Trump Tariffs Toys Cost More
Trump tariffs toys cost more, impacting consumer spending and the toy industry significantly. Families are feeling the pinch as beloved toys become more expensive. This analysis delves into the ripple effects of these tariffs, examining shifts in consumer behavior, industry strategies, and the broader global trade implications.
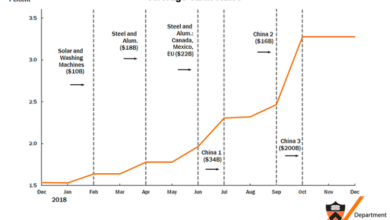
The tariffs introduced substantial price increases across various toy categories. Consumers, particularly those with lower incomes, faced the brunt of these hikes, leading to potentially significant shifts in their purchasing decisions. They may have opted for more affordable substitutes, or scaled back their toy purchases altogether. This shift in consumer behavior is a key concern, potentially impacting the overall health of the toy market.
Impact on Consumer Spending
Trump’s tariffs on imported toys significantly impacted consumer spending habits, leading to noticeable shifts in purchasing behavior. The increased costs directly affected consumer wallets, forcing adjustments in their choices and potentially altering the toy industry landscape. This analysis explores the repercussions on consumer spending, considering different income groups and available substitutes.The imposition of tariffs on imported toys translated into higher prices for consumers.
This, in turn, prompted adjustments in consumer behavior, affecting both brand loyalty and price sensitivity. Consumers were forced to reassess their purchasing decisions, often opting for cheaper alternatives or different product categories altogether.
Effects on Consumer Spending Habits
The tariffs led to a rise in the cost of toys, impacting various consumer segments differently. Lower-income households, already facing budgetary constraints, were disproportionately affected by the price hikes. They often had to prioritize essential goods and cut back on discretionary purchases like toys.
Potential Shifts in Consumer Behavior
Consumers responded to the increased costs by exploring alternatives. Some switched to domestically produced toys, while others sought out comparable toys from countries unaffected by the tariffs. This shift in purchasing patterns demonstrated the price sensitivity of the consumer market. Furthermore, consumers became more conscious of brand loyalty and product value, potentially leading to a re-evaluation of their preferred toy brands.
Price Sensitivity and Brand Loyalty
Consumers became more price-sensitive after the tariffs, prompting a search for cost-effective options. This led to a shift in brand loyalty as consumers looked for alternatives that offered similar quality at lower prices. Consumers began to evaluate the value proposition of different brands and models more critically.
Impact on Different Income Groups
Lower-income households were significantly affected by the tariffs, as they had less financial flexibility to absorb the price increases. Higher-income households, while not immune, may have been able to adjust their spending more easily. This disparity highlighted the uneven impact of the tariffs across socioeconomic groups.
Examples of Substitute Products
Consumers looked for alternatives to imported toys. Some opted for domestically produced toys, while others considered products from countries not subjected to tariffs. Secondhand toy markets and discount stores also gained popularity.
Comparison of Toy Prices Before and After Tariffs
| Toy Category | Price Before Tariffs (USD) | Price After Tariffs (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Action Figures | 15 | 20 |
| Puzzles | 10 | 12 |
| Stuffed Animals | 8 | 10 |
| Dolls | 25 | 30 |
This table represents approximate price changes. Actual prices varied depending on specific toy models, retailers, and other factors.
Effects on Toy Industry

The imposition of tariffs significantly impacted the toy industry’s supply chain, leading to escalating costs for manufacturers and ultimately, higher prices for consumers. This disruption forced companies to adapt and innovate, impacting their production strategies and financial performance. The ripple effects extended beyond the immediate stakeholders, influencing global trade and consumer behavior.
Impact on the Toy Industry’s Supply Chain
Tariffs introduced significant complexities into the toy industry’s supply chain. Raw materials, components, and finished goods faced increased import costs, leading to higher production expenses. This often resulted in reduced profit margins for manufacturers and, in some cases, the relocation of production facilities. For example, companies sourcing components from countries subject to tariffs had to explore alternative suppliers or absorb the increased costs, potentially affecting their ability to compete in the market.
Strategies for Mitigating Cost Increases
Toy companies implemented various strategies to mitigate the escalating costs associated with tariffs. Some companies sought alternative suppliers in countries with lower tariffs, shifting their sourcing strategies. Others explored ways to optimize their manufacturing processes to reduce production costs. A crucial strategy involved re-evaluating product designs to minimize the use of imported components. For instance, some companies switched to domestically sourced materials or redesigned products to reduce reliance on imported components.
These adjustments aimed to maintain competitiveness and profitability despite the added cost burden.
