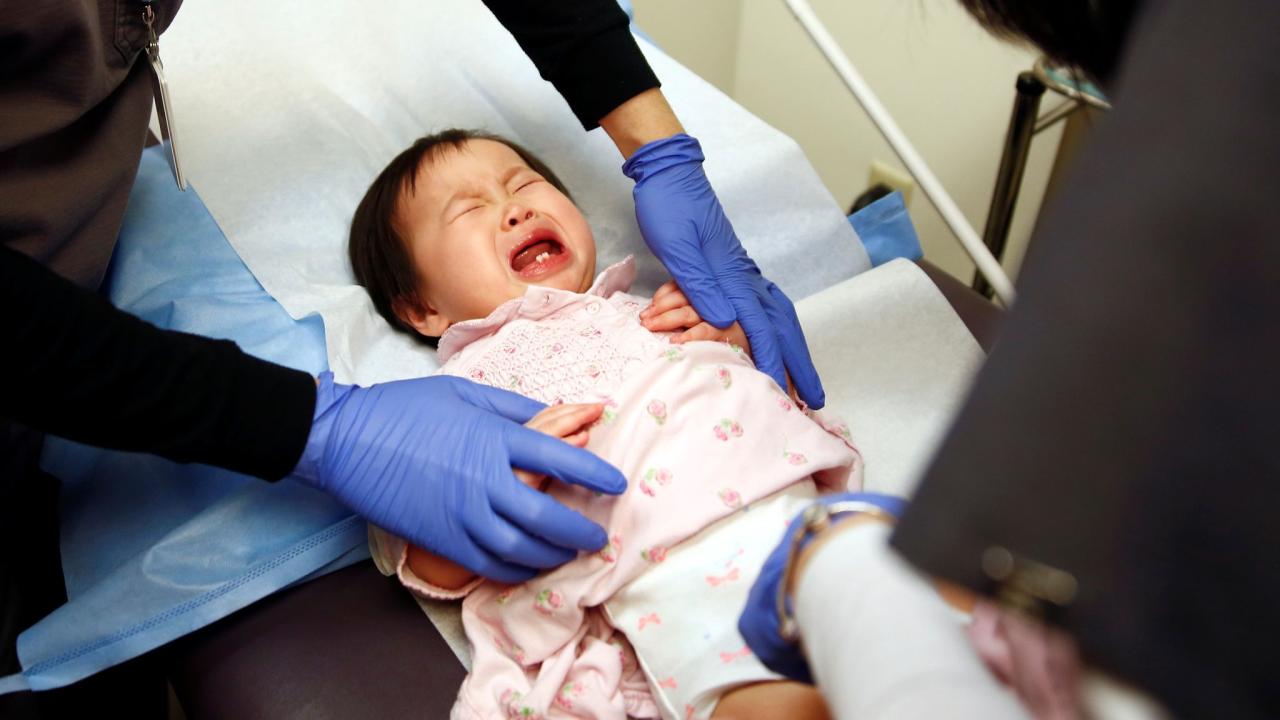
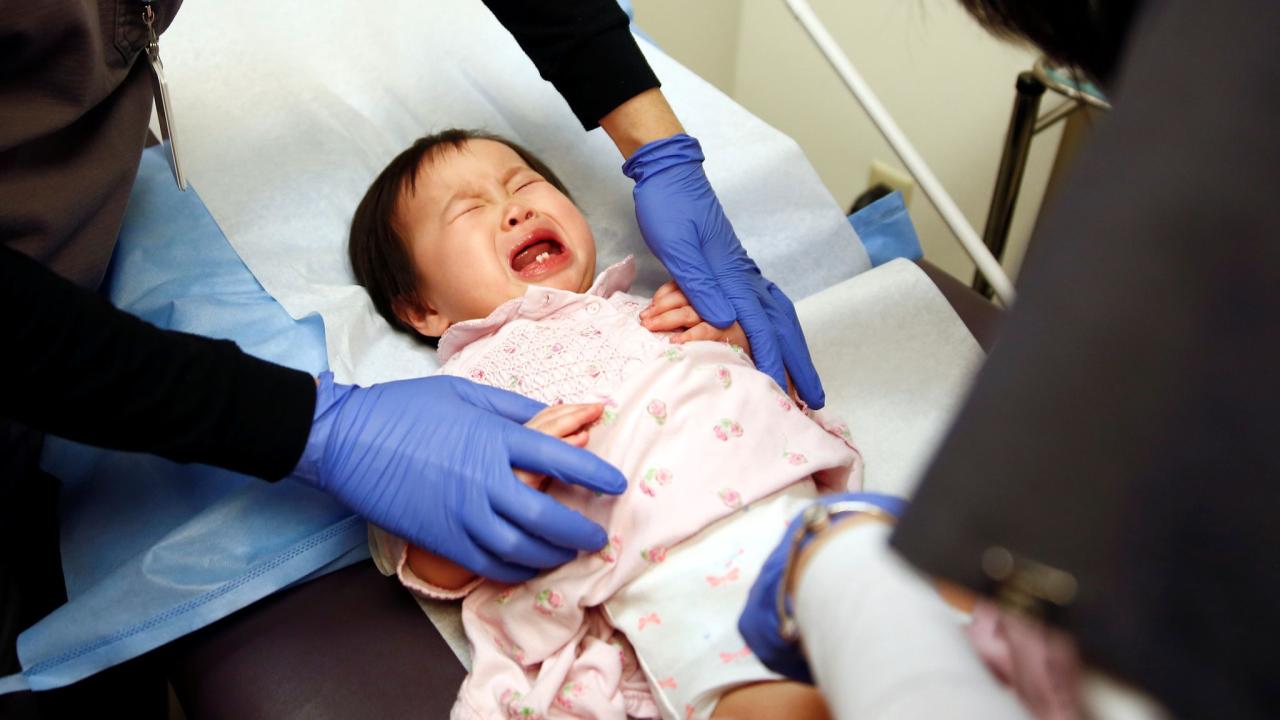
Texas Measles Second Child Dies
a second child with measles has died in texas as the outbreak continues to spread, highlighting the urgent need for preventative measures. This tragic event underscores the severity of the ongoing measles outbreak in Texas, affecting a growing number of communities and demanding immediate attention from public health officials. The spread of this highly contagious virus is alarming, particularly given the potential long-term health consequences for children.
This article delves into the current situation, examining the contributing factors, public health response, and the profound impact on affected children. It also explores the crucial role of vaccination, the challenges posed by misinformation, and the importance of community engagement in preventing future outbreaks. The tragic loss of a second child emphasizes the critical need for swift and decisive action to contain the spread of measles.
Overview of the Situation
A tragic second death of a child due to measles has underscored the severity of the ongoing outbreak in Texas. This heartbreaking development further highlights the urgent need for vaccination and public health interventions to control the spread of this highly contagious disease. The situation demands immediate attention and proactive measures to prevent further fatalities and protect vulnerable populations.The measles outbreak in Texas is concentrated in specific regions, impacting communities across the state.
The geographic scope of the outbreak, while not encompassing the entire state, underscores the importance of localized interventions and emphasizes the vulnerability of particular regions to disease transmission. The severity of the outbreak is evident in the number of reported cases and, unfortunately, the loss of life. This necessitates a robust and multifaceted approach to address the root causes of the spread and prevent further complications.
Geographical Area Affected
The measles outbreak is concentrated in several counties in North Texas, primarily impacting densely populated areas. This concentration suggests that community transmission within these areas is driving the spread of the disease, and emphasizes the importance of targeted interventions in those specific regions.
Severity of the Outbreak
The recent measles outbreak in Texas has demonstrated a concerning rate of transmission. The number of confirmed cases and the unfortunate death toll clearly indicate the severity of the outbreak. The long-term health implications for affected children, particularly those with weakened immune systems, are substantial and warrant careful monitoring. This severity underscores the need for swift and effective public health measures to contain the outbreak.
