LA Fires Cannabis Crop Impacts
How the LA fires will effect cannabis crops is a crucial question facing growers and the industry as a whole. The devastating blazes have left a trail of destruction, impacting everything from plant growth to water availability and soil quality. This analysis delves into the complex effects of these wildfires on cannabis cultivation, exploring the immediate and long-term consequences.
The fires have irrevocably altered the landscape, introducing unique challenges for cannabis growers. From the toxic ash contaminating the soil to the potential for water scarcity, these fires pose significant threats to the region’s cannabis industry. Understanding these impacts is vital for effective recovery and adaptation strategies.
Impact on Plant Growth
The devastating 2023 La fires have left an indelible mark on the landscape, including the cannabis crops in the affected areas. Understanding the multifaceted impact of wildfire smoke and ash on cannabis plant growth is crucial for farmers to mitigate losses and adapt cultivation practices. The immediate and long-term effects can vary significantly, impacting everything from photosynthetic efficiency to nutrient uptake.Wildfire smoke, a complex mixture of particulate matter, gases, and volatile organic compounds, can directly affect cannabis plants.
The physical deposition of ash and soot can hinder photosynthesis and alter nutrient availability, while inhalation of smoke particles can cause physiological stress and reduce yield. Understanding the specific mechanisms behind these effects will enable cultivators to proactively address these challenges.
Smoke Inhalation Effects
Smoke inhalation, a major concern, can lead to immediate and long-term effects on cannabis plant development. Immediate effects can manifest as wilting, reduced growth rates, and stunted development. Prolonged exposure can lead to more severe consequences, including chlorosis (yellowing of leaves), necrosis (tissue death), and ultimately, reduced yields. The concentration and composition of the smoke directly influence the severity of the impact.
Altered Sunlight Penetration
Wildfire smoke and ash can significantly alter sunlight penetration, impacting the crucial process of photosynthesis. The particulate matter in the smoke can act as a physical barrier, reducing the amount of sunlight reaching the leaves. This reduction in light availability directly impacts the plant’s ability to convert light energy into chemical energy, thereby hindering growth and potentially leading to reduced yields.
The degree of impact depends on the density and duration of the smoke cloud.
Impact on Nutrient Uptake
Wildfire ash can alter soil chemistry, potentially affecting nutrient uptake by cannabis plants. The ash, while containing some nutrients, can also introduce harmful substances like heavy metals and alter the pH balance of the soil. This can lead to nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, further impacting plant growth and development. The composition of the ash, determined by the type of vegetation burned, plays a crucial role in these alterations.
Soil Contamination
The deposition of wildfire ash can contaminate soil, potentially introducing harmful elements. This can affect the availability of essential nutrients for the plants. Heavy metals and other contaminants can accumulate in the soil, potentially impacting the quality of the final product. This is a significant concern for cultivators, as it can impact the overall health of the plants and the safety of the harvested product.
Comparison of Wildfire Intensity Levels
| Wildfire Intensity Level | Cannabis Strain | Short-Term Effects | Long-Term Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low | Indica-dominant strains | Reduced growth rate, mild chlorosis | Potential for reduced yield, minor nutrient deficiencies |
| Medium | Sativa-dominant strains | Stunted growth, severe chlorosis, necrosis | Significant yield reduction, potential for impaired terpene production |
| High | Hybrid strains | Extensive damage, complete defoliation, potential death | Complete loss of yield, soil contamination |
This table provides a general comparison. Specific effects will depend on factors such as the proximity to the fire, the duration of exposure, and the specific characteristics of the cannabis strain. Factors such as the local soil composition and the specific composition of the smoke play an important role in the plant’s reaction to the wildfire.
Soil Contamination and Remediation
Wildfires leave behind a complex legacy, impacting not only the immediate environment but also the long-term health of the land. Cannabis cultivation, particularly in fire-prone regions, requires careful consideration of post-fire soil conditions. Understanding the nature of soil contamination and effective remediation strategies is crucial for ensuring sustainable and safe cannabis production.The intense heat and rapid combustion of wildfires introduce various contaminants into the soil, ranging from ash and heavy metals to organic compounds.
These contaminants can significantly alter the soil’s chemical and physical properties, posing a significant threat to cannabis plants’ health and overall yield. Thorough assessment and remediation are necessary to mitigate these risks and restore the soil’s fertility.
