Family Tree Creating Tools Your Guide
Family tree creating tools are revolutionizing how we document and share our family histories. From simple online platforms to powerful software suites, there’s a tool for every family, every skill level, and every research need. This guide explores the landscape of these tools, delving into their features, functionalities, and user experiences, helping you navigate the choices and find the perfect fit for your family’s needs.
We’ll cover everything from the basics of creating a family tree to advanced functionalities like importing data, collaborating with family members, and exploring specialized tools for specific genealogical research. Prepare to discover the fascinating world of family history, easily accessible with the right tools.
Introduction to Family Tree Tools
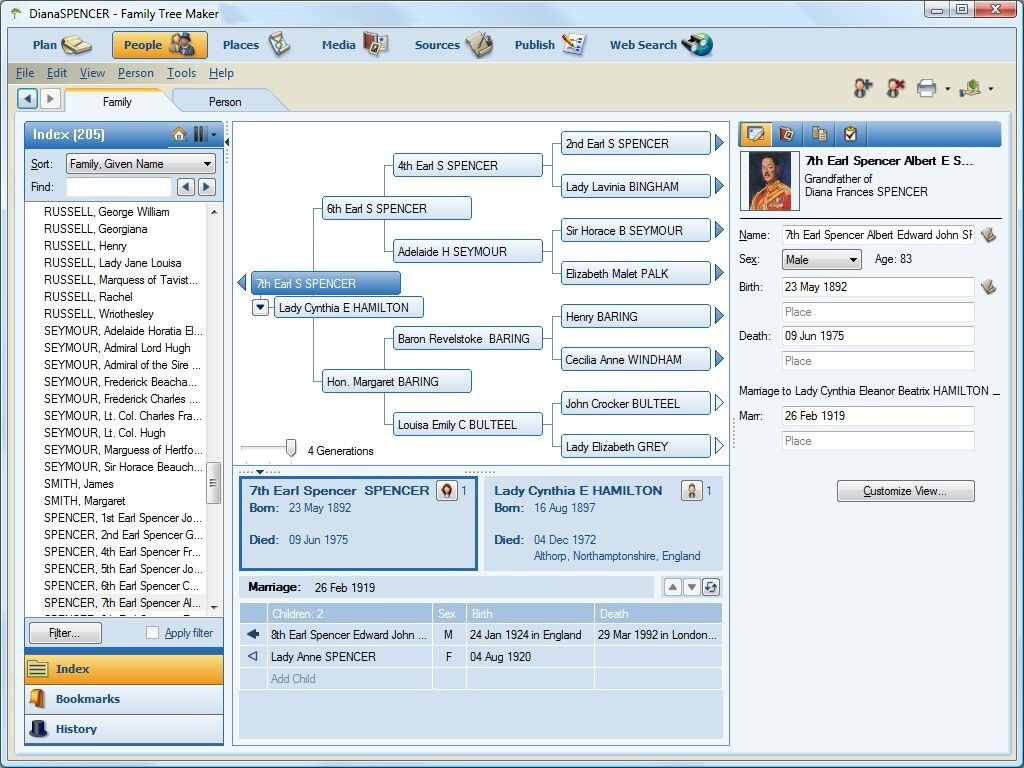
Unraveling the intricate tapestry of family history has never been easier. Modern technology offers a wealth of tools to meticulously document, organize, and visualize family connections. These tools range from simple websites to sophisticated software programs, catering to various needs and technical abilities. From tracing ancestral roots to sharing family stories with future generations, these tools empower individuals to explore their heritage.Family tree creation tools provide a structured approach to documenting lineage.
They allow users to input and manage information about their family members, creating a visual representation of relationships. This facilitates easy understanding of family connections, identifies common ancestors, and helps to piece together a more complete family history.
Types of Family Tree Tools
Various platforms cater to the needs of family historians. These platforms include software applications, user-friendly websites, and mobile apps, each offering a different level of features and complexity. Software solutions often provide more robust features and customization options. Websites offer a convenient, often free, way to create and share family trees. Mobile applications are designed for on-the-go access and data management.
Popular Family Tree Creation Tools
Several popular tools have emerged as favorites among family historians. These tools include Ancestry.com, FamilySearch, and MyHeritage. These platforms offer comprehensive features, user-friendly interfaces, and a vast database of historical records. Each tool has a specific approach and range of features, tailoring to different needs and levels of experience.