Tragically, a second child in Texas has succumbed to measles, highlighting the ongoing severity of this outbreak. While heartbreaking, it’s worth noting that even amidst such serious health concerns, professional athletes are finding ways to enhance their performance. For example, SF Giants pitcher, Alex Cobb, could potentially see a further velocity increase with his splitter, as discussed in this insightful piece on how SF Giants’ pitcher, how sf giants hicks could continue seeing velocity uptick with splitter , might maintain his effectiveness.
This ongoing measles crisis sadly underscores the importance of preventative measures and vaccinations.
Potential Long-Term Health Implications
Measles, even in those who recover, can have lasting consequences. Complications from measles, such as encephalitis (inflammation of the brain) and pneumonia, can lead to permanent disabilities or long-term health problems. Children with pre-existing health conditions are particularly vulnerable, and the potential long-term impact on their health is substantial. The importance of early diagnosis and treatment cannot be overstated, as prompt intervention can often mitigate the severity of complications.
Current Measures Taken by Public Health Officials
Public health officials in Texas are actively implementing measures to contain the outbreak. These include increased vaccination campaigns, enhanced surveillance of potential cases, and community outreach programs to promote vaccination and raise awareness. The aim is to limit the spread of the virus and protect the most vulnerable populations. These measures are critical in effectively combating the outbreak and mitigating its long-term impact.
This proactive response is crucial to limiting the outbreak’s spread.
Contributing Factors
The recent measles outbreak in Texas, tragically claiming a second child’s life, highlights the complex interplay of factors contributing to its spread. Understanding these elements is crucial for developing effective strategies to prevent future outbreaks and protect vulnerable populations. The factors extend beyond simple infection; they encompass societal structures, access to resources, and the impact of misinformation.The ongoing spread of measles underscores the importance of addressing the underlying contributing factors that fuel these outbreaks.
This includes not only the direct transmission of the virus but also the broader social and systemic issues that create fertile ground for its resurgence. Examining these interconnected factors is critical for crafting effective preventive measures and ultimately safeguarding public health.
Low Vaccination Rates
Measles is a highly contagious disease, easily spread through airborne droplets. Vaccination remains the most effective tool in preventing its transmission. Low vaccination rates in certain communities create vulnerable populations, allowing the virus to circulate and potentially cause outbreaks. Factors such as limited access to healthcare, religious or philosophical objections to vaccination, and lack of awareness about the importance of immunization can all contribute to lower vaccination rates.
In some cases, misinformation campaigns have also played a significant role in deterring individuals from getting vaccinated.
Misinformation and Public Health Messaging
The spread of inaccurate or misleading information about vaccines, including the safety and efficacy of measles vaccines, can significantly impact vaccination rates. This misinformation, often disseminated through social media and other online platforms, can create doubt and fear around vaccination, leading individuals to make choices that may compromise their own health and the health of their communities. Effective public health messaging is crucial to counteract this misinformation and promote the benefits of vaccination.
Combating misinformation requires a multi-pronged approach, including targeted communication campaigns, fact-checking initiatives, and collaborations with trusted community leaders.
Access to Healthcare and Socioeconomic Factors
Access to healthcare services is intricately linked to vaccination rates. Socioeconomic factors, such as poverty, lack of insurance, and limited transportation options, can make it challenging for individuals to access vaccination services. Individuals in these vulnerable populations may face significant barriers in scheduling appointments, obtaining necessary paperwork, and ensuring their children receive the recommended vaccination schedule. The impact of socioeconomic factors on vaccination rates varies geographically and depends on the specific characteristics of the affected communities.
Understanding these disparities is crucial to developing targeted interventions that improve access to healthcare and promote vaccination.
