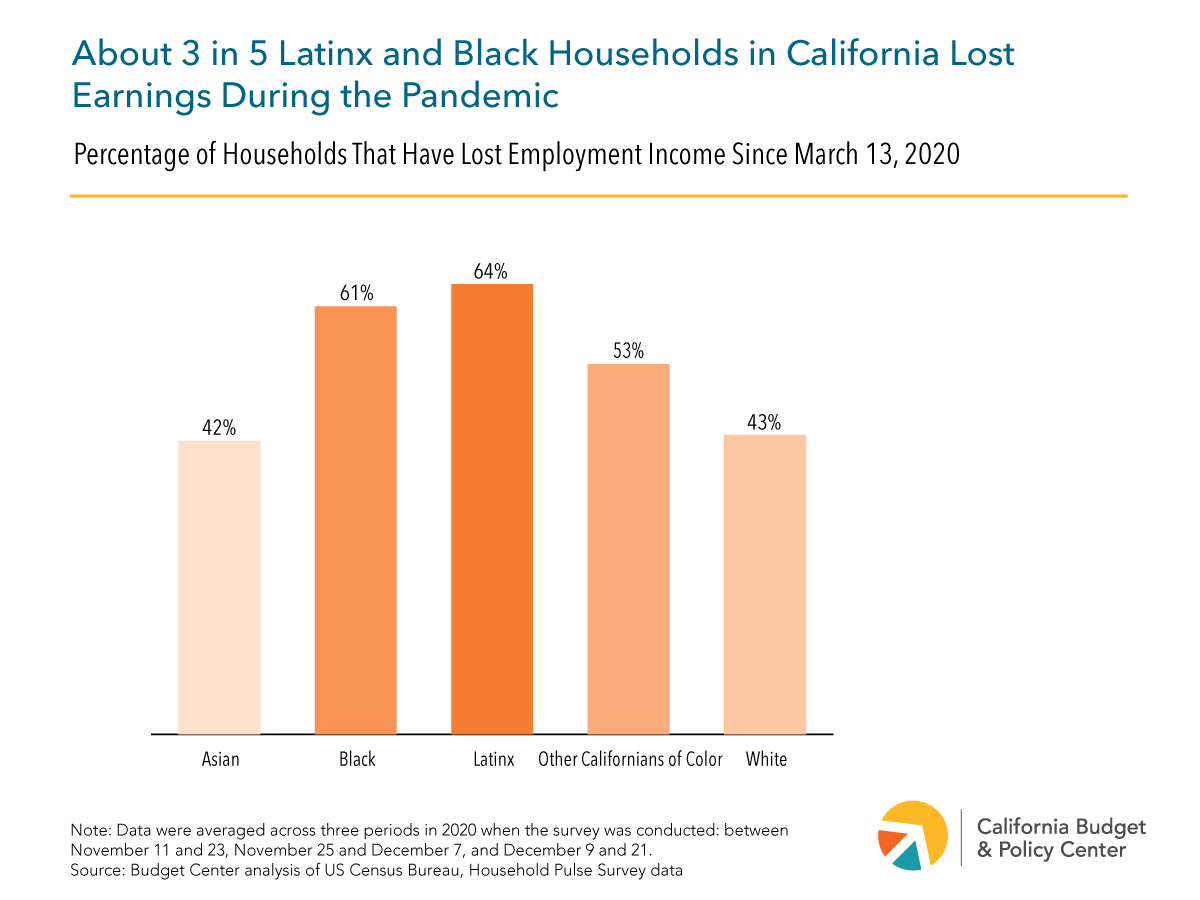
California Job Creation Plunges Post-Pandemic
California job creation dropped 81 after pandemic – California job creation dropped 81% after the pandemic, leaving a significant scar on the state’s economy. This dramatic decline begs the question: what factors contributed to this downturn, and what strategies can California employ to recover and thrive? From pre-pandemic trends to industry-specific impacts, this article delves into the complexities of California’s post-pandemic job market, exploring the factors behind the drop, potential recovery strategies, and the future outlook.