Key Features and Functionalities
Common features across these tools include the ability to add and edit individual profiles, map relationships, import data from various sources, and create visual representations of family trees. The ability to integrate external records and documents is also a crucial functionality. The user-friendliness of the interface and the ease of navigation are essential for effective usage. Many tools also provide options for sharing and collaborating on family trees with other members.
“The ease of use and the ability to visualize family relationships are critical factors in the success of these tools.”
Comparison of Popular Tools
The following table compares three popular family tree tools based on ease of use, features, and cost. These factors are essential for choosing the most suitable tool for individual needs.
| Tool | Ease of Use | Features | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ancestry.com | High, intuitive interface | Extensive database of historical records, advanced search capabilities, sophisticated visualization tools | Subscription-based, ranging from a few to multiple levels of access |
| FamilySearch | High, user-friendly design | Free access, vast genealogical records, collaboration tools, international focus | Free basic access, paid options for advanced features |
| MyHeritage | High, user-friendly interface | DNA matching tools, extensive historical records, interactive family tree visualization | Subscription-based, with options for varying features and levels of access |
Features and Functionalities
Family tree creation tools have evolved significantly, offering a wide array of features to help genealogists and family historians organize, visualize, and share their research. These tools are no longer just simple databases; they’re powerful platforms for exploring and documenting family history, enabling deeper understanding of ancestral connections.These tools go beyond simply recording names and dates. They provide sophisticated features for managing complex relationships, incorporating diverse data types, and ultimately, facilitating the discovery of hidden stories within family lineages.
Robust tools allow users to not only compile information but also to analyze it, identify patterns, and present their findings in compelling ways.
Ever wanted to trace your family history? Family tree creating tools are fantastic for piecing together the past. It’s fascinating to see how those connections form, especially when considering a recent news story like the case of a San Jose former police union executive getting probation for an opioid conviction, here’s the article. These online tools can be invaluable for delving into the past, connecting seemingly disparate threads and adding depth to our understanding of our own roots.
Essential Features for Effective Family Tree Building
Essential features in robust family tree creation tools are crucial for effective and organized family history research. These features facilitate the collection, management, and presentation of family data. A strong foundation in basic functionality ensures the long-term usability and value of the family tree.
- Name and Relationship Tracking: The ability to input and manage names, dates of birth, marriage, and death, along with accurate recording of relationships (parent-child, sibling, spouse) is fundamental. This ensures that the tree is well-structured and avoids confusion or contradictions.
- Detailed Information Input: Beyond basic details, tools should allow for the entry of additional information like locations, occupations, and brief biographical notes. This richness of data adds depth to the family tree and allows for a more complete picture of each individual’s life.
- Supporting Documents Integration: Tools should facilitate the integration of supporting documents like birth certificates, marriage licenses, and death certificates. This crucial feature enhances the accuracy and credibility of the family tree, making it a reliable source of information.
Advanced Functionalities for Enhanced Research
Advanced functionalities elevate family tree tools beyond basic record-keeping, empowering users to analyze and share their findings.
- Data Importing: The capability to import data from various sources (e.g., spreadsheets, databases, online records) is invaluable. This saves significant time and effort, especially for individuals with large amounts of existing data or those working with multiple sources.
- Chart Creation: The ability to generate charts, like family tree diagrams, timelines, or migration maps, significantly enhances the visualization of family history. These visual representations can highlight patterns, identify connections, and tell a story more effectively than a list of names and dates.
- Tree Sharing and Collaboration: The ability to share family trees with other family members, researchers, or the public, allows for collaborative efforts and broader access to the compiled information. This facilitates the discovery of previously unknown details and fosters a sense of shared heritage.
Benefits for Genealogists and Family Historians
The benefits of these features extend beyond mere organization. Robust family tree tools provide valuable insights into family history, enabling researchers to explore their heritage and uncover hidden stories.
- Improved Organization: Tools allow for systematic and comprehensive record-keeping, making it easier to track and manage large amounts of information, reducing the chance of errors and oversights.
- Enhanced Visualization: The creation of visual representations (like charts and timelines) makes it easier to identify patterns and relationships within the family history, offering new insights.
- Increased Accessibility and Collaboration: Sharing family trees with others empowers collaborative research and knowledge-sharing, allowing for a more thorough understanding of the family’s history.
