Setting Up 2FA with Microsoft Authenticator
Setup 2fa with microsoft authenticator – Setting up 2FA with Microsoft Authenticator is crucial for boosting your online security. This guide walks you through the process, from understanding the basics of two-factor authentication to troubleshooting common problems and exploring advanced configurations. We’ll cover everything you need to know, making your online experience safer and more secure. We’ll dive deep into the details, covering different platforms and troubleshooting steps.
Get ready to supercharge your security!
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security to your accounts by requiring two forms of verification. This method significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. This extra step often involves a code generated by an authenticator app, like Microsoft Authenticator, making it harder for hackers to gain access even if they know your password.
Introduction to Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Setup 2fa With Microsoft Authenticator
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is a crucial security measure that adds an extra layer of protection to online accounts. It significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access by requiring two forms of verification, typically something you know (password) and something you have (a device like a smartphone). This approach makes it far harder for attackers to gain access, even if they manage to steal a password.The fundamental principle behind 2FA is the concept of multi-factor authentication.
By combining multiple verification methods, 2FA significantly strengthens the security posture of a user’s digital assets. This approach is essential in today’s interconnected world, where cyber threats are ever-present and sophisticated. It’s a simple yet powerful technique for enhancing security against various types of cyberattacks, including phishing, brute-force attacks, and malware infections.
General Process of 2FA
The general process of 2FA involves a series of steps designed to verify the user’s identity. The first step typically involves entering a username and password, which is the “something you know” factor. Following successful password verification, the system prompts the user for a second verification code. This code is usually generated by an authentication app or sent via SMS.
Setting up 2FA with Microsoft Authenticator is a crucial step for bolstering your online security. It’s a simple process that adds an extra layer of protection to your accounts. Remember, enhancing your online security isn’t just about individual accounts; it’s about the whole ecosystem. For example, consider implementing best practices for static site security, such as static site security tips , to protect against common vulnerabilities.
Ultimately, robust security measures like 2FA with Microsoft Authenticator are essential for keeping your data safe in today’s digital landscape.
This second verification, the “something you have” factor, confirms the user’s possession of a legitimate device. The combination of these two factors makes unauthorized access considerably more difficult.
Role of Microsoft Authenticator in 2FA
Microsoft Authenticator is a widely used mobile application for enabling 2FA. It acts as a secure key generator, creating unique time-based codes that are used as the second verification factor. The app generates these codes in a secure manner, making it virtually impossible for attackers to intercept or replicate them. This app-based approach offers a significant advantage over SMS-based verification, as it’s less susceptible to SIM swapping attacks and other SMS-related vulnerabilities.
Microsoft Authenticator integrates seamlessly with various online services, including Microsoft accounts, enabling users to protect their accounts with a robust 2FA system.
Setting up 2FA with Microsoft Authenticator is a pretty straightforward process. It’s a great way to add an extra layer of security to your accounts, which is always a good idea, especially given the recent rise in cyber threats. Thinking about that, the recent Trump inaugural prayer service trump inaugural prayer service also highlights the importance of robust security measures, particularly in sensitive situations.
Ultimately, securing your online accounts is crucial, and 2FA with Microsoft Authenticator is a fantastic way to get started.
Comparison of 2FA Methods
Different methods of 2FA offer varying levels of security and convenience. The table below compares some common methods, including Microsoft Authenticator.
| Method | Description | Security | Convenience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Authenticator | Generates time-based codes on a mobile app. | High; codes are generated securely and are difficult to replicate. | High; no need to manually type codes. |
| SMS-based verification | Verification codes sent via text message. | Moderate; vulnerable to SIM swapping attacks. | Moderate; requires user to have phone access. |
| Hardware tokens | Physical devices that generate codes. | High; physical security of the token is crucial. | Low; requires carrying a physical device. |
| Biometrics (e.g., fingerprint) | Uses unique biological characteristics for authentication. | High; difficult to replicate. | High; convenient and quick. |
Setting up 2FA with Microsoft Authenticator on Different Platforms
Two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security to your Microsoft accounts, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Using Microsoft Authenticator, you can easily secure your personal, work, and other accounts by verifying your identity with a second device. This guide will detail the process of setting up 2FA across various Microsoft platforms and applications.Setting up 2FA with Microsoft Authenticator is a straightforward process that significantly enhances the security of your online accounts.
