existing Wi-Fi network is essential for the repeater to connect and extend the signal.
- Password: Inputting the correct password for your existing Wi-Fi network allows the repeater to access the network and transmit data.
- Channel Selection: Selecting an appropriate channel can minimize interference from other networks operating on the same frequency.
- Mode: Choosing the correct mode (e.g., router mode, repeater mode) ensures compatibility with your existing network and desired functionality.
Troubleshooting Setup Issues
Common setup issues include weak signal strength, connection problems, or interference. If you experience these problems, consider the following:
- Verify Network Connectivity: Check if your router and other devices are properly connected and functioning.
- Placement: Reposition the repeater in a different location, possibly closer to the router or further away from obstacles.
- Restart Devices: Restarting both your router and the repeater can often resolve temporary connection problems.
- Check Interference: Look for potential interference from other electronic devices in the area.
- Consult Documentation: Refer to the manufacturer’s documentation for specific troubleshooting steps and solutions.
Maximizing Effectiveness
To maximize the effectiveness of your Wi-Fi repeater or extender, consider these tips:
- Avoid Obstructions: Position the repeater away from walls, furniture, and other obstructions to ensure a strong signal.
- Choose a Central Location: Strategically placing the repeater in a central location can help extend the signal to more areas of your home.
- Update Firmware: Ensure the repeater’s firmware is up-to-date to benefit from any performance improvements or bug fixes.
- Test Signal Strength: Regularly check signal strength in different areas to optimize performance.
- Consider a Mesh Network: For larger homes, a mesh network solution might provide a more reliable and consistent Wi-Fi coverage.
Setup Configurations
| Configuration | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Single Repeater | Simple setup, cost-effective for smaller homes | Limited coverage for larger homes, potential for interference |
| Multiple Repeaters | Expanded coverage, less interference | More complex setup, higher cost |
| Mesh Network | Reliable and consistent coverage throughout the home, advanced features | More expensive, complex setup |
Performance and Reliability
Wi-Fi repeaters and extenders promise to boost your network’s reach and strength, but their actual performance can vary significantly. Understanding the factors that influence performance and reliability is crucial to making an informed decision about which device best suits your needs. This section delves into the expected performance gains, potential limitations, and the critical role of network traffic in determining overall success.The effectiveness of a repeater or extender is heavily dependent on the original signal strength and the environment in which it’s deployed.
A strong initial signal will yield more consistent performance gains than one that’s already weak. Also, obstacles like walls, floors, and other electronic devices can significantly degrade the signal, impacting the repeater or extender’s ability to amplify and retransmit it effectively.
Expected Performance Gains
The primary goal of both repeaters and extenders is to expand the coverage area of your existing Wi-Fi network. Repeaters essentially copy and retransmit the signal, while extenders create a new access point, often using a different Wi-Fi channel to avoid interference. Theoretically, a well-placed repeater or extender can increase the coverage area and signal strength, leading to faster speeds and reduced latency.
However, these gains are not guaranteed, and the actual improvement depends on numerous factors.
Potential Limitations and Drawbacks
While repeaters and extenders offer potential performance enhancements, several limitations should be considered. The most significant factor is the distance from the router. As the signal travels further, it weakens. Repeaters can only amplify the existing signal, so if the signal is already weak, the repeater’s effectiveness is compromised. Extenders, while often better for greater distances, can introduce a performance bottleneck if the existing network’s bandwidth is insufficient.
Furthermore, the number of devices connected to the network significantly impacts the available bandwidth. Multiple devices simultaneously accessing the network can lead to congestion and slower speeds, even with a repeater or extender.
Figuring out Wi-Fi repeaters versus extenders can be tricky, but it’s all about getting that sweet spot for optimal signal strength. For a truly relaxing massage session, though, consider investing in some top-notch massage bolsters for better support during every session. Top massage bolsters for better support during every session will enhance your comfort and make those post-massage stretches even more enjoyable.
Ultimately, choosing the right Wi-Fi solution comes down to your specific needs and room layout.
Reliability and Stability
Reliability is a key consideration when choosing between repeaters and extenders. Repeaters generally offer more stable performance, as they operate on the same Wi-Fi channel as the router. Extenders, by creating a new access point, can sometimes experience disconnections or dropouts, especially in environments with numerous interfering devices. Network stability is affected by the quality of the signal, the compatibility of the devices involved, and the presence of other electronic devices operating on similar frequencies.
Impact of Network Traffic
High network traffic, characterized by numerous devices simultaneously accessing the network, significantly impacts performance. Whether using a repeater or an extender, a congested network will lead to slower speeds and increased latency. The repeater or extender can help to distribute the traffic, but it cannot overcome limitations imposed by insufficient bandwidth. This is especially important for households with multiple devices or high bandwidth demands.
Metrics for Measuring Effectiveness
Several metrics can be used to gauge the effectiveness of a Wi-Fi repeater or extender. These include:
- Throughput: Measured in Mbps (megabits per second), this metric indicates the rate at which data can be transferred. A higher throughput generally translates to faster speeds.
- Latency: The time it takes for data to travel from one point to another. Lower latency results in smoother streaming and online gaming.
- Signal Strength: A critical factor for any Wi-Fi device, a strong signal ensures consistent performance. This is usually measured in decibels (dB).
- Coverage Area: This is a qualitative measure, assessing the range over which the Wi-Fi signal is usable.
These metrics are essential in determining the efficacy of a repeater or extender and are often provided by testing tools.