Using Tools to Organize and Visualize Family History
Family tree tools provide a structured approach to organizing and visualizing family history information. This systematic approach enhances the overall understanding and presentation of the family’s story.
- Gather Data: Collect relevant information from various sources, including documents, interviews, and online resources.
- Input Information: Enter the collected data into the chosen family tree tool, ensuring accuracy and completeness.
- Create Charts and Diagrams: Use the tool’s visualization capabilities to create family tree diagrams, timelines, and other visual representations to reveal patterns and relationships.
- Share and Collaborate: Share the completed family tree with family members and other researchers for collaboration and knowledge-sharing.
User Experience and Interface
Creating a family tree can be a rewarding but sometimes daunting task. A user-friendly interface in a family tree creation tool significantly impacts the user’s overall experience, making the process enjoyable and efficient. A well-designed interface streamlines the input of data, allowing users to focus on the emotional connection with their family history rather than struggling with complex software.A poor interface, on the other hand, can quickly frustrate users, leading to abandoned projects and lost family memories.
A tool with a complicated navigation system or confusing input fields can discourage even the most enthusiastic genealogist. A positive experience fosters engagement and encourages the user to continue exploring their family’s history.
Importance of Intuitive Interfaces
A user-friendly interface is crucial for successful family tree creation. It should guide users effortlessly through the process, minimizing frustration and maximizing engagement. Intuitive design allows individuals with varying technical skills to easily input information, manage relationships, and visualize their family tree.
Examples of Good and Bad Interfaces
A good example of an intuitive interface would be one that uses clear visual cues, such as color-coding for different family relationships (e.g., parents in a different color than children). Drag-and-drop functionality for adding and moving individuals within the tree, along with clear labeling and prompts, would also be considered intuitive.Conversely, a poorly designed interface might present overwhelming lists of options without clear visual cues.
A confusing layout or lack of visual feedback when adding individuals can quickly deter users. Difficulty in navigating between different generations or in adding relationships could be problematic. Hidden or poorly labeled features also contribute to a negative user experience.
Factors Contributing to a Positive User Experience
Several factors contribute to a positive user experience in family tree tools. These include:
- Clear Visual Hierarchy: Visual elements, such as fonts, colors, and spacing, should effectively guide the user’s eye to essential information and actions.
- Intuitive Navigation: The tool should allow users to easily move between different parts of the family tree, such as different generations or specific individuals, with clear visual cues and logical pathways.
- Accessibility Features: Tools with features such as adjustable font sizes, screen reader compatibility, and keyboard navigation are important for a diverse user base.
- Effective Feedback Mechanisms: The tool should provide immediate and clear feedback on actions, such as confirming successful data entry or highlighting potential errors.
- User-Customizable Options: Allowing users to customize aspects like the appearance of the tree (colors, fonts) or the display of information enhances personalization and engagement.
Methods for Navigating and Using Tools Effectively
Effective navigation and use of family tree tools depend on the specific tool’s design. However, some general strategies apply. Familiarize yourself with the tool’s interface by experimenting with different features and exploring examples. Many tools have tutorials or help sections that can be invaluable. Take advantage of these resources to learn how to utilize the tools’ specific functions.The use of keyboard shortcuts and the understanding of visual cues (e.g., color-coded branches, different font styles) can significantly speed up the process.
It is crucial to be mindful of the data input, double-checking accuracy, and using the tools’ built-in validation features to ensure data integrity.