It involves verifying your identity through a second device, typically a smartphone, using the Microsoft Authenticator app. This added layer of security protects your accounts from unauthorized access attempts, even if someone manages to gain access to your password.
Setting up 2FA on Microsoft Accounts
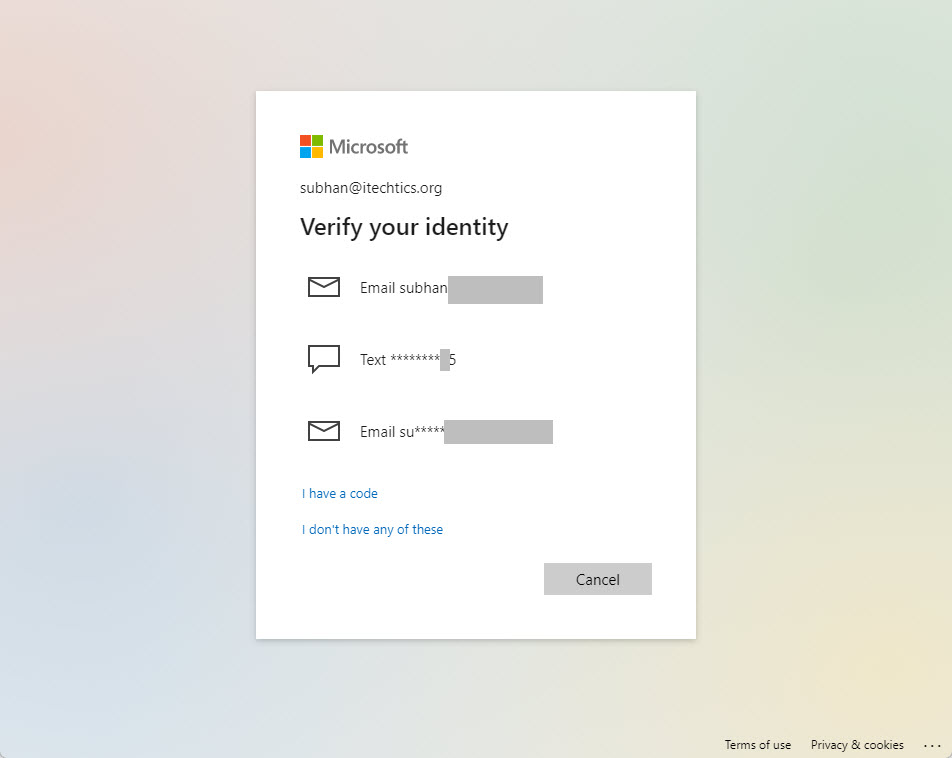
Different types of Microsoft accounts, such as personal, work, or school accounts, might have slightly varying setup procedures. However, the fundamental steps generally remain consistent. Navigate to your account’s security settings page. Look for the option to add or enable 2FA. Follow the on-screen instructions, which usually involve downloading the Microsoft Authenticator app and scanning a QR code.
Configuring 2FA on Various Applications
The setup process for 2FA on applications like Outlook, Teams, and OneDrive is integrated with your Microsoft account. You’ll typically find a dedicated security settings section within each application. Enabling 2FA on these applications ensures that only authorized users can access them.
Setting up 2FA on a Website or Mobile App
The process for setting up 2FA on a specific website or mobile application varies based on the platform’s design. Most platforms will guide you through the necessary steps to add your Microsoft Authenticator app for verification.
Table of Application Setup Procedures
| Application | Setup Procedure |
|---|---|
| Microsoft Outlook | Locate the security settings within Outlook. Enable 2FA and follow the prompts. You’ll typically need to download and use the Microsoft Authenticator app to complete the setup. |
| Microsoft Teams | Navigate to the Teams security settings. Enable 2FA and complete the setup process using the Microsoft Authenticator app. |
| Microsoft OneDrive | Access the OneDrive security settings. Enable 2FA. Follow the prompts and use Microsoft Authenticator to finalize the setup. |
| Specific Website/Mobile App | The website or mobile app will provide specific instructions for enabling 2FA. This often involves adding the Microsoft Authenticator app and scanning a QR code. The steps will be platform-dependent. |
Troubleshooting Common Issues

Setting up two-factor authentication (2FA) with Microsoft Authenticator should be straightforward, but occasional hiccups can occur. This section details common problems encountered during the setup process and provides solutions to get you back on track. Understanding these potential issues and their resolutions will empower you to confidently use 2FA for enhanced security.Often, users encounter difficulties with receiving login codes, the app failing to connect to their account, or problems with service-specific connections.
