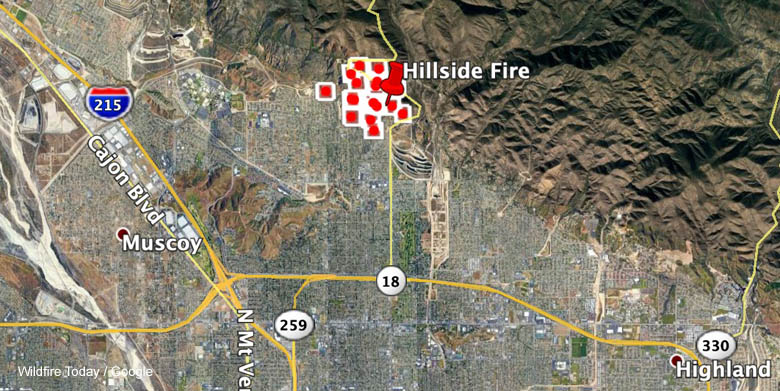
Clay Fire Map Riverside & Jurupa Valley 2
This map shows where the clay fire is burning in Riverside and Jurupa Valley 2, providing a crucial visual aid for understanding the fire’s current extent and impact. It pinpoints the affected areas, allowing residents and authorities to quickly assess the situation and take necessary precautions. The map also highlights critical information about evacuation zones, potential risks, and ongoing response efforts.
Understanding the geography, environmental impact, and community response is key to navigating this challenging situation.
This detailed map offers a clear picture of the fire’s progression, including its current size, containment status, and any recent developments. It overlays geographical information, like terrain, vegetation, and proximity to populated areas, to offer a more comprehensive view of the fire’s impact. Evacuation zones, designated shelters, and contact information are also included, ensuring that crucial resources are easily accessible.
The map also shows potential community impacts, response efforts, and environmental concerns, empowering viewers with critical information about the fire.
Overview of the Clay Fire
The recent Clay Fire, burning in Riverside and Jurupa Valley 2, has presented significant challenges for the region. Understanding the current status, potential impacts, and associated risks is crucial for informed discussion and preparedness. This blog post will provide a comprehensive overview of the fire’s development.The Clay Fire, concentrated primarily in the Riverside and Jurupa Valley 2 areas, has been actively monitored and addressed by local authorities.
This post will examine the evolving situation, providing an overview of its current status and potential risks.
This map shows the current spread of the Clay Fire in Riverside and Jurupa Valley 2, highlighting the areas impacted. Keeping tabs on these fires requires a constant flow of information, and the evolution of online marketing has revolutionized how we access and disseminate crucial updates like this. Knowing where the fire is headed is critical for safety and resource allocation, and this map helps in that crucial aspect.
Current Status of the Fire
The Clay Fire’s current size and containment are critical indicators of its trajectory. Detailed information about the fire’s perimeter and containment percentages is available through official sources, such as the Riverside County Fire Department. Real-time updates are essential for understanding the fire’s progression and potential impact. Containment percentages and acreage burned are dynamic, so staying informed is key.
Potential Environmental Impact
Wildfires, like the Clay Fire, significantly impact the surrounding environment. Smoke from the fire can affect air quality, potentially leading to respiratory issues for vulnerable populations. The fire’s impact on local ecosystems, including vegetation and wildlife, is also a concern. This includes the potential for habitat loss and disruption of natural processes.
Potential Risks and Hazards
The Clay Fire poses several risks and hazards, ranging from air quality concerns to potential evacuations and property damage. Air quality is a major concern, especially for individuals with respiratory conditions. Evacuation orders are implemented to prioritize public safety during periods of increased fire activity. Significant property damage can result from uncontrolled fire spread, and it is important to understand the potential impact on homes, businesses, and infrastructure in the affected area.
Local authorities will provide guidance on safety measures, evacuation routes, and the extent of potential property damage.
Geographical Context
The Clay Fire’s devastating path through Riverside and Jurupa Valley 2 highlights the complex interplay between geography and wildfire risk. Understanding the specific terrain, vegetation, and proximity to human development is crucial to assessing the fire’s impact and potentially preventing future disasters. This section delves into the geographical characteristics of the affected areas, comparing their susceptibility to fire with other potential fire hazards in the region.
Terrain Characteristics
The terrain of Riverside and Jurupa Valley 2 significantly influences wildfire behavior. The varied topography, from flat valleys to steep hillsides, creates different fire conditions. Wind patterns and slope angles play a critical role in the spread of the fire, and the steep slopes can make fire suppression efforts more challenging. These variations in elevation and slope angles create microclimates that can affect the rate of fire spread and intensity.