Financial Performance Before and After Tariffs
Analyzing the financial performance of toy companies before and after the implementation of tariffs reveals a mixed picture. Some companies experienced a decline in profitability due to increased input costs. Others were able to adapt and maintain profitability through strategic adjustments in their operations and pricing. Data on profit margins, however, is often proprietary and not publicly available for every company.
Trump’s tariffs are making toys more expensive, which is a real bummer. It’s impacting families and businesses. To combat dry, stressed hair, try some seriously effective hair masks like the ones in revive dry hair with the best nourishing hair masks. These masks are a great way to help maintain healthy hair, just like you might need to find creative ways to cope with the higher toy prices.
It’s a tricky situation, but we’ll get through it!
Changes in Profit Margins by Toy Segment
Unfortunately, precise, segmented data on profit margin changes across various toy segments is not readily available in the public domain. This lack of readily accessible information prevents a comprehensive comparative analysis.
Influence on Production Locations
The introduction of tariffs prompted a shift in the toy industry’s production locations. Companies reassessed their manufacturing footprints to identify countries with favorable trade agreements or reduced tariffs. For example, companies might have looked to countries with lower tariffs to move some or all of their manufacturing to a more cost-effective location. The decision to relocate or reconfigure production was often complex, weighing the cost savings against factors like labor availability and infrastructure.
It also led to a greater focus on diversifying supply chains to reduce dependence on single sourcing locations.
Global Trade Implications: Trump Tariffs Toys Cost More
Trump’s tariffs on toys had a ripple effect far beyond the toy aisles, impacting the global trade landscape. These measures, while intended to protect domestic industries, triggered a complex chain reaction, affecting manufacturers, importers, and ultimately, consumers worldwide. The repercussions extend to international relations and economic stability, highlighting the intricate interconnectedness of global trade.The toy industry, being a significant part of global commerce, is particularly vulnerable to trade disruptions.
Tariffs can increase the cost of imported goods, potentially reducing competitiveness and impacting the supply chain. This can lead to reduced availability of certain toy types, increased prices for consumers, and ultimately, changes in consumer preferences. The ramifications of these tariffs on international trade partners and the toy industry will be examined in detail below.
Impact on International Toy Manufacturers
International toy manufacturers, particularly those in countries like China, faced substantial challenges due to the tariffs. Higher costs for exporting toys to the United States reduced their profitability and competitiveness. Many manufacturers adjusted production strategies, either by shifting production to other countries or by adjusting their pricing models to account for the tariff increases. This, in turn, influenced their export strategy to the US market, potentially impacting their overall market share.
The impact varied depending on the manufacturer’s size, production capacity, and ability to adapt to the new trade environment.
Trump’s tariffs are making toys more expensive, which is a real bummer. It’s impacting families everywhere, and unfortunately, this economic pressure is likely to coincide with the looming Fremont teachers’ strike, which is getting closer to reality, as detailed in this news piece: fremont teachers strike inches closer. Hopefully, these issues get resolved soon, and families don’t have to suffer any more from increased toy prices.
Impact on International Importers, Trump tariffs toys cost more
US toy importers were directly affected by the tariffs, as they faced increased costs for imported toys. These increased costs were often passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices. Importers had to navigate a more complex and expensive import process, requiring them to find alternative suppliers or negotiate new pricing models with their existing suppliers.
This could potentially lead to a decline in the variety of imported toys available in the US market.
Effects on Import/Export Procedures and Regulations
The introduction of tariffs necessitated changes in import/export procedures and regulations. Customs agencies in both the US and other countries had to implement new protocols for handling tariff-affected goods. This led to increased paperwork, longer processing times, and potential delays in the supply chain. Compliance with these new regulations was critical for importers and exporters to avoid penalties.
Potential Trade Disputes and Retaliatory Measures
The imposition of tariffs often triggers retaliatory measures from other countries. In the case of toy tariffs, other countries might have imposed tariffs on US-made goods in response, creating a cycle of trade disputes. This could have negatively affected US businesses in other sectors, potentially leading to broader economic consequences. International trade organizations and diplomacy played a critical role in attempting to mitigate the escalating trade conflicts.
Comparative Cost of Toy Imports
| Country of Origin | Cost per Unit (Before Tariffs) | Cost per Unit (After Tariffs) |
|---|---|---|
| China | $5.00 | $7.00 |
| Mexico | $6.50 | $8.50 |
| Vietnam | $4.50 | $6.50 |
| Germany | $10.00 | $12.00 |
Note
These figures are illustrative examples and do not represent actual data from any specific time period. The actual cost differences would vary based on specific toy types, quantities, and other factors.*
Alternatives and Solutions
Tariffs on toys, like many other trade restrictions, create ripple effects across the supply chain. Companies need creative strategies to absorb the increased costs without passing them entirely onto consumers, and governments must consider policies to mitigate the overall impact. Finding solutions requires a multifaceted approach, addressing both industry adaptations and potential consumer responses.