This section provides clear guidance to overcome these obstacles and successfully implement 2FA.
Login Codes Not Being Received
Issues with receiving login codes are frequently encountered. These problems typically stem from network connectivity issues, app configuration problems, or problems with the service itself. To resolve this, ensure your device has a stable internet connection. If using mobile data, ensure sufficient data allowance and proper network settings.
- Verify that the Microsoft Authenticator app is properly installed and updated to the latest version. Outdated versions may have compatibility issues with certain services.
- Check your device’s notification settings to confirm that notifications for the app are enabled. Ensure the app isn’t blocked by any app permissions or restrictions.
- Try using a different network connection, such as a Wi-Fi network, to rule out potential network issues affecting code delivery.
- If the problem persists, contact the service provider’s support team to check if there are any service-specific issues preventing the code delivery. They may have temporary outages or other technical problems.
App Not Connecting to the Account
Problems with the Microsoft Authenticator app not connecting to the account are often linked to account authentication issues, server outages, or issues with device compatibility. Here’s a systematic approach to troubleshooting.
- Ensure that your account is properly configured and is accessible with correct credentials. Verify account status and ensure there are no temporary account restrictions or suspensions.
- Check if there are any updates or maintenance schedules planned for the specific service account. Service outages or maintenance might cause connection issues. Check the service provider’s status page for updates.
- Verify that your device meets the minimum requirements for the Microsoft Authenticator app. Check the app’s compatibility with your specific operating system version and device model.
- Try restarting the app and your device. A simple restart can often resolve temporary glitches or cache issues preventing the app from connecting to the account.
Troubleshooting Connection Problems with a Specific Service
Connection problems between Microsoft Authenticator and a specific service can arise from misconfigurations, outdated software, or service-specific issues. A step-by-step guide to troubleshooting such problems is crucial.
Setting up 2FA with Microsoft Authenticator is a crucial step for boosting online security. With the recent news of a two bedroom home in Piedmont selling for a cool 2 million two bedroom home in piedmont sells for 2 million , it’s clear that protecting your digital assets is just as important as safeguarding your financial ones.
This extra layer of protection is well worth the effort, especially when dealing with sensitive accounts.
- Verify Service Status: Check the service provider’s website or status page for any reported outages or maintenance affecting the service. Verify if other users are also experiencing similar problems.
- Check Service Compatibility: Ensure that the specific service is compatible with the Microsoft Authenticator app version you’re using. Check the service provider’s documentation for compatibility details.
- Review App Settings: Verify that the correct service is added in the Microsoft Authenticator app. Ensure the settings for the specific service are correctly configured.
- Clear Cache and Data: Clear the cache and data of the Microsoft Authenticator app. Sometimes, outdated or corrupted data can prevent the app from connecting to the service properly.
- Re-add Service: If the issue persists, remove the service from the app and then re-add it. This process can sometimes resolve misconfigurations or temporary errors.
- Contact Support: If the issue persists after all the above steps, contact the service provider’s support team for further assistance. They might have specific solutions or insights into the issue.
Potential Problems and Solutions
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Login codes not received | Verify network connection, notification settings, app updates, and contact service provider. |
| App not connecting to account | Check account status, service status, device compatibility, and restart the app/device. |
| Connection problems with a specific service | Verify service status, compatibility, app settings, clear cache/data, re-add service, and contact service support. |
Security Considerations and Best Practices
Securing your two-factor authentication (2FA) setup is paramount. A compromised 2FA system can grant unauthorized access to your accounts, leading to significant financial and personal losses. Understanding the intricacies of securing your Microsoft Authenticator app and implementing robust password management practices is critical for mitigating risks.Protecting your Microsoft Authenticator app is just as crucial as safeguarding your passwords.
The app, acting as a critical intermediary in your 2FA process, must be treated with the same level of care as your primary accounts. Failure to implement these security measures can expose you to vulnerabilities that could lead to account compromise.