Types of Soil Contaminants
Wildfires introduce a wide array of pollutants into the soil. Ash, a byproduct of incomplete combustion, is a common contaminant, often containing trace amounts of heavy metals. These metals, including lead, cadmium, and mercury, can accumulate in the soil and potentially enter the cannabis plant’s tissues. Further, organic compounds, such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), formed during the combustion process, can also be present in the soil.
The concentration and type of contaminants depend on factors like the type of vegetation burned, the intensity of the fire, and the soil composition. These contaminants can disrupt nutrient uptake, hinder plant growth, and potentially affect the final product’s quality and safety.
Assessment of Soil Contamination
A thorough assessment of soil contamination is crucial for determining the extent of damage and necessary remediation strategies. This process involves sampling the soil at various depths and locations within the affected area. The samples are analyzed in a laboratory to identify the types and concentrations of pollutants. The results help determine the severity of contamination and guide the selection of appropriate remediation methods.
Key factors for sample collection include the depth of the soil layer, distance from the fire’s epicenter, and the type of vegetation that was burned.
Soil Remediation Methods
Various techniques can be employed to remediate contaminated soil suitable for cannabis cultivation. These methods aim to either remove or reduce the concentration of contaminants to levels safe for plant growth. Some methods focus on physically removing the contaminated soil, while others focus on using biological or chemical agents to break down or sequester pollutants.
- Physical Removal: This involves excavating and removing contaminated soil, followed by replacing it with clean soil. This method is often effective for high levels of contamination but can be costly and labor-intensive, particularly for large areas. The process necessitates careful planning and execution to avoid disturbing the surrounding soil and potentially exposing further contaminants.
- Chemical Remediation: This approach uses chemicals to neutralize or remove contaminants from the soil. Phytoremediation, a biological method, uses plants to absorb or break down pollutants. Specific chemicals and methods depend on the type and concentration of contaminants. This method can be environmentally friendly and effective, but careful monitoring and proper disposal of byproducts are essential.
- Biological Remediation: This method employs microorganisms to break down or transform pollutants into less harmful substances. This is often a slower process but can be more environmentally friendly than chemical methods. Specific microorganisms, tailored to the type of contaminants present, are essential for the success of this approach.
- Thermal Remediation: This technique uses high temperatures to destroy or volatilize pollutants. This is often a suitable option for organic compounds, though it may not be suitable for all contaminant types. Careful consideration of the soil type and potential environmental impacts is essential.
Effectiveness of Remediation Techniques
The effectiveness of soil remediation techniques varies depending on factors such as the type and concentration of contaminants, soil properties, and the chosen remediation method. A comprehensive analysis of these factors is crucial to determine the best course of action.
The LA fires are wreaking havoc on local cannabis crops, and the devastation is likely to ripple through the industry. While the exact extent of the damage is still unfolding, the impact on supply chains and production will be significant. Meanwhile, a luxury single-family home in Pleasanton recently sold for a staggering $1.7 million! single family home in pleasanton sells for 1 7 million 3 This stark contrast highlights the economic disparities, as the value of a home can skyrocket while the future of local cannabis farms hangs in the balance.
The fires’ impact on cannabis production is a real concern for the local economy and the future of the industry.
| Remediation Technique | Effectiveness | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Removal | High for severe contamination | Relatively quick | High cost, significant soil disturbance |
| Chemical Remediation | Variable, depends on contaminant type | Can be effective for specific contaminants | Potential for chemical residues, environmental concerns |
| Biological Remediation | Moderate to high, slower process | Environmentally friendly, cost-effective | Dependent on microorganisms and soil conditions |
| Thermal Remediation | High for specific contaminants | Can destroy contaminants | Can be energy intensive, potential for soil damage |
Water Quality and Availability: How The La Fires Will Effect Cannabis Crops
Wildfires dramatically impact the delicate balance of ecosystems, and cannabis cultivation is no exception. The immediate and long-term effects on water sources are crucial considerations for growers. Changes in water quality and availability can significantly hinder plant growth and even threaten the entire harvest. Understanding these impacts and implementing effective strategies for water management is vital for ensuring the resilience of cannabis operations in fire-prone regions.The devastating effects of wildfires extend far beyond the immediate devastation of homes and infrastructure.