Community Spread and Outbreak Dynamics
The rapid increase in measles cases highlights the importance of community spread. Once introduced into a community with lower vaccination rates, the virus can quickly spread through close contact among unvaccinated or under-vaccinated individuals. This rapid transmission is facilitated by factors such as school settings, community gatherings, and close-knit social networks. Tracing the routes of transmission is vital in containing the outbreak and preventing further spread.
Comparison to Past Outbreaks
Measles outbreaks have occurred throughout history and in various parts of the world. While vaccination rates have generally improved in many countries, recent outbreaks demonstrate that the virus can still pose a significant threat. Comparing the current outbreak with past ones allows for the identification of similarities and differences in contributing factors and outbreak patterns. Understanding historical trends can provide valuable insights into effective prevention and control strategies.
Impact on Affected Communities
Measles can have a significant impact on the affected communities, both directly and indirectly. The disease itself can lead to severe complications, hospitalization, and even death, particularly in vulnerable populations. The outbreak also disrupts daily routines, strains healthcare resources, and potentially disrupts community activities. The indirect impact includes fear, anxiety, and decreased trust in public health systems.
Understanding these impacts is essential for developing comprehensive support systems to help communities cope with the challenges posed by the outbreak.
Public Health Response
The tragic death of a second child in Texas due to measles underscores the critical need for swift and decisive public health action. Effective responses to outbreaks, especially in vulnerable populations, require coordinated efforts, robust communication strategies, and a deep understanding of the disease’s transmission dynamics. This section details the actions taken and examines the effectiveness of strategies employed in previous similar outbreaks.
Vaccination Campaigns
Public health officials have a crucial role in implementing and promoting vaccination programs. These campaigns are vital for achieving herd immunity, a critical factor in preventing outbreaks. Effective campaigns encompass targeted outreach to vulnerable populations, including those with lower vaccination rates, and clear communication about the importance of vaccination. A well-structured campaign also emphasizes the safety and efficacy of the measles vaccine.
Past successful campaigns demonstrate the power of community engagement and the importance of addressing misinformation and concerns about vaccination.
Public Awareness Initiatives
Public health officials must employ comprehensive public awareness campaigns to educate the public about the symptoms, transmission, and prevention of measles. Effective strategies involve clear and accessible information, including the use of multiple communication channels (social media, community meetings, local news). Public awareness campaigns also address common misconceptions about measles and vaccination. This proactive approach is crucial in fostering informed decision-making and promoting vaccination uptake.
Examples of Successful Public Health Strategies
Several past measles outbreaks have highlighted effective public health strategies. For instance, the successful containment of a large measles outbreak in a specific region often involved targeted vaccination campaigns focusing on high-risk groups. These campaigns were complemented by robust contact tracing and isolation procedures to limit the spread of the virus. Another crucial component was public education to address concerns about the vaccine and dispel misinformation.
Effectiveness of Containment Strategies, A second child with measles has died in texas as the outbreak continues to spread
The effectiveness of current containment strategies is directly tied to factors like the prompt identification of cases, timely isolation procedures, and the speed of vaccination efforts. The degree to which these strategies are effectively implemented determines their success in reducing transmission. Factors such as the degree of community engagement and the prevalence of vaccine hesitancy also influence the success rate.
Collaboration Between Agencies
Effective collaboration between local, state, and federal health agencies is essential for a coordinated response to a measles outbreak. This collaboration is vital for sharing data, resources, and expertise. The establishment of clear communication channels and protocols is essential for rapid decision-making and resource allocation. Effective coordination allows for a unified and comprehensive approach, ensuring that all necessary measures are taken to contain the outbreak and prevent further spread.
Impact on Children

The recent measles outbreak in Texas has tragically highlighted the devastating impact this highly contagious virus can have on children. Beyond the immediate health risks, the emotional toll on families and the potential for long-term complications are significant concerns. Understanding the severity of this outbreak requires careful consideration of the risks to children’s health and well-being.Measles, a highly contagious respiratory illness, poses serious health risks for children, particularly those with weakened immune systems or pre-existing health conditions.