Protecting Your Microsoft Authenticator App
The security of your Microsoft Authenticator app hinges on its proper management. Ensure the app is installed on trusted devices, and consider using strong passwords for your phone and any other devices associated with your 2FA setup. Regularly reviewing and updating the app’s permissions is also vital.
Managing 2FA Codes and Passwords
Effective management of 2FA codes and passwords is crucial for robust security. Implement a strong password manager to securely store and generate complex passwords. Do not reuse passwords across different accounts, and regularly change them. Keep a record of 2FA codes, but prioritize secure storage methods, and avoid storing them in easily accessible locations.
Strategies Against Phishing Attacks
Phishing attacks are a common threat to 2FA security. Be wary of suspicious emails, text messages, or phone calls that request your 2FA codes or login credentials. Never click on links or open attachments from unknown sources. Always verify the authenticity of requests for your 2FA codes, especially if they seem out of the ordinary.
Security Measures to Enhance 2FA Protection
Implementing additional security measures can significantly strengthen your 2FA protection. Enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) wherever possible. Use a strong, unique password for your Microsoft account, and consider enabling two-step verification on all your online accounts.
Best Practices and Security Precautions Summary
| Best Practice | Security Precaution |
|---|---|
| Strong passwords | Use a password manager and unique passwords for all accounts. |
| Trusted devices | Install the Authenticator app only on devices you trust. |
| Regular app updates | Ensure the Microsoft Authenticator app is updated to the latest version. |
| Review permissions | Periodically review and adjust permissions for the Authenticator app. |
| Secure storage | Store 2FA codes securely, preferably in a password manager. |
| Phishing awareness | Verify the legitimacy of requests for 2FA codes before providing them. |
| Multi-factor authentication | Enable MFA wherever possible to add an extra layer of security. |
Alternative Methods and Comparisons
Two-factor authentication (2FA) offers a crucial layer of security beyond simple passwords. Beyond Microsoft Authenticator, various other methods provide robust protection. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of these alternatives empowers informed choices for bolstering account security.While Microsoft Authenticator is a popular and effective 2FA method, exploring other options allows for personalized security strategies. Each method has unique characteristics and potential benefits, which will be discussed below.
Alternative 2FA Methods
Several 2FA methods extend beyond the familiar mobile app. These alternatives offer distinct advantages and considerations. Different solutions cater to varying needs and preferences, from physical security keys to SMS-based verification.
- SMS-based verification: This traditional method utilizes text messages to send a one-time code to your mobile phone. It’s widely accessible and straightforward to implement, but it relies on the security of your phone number and carrier infrastructure. A potential vulnerability lies in compromised SIM cards or phone numbers.
- Hardware Security Keys: These physical devices offer a strong form of 2FA. They use unique cryptographic keys to verify your identity, often without needing an internet connection. They eliminate reliance on potentially vulnerable software or network infrastructure. Security keys are highly secure, but their adoption may be slower due to the additional cost and setup required.
- Authenticator Apps (Beyond Microsoft Authenticator): Other authenticator apps, like Google Authenticator, offer similar functionality to Microsoft Authenticator. These apps generate time-based one-time passwords (TOTPs). The security and features of these apps are comparable to Microsoft Authenticator, and user experience can vary.
- Security Tokens: These devices, either physical or virtual, generate one-time passwords or other verification codes. They typically rely on hardware or strong encryption for security. Their setup and use can vary, but they provide a reliable alternative for 2FA.
Comparison of 2FA Methods
Evaluating different 2FA methods necessitates considering their features and security strengths. A comprehensive comparison highlights the advantages and disadvantages of each.
| Method | Security | Ease of Use | Cost | Vulnerabilities |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microsoft Authenticator | High | High | Low (often free) | Compromised phone, phishing |
| SMS-based Verification | Moderate | High | Low (often free) | SIM swapping, compromised phone number |
| Hardware Security Keys | Very High | Moderate | High | Physical loss or theft |
| Authenticator Apps (e.g., Google Authenticator) | High | High | Low (often free) | Compromised phone, phishing |
| Security Tokens | High | Variable | Variable | Physical loss, technical issues |
Pros and Cons of Microsoft Authenticator
A detailed examination of Microsoft Authenticator reveals its advantages and disadvantages in the context of 2FA.