Creating a Basic Family Tree (Example)
This flowchart illustrates a simplified process for creating a basic family tree using a hypothetical tool named “FamilyTree Pro”:
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Open the FamilyTree Pro application. |
| 2 | Select “New Tree” from the main menu. |
| 3 | Enter the name of the first individual (e.g., “John Doe”). |
| 4 | Select the relationship of the individual (e.g., “Ancestor”). |
| 5 | Enter the date of birth and other relevant information. |
| 6 | Add additional individuals (e.g., “Jane Doe,” their spouse). |
| 7 | Specify relationships between individuals (e.g., parent-child, siblings). |
| 8 | Review and save the created family tree. |
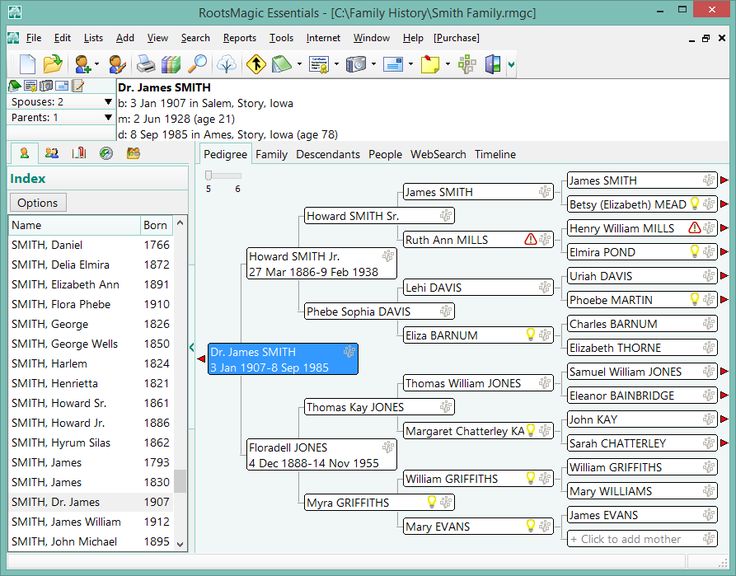
Data Management and Import/Export
Family tree tools play a crucial role in organizing and preserving genealogical information. Effective data management is essential for maintaining accuracy and allowing users to easily navigate and expand their family history. Import and export capabilities are equally important, enabling users to integrate existing data and share their research with others.This section delves into how various family tree tools handle data entry, management, and the processes of importing and exporting data.
We’ll examine different data formats supported by these tools, along with practical methods for importing existing family data and exporting results in various formats. The comparison will also cover importing data from different sources, including digital and printed records.
Data Entry and Management
Family tree tools employ various methods for data entry. Some utilize intuitive forms, allowing users to input information such as names, dates, locations, and relationships directly into the system. Others use more structured approaches, requiring specific fields for each piece of data, enhancing data integrity and enabling the system to automatically calculate relationships. These methods often include validation checks, ensuring data accuracy and consistency.
The choice of data entry method depends on the complexity of the family tree and the tool’s specific features.
Supported Data Formats
Different family tree tools support various data formats. Commonly supported formats include GEDCOM, a standardized format for exchanging genealogical data; CSV (Comma Separated Values) for tabular data; and JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) for structured data. Each format has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of complexity, flexibility, and compatibility with other tools. The ability to import and export data in different formats enhances the flexibility and interoperability of these tools.
Importing Existing Family Data
Importing existing family data is a crucial aspect of using family tree tools. Many tools offer the ability to import data from GEDCOM files, enabling users to combine their research with data from other sources. The import process often involves a series of steps, such as selecting the file to import, specifying the data mapping between the source and the target format, and resolving potential conflicts or discrepancies.
Importing from CSV or other formats often requires careful mapping to match data fields in the source to the fields within the family tree software.
Exporting Family Tree Data
Exporting family tree data allows users to share their research or transfer it to other platforms. Tools often support exporting in formats such as GEDCOM, allowing users to easily share their data with other researchers or family members. The option to export data in CSV or other formats allows for flexibility in data analysis and use in other applications.
This capability enhances the utility of family tree tools, enabling users to share their research with others and to use their data in different ways.
Importing from Different Sources
Importing data from various sources, including digital documents and printed records, presents unique challenges. Digital documents, such as scanned PDFs of birth certificates or marriage licenses, can be imported using optical character recognition (OCR) software to convert the text into a digital format. Printed records may require manual data entry into the family tree software. This process can be time-consuming but is essential for preserving historical information.
Tools often offer different methods for importing data from different sources to facilitate the integration of diverse genealogical materials. Some tools support direct import from specific document types.
