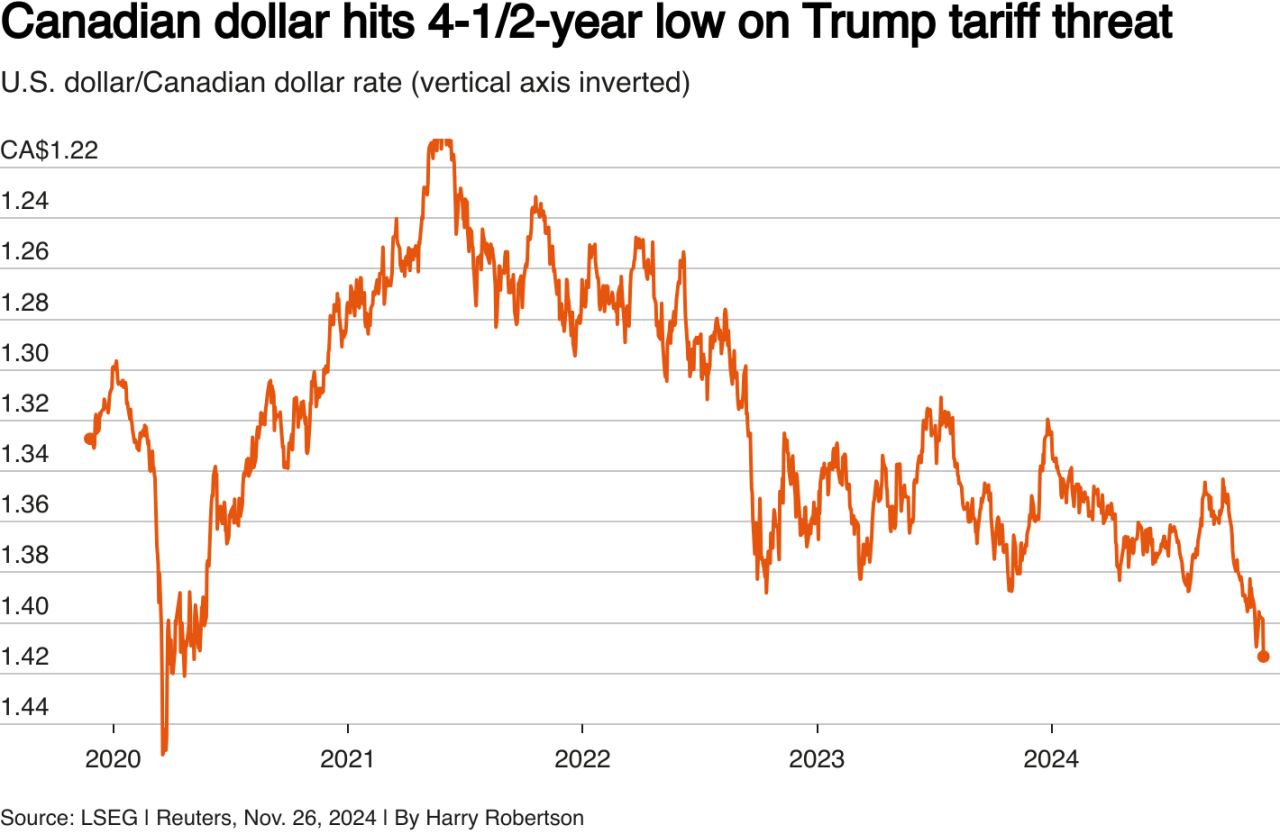
Trump Tariff Threat Canada, Mexico
Trump tariff threat Canada Mexico hangs heavy in the air, a potential storm cloud threatening to disrupt decades of trade relationships. This complex issue involves a tangled web of historical disputes, Trump’s unique trade policies, and the potential economic fallout for all three countries. From the legacy of NAFTA to the specific industries at risk, this analysis delves into the potential consequences of this escalating trade conflict.
The historical context reveals a pattern of trade disputes between the US, Canada, and Mexico, showcasing the evolution of their economic interdependence. Trump’s approach, contrasting with previous administrations, stands out with its emphasis on protectionist measures. This analysis explores the potential impacts on Canadian and Mexican economies, considering the interconnectedness of industries and the potential for supply chain disruptions. International responses and reactions vary, highlighting the global implications of this potential trade war.