Tragically, a second child with measles has died in Texas, highlighting the alarming spread of this preventable illness. While this is deeply concerning, it’s also a reminder of the importance of proactive safety measures. Consider investing in some top-tier security cameras, like the best ptz security cameras , to keep an eye on your loved ones and potentially deter any potential issues.
The situation in Texas demands vigilance and a continued focus on preventing further outbreaks.
The virus spreads rapidly through respiratory droplets and can lead to severe complications, sometimes resulting in long-term disabilities.
Health Risks Associated with Measles Infection
Measles can cause a range of complications, some of which can be life-threatening. These complications include pneumonia, encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), and myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle). The severity of these complications can vary significantly, with some children experiencing mild symptoms while others face life-altering consequences. In severe cases, measles can lead to death. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to minimizing the risk of serious complications.
Potential Long-Term Complications and Disabilities
Measles infection can have long-lasting effects, even in cases where initial symptoms appear mild. Post-measles encephalitis, for instance, can result in permanent neurological damage, leading to cognitive impairment, learning disabilities, or seizures. Furthermore, children who develop myocarditis may experience heart problems later in life. The long-term effects can significantly impact a child’s development and quality of life.
The specific long-term consequences are often unpredictable and depend on the individual’s immune response and the severity of the infection.
Emotional and Psychological Impact on Families Affected by the Outbreak
The emotional toll on families affected by the measles outbreak extends beyond the physical health of the child. The fear and anxiety surrounding the contagious nature of the disease, the uncertainty about the child’s recovery, and the potential for long-term consequences can create significant emotional distress for parents and siblings. The burden of caring for a sick child, coupled with the fear of spreading the illness, can strain family relationships and overall well-being.
Support systems, counseling, and access to medical care are crucial for families navigating this challenging period.
Comparison of Severity with Other Infectious Diseases
While many infectious diseases can impact children, measles stands out due to its potential for severe complications and long-term disabilities. While other childhood illnesses, like influenza or bacterial infections, can also be serious, measles carries a unique risk of encephalitis, myocarditis, and other potentially debilitating conditions. The unpredictable nature of the long-term effects differentiates measles from other infectious diseases, requiring ongoing monitoring and support for affected children and families.
Vaccination and Immunization
Protecting our children from preventable illnesses like measles is paramount. Vaccination plays a critical role in achieving this, offering a safe and effective way to build immunity and safeguard public health. Understanding the importance of vaccination, its safety, and the available resources is crucial for informed decision-making.
The Importance of Vaccination
Vaccination is a cornerstone of public health, safeguarding individuals and communities from a wide range of infectious diseases. It works by introducing a weakened or inactive form of a pathogen into the body. This triggers an immune response, stimulating the body’s natural defenses to recognize and fight off the actual pathogen if encountered later. This protective response, known as immunity, is vital in preventing outbreaks and controlling the spread of diseases.
Measles, in particular, can have severe complications, including pneumonia, encephalitis, and even death. Vaccination significantly reduces the risk of these devastating outcomes.
Safety and Efficacy of Measles Vaccines
Measles vaccines are rigorously tested and proven to be safe and highly effective. Extensive research has demonstrated their safety profile, with adverse events being extremely rare. The benefits of vaccination far outweigh the potential risks. The vaccine is administered in two doses, typically during childhood, and is crucial in achieving herd immunity, a level of protection where the majority of the population is immune, effectively reducing the risk of disease transmission.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and other reputable organizations provide comprehensive information on the safety and efficacy of vaccines.
Resources for Parents
Parents seeking information on vaccination can find reliable resources from various sources. The CDC website is a comprehensive resource, offering detailed information on vaccination schedules, side effects, and frequently asked questions. Local health departments are also valuable resources, providing personalized information and addressing specific concerns. Healthcare providers can offer personalized guidance based on individual circumstances and medical history.
Many organizations dedicated to public health also offer educational materials and support for parents.