Runoff from burned areas carries a complex cocktail of pollutants, impacting the quality and availability of water sources. This contamination poses a significant threat to cannabis crops, which are highly sensitive to water quality fluctuations. Moreover, the altered hydrological cycles can lead to unpredictable water shortages, exacerbating the challenges for growers.
Potential Impacts of Wildfire Runoff on Water Sources
Wildfire runoff carries a multitude of contaminants, including ash, sediment, and various chemicals. These pollutants can contaminate water sources, including rivers, streams, and reservoirs, used for irrigation. The sediment load can clog irrigation systems, reducing water flow and increasing maintenance requirements. Chemical contaminants like heavy metals and organic compounds can leach into water, potentially impacting the health of cannabis plants and posing risks to human consumption.
For example, studies have shown that heavy metals like lead and mercury can accumulate in plant tissues, potentially leading to health concerns if consumed.
Water Quality Testing and Monitoring
Post-fire water quality testing is essential for assessing the extent of contamination and guiding remediation efforts. Regular monitoring allows growers to identify the presence and levels of harmful substances. This data-driven approach helps in making informed decisions about water usage, including determining if water sources are safe for irrigation. Testing should encompass a comprehensive analysis of various parameters, including turbidity, pH, dissolved oxygen, and the presence of heavy metals, nutrients, and organic matter.
The LA fires are a serious concern for cannabis crops, threatening yields and potentially impacting the entire industry. With the recent news of Oakland temporarily closing two fire stations, and several more brownouts likely on the way here’s a report on the situation , the already fragile infrastructure needed to maintain these delicate crops is further jeopardized. This could lead to significant losses and long-term challenges for the region’s cannabis farms.
This comprehensive approach provides a clearer picture of the water’s condition and its suitability for cannabis cultivation.
Strategies for Sourcing and Managing Water Supplies
During and after wildfire events, alternative water sources may be necessary. This might involve using groundwater wells, connecting to municipal water systems, or utilizing rainwater harvesting techniques. The choice of water source should consider the specific needs of the crop and the long-term implications. Effective water management strategies should also include practices to minimize water waste and maximize efficiency, such as drip irrigation systems and smart irrigation controllers.
Water Conservation Techniques in Cannabis Cultivation
Water conservation is crucial for sustainable cannabis cultivation, especially in fire-prone regions. Employing efficient irrigation techniques, such as drip irrigation, can significantly reduce water consumption. Cover crops and mulching can help retain soil moisture, minimizing water needs. Properly maintaining irrigation systems and addressing leaks promptly can prevent water loss. Furthermore, growers can monitor plant water requirements through regular checks and adjust irrigation schedules accordingly.
Implementing these techniques can lead to considerable water savings, contributing to long-term sustainability and reducing the impact on water resources.
Post-Fire Cannabis Cultivation Practices
Recovering from wildfires is a complex process, and cannabis cultivation is no exception. Understanding the specific needs of cannabis plants after a fire is crucial for successful regrowth and ensuring the quality of the harvest. This requires careful consideration of soil preparation, plant selection, nutrient management, and pest/disease control. The following sections will detail these essential aspects for post-fire cultivation.
Soil Preparation for Planting
Post-fire soil often contains ash, altered nutrient composition, and varying degrees of contamination. Thorough soil preparation is paramount for successful planting. This involves removing any significant debris and assessing the soil’s pH and nutrient levels. A soil test is crucial to determine the precise needs of the soil and plants.
- Debris Removal: Carefully remove large debris, rocks, and charred organic matter. This ensures better aeration and prevents the accumulation of harmful substances in the soil.
- Soil Testing: A soil test is essential to determine the pH, nutrient levels, and potential contaminants. This information guides the selection of appropriate fertilizers and amendments.
- Soil Amendment: Depending on the soil test results, organic matter like compost or well-rotted manure can be added to improve soil structure, drainage, and nutrient retention. Compost provides essential nutrients and improves water retention. Consider adding perlite or vermiculite for enhanced drainage.
Selecting Suitable Cannabis Varieties
Choosing the right cannabis variety is crucial for successful post-fire cultivation. Certain strains are better adapted to the unique conditions and challenges presented by fire-affected environments.
- Resilient Varieties: Consider strains known for their resilience to environmental stressors, including heat, drought, and nutrient deficiencies. These strains often have a higher tolerance for post-fire conditions and may recover faster.