The potential outcomes, from short-term economic fluctuations to long-term shifts in trade relations, are all carefully considered. The analysis also examines the specific industries most vulnerable to tariffs, along with the implications for employment, production, and supply chains. Finally, an examination of existing trade agreements, particularly NAFTA/USMCA, and their potential violation by the tariff threats is presented.
Historical Context of Trade Disputes
The ongoing economic relationship between the US, Canada, and Mexico is complex, shaped by decades of trade agreements, disputes, and evolving global economic landscapes. Understanding the historical context provides crucial insight into the current dynamics and potential outcomes of any trade tensions. This exploration will delve into key events, agreements, and resolutions (or lack thereof) to shed light on the intricate tapestry of trade relations among these nations.The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), and its successor the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), represent major milestones in the trilateral trade relationship.
These agreements aimed to reduce tariffs and trade barriers, fostering economic integration and growth. However, these agreements have also faced challenges and criticisms, highlighting the inherent complexities of international trade negotiations.
Key Trade Agreements and Disputes
The history of trade between the US, Canada, and Mexico is marked by a series of agreements and disputes. These agreements have aimed to streamline trade, reduce tariffs, and promote economic integration.
| Date | Event | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| 1994 | North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) signed | NAFTA aimed to eliminate tariffs and other trade barriers between the three countries, leading to increased trade and investment. However, it also sparked debates about job losses and economic impacts in certain sectors. |
| 2018 | United States initiated tariffs on steel and aluminum imports from Canada and Mexico. | Canada and Mexico retaliated with tariffs on U.S. goods, leading to trade tensions and uncertainty. Negotiations ultimately resulted in the USMCA. |
| 2020 | Implementation of the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) | The USMCA aimed to modernize NAFTA, addressing concerns regarding intellectual property, labor standards, and environmental protection. The agreement also contained provisions for dispute resolution. |
| Ongoing | USMCA implementation and enforcement | The USMCA continues to be implemented, and disputes regarding its provisions may arise. Enforcement mechanisms and ongoing monitoring of trade flows are essential to ensure its success. |
Evolution of the Trilateral Relationship
The evolution of trade relations between the US, Canada, and Mexico is characterized by a complex interplay of cooperation and conflict. Initially driven by the desire to reduce trade barriers and foster economic integration, the relationship has been marked by periods of both collaboration and contention.
- NAFTA’s initial impact on trade flows was significant. Increased trade and investment were observed, but concerns about job displacement and economic inequality in some sectors persisted.
- The implementation of the USMCA sought to address some of these concerns by incorporating provisions regarding labor standards and environmental protection. The USMCA aimed to create a more balanced and sustainable trade relationship.
- The ongoing disputes, including those related to tariffs, illustrate the complexities of international trade negotiations and the challenges of maintaining a stable and equitable trade environment. The relationship has evolved from a simple trade agreement to a complex economic relationship involving various stakeholders.
Examples of Previous Trade Disputes
Numerous disputes have arisen over the years, often related to trade practices, tariffs, and intellectual property rights. These disputes often highlight the inherent tension between promoting economic growth and protecting domestic industries.
- The 2018 tariffs imposed by the U.S. on steel and aluminum imports from Canada and Mexico illustrate a dispute concerning national security concerns and trade imbalances. Retaliatory tariffs by Canada and Mexico followed, creating a significant disruption to the trilateral trade relationship.
Trump’s Trade Policies and Stance
Donald Trump’s approach to international trade was characterized by a significant departure from previous administrations. He prioritized a protectionist stance, emphasizing renegotiating existing trade agreements and imposing tariffs on goods from various countries. This approach, while intended to benefit American industries, sparked considerable debate and resulted in trade tensions with key partners.
Trump’s Overall Approach to International Trade
Trump’s trade policies were largely driven by a belief that existing trade deals were disadvantageous to the United States. He argued that these agreements led to job losses and a decline in American manufacturing. A central component of his strategy was the use of tariffs, which he viewed as a tool to pressure other countries into renegotiating more favorable trade terms for the US.
Trump’s tariff threat against Canada and Mexico is definitely a hot topic right now, but it’s worth remembering that other things are happening in the world too. For example, a man who helped rob a Secret Service agent in Tustin, California, recently received a 4-year prison sentence. This highlights the need for strong law enforcement and justice systems, and perhaps, in the bigger picture, a need to find more constructive ways to resolve trade disputes than imposing tariffs.