Collaboration and Sharing
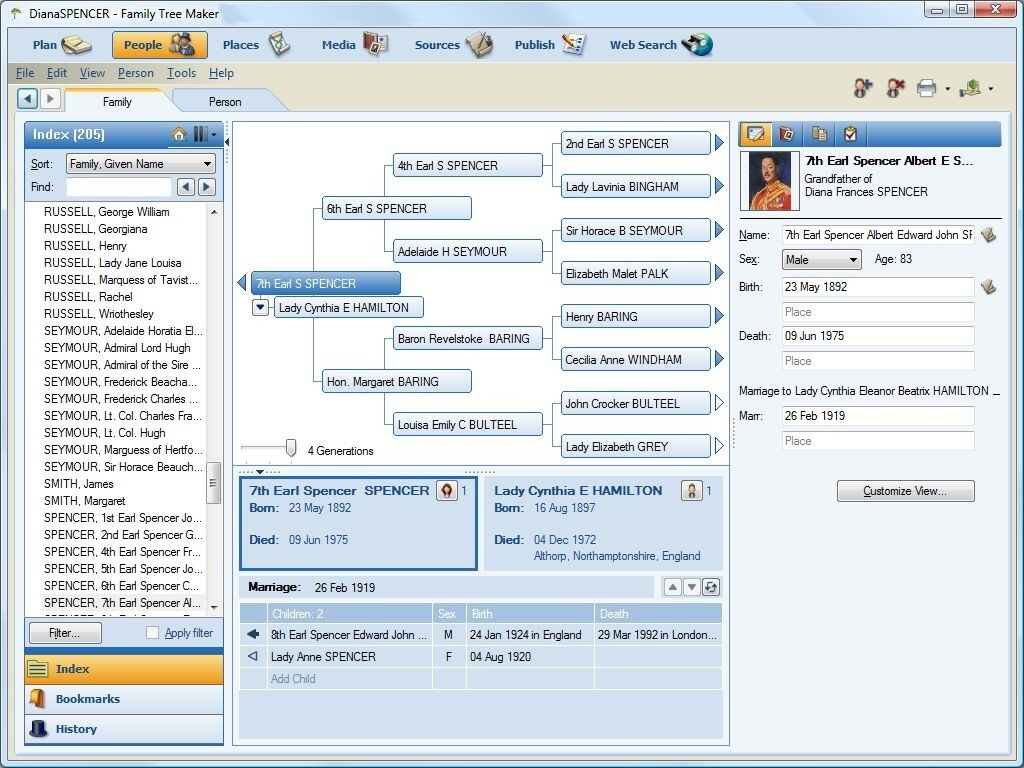
Family tree creation tools are no longer solitary endeavors. They empower families to connect, share, and collectively build a richer understanding of their shared history. These tools offer a range of features that facilitate collaboration, making the process more engaging and productive for everyone involved.Modern family history tools offer sophisticated ways to share and collaborate on family trees, allowing multiple individuals to contribute and edit the same tree simultaneously.
This collaborative approach ensures accuracy, prevents duplication of effort, and allows for the rapid expansion of family knowledge.
Facilitating Collaboration Among Family Members
Tools often include features like shared access and real-time editing. This allows multiple family members to work on the same tree simultaneously, ensuring that everyone has access to the most up-to-date information. This can be especially helpful when dealing with large families or dispersed relatives.
Examples of Sharing Family Trees
Family tree tools offer diverse methods for sharing. These can include email, social media links, or direct sharing with family members. These tools often offer the ability to export the tree in various formats, such as PDF or image files, for printing or sharing with those who don’t use the specific platform.
Options for Sharing with Different Access Levels
Many tools allow administrators to control who can view, edit, or add to the family tree. This is crucial for maintaining privacy and preventing accidental changes. Users can create different roles (e.g., viewer, editor, administrator) and assign permissions to each family member.
Benefits of Collaboration for Maintaining and Expanding Family History Knowledge
Collaboration ensures that family history is accurately documented and maintained. Multiple perspectives can reveal new insights and correct inaccuracies. This collective effort can lead to the discovery of previously unknown family members, locations, and significant events. It fosters a sense of community and shared ownership of the family history.
Sharing a Family Tree with Specific Individuals or Groups
Sharing is often a simple process. Many tools allow users to create specific sharing groups. For instance, a user could create a group for “Cousins on Mom’s Side” or “Grandparents’ Generation.” Then, they can invite specific individuals to the group. This targeted approach allows for more controlled sharing and ensures that only authorized individuals have access to the tree.
Sharing with an entire group is often facilitated through group email lists or social media groups. Once invited, family members can easily access the shared tree and contribute their own information. This method avoids sending individual invitations and maintains a sense of community within the sharing group.
Tools for Different Needs
Family tree tools cater to a diverse range of users, from casual hobbyists to professional genealogists. Understanding the specific needs of each user group is crucial for choosing the right tool. This allows for a more satisfying and productive experience, regardless of the user’s technical expertise or research goals.Tools are designed with varying degrees of complexity and features, catering to different skill levels and research ambitions.