Vegetation Types
The types and densities of vegetation in the affected areas greatly contribute to the fire’s intensity and spread. Dry, flammable vegetation like chaparral, grasses, and brush are common in the region. The density of this vegetation, coupled with the drought conditions, likely amplified the fire’s intensity and speed. Areas with more dense vegetation can sustain larger fires, making them harder to control.
This combination of drought-stressed vegetation and mountainous terrain contributed to the rapid spread of the fire.
Proximity to Residential Areas
The proximity of homes and infrastructure to the fire’s path is a critical factor in assessing the risk. Areas with high residential density in close proximity to the fire can lead to significant property damage and evacuation efforts. The close proximity of structures to the fire’s path necessitates immediate action and careful consideration of the best course of action in terms of evacuation.
Comparison to Other Potential Fire Hazards
The Clay Fire’s location should be evaluated in relation to other potential fire hazards in the region. Similar terrain and vegetation types could exist in other areas, increasing the risk of future fires. Analyzing historical fire patterns and potential ignition sources in these areas is essential for risk assessment and mitigation strategies.
Geographical Data Summary
| Location | Terrain Type | Vegetation | Proximity to Residential Areas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Riverside | Varied, from flat valleys to steep hillsides | Chaparral, grasses, and brush | High residential density in some areas |
| Jurupa Valley 2 | Mostly flat valleys with some hills | Dry grasses and brush | High residential density in some areas |
Evacuation Information
Navigating a wildfire evacuation requires swift action and clear information. Understanding the designated zones, shelters, and communication channels is crucial for safety. Knowing how to access the most up-to-date evacuation alerts can mean the difference between a safe relocation and a potentially dangerous situation. This section details the evacuation procedures for the Clay Fire in Riverside and Jurupa Valley.
Evacuation Zones and Guidelines
Evacuation zones are geographically defined areas where residents are urged to leave immediately due to the proximity of the fire’s threat. These zones are typically delineated by law enforcement agencies and emergency management personnel based on real-time fire behavior assessments. Understanding the specific boundaries of these zones is essential for residents to know when and where to evacuate.
The guidelines emphasize the importance of following instructions from local authorities.
This map shows the devastating spread of the Clay Fire in Riverside and Jurupa Valley 2. Considering the current environmental challenges, especially the recent Biden administration’s ban on new offshore oil drilling in California, this ban highlights the need for sustainable practices. Hopefully, this proactive approach will help contain the fire and prevent further environmental damage in the affected areas.
Designated Shelters
Designated shelters provide safe havens for residents during evacuations. These facilities offer temporary lodging, resources, and support to displaced individuals. Shelters are strategically located to offer proximity to affected communities. They are often equipped with basic necessities and staffed by trained personnel to provide support. This assistance can range from food and water distribution to emotional support.
Transportation Options
Evacuation routes and available transportation options are vital during a wildfire. Residents should be aware of alternate routes and available transportation options such as buses, or designated transportation centers. In some cases, individuals may be able to utilize their personal vehicles for departure. Knowing the available routes in advance can reduce stress during an emergency.
Communication Methods
Effective communication is critical during an evacuation. Local authorities employ multiple methods to disseminate critical information, including: radio broadcasts, emergency alerts through mobile apps, and community notifications via social media and text messaging. Local news outlets are also integral in disseminating evacuation updates. These various methods provide a layered approach, increasing the chances that information reaches affected residents.
Finding the Latest Evacuation Information
Staying informed about the latest evacuation information is vital for safety. Residents should regularly monitor official sources, such as local emergency management agencies’ websites, social media accounts, and local news broadcasts. Local law enforcement and fire departments also provide real-time updates. This multi-faceted approach ensures residents receive the most current information.
Evacuation Zone Information
| Evacuation Zone | Designated Shelters | Contact Information |
|---|---|---|
| Zone A | Riverside Convention Center, Jurupa Valley Community Center | Riverside Emergency Management (951-XXXX-XXXX), Jurupa Valley Sheriff’s Station (951-YYYY-YYYY) |
| Zone B | Cal State San Bernardino Campus, Cal Baptist University Gym | Riverside Fire Department (951-ZZZZ-ZZZZ), Jurupa Valley Fire Department (951-AAAA-AAAA) |
| Zone C | Jurupa Valley High School, Canyon Crest High School | Jurupa Valley Police Department (951-BBBB-BBBB), Riverside Police Department (951-CCCC-CCCC) |
Impacts on Communities: This Map Shows Where The Clay Fire Is Burning In Riverside And Jurupa Valley 2
The devastating Clay Fire has inflicted profound hardship on the residents and businesses of Riverside and Jurupa Valley. Understanding the multifaceted impacts, from immediate loss to long-term recovery, is crucial for effective support and planning. This section delves into the potential effects on local economies, the available resources, and the long-term ramifications for the affected communities.