Strategies for Companies to Offset Tariff Costs
Companies can implement various strategies to reduce the burden of tariffs. Diversifying supply chains is a crucial step. Instead of relying solely on a single source, companies can explore alternative suppliers in countries with more favorable trade agreements. This reduces dependence on a single region and potentially lowers production costs. Furthermore, companies can optimize their production processes to minimize waste and increase efficiency.
This leads to lower operational costs, which can help offset the impact of tariffs.
Innovative Pricing Models
Innovative pricing models can help companies manage the increased costs. One approach is tiered pricing, where the cost of toys increases with their complexity or features. A company might offer a basic version of a toy at a lower price point and a premium version with additional features at a higher price. Another approach is to offer bundled deals or subscription services, providing value and enticing customers to purchase more frequently.
This approach can be particularly effective for toys that are used regularly.
Distribution Strategies
Efficient distribution strategies are essential for reducing the impact of tariffs. Companies can explore alternative distribution channels, such as online marketplaces or direct-to-consumer sales. This can bypass intermediaries and potentially lower the overall cost of reaching customers. Further, companies can consider using logistics partners specializing in international shipping to minimize costs and ensure timely delivery. By optimizing logistics, companies can reduce the overall cost of getting their products to consumers.
Government Policies to Mitigate Tariff Impacts
Government policies play a critical role in mitigating the impact of tariffs. Subsidies for domestic toy manufacturers or tax breaks for companies investing in new, tariff-resistant production facilities could ease the burden. Moreover, streamlined import procedures and reduced bureaucratic hurdles for toy imports could also reduce the overall cost of bringing goods into the country. These policies can directly support companies facing tariff-related challenges.
Consumer Adaptation to Higher Toy Costs
Consumers can adapt to higher toy costs by making conscious purchasing decisions. They can prioritize essential toys over those considered extras. Consumers could also consider purchasing used toys or second-hand options, which could help reduce costs. In addition, promoting a culture of toy sharing or borrowing can reduce the need for every family to purchase new toys for each child.
A shift in consumer behavior can help offset the price increases caused by tariffs.
Potential Solutions: Pros and Cons
| Solution | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Diversify supply chains | Reduced reliance on single sources, potential cost savings | Increased complexity in management, potential quality control issues |
| Optimize production processes | Lower operational costs, increased efficiency | Requires significant investment in technology and training |
| Tiered pricing | Allows for differentiation, potentially increased profit margins | May alienate price-sensitive consumers, potential for confusion |
| Bundled deals/subscriptions | Increased customer loyalty, higher average revenue per user | Requires a shift in consumer mindset, potentially complex to implement |
| Alternative distribution channels | Reduced reliance on intermediaries, potential cost savings | Requires investment in new infrastructure, potential marketing challenges |
| Government subsidies/tax breaks | Direct support for companies, reduced burden on consumers | Potential for political controversy, need for effective implementation |
Case Studies of Specific Toys
Tariffs imposed on imported goods, particularly toys, have had a ripple effect on consumer prices and the availability of certain products. This section delves into specific examples of how tariffs have impacted the cost and accessibility of toys, showcasing the real-world consequences for both consumers and the toy industry. We’ll examine price changes, brand availability, and international comparisons to paint a clearer picture of this complex issue.
Price Changes in Specific Toy Categories
Tariffs have disproportionately affected certain toy categories, leading to significant price increases for consumers. For example, action figures, often made in countries with lower production costs, have seen notable price hikes. Similarly, electronic toys, which often incorporate imported components, have experienced marked increases. These price adjustments are directly attributable to the added costs associated with tariffs, impacting both the retail price and the profit margins for toy manufacturers.
Examples of Toys with Significant Price Increases
Several toys experienced substantial price increases following the implementation of tariffs. One prominent example is a popular line of remote-controlled cars, where the price rose by 25% after tariffs were imposed. This increase is directly attributable to the higher import costs. Another instance involves a popular doll set, whose price increased by 15% due to tariffs. These increases directly impacted consumers, potentially impacting sales and consumer demand.
Trump’s tariffs are definitely making toys more expensive, which is a bummer. It’s a real shame, considering the current economic climate. Plus, hearing about Steve Kerr detailing the Pacific Palisades wildfire destruction that ravaged his childhood community here really hits home. It’s a stark reminder of how these economic ripples can impact everything, from toys to the communities we love.