- Local Adaptations: Consult with local growers or agricultural experts to identify strains that have proven successful in similar post-fire environments. Local knowledge is valuable in selecting varieties adapted to specific regional conditions.
- Specific Needs: Evaluate the specific challenges presented by the fire, such as soil composition, water availability, and potential contaminants. Select strains that demonstrate tolerance to these conditions.
Fertilizer and Nutrient Regimen
A carefully tailored fertilizer and nutrient regimen is vital for supporting cannabis growth after a wildfire. Post-fire soils often lack essential nutrients, and adjusting the regimen is crucial for healthy plant development.
- Nutrient Deficiencies: Post-fire soils often exhibit deficiencies in key nutrients. Adjusting fertilizer application rates to address these deficiencies is crucial.
- Targeted Supplementation: Employ a balanced fertilizer program, incorporating specific nutrient supplements, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, to address the identified needs of the plants.
- Slow-Release Formulations: Consider slow-release fertilizers to provide consistent nutrient delivery over time. This can help minimize nutrient fluctuations and ensure steady plant growth.
Pest and Disease Management
Wildfires can disrupt the natural balance of the ecosystem, creating favorable conditions for pest and disease outbreaks. Implementing proactive pest and disease management strategies is essential.
- Monitoring: Regular monitoring of plants for signs of pests or diseases is critical. Early detection and intervention are key to preventing widespread infestations.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Implementing IPM strategies, which integrate biological control methods, cultural practices, and targeted pesticide applications, is vital.
- Biological Controls: Utilize beneficial insects and microorganisms to control pest populations naturally. This approach minimizes the use of harmful chemicals.
Examples of Successful Cultivation
Several examples demonstrate the resilience of cannabis cultivation after wildfires. These experiences highlight the importance of careful planning, proactive measures, and adaptability. Many organic farmers who have experience cultivating in areas affected by wildfires often find success by adopting similar practices.
Market Impacts
Wildfires dramatically reshape the cannabis market, creating both challenges and opportunities for cultivators, processors, and consumers. The immediate impact is often devastating, but the long-term effects can be complex and surprising. Disruptions in supply chains, shifts in consumer preference, and altered regulatory landscapes are just a few of the factors that need to be considered. Understanding these impacts is critical for navigating the post-fire landscape and ensuring a sustainable cannabis industry.The economic ripple effects of wildfires on cannabis cultivation regions can be substantial.
Regions heavily reliant on cannabis farming for their economies face significant losses. This can translate to job losses, decreased tax revenue, and hindered local economic growth. Furthermore, the impact extends beyond the immediate harvest, affecting the entire value chain from seed to sale.
Potential Market Disruptions
Wildfires disrupt the supply chain in multiple ways. Crop losses lead to reduced availability, increasing the pressure on existing growers and processors. This shortage can lead to higher prices, making cannabis less accessible to consumers. Transportation and logistical issues can further exacerbate these problems, potentially leading to delays and shortages in specific markets. The disruptions to production facilities and processing plants can also impact the quality and consistency of products.
The LA fires are going to wreak havoc on cannabis crops, unfortunately. Smoke inhalation and ash fallout will undoubtedly impact the quality and yield of the plants. Meanwhile, the box office success of Mel Gibson’s Flight Risk is surprising, especially given the brutalist aesthetic of the film, as seen in the recent article mel gibsons flight risk is no 1 at box office the brutalist expands.
This is certainly a distraction from the devastating effects on local farms and the future of LA’s cannabis industry.
Potential Market Opportunities
While wildfires present challenges, they also create opportunities for adaptation and innovation. The emergence of new cultivation techniques and sustainable practices can improve the resilience of cannabis operations. This can attract new investors and businesses, leading to diversification and innovation in the sector. Additionally, increased demand for relief efforts and support for affected communities could present new avenues for social enterprise.
The rebuilding and recovery phase offers chances for revitalizing and modernizing cultivation methods and facilities.
Effects on Cannabis Prices and Availability
The immediate aftermath of wildfires often sees a dramatic increase in cannabis prices. Reduced supply, combined with the need for increased production in unaffected areas, leads to a higher cost for consumers. Availability in affected regions is severely limited, while unaffected areas might experience temporary surpluses, leading to price fluctuations across the market. The long-term price stabilization will depend on the speed of recovery and the adoption of new cultivation practices.