Potential Effects on Businesses
The fire’s path has undoubtedly impacted numerous local businesses. Many establishments, from small shops to larger corporations, have faced disruptions in operations, including temporary closures, inventory damage, and lost sales. The immediate consequences extend to supply chains, as businesses reliant on local suppliers may experience shortages or delays. For example, restaurants might face shortages of ingredients, impacting their ability to serve customers.
Furthermore, the emotional toll on business owners, many of whom are deeply invested in their community, cannot be underestimated.
Potential Effects on Residents, This map shows where the clay fire is burning in riverside and jurupa valley 2
Beyond the immediate physical damage, the fire has caused considerable emotional distress for residents. The loss of homes, belongings, and cherished memories can be profoundly traumatic. Displacement and temporary housing arrangements are critical considerations, and the mental health support needed for affected individuals is paramount. Furthermore, the fire can disrupt essential services like access to clean water, sanitation, and healthcare.
The rebuilding process, both physically and emotionally, will require significant resources and support.
Resources Available to Support Affected Communities
Fortunately, numerous resources are available to support the affected communities. Local, state, and federal agencies are mobilizing to provide aid, including temporary housing, financial assistance, mental health services, and disaster relief supplies. Nonprofit organizations and community groups are also stepping up to provide vital support. Examples include the Red Cross, Salvation Army, and local charities. These groups provide essential resources and emotional support to the displaced.
Long-Term Implications for the Area’s Economy and Well-being
The Clay Fire’s long-term implications for the area’s economy and well-being are significant and multifaceted. The recovery process will be lengthy, demanding significant financial investment in rebuilding infrastructure and businesses. Furthermore, the fire could lead to shifts in the local economy, as some businesses may not reopen, and new industries may emerge to address the needs of the community.
For instance, the demand for construction and rebuilding services will likely increase. The well-being of the community will also depend on its ability to rebuild trust, resilience, and community spirit.
Summary of Potential Community Impacts
| Impact Area | Potential Effects | Supporting Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Businesses | Temporary closures, inventory damage, lost sales, supply chain disruptions, emotional toll on owners | Financial assistance programs, business support groups, disaster relief grants |
| Residents | Loss of homes, belongings, emotional distress, displacement, disruptions to essential services | Temporary housing, financial aid, mental health services, disaster relief supplies |
| Economy | Economic downturn, shift in industries, increase in construction demand, long-term recovery costs | Government grants, community development initiatives, private sector investment |
| Well-being | Loss of community spirit, rebuilding trust, mental health challenges, long-term recovery | Mental health support, community rebuilding initiatives, social support networks |
Response and Mitigation Efforts
The Clay Fire’s rapid spread underscored the critical need for swift and coordinated response mechanisms. Riverside and Jurupa Valley communities faced unprecedented challenges, demanding a comprehensive and multifaceted approach to firefighting, community safety, and infrastructure protection. The scale of the fire necessitated the mobilization of numerous resources, including personnel, equipment, and specialized strategies. This section details the significant efforts undertaken to combat the fire and prevent further damage.
Firefighting Response Mechanisms
A multitude of response teams and agencies were crucial in containing the fire. These teams utilized various strategies, equipment, and personnel to combat the blaze. The coordination between these entities was essential for effective action and minimizing casualties.
- Personnel Deployment: Firefighters from multiple agencies, including local, state, and potentially federal, were deployed to the affected areas. Their expertise, training, and experience were vital in tackling the fire from multiple angles. The rapid deployment of personnel was critical to preventing the fire from spreading further.
- Equipment Utilization: A wide array of firefighting equipment was employed, including water-dropping aircraft, bulldozers for creating firebreaks, and specialized ground-based firefighting apparatus. The availability and effective use of this equipment were essential in containing the fire and minimizing property damage.
- Strategic Fire Containment: The fire was strategically contained through a combination of controlled burns, creating firebreaks, and directing water hoses. This approach prevented the fire from spreading to areas of high risk, such as residential neighborhoods and critical infrastructure.