All in all, it’s a complex web of issues, and I think it’s important to look at the wider context of events when discussing the tariff threat.
He often cited national security concerns and the need to protect American industries as justifications for his actions.
Trump’s Trade Policies Targeting Canada and Mexico
Trump initiated several trade disputes with Canada and Mexico, primarily focused on the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA). His administration renegotiated NAFTA, ultimately resulting in the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA). Key elements of these disputes included tariffs on steel and aluminum imports from both countries, with the argument that these tariffs were necessary to protect American industries.
The tariffs were a contentious aspect of these trade disputes, prompting retaliatory measures from Canada and Mexico.
Rationale Behind Trump’s Decisions
Trump’s rationale for his trade policies was multifaceted. He emphasized the need to bring back manufacturing jobs to the US and reduce the trade deficit. He often framed these decisions as a way to protect American workers and industries from unfair competition. The perceived unfair trade practices of other countries, such as alleged currency manipulation, were also frequently cited as a justification.
Comparison of Trump’s Trade Policies with Previous Administrations
| Characteristic | Trump Administration | Previous Administrations (e.g., Obama) |
|---|---|---|
| Overall Approach | Protectionist, focused on renegotiating trade deals and imposing tariffs. | Generally more supportive of free trade agreements. |
| Tariffs | Extensive use of tariffs on various goods from different countries, including Canada and Mexico. | Limited use of tariffs, primarily in response to specific, egregious violations of trade rules. |
| Trade Agreements | Renegotiation of existing agreements (e.g., NAFTA to USMCA). | Emphasis on negotiating and enforcing existing agreements. |
| Focus | Protecting American industries and jobs, reducing trade deficits. | Balancing economic interests with global trade relations. |
Impact on the Canadian and Mexican Economies
Trump’s tariff threats, particularly those targeting Canada and Mexico, posed significant economic risks. These actions, part of a broader trade strategy, threatened to disrupt established supply chains and potentially damage the economies of all three nations involved. The consequences varied considerably depending on the specific sector and the country affected.The potential economic consequences of these tariff threats were complex and multifaceted, with ripple effects extending far beyond the immediate participants.
Analyzing the potential impacts required a thorough understanding of the intricate web of trade relationships and the specific vulnerabilities of each nation’s economy. This analysis considers the potential for supply chain disruptions, sector-specific vulnerabilities, and the broader economic fallout.
Potential Economic Consequences for the Canadian Economy
Canada’s economy is heavily reliant on trade, particularly with the US. Tariffs imposed by the US would likely lead to higher prices for Canadian exports, potentially impacting sectors like agriculture, automotive, and manufacturing. The impact would be felt across various parts of the economy. For example, a significant portion of Canada’s agricultural output is exported to the US, making it vulnerable to retaliatory tariffs.
- Agricultural Sector: Canada’s agricultural sector, a crucial part of the Canadian economy, would face challenges if US tariffs are implemented. Products like wheat, soybeans, and dairy would likely experience reduced demand in the US market, impacting farmers’ income and potentially leading to job losses. This could trigger a domino effect throughout the supply chain, affecting input suppliers and processing facilities.
- Automotive Industry: The North American automotive industry is heavily integrated. Tariffs would disrupt the flow of parts and finished vehicles across the border, potentially increasing production costs and impacting competitiveness. The impact could extend to jobs and investment within the sector. Automakers could face increased costs due to tariffs on parts, affecting their profit margins and potentially leading to price increases for consumers.
- Manufacturing Sector: Many Canadian manufacturing sectors rely on the US market for raw materials and finished goods. Tariffs would make these imports more expensive, raising production costs for Canadian manufacturers and potentially reducing their competitiveness in both the domestic and international markets.
Potential Economic Consequences for the Mexican Economy
Mexico, similarly to Canada, is deeply intertwined with the US economy through trade. A significant portion of its exports go to the US. Tariffs would directly affect Mexican exports, potentially leading to a decline in overall economic activity and a decrease in employment.
- Manufacturing Sector: Mexico is a major manufacturing hub, particularly in the automotive industry. Tariffs would increase production costs for Mexican manufacturers, potentially impacting their profitability and competitiveness. This sector is highly reliant on the US market for components and final products.