Influence on Consumer Perception
Consumer perception of cannabis products can be influenced by wildfire events. Consumers may be concerned about the safety and environmental impact of cannabis grown in affected regions. The quality of products from regions impacted by wildfire may also come into question, leading to a shift in consumer preference. Transparency and communication regarding post-fire cultivation practices and environmental safeguards will be crucial for maintaining consumer trust.
Comparison of Economic Impacts
The economic impact of wildfires on different cannabis cultivation regions varies significantly. Regions with a larger cannabis industry concentration will experience greater economic losses. The long-term effects will also be influenced by the region’s overall economic resilience, the speed of recovery, and the availability of government support. Factors such as the size of the cannabis industry in a region, the level of government support, and the availability of alternative income sources play a significant role.
Potential Market Trends Following Wildfires
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Focus on Sustainability | Growers will likely prioritize sustainable practices to mitigate future risks. This includes water conservation, drought-resistant strains, and alternative growing methods. |
| Rise in Demand for Local Products | Consumers might favor cannabis products sourced from unaffected regions, potentially boosting the local economy. |
| Innovation in Cultivation Techniques | The need for resilience will drive innovation in growing methods and seed selection. |
| Emphasis on Transparency and Traceability | Consumers will likely demand greater transparency in the supply chain to ensure quality and safety. |
| Government Support and Regulations | Government regulations and funding will likely focus on assisting the recovery and promoting sustainable practices. |
Environmental Considerations
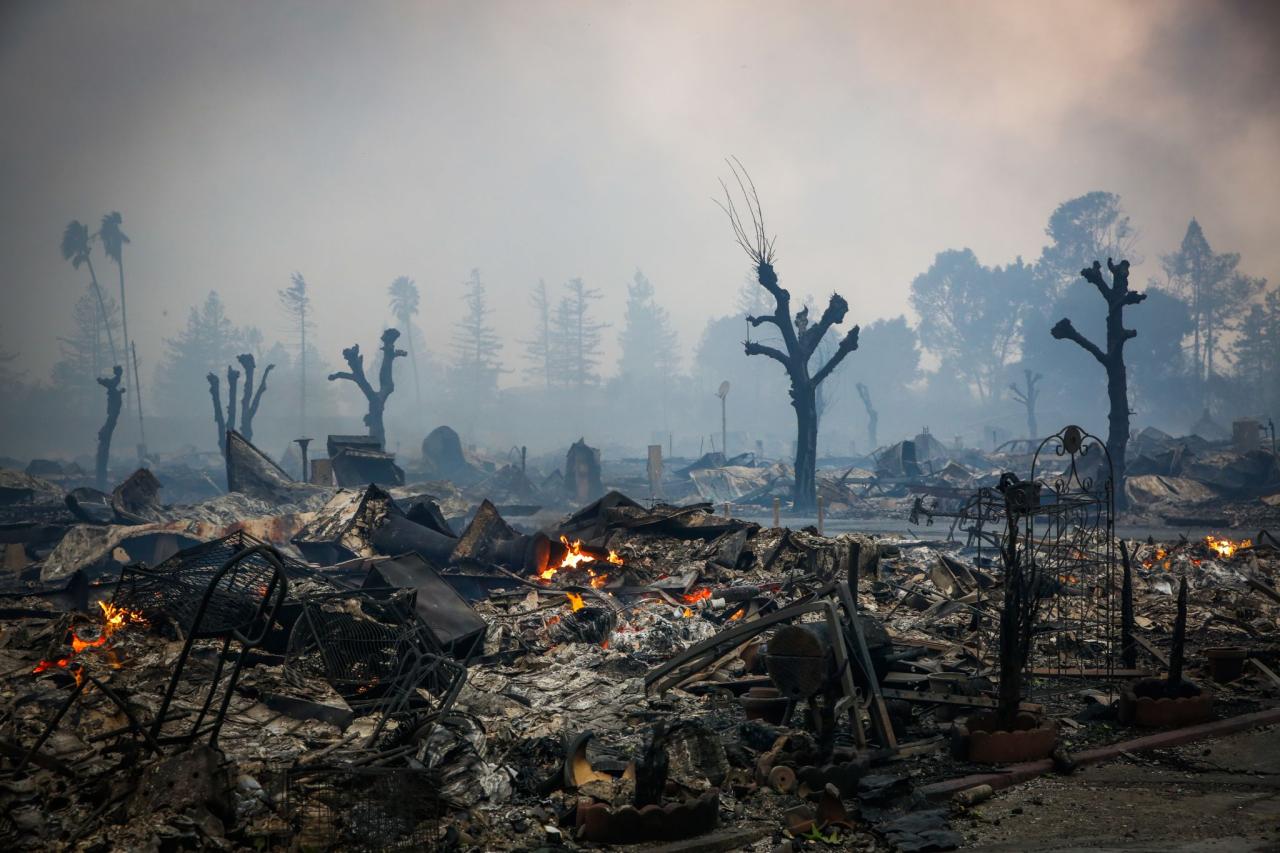

Cannabis cultivation, while offering numerous benefits, can have significant environmental impacts. These impacts range from water usage and soil degradation to potential air pollution and biodiversity loss. Understanding these factors is crucial, especially in the context of post-fire recovery, where existing environmental vulnerabilities are amplified. Implementing sustainable practices is paramount for ensuring the long-term viability and environmental responsibility of cannabis cultivation.