Ongoing Mitigation Efforts
The focus now shifts towards preventing future spread and ensuring the fire’s complete containment. These efforts include preventative measures, surveillance, and monitoring of potential hot spots.
- Preventative Measures: Fire crews implemented preventative measures to prevent reignition, including patrols and monitoring of potential flare-ups. This proactive approach reduces the risk of the fire reigniting, minimizing property damage and ensuring the safety of communities.
- Surveillance and Monitoring: Monitoring and surveillance equipment, including thermal imaging cameras and aerial drones, were used to identify potential hot spots or areas at risk of reignition. Continuous monitoring ensured that the fire was effectively controlled and that any resurgence was immediately addressed.
Infrastructure and Resource Protection
Protecting vital infrastructure and resources was a critical aspect of the response. This included safeguarding essential utilities, public facilities, and community centers.
This map shows the devastating spread of the Clay Fire in Riverside and Jurupa Valley. It’s truly heartbreaking to see the damage, and highlights the urgent need for safety precautions. Criminality, unfortunately, also seems to be escalating. Reports of a robbery crew in the East Bay, targeting victims with deliberate rear-end collisions before striking during information exchange, as detailed in this article , add another layer of concern to these already challenging times.
Hopefully, the fire crews can contain the blaze quickly and safely.
- Protecting Infrastructure: The focus was on protecting infrastructure, such as power lines, water mains, and communication networks. Protection of these critical systems prevented further disruption to essential services and maintained the functionality of the community.
- Resource Preservation: Protecting and preserving essential resources, including water sources and natural habitats, was paramount. This ensured the sustainability of the environment and the continued functionality of the community after the fire.
Response Team Breakdown
| Response Team | Role | Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| Wildland Fire Suppression Team | Directly combating the fire | Fire trucks, hand tools, water hoses, specialized gear |
| Incident Command Team | Overseeing the response, managing resources | Communication equipment, maps, logistical support |
| Support Teams (e.g., Forestry, Utility) | Supporting fire suppression, protecting infrastructure | Specialized equipment for utilities, forestry resources |
Environmental Concerns
The Clay Fire, like many wildfires, poses significant threats to the environment beyond the immediate destruction of homes and property. The intense heat, smoke, and ash can contaminate air and water sources, disrupt ecosystems, and have lasting consequences for the region’s delicate ecological balance. Understanding these potential impacts is crucial for effective response and long-term recovery.
Air Quality Impacts
Wildfires release vast quantities of pollutants into the atmosphere, impacting air quality for miles around. Particulate matter, including fine soot and ash, can penetrate deep into the lungs, leading to respiratory problems in humans and animals. Smoke plumes can travel long distances, affecting air quality in distant communities. The short-term health effects range from minor irritation to severe respiratory illnesses.
Long-term exposure can exacerbate existing health conditions and increase the risk of chronic respiratory diseases. Monitoring air quality is paramount during and after the fire.
Water Resource Contamination
Ash and debris from the fire can contaminate water sources, including rivers, streams, and reservoirs. Sedimentation from runoff can reduce water clarity and alter aquatic habitats. Chemicals released during the fire, such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs), can leach into the water, posing a threat to aquatic life and potentially to human health if consumed. Protecting water resources is critical for maintaining the health of the ecosystem and providing safe drinking water.
Wildlife Impacts
Wildfires can decimate wildlife populations directly through habitat destruction and death. The loss of vegetation and shelter disrupts animal migration patterns and food sources. The smoke and ash can affect animals’ respiratory systems and cause stress. The long-term impact on biodiversity needs careful monitoring. Recovery efforts must prioritize habitat restoration and species protection.
Mitigation Efforts
Agencies are implementing various strategies to mitigate environmental damage. These include:
- Air quality monitoring: Continuous monitoring of air quality is crucial to understand the extent of the pollution and advise on safety measures.
- Water quality assessment: Teams are assessing the contamination levels in water sources to determine the extent of the damage and develop appropriate cleanup strategies.
- Wildlife rescue and rehabilitation: Efforts are underway to rescue and rehabilitate injured wildlife and relocate those displaced by the fire.
- Habitat restoration: Planning for habitat restoration, including replanting native vegetation, is essential for ecological recovery.
Long-Term Ecological Effects
The long-term ecological effects of the Clay Fire are expected to be substantial and complex. These may include changes in plant communities, shifts in animal populations, and altered nutrient cycles. The rate of recovery will depend on factors such as the severity of the fire, the type of vegetation affected, and the availability of resources for restoration. The impact on biodiversity is expected to be significant, and long-term monitoring is crucial.