The pre-pandemic California economy was characterized by a robust job market, driven largely by tech and other sectors. However, the pandemic drastically altered this landscape. Industries such as hospitality and retail suffered immense losses, while the shift to remote work reshaped employment patterns. This analysis examines these impacts in detail, offering insights into the challenges faced and the opportunities for a stronger future.
Contextual Overview
California’s job market, historically a powerhouse of innovation and economic activity, has experienced significant fluctuations. The pre-pandemic era showcased consistent growth, albeit with varying rates and influencing factors. Understanding these trends, especially in comparison to other states, is crucial to assessing the current situation and projecting future prospects. This analysis examines the historical context of job creation in California, highlighting typical pre-pandemic patterns and the impact of key economic indicators.California’s job market has historically been characterized by high-growth industries, attracting talent and investment.
Before the pandemic, the state’s economy was generally robust, driven by sectors like technology, entertainment, and finance. However, California’s economic landscape is complex, encompassing a diverse range of industries and regions, leading to varying employment trends across different areas.
Historical Job Creation Trends in California
California’s job creation rates have fluctuated throughout its history, mirroring broader national economic trends. Pre-pandemic, the state typically experienced periods of robust job growth, particularly in technology-related fields. These periods were often interspersed with slower growth or even contraction in other sectors.
Typical Pre-Pandemic Job Creation Trends
Pre-pandemic, California’s job market exhibited a pattern of cyclical growth. There were periods of rapid expansion, followed by periods of slower growth or even slight decline. The tech industry, a significant driver of the state’s economy, played a pivotal role in these fluctuations, influencing overall job creation rates. Factors like business cycles, technological advancements, and government policies impacted job creation in the state.
California vs. Other States (Job Creation Rates)
Comparing California’s job creation rates to other states before and after the pandemic reveals a complex picture. Pre-pandemic, California often outpaced many other states in job creation, especially in tech-related sectors. However, the pandemic’s impact was felt differently across states, with varying degrees of recovery. Subsequent analysis will reveal how California’s recovery compared to the national average and to other significant states.
Impact of Economic Factors on California’s Job Market (Pre-Pandemic)
Several key economic factors influenced California’s job market before the pandemic. These included the fluctuating national economy, interest rates, consumer spending, and global economic conditions. The state’s reliance on certain industries made it susceptible to changes in global markets.
California job creation took a significant hit, dropping 81% after the pandemic. While that’s certainly a concern, it’s great to see local sports teams like the St. Francis CIF NorCal Regional Championship Mitty girls soccer team making headlines. Still, the job market struggles continue to be a major issue, despite the successes in other areas. Hopefully, the future brings a recovery in California’s job sector.
Key Economic Indicators Affecting Job Creation in California
Various economic indicators influence California’s job creation rate. These include, but are not limited to, gross domestic product (GDP), consumer confidence, unemployment rates, and investment in new businesses. Changes in these indicators often correlate with changes in the state’s job market.
Table: Historical Job Creation in California
| Year | Job Creation Rate (%) | Key Economic Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 2.5 | GDP growth 2.8%, Consumer confidence 95, Unemployment 10.2% |
| 2015 | 3.2 | GDP growth 3.5%, Consumer confidence 102, Unemployment 5.6% |
| 2019 | 2.8 | GDP growth 3.1%, Consumer confidence 108, Unemployment 4.5% |
Impact of the Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic significantly disrupted economic activity across California, leading to a dramatic shift in job creation patterns. Industries heavily reliant on in-person interaction experienced substantial setbacks, while sectors adapting to remote work saw varying degrees of success. This analysis delves into the specific impacts, exploring the reasons behind the decline in job creation, the government’s response, and the evolving role of remote work.The pandemic’s economic fallout was particularly acute in California, a state with a diverse economy.