The Role of Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in promoting vaccination and answering parents’ questions. They act as trusted advisors, providing accurate information and addressing any concerns. Healthcare providers are trained to recognize potential side effects and provide appropriate care if needed. Open communication between parents and healthcare providers is essential in making informed decisions about vaccination. Providers can offer personalized recommendations based on individual medical history and risk factors.
They can also address misconceptions and anxieties about vaccination, fostering trust and encouraging vaccination uptake.
Misinformation and Public Perception
The recent measles outbreak, tragically marked by a death of a second child in Texas, underscores the critical role of accurate information in public health. Misinformation surrounding vaccines, often amplified by social media and online platforms, can undermine public trust and lead to preventable illnesses. This creates a dangerous environment where individuals may choose not to vaccinate their children, jeopardizing the health of the entire community.Misinformation about vaccines is a significant obstacle to effective vaccination campaigns.
It can create doubt and fear, leading to vaccine hesitancy and refusal. This hesitancy, when widespread, allows outbreaks to occur and spread more easily, impacting vulnerable populations. Addressing this issue requires a multi-pronged approach that focuses on countering false claims with evidence-based information.
The Role of Misinformation in Hindering Vaccination Efforts
Misinformation surrounding vaccines often centers on unsubstantiated claims of adverse effects, falsely linking vaccines to autism or other health problems. These narratives, though lacking scientific backing, can be incredibly persuasive, particularly to those seeking information online. The ease with which false information spreads on social media platforms can exacerbate the problem. This widespread dissemination of misinformation can lead to a loss of confidence in the safety and efficacy of vaccines.
Strategies to Combat Misinformation Surrounding Vaccines
Effective strategies to counter vaccine misinformation must go beyond simply debunking false claims. A crucial element is to proactively promote accurate and evidence-based information. Public health campaigns should target specific demographics, using channels like community events, social media, and trusted healthcare providers to disseminate accurate information. This requires a collaborative effort involving medical professionals, educators, and community leaders.
A key component is to emphasize the importance of getting vaccinated to protect the community as a whole, particularly vulnerable individuals.
Examples of Effective Communication Strategies
Many organizations have successfully addressed vaccine hesitancy through clear, concise, and empathetic communication. These strategies often involve using relatable language, addressing concerns directly, and providing easily accessible sources of credible information. For example, educational materials can explain the scientific basis for vaccine safety and efficacy in a simple, understandable format. These campaigns should also be tailored to specific populations, recognizing their unique concerns and priorities.
Identifying and Discussing Sources of Misleading Information
Misinformation about vaccines originates from various sources, including social media posts, misleading articles, and even certain websites posing as credible health information providers. Distinguishing credible sources from those disseminating false information is a critical step in combating the spread of misinformation. The use of reliable websites and information from reputable medical organizations can be invaluable in combating these misleading sources.
This requires media literacy and the ability to discern trustworthy sources from those presenting biased or false information.
Community Engagement
The tragic loss of a second child to measles in Texas underscores the urgent need for community-wide action. Effective community engagement isn’t just a desirable strategy; it’s a critical component in containing outbreaks and building public health resilience. This approach recognizes that individual actions are intertwined with collective responsibility, and that a unified front is essential in fostering trust and promoting health.Community engagement goes beyond simply informing people about the risks of measles.
It’s about fostering a culture of health where vaccination is viewed as a shared responsibility and where concerns are addressed proactively. It recognizes the diversity of perspectives and backgrounds within communities, ensuring that everyone feels heard and valued in the effort to protect public health.
Importance of Community Leaders
Community leaders play a vital role in promoting vaccination and fostering trust within their communities. Their influence can be instrumental in shaping public opinion and encouraging participation in health initiatives. Leaders who actively advocate for vaccination, share accurate information, and address concerns directly can create a powerful ripple effect. This approach is especially crucial when misinformation or distrust regarding vaccination spreads rapidly.
By aligning with credible health authorities and proactively countering false narratives, community leaders can effectively build confidence in the safety and efficacy of vaccines.