- Agricultural Sector: Mexico’s agricultural exports to the US could be affected by tariffs. This could result in lower export revenues and potential job losses in the agricultural sector.
- Tourism Sector: A decline in the US economy or increased trade tensions could potentially affect tourism to Mexico, potentially impacting related businesses and jobs.
Supply Chain Disruptions
The potential for supply chain disruptions was a significant concern. The intricate network of suppliers and manufacturers across North America would likely be affected by tariffs. The disruption could lead to delays, increased costs, and a reduction in overall efficiency. The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) played a critical role in facilitating the flow of goods and services.
Comparative Analysis of Impacts
While both Canada and Mexico faced potential economic repercussions from the tariff threats, the specific impacts varied depending on the sector and the nature of trade relationships. Canada’s reliance on agricultural exports to the US, for example, meant that the agricultural sector was especially vulnerable. Mexico’s manufacturing sector, heavily involved in the production of automotive parts and other goods for the US market, was similarly at risk.
The potential for supply chain disruptions would affect both countries, potentially creating a domino effect throughout the region’s economy.
International Responses and Reactions: Trump Tariff Threat Canada Mexico
Trump’s tariff threats against Canada and Mexico sparked a wave of international reactions, ranging from outright opposition to attempts at negotiation and compromise. The global implications of these actions extended far beyond bilateral trade, highlighting the complexities of international relations in the 21st century. Understanding these responses is crucial to comprehending the ripple effects of protectionist trade policies.
Reactions from Other Countries
Numerous countries voiced concerns and criticisms regarding Trump’s tariff threats. Canada and Mexico, direct targets, actively sought alternative trade agreements and alliances to mitigate the negative impacts. Other nations, recognizing the potential for trade wars and disruptions, expressed their apprehension. For example, the European Union issued statements condemning the tariffs, emphasizing the importance of multilateral trade agreements.
Responses from International Organizations
International organizations like the World Trade Organization (WTO) played a critical role in addressing the situation. The WTO’s dispute settlement mechanism was invoked, highlighting the organization’s role in mediating trade disagreements. The WTO’s stance often aligned with the principles of free and fair trade, creating friction with protectionist policies. Moreover, the United Nations expressed concerns about the potential for trade conflicts to harm global economic stability.
Trump’s tariff threat against Canada and Mexico feels pretty insignificant compared to the groundbreaking discoveries NASA is making with asteroid samples from a watery world. Scientists are analyzing these samples to potentially unravel the secrets of life beyond Earth, while the trade disputes seem stuck in a bureaucratic loop. This new information from nasa asteroid samples watery world might just inspire some fresh thinking about global trade, perhaps even leading to a solution for the ongoing Canada/Mexico tariff issue.
Their stance frequently focused on the broader implications of such actions for developing nations.
Global Implications of Tariff Threats
The tariff threats had significant global implications, impacting not only the targeted economies but also the broader global economic landscape. The uncertainty created by these threats led to market volatility, as investors and businesses grappled with the potential for trade disruptions. Reduced trade volumes, decreased foreign investment, and rising prices were anticipated outcomes. Historical precedents, such as the 1930 Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act, demonstrate how protectionist policies can negatively impact international cooperation and economic growth.
Categorization of International Reactions
| Country/Organization | Alignment with Trump’s Policies | Specific Actions/Statements |
|---|---|---|
| Canada | Opposition | Negotiation efforts, diversification of trade partners. |
| Mexico | Opposition | Negotiation efforts, exploring alternative trade agreements. |
| European Union | Opposition | Statements condemning the tariffs, advocating for multilateral trade agreements. |
| World Trade Organization (WTO) | Opposition | Invoking dispute settlement mechanisms, upholding principles of free and fair trade. |
| United Nations | Opposition | Expressing concerns about the potential harm to global economic stability. |
| China | Indirect Opposition (or cautious response) | Potentially retaliatory measures and seeking alternative trade partners. |
| Other Countries (e.g., South America, Asia) | Mixed/Concerned | Varying degrees of concern and attempts to navigate the changing trade landscape. |
This table categorizes various international responses based on their stance toward Trump’s tariff threats. The table shows a clear pattern of opposition from key international players to the protectionist policies. Note that some countries might exhibit a cautious or indirect opposition, potentially due to their own economic interests or political considerations.