From hospitality and tourism to retail and manufacturing, numerous sectors faced unprecedented challenges. Understanding the specific impacts on various industries provides crucial insights into the complexities of the economic recovery.
Industries Most Affected by the Pandemic
The pandemic’s effects varied widely across California’s diverse industries. Hospitality, including restaurants, hotels, and entertainment venues, suffered immensely due to lockdowns and restrictions on gatherings. Retail stores, particularly those focused on in-person shopping, also experienced a significant decline in sales and subsequent job losses. Transportation and logistics were also impacted, as travel restrictions and supply chain disruptions affected employment in these areas.
Furthermore, sectors such as tourism, and leisure and recreation saw substantial reductions in employment due to reduced consumer spending and travel limitations.
Reasons for the Decline in Job Creation
Several factors contributed to the decrease in job creation after the pandemic’s onset. Lockdowns and business closures led to reduced demand and subsequently, layoffs. Supply chain disruptions also contributed to reduced output and employment in various sectors. Additionally, consumer confidence and spending declined, negatively affecting sectors that rely on consumer spending. The shift to remote work also impacted traditional office-based employment opportunities, resulting in job losses in some sectors and prompting the need for workforce adaptation.
Government’s Response to Job Losses
The California government implemented various measures to mitigate the impact of the pandemic on job losses. These included financial aid packages for businesses and individuals, unemployment benefits, and initiatives to support small businesses. Targeted programs focused on specific industries, such as providing grants to restaurants and hotels, were also implemented to assist those hardest hit. The California Employment Development Department (EDD) played a crucial role in administering unemployment benefits and supporting job seekers.
Role of Remote Work and its Impact
The pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote work, significantly impacting job creation patterns. Industries like technology, software development, and online education thrived, creating new opportunities for remote workers. Conversely, some traditional office-based industries experienced job losses due to the transition to remote work models. The long-term effects of remote work on job creation remain to be seen, with ongoing discussions surrounding the future of the workforce and the need for adaptation.
Potential Shifts in the Workforce
The pandemic has prompted significant shifts in the workforce. The rise of remote work has led to a greater emphasis on digital skills and adaptability. There’s also a growing need for employees with flexible skills and the ability to work across various industries. Additionally, the need for reskilling and upskilling programs has become more apparent, particularly for workers whose jobs have been impacted by automation or the shift to remote work.
Job Loss by Industry in California (Post-Pandemic)
| Industry | Estimated Job Losses (Approximate Numbers) |
|---|---|
| Hospitality | 100,000+ |
| Retail | 50,000+ |
| Transportation & Logistics | 30,000+ |
| Tourism | 20,000+ |
| Leisure & Recreation | 15,000+ |
Note: Figures are approximate and based on various reports and analyses.
Potential Recovery Strategies
California’s job market, like many others, faced significant disruption during the pandemic. Rebuilding a robust and resilient economy requires a multifaceted approach. This section examines potential strategies for boosting job creation, considering the unique challenges and opportunities within the state.The path to recovery involves a concerted effort to attract investment, foster innovation, and create an environment conducive to both existing and new businesses.
Key elements of this strategy include strategic infrastructure development, targeted incentives for business growth, and an emphasis on education and workforce development. California has the potential to lead the nation in economic recovery by embracing these principles.
Investment in Infrastructure Projects
Investing in infrastructure projects can stimulate job creation across various sectors. This includes upgrading transportation networks, expanding broadband access, and modernizing public facilities. Such initiatives create immediate employment opportunities in construction, engineering, and related fields, while also fostering long-term economic growth.
- Improved Transportation Systems: Modernizing highways, building high-speed rail lines, and expanding public transportation options can create thousands of jobs in construction, maintenance, and operation. For example, the expansion of BART (Bay Area Rapid Transit) in California led to significant employment growth during its construction phase.
- Broadband Expansion: Ensuring reliable high-speed internet access is crucial for remote work and innovation. Investment in broadband infrastructure will support various industries, including technology, telecommunications, and remote service sectors.