- Pros: Wide platform compatibility, easy setup, integration with Microsoft services, and high security with proper use. The ease of use contributes to its popularity.
- Cons: Reliance on a mobile device, potential vulnerabilities if the device is compromised, and the need for internet access (though offline codes can mitigate this). User experience can vary depending on the platform and specific device.
Advanced Configurations and Customization
Beyond the basic setup, Microsoft Authenticator offers advanced configurations to tailor your 2FA experience. These options allow you to fine-tune notifications, manage security settings, and personalize the application to your workflow, enhancing both convenience and security. Understanding these advanced features is crucial for optimal use of 2FA.Careful configuration of notification settings and security protocols ensures that your accounts are protected without unnecessary interruptions.
Personalization enables a more efficient and user-friendly experience with Microsoft Authenticator.
Notification Customization
This section details the options available for customizing notification preferences within Microsoft Authenticator. These adjustments allow users to receive alerts in ways that best suit their needs and work style, balancing security with usability. Notifications are a key component of 2FA, and tailoring them enhances the user experience.
- Notification Timing and Method: Users can specify the type of notification (e.g., sound, vibration, banner) and the frequency (e.g., immediate, delayed) for various authentication events. Adjustments in these parameters improve responsiveness and prevent missed alerts, maintaining a high level of account security.
- Customizable Alert Sounds: Users can choose specific sounds for different authentication events, further personalizing the application and allowing for more specific alerting based on context. This feature allows for distinct auditory signals for login attempts, potentially helping to identify suspicious activity more readily.
- Silent Notifications: Some situations require a silent authentication method, such as when working in a public space. Enabling silent notifications allows for verification without disturbing surroundings.
Security Settings and Protocols, Setup 2fa with microsoft authenticator
Managing security settings is crucial for maintaining account protection. The following details advanced options within Microsoft Authenticator to secure access and prevent unauthorized activity. Implementing these security protocols helps to protect your accounts from potential threats.
- Account Recovery: This feature allows users to designate backup contacts for account recovery in case of device loss or compromise. Establishing a robust recovery process provides a safety net for regaining access to accounts.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Options: Users can select specific authentication methods beyond the standard code, such as biometric verification or specific hardware tokens, for enhanced security measures. Employing diverse MFA options adds another layer of protection against unauthorized access.
- Time-Based Expiry: Enabling time-based expiry limits the validity of authentication codes. This feature enhances security by reducing the window of opportunity for attackers to exploit potential vulnerabilities.
Customization Table
This table demonstrates the variety of customization options available and their respective implications for user experience and security.
| Customization Option | Description | Implications |
|---|---|---|
| Notification Timing | Choose when and how notifications are delivered. | Ensures timely alerts and prevents missed verification requests. |
| Alert Sounds | Select specific sounds for different events. | Improves situational awareness and helps identify authentication requests. |
| Account Recovery | Designate backup contacts for account recovery. | Facilitates access recovery in case of device loss or compromise. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication | Choose from various authentication methods. | Enhances security by adding extra verification layers. |
| Time-Based Expiry | Limit the validity of authentication codes. | Reduces the timeframe for potential exploitation. |
Mobile Device Management (MDM) Integration
Mobile Device Management (MDM) solutions play a crucial role in securing and managing company-owned devices, especially when it comes to two-factor authentication (2FA). Integrating 2FA with MDM allows organizations to centrally control and enforce security policies related to authentication, ensuring consistent security posture across all devices. This integration streamlines the 2FA setup process and reduces the risk of security vulnerabilities.MDM platforms provide a centralized dashboard for managing device configurations, including the deployment and enforcement of security policies.
This centralized control is vital for organizations that want to ensure a consistent security posture for all employees. When 2FA is integrated with MDM, IT administrators can automatically deploy the Microsoft Authenticator app to company-owned devices, ensuring that all employees have the necessary tools for secure access. This also facilitates compliance with security policies.
MDM Integration Benefits
Integrating Microsoft Authenticator with MDM solutions offers significant advantages for organizations. Centralized management simplifies the 2FA deployment process, ensuring consistent security across all devices. Automated deployment and enforcement of security policies reduce the risk of misconfigurations and human error, strengthening overall security posture. Moreover, IT administrators gain granular control over the 2FA setup on each device, facilitating rapid troubleshooting and remediation in case of issues.