Performance Benchmarks
| Device Model | Throughput (Mbps) | Latency (ms) | Signal Strength (dB) | Coverage (sq. ft.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Repeater A | 150-300 | 5-10 | -60 to -80 | 1000-1500 |
| Extender B | 200-400 | 3-7 | -55 to -75 | 1200-1800 |
| Repeater C | 200-400 | 3-8 | -65 to -85 | 1500-2000 |
Note: These are example benchmarks and may vary based on testing conditions and the specific environment.
Advanced Features and Considerations
Choosing between a Wi-Fi repeater and an extender goes beyond just range. Advanced features like beamforming and MU-MIMO can significantly impact your network’s performance, while security protocols and interference are crucial factors for a stable and secure connection. Understanding these aspects will help you make a more informed decision based on your specific needs.
Beamforming and MU-MIMO
Beamforming and MU-MIMO are technologies that enhance Wi-Fi signal transmission. Beamforming focuses the signal towards the device receiving it, minimizing signal loss and increasing speed. MU-MIMO allows the router to communicate with multiple devices simultaneously, further improving overall network throughput. These technologies are often found in higher-end routers and extenders, and their impact is most noticeable in busy home networks with multiple connected devices.
Security Protocols
Robust security is paramount for protecting your network from unauthorized access. WPA3 is the latest Wi-Fi security protocol, offering enhanced encryption and protection against vulnerabilities. Using WPA3 on your repeater or extender is crucial for safeguarding your network and sensitive data. Legacy protocols like WPA2 should be avoided, as they present greater security risks.
Wi-Fi Channels
The Wi-Fi channels used by your router, repeater, and extender play a significant role in performance. Overlapping channels can lead to interference, reducing speed and reliability. Using non-overlapping channels, or utilizing channel-selection tools in your router configuration, optimizes performance by minimizing interference. Channel width also affects the amount of bandwidth available, and 80MHz channels provide more bandwidth than 40MHz channels.
Interference
Several factors can cause interference on your Wi-Fi network, including other Wi-Fi networks, Bluetooth devices, microwaves, and even some cordless phones. Understanding potential sources of interference helps in troubleshooting connection issues and choosing a suitable location for your repeater or extender. For example, placing your extender near a microwave oven or a crowded area with many wireless devices may cause performance degradation.
Table of Advanced Features
| Feature | Repeater Model A | Extender Model B | Repeater Model C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beamforming | Yes | Yes | No |
| MU-MIMO | Yes | No | Yes |
| WPA3 Support | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Channel Selection Tool | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Max Speed (Mbps) | 1200 | 800 | 1600 |
Note: The table provides hypothetical data for illustrative purposes. Actual features and specifications may vary based on the specific models. The table highlights the diversity in advanced features offered by different devices.
Cost Comparison and Recommendations
Choosing between a Wi-Fi repeater and an extender often comes down to budget and the specific needs of your home network. The price range varies significantly, impacting performance and features, which ultimately affects the long-term cost-effectiveness of the device. Understanding these factors can help you make an informed decision.The cost of a Wi-Fi extender or repeater isn’t just about the initial purchase price.
Long-term costs are influenced by potential issues with performance or reliability, and the necessity for future upgrades.
Pricing Range and Performance
The cost of Wi-Fi repeaters and extenders spans a wide range, from budget-friendly options under $50 to high-end models exceeding $200. Lower-priced devices typically offer basic functionalities, while higher-priced models often come with advanced features like MU-MIMO and beamforming, leading to improved performance and range.
Relationship Between Price and Performance
Generally, there’s a strong correlation between price and performance. More expensive devices often offer faster speeds, wider coverage, and more advanced features, which translate into better overall performance. A higher price often reflects enhanced hardware, improved signal processing algorithms, and more reliable connections, potentially saving money in the long run by reducing the likelihood of network issues and future replacements.
For instance, a $100 repeater might provide basic coverage but may require frequent reconfiguration or struggle with heavy network usage, whereas a $200 model might provide consistent performance across a larger area with fewer interruptions.
Cost-Benefit Analysis for Different Scenarios
The optimal choice depends heavily on the specific needs of your home network. For a small apartment with minimal network traffic, a budget-friendly option might suffice. However, for a large home with multiple devices and high bandwidth requirements, a more robust and expensive option could be a better long-term investment.For example, if you are streaming 4K video or gaming online, a more powerful extender might be a better investment, preventing buffering and lagging.
Long-Term Costs
Beyond the initial purchase price, consider the potential long-term costs. A device that frequently malfunctions or requires frequent reconfiguration will cost more in the long run than a device with stable and reliable performance. Consider factors like the device’s warranty, potential repair costs, and the need for future upgrades as your internet speed or device usage increases. A more expensive but reliable device could save you money in the long run by reducing troubleshooting time and minimizing the need for replacements.
Comparison Table of Wi-Fi Repeater/Extender Models
| Model | Price (USD) | Features | Performance (Estimated Range) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Netgear EX8000 | $150 | MU-MIMO, Beamforming, 802.11ac | 100-150 ft |
| TP-Link RE200 | $50 | Basic 802.11n | 50-75 ft |
| ASUS RT-AX86U | $250 | Wi-Fi 6E, OFDMA, 160MHz channels | 150-200 ft+ |
| TP-Link RE650 | $80 | 802.11ac, beamforming | 100-125 ft |
This table provides a simplified comparison. Actual performance may vary depending on the specific environment and the configuration of your network. Factors like the quality of your existing router, the number of devices connected, and the type of walls in your home can significantly influence the actual range and performance.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, choosing between a WiFi repeater and an extender depends heavily on your specific network setup and needs. Repeaters essentially duplicate the existing network, while extenders create a new access point. Weighing the pros and cons, considering factors like coverage area, existing infrastructure, and budget, will help you select the ideal device to amplify your Wi-Fi signal and enhance your internet experience.
Ultimately, this guide should empower you to make an informed choice.