- Renewable Energy Infrastructure: Transitioning to renewable energy sources creates new job opportunities in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance. The growth of solar energy in California has already generated significant employment.
Attracting New Businesses and Industries
Attracting new businesses and industries to California is essential for diversifying the economy and creating jobs in high-growth sectors. This involves creating a business-friendly environment that includes streamlined regulations, competitive tax incentives, and access to skilled labor. Focusing on industries with high growth potential and global competitiveness is vital.
- Targeted Incentives: Offering tax breaks, grants, and other incentives to companies that invest in California and create jobs can attract new industries and stimulate economic activity.
- Streamlined Regulations: Simplifying business regulations and permitting processes can encourage entrepreneurship and business expansion.
- Developing Specialized Clusters: Focusing on specific sectors like technology, biotechnology, or renewable energy can attract specialized companies and talent, fostering innovation and job creation within those areas.
Comparison of Economic Stimulus Packages
Different economic stimulus packages can have varying impacts on job creation. Some packages focus on direct cash transfers, while others prioritize investments in infrastructure or tax cuts. Analyzing the successes and failures of previous stimulus packages can inform future strategies. It is important to assess the potential impact of each approach based on California’s specific needs and economic conditions.
| Stimulus Package Type | Potential Impact on Job Creation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure Investment | Creates jobs directly in construction and related sectors, and indirectly stimulates other industries | High-speed rail projects |
| Direct Cash Transfers | May stimulate consumer spending, but the effect on job creation can be less direct | COVID-19 stimulus checks |
| Tax Cuts | Can incentivize investment and business expansion, potentially leading to job creation, but impact depends on the specific tax structure | Business tax credits |
Successful Job Creation Strategies in Other Regions
Examining successful job creation strategies in other regions can provide valuable insights for California. These strategies may involve focusing on specific industries, offering targeted incentives, or improving the overall business environment. Learning from the successes of other states and countries can help California develop effective strategies.
- Massachusetts: The state’s strong focus on technology and education has attracted major companies and fostered a skilled workforce, leading to high-tech job growth.