Providing Accurate Information and Addressing Concerns
Accurate information is paramount in addressing community concerns and promoting trust in public health initiatives. A transparent approach that acknowledges the validity of concerns while presenting factual data can effectively address misconceptions. It is crucial to use accessible and culturally appropriate communication strategies, tailoring messages to diverse audiences. Open forums, community meetings, and accessible resources can facilitate dialogue and provide avenues for people to voice their questions and concerns.
Examples of Successful Community Engagement Strategies
Numerous successful community engagement strategies have been employed in previous outbreaks. One common strategy is the establishment of community health workers or trusted messengers. These individuals, often from within the community, can disseminate accurate information and address concerns in a culturally sensitive manner. Furthermore, participatory approaches where community members are actively involved in the planning and implementation of health initiatives can foster a sense of ownership and engagement.
- Targeted Outreach: Strategies focused on specific demographic groups or communities that may have lower vaccination rates can be effective in reaching those who need information the most.
- Partnerships: Collaborating with community organizations, religious leaders, and other influential figures can broaden the reach of health messages and enhance trust.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Adapting communication strategies to different cultural backgrounds and addressing cultural sensitivities is essential to ensure that health messages are received and understood effectively.
Future Prevention Strategies: A Second Child With Measles Has Died In Texas As The Outbreak Continues To Spread
The tragic loss of a second child to measles in Texas underscores the urgent need for proactive measures to prevent future outbreaks. This crisis demands a comprehensive approach that prioritizes community health, addresses misinformation, and strengthens public health infrastructure. Effective prevention strategies are crucial to protecting vulnerable populations and safeguarding the well-being of future generations.
Strengthening Vaccination Programs
Measles remains a highly contagious disease, and vaccination remains the cornerstone of prevention. A robust vaccination program, coupled with strong community engagement, is essential to achieve herd immunity. This includes ensuring adequate vaccine supply, accessibility, and affordability, particularly for underserved communities. Dedicated outreach programs focusing on education and dispelling myths about vaccination are also vital.
- Expanding Vaccination Access: Targeted outreach programs in underserved communities can address barriers to vaccination, such as logistical challenges, lack of transportation, or language barriers. Community health centers and mobile vaccination clinics can significantly improve access for those who are otherwise unable to reach vaccination centers.
- Improving Vaccination Rates: Monitoring vaccination rates across different demographics and geographic areas can help identify disparities and guide targeted interventions. This data-driven approach allows for the development of specific strategies to reach those with lower vaccination rates. For example, implementing incentives, such as free or discounted vaccines, can encourage vaccination in communities with lower compliance.
- Strengthening Vaccination Campaigns: Public health campaigns need to focus on clear, accessible messaging about the benefits of vaccination. Educational materials should address the safety and efficacy of vaccines, dispelling common myths and misconceptions. These materials should be available in multiple languages and formats to ensure accessibility and understanding for all community members.
Addressing Misinformation and Building Trust
The spread of misinformation regarding vaccines has contributed to the current measles outbreak. Combating this misinformation requires a multi-pronged approach, focusing on education, transparency, and building public trust in public health agencies.
Tragically, a second child with measles has succumbed in Texas, highlighting the alarming spread of this preventable illness. Meanwhile, concerningly, the San Francisco Marin Food Bank recently reported a data breach, raising serious questions about the security of sensitive information. This unfortunate event, alongside the ongoing measles outbreak, underscores the importance of proactive measures to protect public health and sensitive data alike.
Hopefully, swift action will be taken to control the spread of measles and prevent further tragedies. san francisco marin food bank reports data breach This situation is deeply concerning and emphasizes the need for both robust health initiatives and data protection measures.
- Fact-Checking and Counter-Messaging: Actively monitoring and addressing misinformation through credible sources is vital. Fact-checking websites and social media posts that contain false information about measles and vaccines can effectively counteract misleading claims.
- Encouraging Dialogue and Engagement: Open forums and town halls can facilitate discussions between healthcare professionals and community members. These opportunities for dialogue can address concerns and build trust in vaccination programs.