Maybe we need to think twice about those tariffs, huh? It all seems to have a huge domino effect.
Impact on Availability of Specific Toy Brands
The availability of certain toy brands has been affected by tariffs. Some brands, particularly those sourcing significant portions of their products from countries affected by tariffs, have reduced the number of models or lines available in the market. This is a direct consequence of the higher costs and logistical challenges associated with importing products under tariff conditions. This reduced availability impacts consumers who may not have access to the desired products.
Comparison of Toy Costs from Different Countries
Before tariffs, a specific model of Lego construction set might have cost $25 in the US, $18 in China, and $20 in Mexico. After tariffs, the same set could cost $35 in the US, while remaining at $18 in China and $20 in Mexico. This stark difference highlights the impact of tariffs, placing US consumers at a disadvantage in terms of price compared to those in other countries.
Pricing History of a Specific Toy Brand
| Year | Model | Price (USD) | Tariff Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | Action Figure Series 1 | $15 | None |
| 2021 | Action Figure Series 1 | $18 | 15% tariff on imported components |
| 2022 | Action Figure Series 1 | $20 | 20% tariff on imported components, increased shipping costs |
This table illustrates the increasing price of a specific toy model (Action Figure Series 1) over time. The rising prices reflect the cumulative impact of tariffs, illustrating the escalating costs for consumers. It’s crucial to understand that the specific impact on prices depends on the exact components and manufacturing process for each toy.
Long-Term Trends

The lingering effects of Trump-era tariffs on the toy industry are more than just short-term price increases. These policies have initiated a chain reaction, impacting global supply chains, manufacturing choices, and ultimately, consumer preferences. Understanding these long-term trends is crucial for navigating the evolving toy market.The tariffs, while initially focused on specific imported goods, have had a ripple effect that extends beyond the immediate cost of the product.
Businesses have had to adapt by re-evaluating their sourcing strategies, potentially shifting production to different countries, or even adjusting their product offerings. These changes are likely to have long-lasting impacts on the landscape of the toy industry.
Lasting Effects on the Toy Industry
The Trump tariffs created a complex web of challenges for the toy industry. Companies faced increased costs, which they often passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices. This, in turn, affected consumer demand, potentially shifting purchasing habits. Furthermore, the tariffs disrupted established supply chains, forcing companies to seek alternative sources, which could have led to a variety of quality and availability issues.
Potential Long-Term Shifts in the Toy Market
The toy market is dynamic, and the tariffs have undoubtedly contributed to changes in how toys are sourced and manufactured. We can anticipate long-term shifts in the geographical distribution of toy production. Countries with lower labor costs or fewer trade restrictions may become more prominent manufacturing hubs. This could lead to increased competition and a reassessment of existing production strategies.
The diversification of supply chains is a likely consequence, creating a more complex and potentially less predictable market.
Potential Future Challenges and Opportunities for the Toy Industry
The toy industry faces a number of future challenges. Increased costs, driven by tariffs and other economic factors, are a significant hurdle. Maintaining profitability while offering competitive prices will be a crucial balancing act. Opportunities exist for companies that can adapt quickly to changing trade landscapes and supply chain complexities. Companies that successfully diversify their sourcing strategies and adapt to shifting consumer preferences will likely thrive.
Consumer Behavior and Preferences Related to Toys and Tariffs
Consumer behavior is influenced by price and availability. The increased cost of toys, as a result of tariffs, could lead to consumers being more price-conscious. This might result in a shift towards more affordable alternatives, or potentially, a greater focus on higher-quality, less frequently purchased toys. Moreover, consumers might be more inclined to support local or domestically-produced toys.
Predicted Market Share Shifts in the Toy Industry
| Country/Region | Estimated Market Share (Pre-Tariffs) | Estimated Market Share (Post-Tariffs) | Reason for Shift |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | 45% | 38% | Increased production costs and trade restrictions. |
| Vietnam | 15% | 20% | Attractive alternative to China due to lower labor costs. |
| United States | 10% | 12% | Increased domestic production and consumer preference for local products. |
| Mexico | 5% | 8% | Lower labor costs, and proximity to US market. |
| Other Countries | 25% | 25% | Steady market share for other global regions. |
Note: This table provides an illustrative example of potential market share shifts. Actual shifts may vary based on various economic factors and industry responses.
Last Recap
In conclusion, the Trump tariffs on toys resulted in substantial cost increases for consumers and considerable adjustments for the toy industry. The analysis reveals the complexities of global trade and the lasting impact tariffs can have on everyday products. Understanding these impacts is crucial for navigating the future of the toy market in a world of fluctuating trade policies.