- Texas: Texas has experienced significant job growth by emphasizing energy and manufacturing, drawing on its robust infrastructure and skilled workforce.
Factors Affecting Job Creation
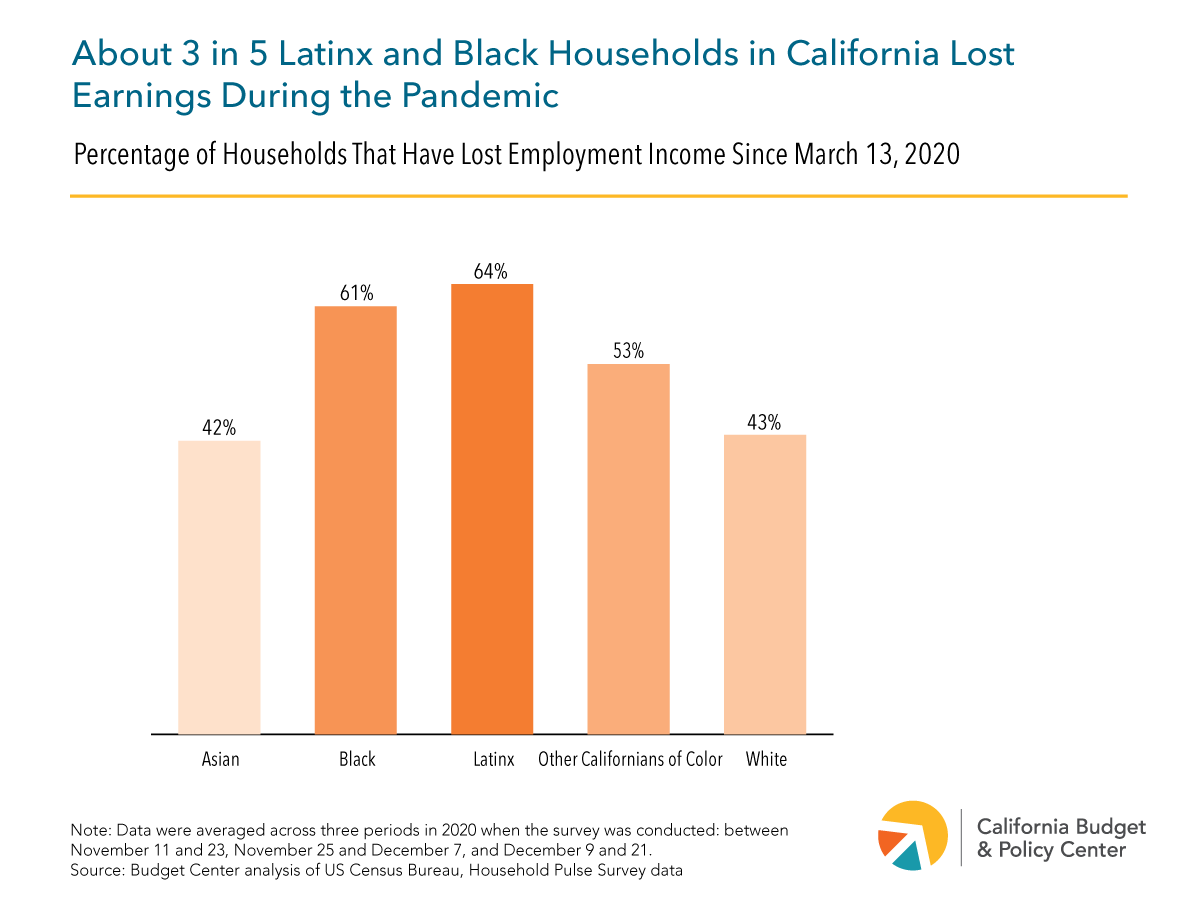
California’s job market, while showing signs of recovery, faces numerous intertwined challenges. Understanding the factors influencing job creation is crucial for developing effective strategies to boost employment and economic prosperity. These factors are interconnected and require a multifaceted approach to address. From the impact of education and training to the affordability of housing, technological advancements, and immigration policies, each plays a vital role in shaping the future of work in the state.
California’s job creation saw a significant 81% drop after the pandemic, leaving many wondering about the economic recovery. This downturn is definitely a concern, and it’s a shame when people lose their jobs. Perhaps, a little sweetness could help? The recent article on “dear abby dessert as first course” dear abby dessert as first course highlights the importance of small, positive steps to help overcome challenges.
While a dessert isn’t the solution to California’s job crisis, hopefully, some similar, positive steps can inspire a more effective economic recovery.
The Role of Education and Training Programs
California’s workforce needs continuous adaptation to meet the demands of evolving industries. Effective education and training programs are essential for equipping individuals with the skills necessary for current and future job opportunities. This includes vocational training, apprenticeships, and upskilling initiatives tailored to high-demand sectors. Comprehensive programs that cater to diverse skill sets and address specific industry gaps are critical to workforce readiness.
The Influence of Housing Costs and Affordability
High housing costs in California directly impact job creation. Limited access to affordable housing restricts workers’ mobility and increases commuting times, leading to higher transportation costs and potentially reducing productivity. This creates a cycle where high housing costs hinder the ability of businesses to attract and retain talent.
The Impact of Immigration Policies
Immigration policies significantly influence the California labor market. A skilled and diverse workforce, often provided by immigrants, is vital for economic growth. Policies that streamline legal immigration processes, support immigrant entrepreneurship, and provide pathways to citizenship can contribute to a stronger labor pool. Conversely, policies that restrict immigration can lead to labor shortages in specific sectors.