From basic data entry to advanced charting and collaboration features, the range of options available ensures that every user can find a tool that meets their needs.
Family tree creating tools are super helpful for tracing your ancestry, especially if you’re interested in learning more about your heritage. It’s a fascinating way to connect with the past, but sometimes, stories like the one about the Laguna Niguel couple held in ICE detention, facing deportation after 35 years in the US, highlight the importance of understanding immigration policies and the challenges faced by many families.
These tools can help us appreciate the richness of human history, and hopefully, foster empathy and understanding of the complex situations different people face.
Tools for Beginners
Beginners often prioritize ease of use and intuitive interfaces. They might not require sophisticated charting or advanced collaboration features, focusing instead on simple data entry and basic visualization. Freeware options often serve this purpose, offering basic functionality without significant financial commitment. Examples include free online tools and downloadable applications specifically designed for beginners. These tools usually have clear instructions and step-by-step guides to help users navigate the platform.
Tools for Hobbyists
Hobbyists typically seek a balance between ease of use and functionality. They may need more advanced features than beginners but are often less focused on intricate analysis and collaboration as compared to professional researchers. These tools frequently provide a range of templates and pre-built forms to streamline the process. Intermediate-priced tools with limited advanced features, such as interactive charts and optional collaboration features, are common choices.
These tools are often designed with a user-friendly interface to allow hobbyists to easily create and maintain their family trees without overwhelming complexity. Examples of such tools often have downloadable desktop versions or web-based options.
Tools for Advanced Researchers
Advanced researchers demand powerful tools capable of handling vast amounts of data, complex analysis, and robust collaboration. These tools typically feature extensive data import/export options, sophisticated charting capabilities, and sophisticated collaboration features. These tools often have extensive customization options and provide options for complex analysis such as statistical modelling or identifying trends within the family tree. Examples include specialized software applications with extensive documentation and dedicated support channels.
The price point for such tools tends to be higher, reflecting the advanced functionalities and support included.
Comparing Beginner and Expert Tools
| Feature | Beginner Tool | Expert Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Data Entry | Simple forms, basic import options (e.g., CSV) | Advanced import/export options (e.g., GEDCOM, XML), complex data entry forms, data validation |
| Charting | Basic charts (e.g., family tree diagrams), limited customization | Sophisticated charts (e.g., interactive timelines, ancestral maps), extensive customization, data visualization options |
| Collaboration | Basic sharing options (e.g., email, social media links) | Real-time collaboration features (e.g., shared documents, version control), advanced permissions and access control |
Cost and Pricing Models
Choosing the right family tree creation tool can be daunting, especially with a wide array of options available. A crucial aspect to consider is the pricing model. Understanding how these tools are priced helps users make informed decisions based on their budget and needs. Different models cater to various user groups, from casual researchers to dedicated genealogists.The pricing models for family tree tools vary significantly.
Some are entirely free, while others offer tiered paid options. This range allows users to select a solution that aligns with their budget and the level of features they require. Free options often come with limitations, such as restricted storage or limited functionalities. Paid options usually offer more features and functionalities, enhanced data management, and advanced search capabilities.
Ultimately, the cost reflects the value proposition and features of the chosen tool.
Pricing Models Overview
Family tree tools often employ a variety of pricing models, including free, freemium, and subscription-based models. Free tools typically offer basic functionalities and limited storage space, ideal for casual users. Freemium models provide a free version with limited features and a paid version unlocking advanced options. Subscription models offer ongoing access to features and updates for a recurring fee.
Examples of Free and Paid Tools
Free tools, such as MyHeritage’s basic offering, often serve as a starting point for users exploring genealogy. These platforms typically allow for basic data entry, limited import/export capabilities, and some visualization options. Paid tools like Ancestry.com, with their extensive historical records and comprehensive features, typically come with more advanced search options, extensive import/export capabilities, and sophisticated visualization tools.
Value Proposition of Different Tiers
The value proposition of each pricing tier varies significantly. Free tiers offer a taste of the platform and may be suitable for users who need basic functionalities or are just starting to explore their family history. Paid tiers often include more robust features, such as enhanced search functionality, expanded data storage capacity, and more advanced tools for collaboration and sharing.