Potential Outcomes and Future Implications

The looming threat of tariffs on Canadian and Mexican goods, imposed by the previous US administration, presents a complex web of potential outcomes. These threats, stemming from disagreements over trade practices and economic policies, could have significant short-term and long-term consequences for the economies of all three nations. Understanding the potential scenarios, the reactions of each country, and the possible alternatives is crucial to predicting the future trajectory of North American trade relations.
Short-Term Outcomes of Tariff Threats
The immediate impact of tariffs would likely be felt by consumers in all three countries. Higher prices for imported goods, particularly those originating from Canada and Mexico, are a near certainty. This could lead to inflation and potentially impact consumer spending habits. Supply chains, already facing disruptions from global events, would likely experience further stress. Businesses relying on imports for raw materials or components could face increased costs and reduced profitability.
Companies in the affected sectors would need to adapt quickly to maintain competitiveness.
Long-Term Impacts on Trade Relations
The long-term consequences of these tariff threats extend beyond immediate economic impacts. Erosion of trust and confidence in trade relationships could lead to a significant restructuring of supply chains. Businesses might seek alternative suppliers, potentially shifting manufacturing and distribution hubs outside of North America. This could create a loss of jobs in sectors reliant on cross-border trade and investment.
It could also lead to retaliatory measures from Canada and Mexico, further escalating the trade conflict. A protracted trade war could have lasting negative effects on the economies of all three countries.
Potential Scenarios Based on Responses
A range of scenarios could unfold, based on the specific responses of the three nations. If the US does not implement tariffs, the existing trade relations could continue. However, if tariffs are imposed, Canada and Mexico could retaliate with their own tariffs, triggering a trade war. A negotiated agreement, addressing the concerns of all parties, would be the most desirable outcome, minimizing the negative impacts on consumers and businesses.
However, finding common ground in complex trade negotiations is often challenging. Historical precedents, such as the trade wars of the past, demonstrate the difficulty of reaching a resolution that satisfies all parties involved.
The Trump administration’s tariff threat against Canada and Mexico is definitely a hot topic right now. It’s a complex issue with potential economic consequences, and it’s certainly impacting global trade. Speaking of impactful events, I was just reading about how Sharks forward, Vitek Vanecek, will be out for some time with a fractured cheek ( vitek vanecek to miss time with fractured cheek tomas hertl reflects on sharks tribute return to san jose ).
Hopefully, these trade disputes get resolved soon, and we can all get back to focusing on things like hockey injuries, instead of tariffs!
Alternative Solutions and Their Viability
Several alternative solutions are possible. A comprehensive trade agreement, renegotiating existing trade pacts to address specific concerns, is a potential pathway to resolve trade disputes. Implementing alternative dispute resolution mechanisms to address trade disagreements could avoid escalating conflicts. Strengthening international trade rules and regulations, through the appropriate forums, might offer a more stable and predictable environment for cross-border trade.
However, the viability of each solution depends on the willingness of all three countries to engage in constructive dialogue and compromise. Historical experience suggests that finding mutually acceptable solutions in complex trade negotiations is difficult. Often, compromise and mutual understanding are necessary to achieve a resolution.
Illustrative Examples of Affected Industries
Tariffs, particularly those imposed on goods traded between the US, Canada, and Mexico, can have significant ripple effects across numerous industries. The interconnected nature of supply chains means that a disruption in one country can quickly impact producers and consumers in the others. Understanding these impacts is crucial for assessing the potential consequences of trade disputes and mitigating their negative effects.
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry serves as a prime example of the complex interdependencies within North American trade. US automakers heavily rely on parts sourced from Canada and Mexico, and vice versa. Tariffs would likely increase the cost of these components, potentially driving up prices for vehicles and reducing competitiveness in the global market. This could lead to job losses in manufacturing and related industries in all three countries.
Moreover, the disruption to supply chains could significantly impact production timelines and efficiency, leading to delays in the manufacturing process.
- US manufacturers of vehicles and parts rely on imports from Canada and Mexico. Increased tariff costs on these parts would directly translate to higher production costs for US companies. This could lead to decreased profitability, potentially forcing companies to cut production or reduce employment.
- Canadian and Mexican automotive manufacturers face similar challenges. Increased tariffs on US-made parts would drive up their costs, affecting their ability to compete in the global market and impacting employment within their automotive sectors.