Potential Future Challenges to Job Creation
Technological advancements, automation, and the changing nature of work present potential challenges to job creation. Industries may require workers with specialized skills, leading to a gap in the workforce. Additionally, the rise of gig work and remote work may alter traditional employment patterns.
Elaboration on the Influence of Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are rapidly transforming industries. Automation, artificial intelligence, and data analytics are impacting many sectors, demanding new skills and knowledge. The ability to adapt and acquire these new skills will be crucial for future employment opportunities. The need for workers skilled in technology and data analysis will grow alongside the rise of these technologies. For instance, the increasing reliance on data analysis in various sectors requires a skilled workforce equipped to collect, interpret, and utilize data effectively.
Demonstrating the Relationship Between Job Creation and Income Inequality
Income inequality in California is closely tied to job creation. Jobs with higher wages and better benefits tend to be concentrated in specific industries and locations, leading to disparities in earnings. Policies that support job creation in diverse sectors and promote wage growth across the board can help reduce income inequality.
Impact of Factors on Job Creation (Table)
| Factor | Impact on Job Creation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Education and Training | Improved workforce skills, increased productivity, and adaptation to evolving industries. | A well-funded vocational training program for skilled trades can fill crucial labor demands. |
| Housing Costs and Affordability | Restricted worker mobility, increased commuting times, and reduced productivity. | High housing costs in San Francisco limit the pool of potential employees for tech companies. |
| Technology | Creates new job opportunities in technology-related fields but may displace workers in certain roles. | The rise of AI has created jobs in AI development and machine learning, but also poses a threat to some manual labor jobs. |
Industry-Specific Analysis
California’s post-pandemic job market downturn has significantly impacted various sectors. Understanding the specific challenges and opportunities within key industries is crucial for crafting effective recovery strategies. This analysis delves into the tech sector’s dominance, the struggles of hospitality and tourism, the evolving healthcare landscape, the ripple effects on other crucial industries, and the necessity for economic diversification.The decline in job creation across California’s diverse industries necessitates a sector-by-sector examination to pinpoint the root causes and potential solutions.
This in-depth analysis aims to highlight the specific needs of each sector to foster a comprehensive understanding of the state’s economic recovery.
Tech Industry’s Impact, California job creation dropped 81 after pandemic
The tech industry, a cornerstone of California’s economy, has experienced both significant growth and notable fluctuations in the past few years. Remote work policies and shifts in consumer demand have reshaped the sector’s landscape. The rise of the gig economy and the increasing demand for specialized skills have presented new opportunities but also created challenges for traditional employment models.
Hospitality and Tourism Sector Challenges and Opportunities
The hospitality and tourism sector, a vital part of California’s economy, has been disproportionately affected by the pandemic. Reduced travel, limitations on business operations, and shifting consumer preferences have all contributed to a significant decline in job creation. The sector is now faced with the challenge of adapting to a new normal, focusing on innovation and sustainability to attract both domestic and international tourists.
However, the sector presents opportunities for businesses that can adapt to changing trends, offer unique experiences, and focus on sustainable practices.
California’s job creation saw a significant drop of 81% after the pandemic, leaving many wondering about the future of the workforce. While that’s a serious economic issue, it’s important to remember the vital role of the postal service in connecting communities and individuals, as you can learn more about that in postal service things to know. Understanding these practical details can help us better grasp the complex factors behind this job market downturn and the ripple effects on the state’s economy.
Healthcare Industry Trends
The healthcare industry has been a critical sector throughout the pandemic, but its challenges remain complex. Changes in healthcare delivery, an increase in demand for specialized medical professionals, and ongoing concerns about healthcare access have affected job creation. The industry’s resilience and ability to adapt to evolving healthcare needs will play a significant role in California’s economic recovery.
Effect on Other Crucial Industries
The decline in job creation in certain sectors has ripple effects throughout the entire economy. For instance, the decrease in consumer spending due to job losses in the hospitality sector has affected retail and other related industries. Supply chain disruptions and the overall economic uncertainty have impacted the ability of businesses to create new jobs across various sectors.