I’ve been digging into family tree creating tools lately, and it’s fascinating how much information you can uncover. The sheer volume of events at the Pebble Beach Food and Wine Festival this year, with more than 60 events in the lineup, like this one , is inspiring. It got me thinking about how these tools can help trace family histories across generations, bringing similar levels of detailed discovery to the past.
Ultimately, these tools are incredibly helpful for connecting the dots of our family history.
The value of a paid tier depends on the features provided and the user’s needs.
Factors Influencing Tool Costs
Several factors influence the cost of family tree creation tools. The scale and complexity of the database of historical records and available features directly affect the price. More comprehensive data sets, advanced search algorithms, and robust user interfaces often come with higher price points. The level of customer support and ongoing updates also contribute to the overall cost.
Additionally, the development, maintenance, and hosting of the software platform are substantial expenses.
Comparison of Pricing and Features, Family tree creating tools
| Tool | Pricing Model | Features |
|---|---|---|
| MyHeritage (Basic) | Free | Basic data entry, limited storage, basic visualization, limited import/export |
| Ancestry.com | Subscription | Extensive historical records, advanced search options, comprehensive import/export, advanced visualization, family group records, collaborative features |
| FamilySearch | Free (with some paid options) | Extensive global historical records, community-based support, vast genealogical data, basic and advanced search tools |
Tools for Specific Genealogy Research: Family Tree Creating Tools
Delving into the intricate world of genealogy often requires specialized tools beyond basic family tree software. These specialized tools cater to particular research needs, allowing you to unlock hidden layers of your family’s past. From uncovering historical records to analyzing DNA matches, these tools are powerful extensions of your family tree building journey.
DNA Matching Tools
Genealogy DNA testing has become a significant aspect of modern research. Specialized DNA matching tools provide a platform for comparing your DNA results with those of other users in a large database. These tools often integrate with existing family tree software, allowing you to link DNA matches to known relatives and further flesh out your family tree.
- Functionality: These tools usually display matching percentages and potential relationships, facilitating the identification of previously unknown relatives. They often offer advanced filtering options to refine searches based on geographic location, ethnicity, or other criteria.
- Benefits: DNA matching tools can significantly accelerate the process of identifying distant relatives and uncovering hidden branches in your family tree. They can provide valuable insights into the geographic origins of your ancestors, or the existence of undocumented relatives.
- Integration: Most reputable DNA testing companies offer integration with popular family tree software, making it easy to import DNA matches directly into your family tree program.
Historical Records Research Tools
Beyond DNA, genealogical research often relies on historical documents. Specialized tools dedicated to accessing and analyzing these records can be invaluable. These tools are frequently designed to search and process specific types of records, such as census data, birth certificates, or immigration documents.
- Functionality: These tools often provide advanced search capabilities, allowing you to pinpoint specific individuals based on a variety of criteria, including names, locations, and dates. Some tools offer features to extract relevant information and organize it in a format compatible with family tree software.
- Benefits: Accessing historical records directly through dedicated tools often saves significant time and effort compared to manually searching through archives. These tools frequently offer advanced search filters, reducing the likelihood of overlooking crucial information.
- Integration: Many tools offer the capability to export results in formats compatible with popular family tree software, enabling seamless integration into your existing tree.
Local Records and Archives Tools
Many communities maintain detailed records of local residents. Specialized tools are available for accessing these records, enabling researchers to uncover insights into local history and family lineages.
- Functionality: These tools are often designed for specific geographic areas and may contain local newspapers, property records, or court documents. They typically provide advanced search functionalities tailored to the particular types of records.
- Benefits: These tools often provide unique access to valuable information that might not be readily available through national archives. They can provide rich context for understanding the lives of your ancestors within their local communities.
- Integration: Depending on the tool, extracted data can often be imported into family tree software, enriching the overall narrative of your family history.
Choosing the Right Tools
Selecting the right tools depends heavily on your specific research focus. If DNA matching is your primary interest, a specialized DNA matching tool is essential. Conversely, if historical records are your target, a dedicated historical records research tool will prove highly beneficial. The key is to align the tool’s capabilities with your specific genealogical goals.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the variety of family tree creating tools available today caters to a wide range of needs and preferences. Whether you’re a seasoned genealogist or just starting your family history journey, there’s a tool designed to make the process engaging and efficient. Understanding the features, user experience, and pricing models empowers you to choose the perfect tool to preserve and share your family’s legacy.