- The impact is not limited to the direct participants. Related industries like logistics, warehousing, and retail would also feel the strain as reduced production and higher prices affect consumer demand.
Agricultural Sector
The agricultural sector, a significant contributor to the economies of all three countries, is highly vulnerable to trade disputes. Tariffs on agricultural products like corn, soybeans, and dairy products can severely impact farmers’ incomes and potentially disrupt the export markets for these commodities. This disruption is amplified by the integration of farming practices and supply chains across borders.
- Farmers in the US, Canada, and Mexico who export products to one another face significant price increases due to tariffs. This can lead to reduced profitability and potentially push farmers to reduce production or even leave the industry.
- The interdependence is further emphasized by the reliance of various sectors on these agricultural products. For example, livestock producers and food processors depend on a stable supply of agricultural commodities.
- The disruption to agricultural trade can impact employment in rural communities, as farms and processing plants may reduce their workforce.
Machinery and Equipment
The machinery and equipment sector is characterized by complex supply chains, with components and manufacturing processes spread across the three countries. Tariffs on these goods would increase the cost of production for manufacturers, potentially impacting their competitiveness and employment prospects. This ripple effect would also affect other industries that rely on these manufactured goods.
| Industry | US Sensitivity | Canada Sensitivity | Mexico Sensitivity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | High | High | High |
| Agricultural | Medium | Medium | Medium |
| Machinery & Equipment | High | Medium | Medium-High |
Note: Sensitivity levels are subjective and can vary depending on specific factors like the degree of import reliance and diversification of supply chains.
Analysis of Existing Trade Agreements
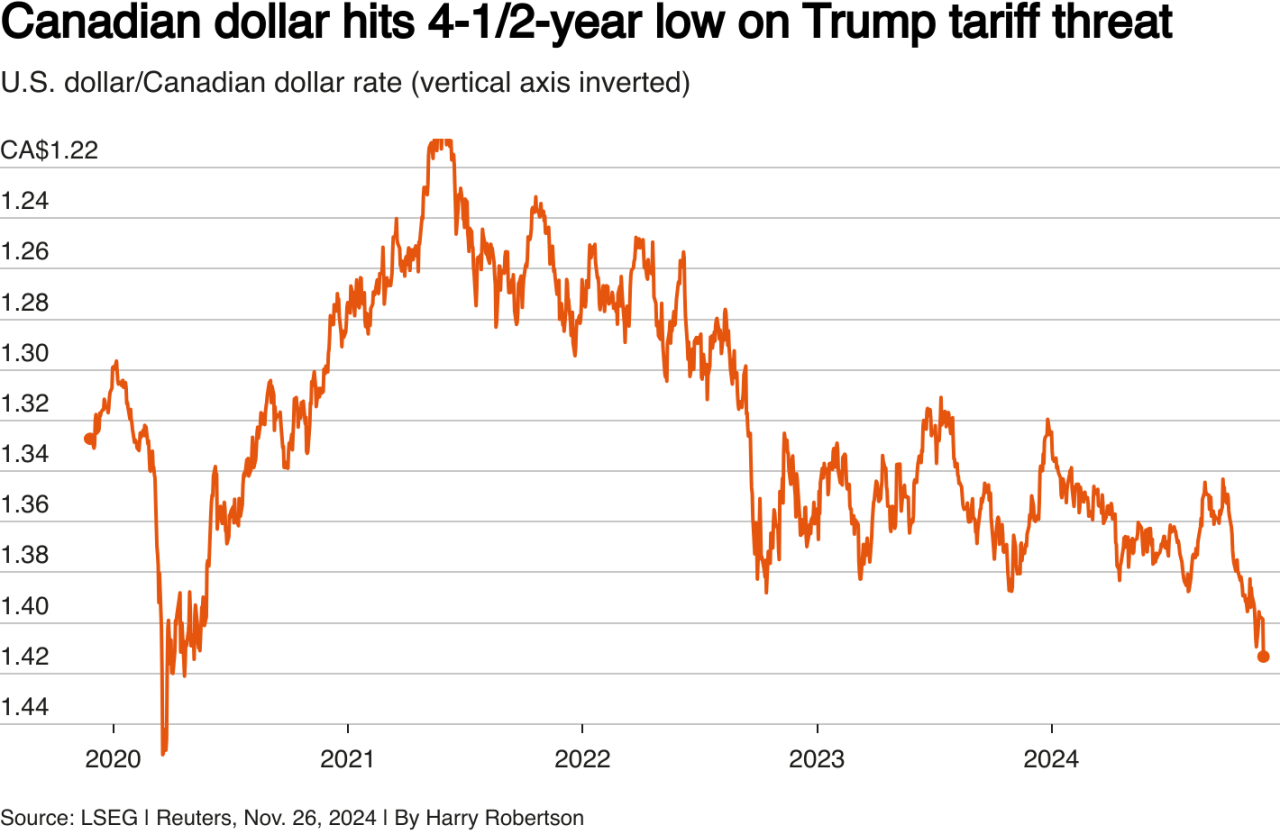
The USMCA, the successor to NAFTA, aims to regulate trade between the US, Canada, and Mexico. Understanding its provisions is crucial in evaluating the potential impact of tariff threats. These threats, if implemented, could significantly alter the existing economic landscape of North America.The USMCA, like its predecessor, seeks to establish a framework for fair and reciprocal trade, fostering economic growth within the region.