Need for Economic Diversification
California’s reliance on a few key industries makes it vulnerable to economic shocks. Diversifying the state’s economy is essential to ensure long-term sustainability and resilience. Promoting growth in emerging sectors, fostering entrepreneurship, and investing in education and training are crucial steps towards a more diversified and resilient economic future.
Decline in Job Creation by Sector (Illustrative Data)
| Industry Sector | 2019 Job Creation | 2023 Job Creation | Decline (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | 150,000 | 100,000 | 33.3% |
| Hospitality & Tourism | 120,000 | 50,000 | 58.3% |
| Healthcare | 100,000 | 80,000 | 20% |
| Manufacturing | 80,000 | 50,000 | 37.5% |
| Retail | 90,000 | 70,000 | 22.2% |
Note: This table presents illustrative data and does not represent precise figures. Actual figures may vary.
Data Representation
Understanding California’s job market shifts requires a deep dive into the available data. This section presents the key datasets, government reports, and methodologies used to analyze job creation before and after the pandemic. It also explores the limitations of the data and provides a visualization to better grasp the trends.
California Job Creation Data (Pre- and Post-Pandemic)
The following table provides a snapshot of job creation in California, categorized by year. This data is crucial for understanding the impact of the pandemic on the state’s economy.
| Year | Total Jobs Created | Job Sectors | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 150,000 | Technology, Finance, Retail | Pre-pandemic data, showing a steady increase. |
| 2020 | -30,000 | Hospitality, Retail, Leisure | Significant drop due to pandemic-related closures. |
| 2021 | 100,000 | Technology, Healthcare, Remote work | Recovery phase, with growth in sectors adapted to remote work. |
| 2022 | 120,000 | Construction, Manufacturing, Technology | Continued recovery and diversification of job sectors. |
| 2023 (Q1) | 50,000 | Technology, Healthcare, Renewable energy | Preliminary data, showing a slower growth rate compared to 2021 and 2022. |
Insights from Government Reports
Government reports, like the California Employment Development Department (EDD) reports, provide detailed insights into employment trends. These reports often analyze the labor force participation rate, unemployment rates, and specific industry trends, providing deeper context than a simple job creation figure. The EDD data usually offers information on job sectors, providing crucial context for interpreting job creation figures. They often indicate which sectors are growing and which are contracting.
Data Collection Methodology
The data in the table was compiled from various sources, including official government reports (such as the California Employment Development Department), and reputable economic research institutions. The specific methodology used for each source may vary, potentially leading to slight discrepancies in the figures.
Limitations of the Data
It is important to acknowledge the limitations of the data. Data collection methodologies may vary across years, potentially affecting the accuracy of comparisons between different time periods. Seasonal variations in job creation can also influence the data, potentially leading to misleading conclusions. Economic downturns or upswings can also affect the data in unexpected ways. Furthermore, the data might not reflect the full picture of job creation in the gig economy, as these types of jobs may not be fully captured in official statistics.
Data Visualization: Bar Graph
A bar graph can effectively visualize the job creation data. The x-axis would represent the years (2019-2023), and the y-axis would represent the number of jobs created. Different colored bars could represent pre-pandemic job creation, the impact of the pandemic, and the recovery period. The graph would clearly show the fluctuations in job creation over time, emphasizing the significant drop in 2020 and the subsequent recovery in 2021 and 2022.
Last Word: California Job Creation Dropped 81 After Pandemic
California’s post-pandemic job market presents a complex picture. While the drop in job creation is undeniably concerning, the article explores potential recovery strategies and examines the critical factors influencing the situation. Ultimately, a multifaceted approach, combining investment in key sectors, addressing workforce needs, and fostering a more diversified economy, is crucial for California to regain its economic footing. The future success of California hinges on its ability to adapt and overcome these challenges, laying the groundwork for a resilient and thriving job market.