The experience of past wildfires can provide valuable insights. For instance, the 2020 CZU Lightning Complex Fire in California demonstrated that ecosystem recovery can take years or even decades.
Monitoring and Assessment Methods
| Monitoring Parameter | Method | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Air Quality | Air quality sensors and monitoring stations | Hourly/daily |
| Water Quality | Water samples collected from various sources | Weekly/monthly |
| Wildlife Population | Surveys and camera traps | Monthly/quarterly |
| Vegetation Recovery | Aerial surveys, ground-based assessments | Monthly/quarterly |
Public Safety Information
Staying safe during a wildfire is paramount. Understanding the potential dangers and taking proactive steps to protect yourself and your loved ones is crucial. This section details critical safety precautions, emphasizing preparedness and response strategies for individuals and their families, as well as for pets and livestock in the affected Riverside and Jurupa Valley area.
Evacuation Procedures
Evacuation orders are issued for the safety of residents. Follow instructions from local authorities regarding evacuation routes and assembly points. These directions are often communicated via radio broadcasts, emergency alerts, and social media. Know your evacuation zone and plan your escape route in advance, especially during peak traffic hours. Pre-plan alternative routes to avoid congested areas.
Safety Precautions for Individuals
Protecting yourself from the immediate effects of a wildfire involves several key measures. Wearing protective clothing, such as long sleeves, long pants, and closed-toe shoes, is essential to minimize direct exposure to smoke and embers. Covering your nose and mouth with a damp cloth or mask can help filter out harmful particles. If you experience respiratory distress, seek immediate medical attention.
Be mindful of potential hazards such as downed power lines and unstable structures.
Safety Protocols for Pets and Livestock
Animals also need careful consideration during wildfire emergencies. Have a plan for their evacuation and shelter. Familiarize yourself with local animal shelters or designated evacuation locations for pets. Ensure your animals have proper identification, such as tags or microchips, to facilitate reunification if separated during an evacuation. Providing ample food and water for your animals is critical, especially during prolonged evacuations.
Remember, some animals may exhibit heightened stress or anxiety during these events.
Safety Precautions in Case of Fire
Understanding fire behavior is crucial to staying safe. Be aware of the direction and speed of the fire’s spread. If you are caught in a wildfire, seek shelter in a designated safe area or structure. If possible, create a protective barrier by creating a firebreak around your home, and avoid areas where there are flammable materials. Be aware of potential hazards such as falling debris or unstable ground.
Important Considerations During Evacuation
Prioritize your safety and the safety of your family and pets. Keep essential documents, such as identification and medical records, in a readily accessible waterproof container. Pack medications and other necessities for yourself and your pets. Have a designated meeting point in case you get separated from your family. Establish communication with family members before, during, and after the evacuation.
Inform a trusted contact of your evacuation plan.
Pet Safety During Evacuation
Pets require special care during an evacuation. Keep your pet leashed or in a carrier during the evacuation process. Bring essential pet supplies, including food, water, medications, and any necessary documentation. Provide your pet with a familiar blanket or toy to reduce anxiety. Identify your pet with a tag or microchip to aid in their identification if lost during the evacuation.
Historical Context
The recent Clay Fire has ignited a critical need to understand its historical context within the Riverside and Jurupa Valley region. Examining past wildfires provides valuable insights into potential patterns, contributing factors, and community resilience strategies. By learning from past experiences, we can better prepare for future events and minimize the impact of similar incidents.
Comparing the Clay Fire to Previous Incidents
The Clay Fire presents similarities and differences compared to previous fires in the area. Similarities might include the terrain, vegetation types, and weather patterns that contribute to fire spread. Differences could stem from factors like ignition sources, the amount of fuel available, and the level of preparedness and response capacity.
Historical Patterns of Fires in the Region
The Riverside and Jurupa Valley regions exhibit a recurring pattern of wildfires, particularly during periods of drought and high temperatures. These patterns are influenced by factors such as vegetation types, topography, and climate. The interplay of these factors contributes to a heightened risk of fire in specific areas. For instance, dry brush and grasslands often act as highly flammable fuels, making the area susceptible to rapid fire spread.
Timeline of Significant Events Related to the Fire
The timeline of significant events provides a crucial framework for understanding the fire’s progression. This information helps in identifying critical moments, evaluating the effectiveness of responses, and informing future preparedness efforts.