- Collaborating with Community Leaders: Engaging community leaders, faith leaders, and influencers to disseminate accurate information about vaccines can amplify the message and increase public awareness and acceptance. Partnering with trusted figures in the community is key to building trust and promoting vaccine uptake.
Reinforcing Public Health Infrastructure
A robust public health infrastructure is essential to prevent and respond to future outbreaks. This includes strengthening surveillance systems, enhancing laboratory capacity, and improving communication protocols.
- Strengthening Surveillance Systems: Investing in and maintaining comprehensive surveillance systems can help detect outbreaks early and effectively respond to them. Real-time data collection and analysis are crucial to understanding trends and adapting prevention strategies.
- Improving Laboratory Capacity: Adequate laboratory capacity for rapid testing and diagnosis of infectious diseases is critical. This ensures timely identification of outbreaks and appropriate interventions. This includes maintaining and upgrading laboratory equipment and training personnel.
- Improving Communication Protocols: Clear, consistent, and accessible communication channels between public health agencies and the community are vital. This includes utilizing various communication methods, including social media, community meetings, and multilingual resources, to reach diverse populations effectively.
Visual Representation
Understanding the scope and impact of the measles outbreak requires a clear visual representation of the affected populations. Visual aids allow for a more comprehensive understanding of the geographic spread, age groups most vulnerable, and the potential complications associated with the disease. This section presents data in a table format, providing a clearer picture of the outbreak’s characteristics.
Geographic Distribution of Measles Cases
The geographic distribution of measles cases is crucial for targeted public health interventions. Identifying areas with high concentrations of cases enables resource allocation and tailored prevention strategies.
| County | Number of Cases | Location (e.g., Rural/Urban) |
|---|---|---|
| County A | 15 | Urban |
| County B | 8 | Rural |
| County C | 22 | Urban |
| County D | 10 | Rural |
| County E | 18 | Urban |
Note: This is a sample table. Actual data would require a detailed dataset and mapping tools.
Age Distribution of Affected Children
The age distribution of affected children provides insights into the effectiveness of vaccination programs and highlights the vulnerability of specific age groups.
| Age Group (years) | Number of Cases | Vaccination Status (estimated) |
|---|---|---|
| 0-1 | 5 | Not fully vaccinated |
| 1-5 | 12 | Partially vaccinated |
| 5-10 | 8 | Fully vaccinated |
| 10-15 | 3 | Fully vaccinated |
Note: Vaccination status is estimated and may not be entirely accurate.
Types of Complications Associated with Measles Infection
Measles can lead to a variety of complications, impacting various organ systems. Understanding these complications is vital for early intervention and treatment.
| Complication | Description | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| Pneumonia | Lung infection | Moderate to Severe |
| Encephalitis | Brain inflammation | Severe |
| Diarrhea | Gastrointestinal distress | Moderate |
| Otitis media | Middle ear infection | Moderate |
Note: This table presents some common complications. The severity and frequency of complications can vary.
Effectiveness of Vaccination Programs
Vaccination programs play a vital role in preventing measles outbreaks. Monitoring the effectiveness of these programs is essential for assessing the public health response and improving future strategies.
| Vaccination Program | Coverage Rate (%) | Effectiveness (estimated) |
|---|---|---|
| Program A | 85 | 90% |
| Program B | 70 | 85% |
| Program C | 92 | 95% |
Note: Vaccination coverage and effectiveness are estimated and may vary based on factors such as community engagement and access to healthcare.
Last Point
The recent measles outbreak in Texas, marked by the tragic death of a second child, serves as a stark reminder of the importance of vaccination and public health measures. This situation underscores the critical need for comprehensive strategies to combat the spread of infectious diseases. Collaboration between communities, healthcare providers, and public health officials is essential to effectively address this crisis and prevent future tragedies.
The ongoing fight against measles requires continued vigilance, accurate information, and a commitment to safeguarding the health and well-being of children across the state.