Overview of Cannabis Cultivation Environmental Impacts
Cannabis cultivation, like any agricultural activity, necessitates significant resource inputs. Water consumption, fertilizer application, and pesticide use are all potential contributors to environmental degradation. The specific environmental footprint varies depending on the cultivation method, climate, and local regulations. For example, indoor cultivation, while potentially less dependent on local water resources, often requires significant energy input for lighting and climate control, which can lead to greenhouse gas emissions.
Exacerbation of Environmental Concerns by Wildfires
Wildfires, particularly in regions where cannabis is cultivated, significantly worsen existing environmental concerns. Post-fire landscapes are often characterized by depleted soil nutrients, increased soil erosion, and altered water cycles. These factors can make it challenging to establish healthy cannabis crops and can potentially exacerbate existing water scarcity issues. The presence of ash and debris in the soil can affect nutrient availability and plant growth, necessitating additional inputs and potentially increasing the environmental impact of cultivation.
Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Cultivation Methods in Post-Fire Scenarios
Implementing sustainable and eco-friendly cultivation methods is critical for mitigating the environmental impact of cannabis cultivation, especially in post-fire regions. These methods encompass a range of practices aimed at minimizing water usage, preserving soil health, and reducing reliance on harmful chemicals.
Sustainable Water Management and Soil Preservation, How the la fires will effect cannabis crops
Sustainable water management is paramount for maintaining soil health and crop productivity. Techniques such as rainwater harvesting, drip irrigation, and efficient water-use practices are essential for minimizing water consumption. Careful soil preservation, including soil amendments and cover cropping, can enhance soil structure, improve water retention, and reduce erosion. Proper soil management can also reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
Methods for Reducing Environmental Impact in Cannabis Cultivation
Numerous methods can reduce the environmental footprint of cannabis cultivation. These include:
- Selecting drought-tolerant cannabis varieties: Certain cannabis strains are inherently more resilient to drought conditions, reducing the need for excessive irrigation.
- Implementing integrated pest management (IPM) strategies: This approach emphasizes prevention and biological control methods to minimize pesticide use.
- Utilizing organic fertilizers and soil amendments: Organic alternatives to synthetic fertilizers can improve soil health and reduce the environmental impact of nutrient management.
- Employing vertical farming techniques: Vertical farming can reduce land use and water consumption compared to traditional field-based cultivation.
- Promoting responsible waste management: Proper disposal of cultivation waste can reduce pollution and ensure responsible resource management.
These sustainable practices are not only environmentally beneficial but also contribute to long-term economic viability by minimizing cultivation costs and enhancing the quality of the final product. By integrating these principles into cultivation practices, cannabis growers can cultivate responsibly and contribute to a healthier environment.
Closing Notes

In conclusion, the LA fires have presented a formidable challenge to cannabis cultivation. The impact on plant growth, soil quality, water resources, and the market will undoubtedly shape the future of cannabis production in the region. The post-fire recovery efforts will require a multifaceted approach, encompassing careful soil remediation, strategic water management, and the selection of resilient cannabis strains.
This analysis highlights the urgent need for growers to adapt and persevere through these challenging times.