However, the potential for conflict and renegotiation exists when one party feels disadvantaged or that the terms of the agreement are not being adhered to.
Key Provisions of USMCA Relevant to Tariff Threats, Trump tariff threat canada mexico
The USMCA encompasses a broad range of trade-related provisions. Crucial elements relevant to potential tariff threats include rules of origin, dispute settlement mechanisms, and national security exceptions.
- Rules of Origin: These stipulations dictate the percentage of a product’s components that must originate within the USMCA bloc to qualify for preferential tariff treatment. Violation of these rules, through the importation of goods not meeting the required standards, could trigger retaliatory tariffs.
- Dispute Settlement Mechanisms: The USMCA Artikels procedures for resolving trade disputes. If a party believes another party is violating the agreement, they can initiate a dispute settlement process. This process often involves consultations, panel reviews, and potential remedies like the imposition of tariffs.
- National Security Exceptions: The USMCA includes provisions that allow for the imposition of tariffs on goods deemed essential to national security. However, these provisions are often subject to scrutiny and legal challenges, as they can be invoked in ways that go beyond genuine national security concerns.
How Tariff Threats Could Undermine USMCA
The threat of tariffs can potentially undermine the USMCA in several ways. A unilaterally imposed tariff, not authorized by the agreement’s dispute resolution procedures, could be viewed as a violation of the agreement’s spirit. The threat of retaliation by other parties is also a major concern.
Potential Legal Challenges to Tariffs
If the tariffs are deemed to violate the USMCA or other international trade agreements, various legal avenues could be explored. Challenges could be based on the premise that the tariffs are not justified by national security concerns or that they violate the agreement’s dispute settlement provisions.
- International Trade Organizations (like the WTO): If the tariffs violate WTO rules, a complaint could be filed at the WTO, potentially leading to rulings that require the removal of the tariffs.
- Bilateral Dispute Resolution: The USMCA itself has provisions for resolving disputes between the member nations. Canadian and Mexican governments could initiate these mechanisms to challenge the legality of the tariffs.
- Domestic Courts: Legal challenges could also be filed in US courts, potentially seeking injunctions or other remedies to block the implementation of the tariffs.
Interrelation of Trade Agreements and Tariff Threats (Visual Representation)
| Trade Agreement | Provisions Relevant to Tariffs | Potential Violations | Legal Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| USMCA | Rules of origin, dispute settlement, national security exceptions | Unilateral imposition of tariffs outside dispute resolution, use of national security exceptions beyond legitimate concerns | WTO complaints, USMCA dispute resolution mechanisms, domestic court challenges |
| WTO | Most-favored-nation principle, dispute settlement | Tariffs not justified by WTO standards, lack of reciprocity in tariff application | WTO dispute settlement proceedings |
Final Conclusion
In conclusion, the potential Trump tariff threat against Canada and Mexico is a significant event with far-reaching implications. The intricate interplay of historical context, Trump’s trade policies, economic impacts, international reactions, and potential outcomes paint a complex picture. The analysis of affected industries and existing trade agreements provides a deeper understanding of the potential disruptions to the North American economic landscape.
The future trajectory of this situation remains uncertain, but this comprehensive overview offers a valuable framework for understanding the potential consequences and potential alternative solutions.