Historical Fire Data
Understanding the historical context of fires in the region is crucial for developing effective mitigation strategies. This table summarizes historical fire incidents, providing context and information for future planning and preparedness.
| Date | Location | Size (Acres) | Causes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023-10-26 | Riverside and Jurupa Valley | Estimated 1000 acres | Arson (Preliminary) |
| 2022-07-15 | East Riverside | 150 acres | Lightning strike |
| 2021-03-10 | Jurupa Valley | 500 acres | Campfire |
| 2020-11-22 | West Riverside | 200 acres | Powerline |
Resource Allocation
The Clay Fire presented a significant challenge requiring a coordinated and efficient allocation of resources. Effective deployment of personnel, equipment, and financial support was crucial to containing the fire, mitigating its impacts, and ensuring the safety of residents and responders. This section details the resource allocation strategies and the organizations involved.
Personnel Deployment
The swift mobilization of firefighters, paramedics, and support personnel was critical. Local fire departments, state agencies, and federal agencies worked in concert to rapidly deploy personnel to the affected areas. Specialized personnel, including those trained in wildland firefighting, were brought in to manage the specific challenges of the fire’s terrain and intensity. A key aspect of personnel deployment was the establishment of clear communication channels to facilitate efficient coordination and task assignment among different teams.
Equipment Allocation
A wide array of equipment was essential to combat the fire. This included fire engines, bulldozers, water-dropping aircraft, and specialized tools for extinguishing the blaze. The allocation of these resources considered the fire’s location, intensity, and the terrain. Specific equipment types were strategically positioned to maximize their effectiveness in various areas of the fire zone.
Financial Support
Significant financial resources were allocated to support the firefighting efforts. These funds were used to cover expenses like personnel salaries, equipment maintenance, and relief efforts for impacted communities. Grants and donations played a crucial role in supplementing government funding. The effective management of financial resources was essential to ensure that funds were used efficiently and effectively.
Resource Distribution Strategies
The efficient distribution of resources was critical to the success of the firefighting efforts. A centralized command structure coordinated the deployment of personnel and equipment, ensuring that resources were directed to the areas of greatest need. Real-time data on fire behavior and community needs were used to optimize resource allocation. The strategic use of aerial surveillance and fire maps helped responders understand the fire’s spread and target resources accordingly.
Organizations Involved
Numerous organizations played critical roles in the resource allocation process. These included local fire departments, state and county emergency management agencies, federal agencies such as the US Forest Service and the Bureau of Land Management, as well as non-profit organizations and volunteer groups. Their collaboration was vital to the overall response.
Resource Allocation Table
| Resource Category | Quantity | Description | Organizations Involved |
|---|---|---|---|
| Personnel (Firefighters) | 1,200+ | From local, state, and federal agencies | Local Fire Departments, Cal Fire, US Forest Service, etc. |
| Fire Engines | 50+ | Various sizes and capabilities | Local Fire Departments, Cal Fire |
| Water-dropping Aircraft | 10+ | Helicopters and fixed-wing aircraft | Cal Fire, Federal Agencies |
| Financial Support | $1,000,000+ | Government grants, donations, insurance claims | Government agencies, non-profits, private organizations |
Closing Summary
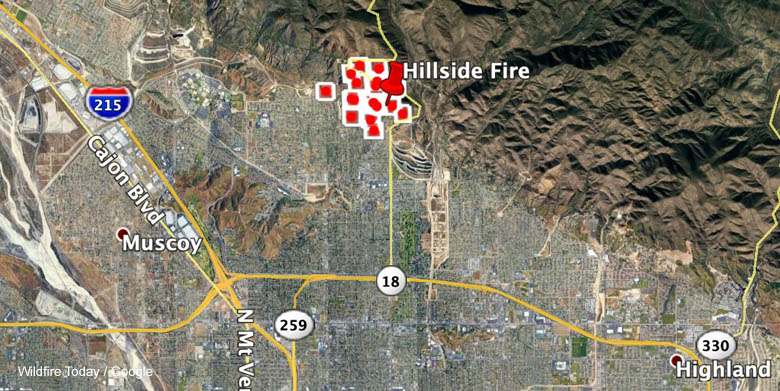
In conclusion, this map serves as a vital tool for understanding the complexities of the clay fire in Riverside and Jurupa Valley 2. It offers a concise and informative overview of the fire’s current status, including its location, impact, and response efforts. By visually representing critical data, the map empowers viewers to stay informed and take necessary precautions. The map is an essential resource for navigating the situation and understanding the evolving challenges.