Use Cases for MDM Integration
MDM integration with Microsoft Authenticator is particularly useful in several scenarios. For example, it’s essential for organizations with BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policies, as it allows them to ensure that all devices meet security standards for access. This is especially critical for sensitive data. In environments with large numbers of employees or geographically dispersed teams, MDM facilitates the consistent enforcement of security protocols, ensuring that all users have the same level of protection.
It is also beneficial for regulatory compliance, as MDM integration ensures adherence to security standards and guidelines.
Process for Implementing MDM Integration
Implementing MDM integration with Microsoft Authenticator involves several steps. The process can vary depending on the specific MDM solution used, but the core principles remain consistent.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. MDM Configuration | Configure the MDM solution to support Microsoft Authenticator. This usually involves setting up the appropriate policies and enabling the necessary integrations. |
| 2. Device Enrollment | Enroll company-owned devices into the MDM solution. This ensures that the device is managed and monitored by the MDM system. |
| 3. Application Deployment | Deploy the Microsoft Authenticator app to the enrolled devices. This ensures that all users have the necessary application for 2FA. |
| 4. Policy Enforcement | Implement policies within the MDM solution to enforce 2FA usage and security protocols. This includes mandatory authentication and automatic enforcement mechanisms. |
| 5. User Training | Provide comprehensive training to users on how to use Microsoft Authenticator with the MDM-integrated 2FA system. This includes educating users about best practices and security protocols. |
Example Scenarios and Use Cases
Two-factor authentication (2FA) with Microsoft Authenticator adds a crucial layer of security to your online accounts. This extra verification step significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, protecting sensitive information from phishing attacks and other malicious activities. Let’s explore how 2FA with Microsoft Authenticator strengthens security in various scenarios.This section details real-world applications of 2FA with Microsoft Authenticator, highlighting how it works in specific use cases like online banking and business applications.
We’ll also examine the setup requirements for different scenarios, providing practical examples and insights.
Online Banking Security
Protecting your financial accounts is paramount. 2FA with Microsoft Authenticator acts as an extra shield against unauthorized access. When you log into your online banking platform, the system prompts you for a code generated by the authenticator app. This code changes every minute, making it virtually impossible for attackers to gain access even if they have your password.
This two-step verification process is critical for safeguarding your funds.
Business Application Access
In the business world, secure access to critical data is essential. Microsoft Authenticator enables robust access controls for applications used in corporate environments. Employees can securely log into business applications, ensuring only authorized personnel have access to sensitive information. This enhanced security posture reduces the risk of data breaches and maintains compliance with security regulations.
Example Scenarios
- Logging into your online bank account: After entering your username and password, the bank’s website sends a verification request to the Microsoft Authenticator app on your phone. You’ll see a unique code; entering this code confirms your identity and allows access to your account.
- Accessing a company’s internal network: Business applications require a second verification step. The Microsoft Authenticator app on your device provides the necessary code for entry into the secure network.
- Protecting your email account: If you receive a suspicious email, the 2FA prompt from Microsoft Authenticator on your phone acts as a vital security measure to confirm your identity before granting access.
- Shopping online: While less critical than banking, 2FA adds an extra layer of security to e-commerce transactions. Entering a code from Microsoft Authenticator on your phone further protects your sensitive financial information.
Use Case Requirements
The security needs and setup requirements for 2FA vary depending on the application. This table provides a general overview of common use cases and their associated requirements:
| Use Case | Setup Requirements |
|---|---|
| Online Banking | Requires enabling 2FA on the banking platform and installing the Microsoft Authenticator app on a mobile device. |
| Business Applications | Requires the business application to support 2FA and the user to have the Microsoft Authenticator app installed. |
| Email Accounts | Requires enabling 2FA on the email provider’s platform and installing the Microsoft Authenticator app. |
| Shopping Websites | Similar to banking, but with varying levels of 2FA support. |
Epilogue
In conclusion, setting up 2FA with Microsoft Authenticator is a vital step in protecting your accounts. We’ve explored the process from initial setup to advanced configurations, highlighting the importance of security best practices. By following this comprehensive guide, you can significantly improve your online security posture and protect your sensitive information. Now go forth and secure your digital life!