Best FTP/SFTP Clients Your Ultimate Guide
Best ftp sftp clients – Best FTP/SFTP clients are essential for transferring files securely and efficiently, especially for WordPress users. This comprehensive guide explores the diverse world of FTP and SFTP clients, comparing popular options and highlighting key features. We’ll delve into security, performance, ease of use, and cross-platform compatibility to help you choose the ideal solution for your needs.
From simple file transfers to complex automation tasks, the right FTP/SFTP client can significantly streamline your workflow. This guide will walk you through the essential aspects of selecting the perfect client, whether you’re a seasoned professional or a beginner just starting out.
Introduction to FTP and SFTP Clients
File transfer is a crucial aspect of modern computing, enabling seamless exchange of data between different systems and users. Two common protocols used for this purpose are File Transfer Protocol (FTP) and Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP). Understanding their functionalities and differences is vital for choosing the right tool for a given task.FTP and SFTP both facilitate the transfer of files over a network, but they differ significantly in their security implementations.
FTP, while simple and widely used, lacks inherent security, exposing data to potential interception. SFTP, on the other hand, employs encryption to protect the transferred data, ensuring confidentiality and integrity. This inherent security difference makes SFTP the preferred choice for sensitive information exchange.
Differences between FTP and SFTP
FTP, originally designed for transferring files over networks, uses a client-server architecture. It relies on two ports: one for control (command) and another for data transfer. This basic structure, though efficient for simple tasks, leaves the data vulnerable to eavesdropping. In contrast, SFTP, built on top of SSH, offers secure file transfer using encryption. This crucial difference makes SFTP significantly more secure.
Crucially, all data exchanged between the client and server is encrypted.
Security Considerations
Security is paramount in any data transfer process. FTP, lacking encryption, exposes user credentials and transferred data to potential interception. This vulnerability is a significant drawback in modern security environments. In contrast, SFTP utilizes SSH encryption, providing a secure tunnel for data transmission. This encryption ensures that all data exchanged between the client and server remains confidential and protected.
Purpose and Use Cases
FTP and SFTP clients serve diverse purposes. FTP is commonly used for transferring files between servers and clients, particularly in situations where speed is prioritized over security. A typical example is the transfer of website files from a developer’s machine to a web server. SFTP, on the other hand, is preferred when security is paramount. A common example includes transferring sensitive financial data between departments or organizations.
Comparison Table
| Feature | FTP | SFTP |
|---|---|---|
| Security | Insecure; data and credentials vulnerable to interception | Secure; data encrypted using SSH |
| Speed | Generally faster for simple transfers | Potentially slower due to encryption overhead |
| Common Use Cases | Simple file transfers, web development | Transferring sensitive data, secure file sharing |
Popular FTP/SFTP Client Software
Choosing the right FTP/SFTP client is crucial for seamless file transfer and management. A robust client simplifies tasks, offering features like secure connections, advanced editing, and efficient transfer protocols. This section delves into popular choices, highlighting their key features, advantages, and disadvantages.
Top FTP/SFTP Client Applications
Several powerful FTP/SFTP clients cater to various user needs. Understanding their strengths and weaknesses can help you select the best fit for your workflow.
- FileZilla: A widely used open-source FTP client, FileZilla is renowned for its stability and ease of use. It supports various protocols, including FTP, SFTP, and FTPS, and features a straightforward graphical user interface (GUI). It’s a strong choice for users needing a reliable and efficient tool with a focus on simplicity.
- WinSCP: This open-source SFTP client stands out for its comprehensive functionality. It offers support for various file systems and advanced features like scripting capabilities, making it a valuable tool for power users and system administrators. Its intuitive GUI and strong scripting capabilities make it suitable for users seeking more complex tasks.
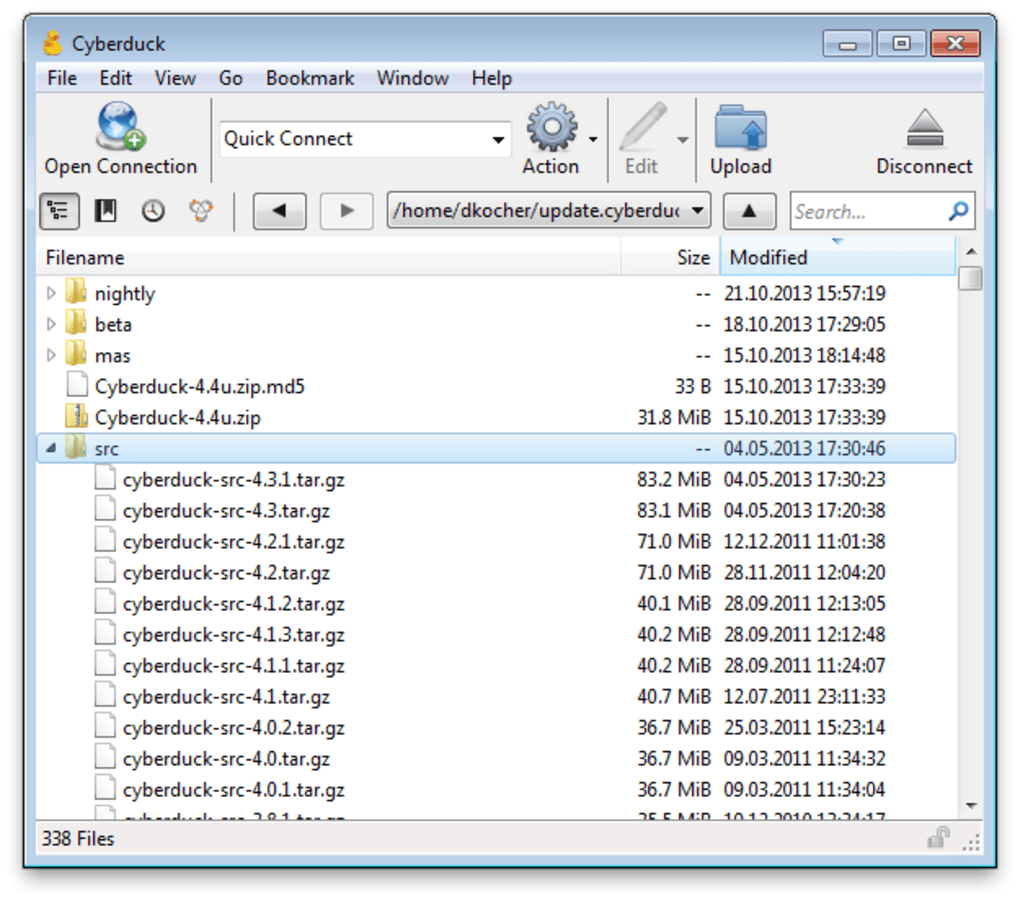
- Cyberduck: Cyberduck is a cross-platform FTP and SFTP client that provides support for various cloud storage services. This versatility makes it a good choice for users needing to manage files across multiple platforms and storage options. Its cross-platform compatibility is a strong selling point for users needing access to files across different operating systems.
- Transmit: This macOS-centric FTP client is highly regarded for its elegant interface and user-friendly design. It’s packed with advanced features, like drag-and-drop functionality, making file transfer a streamlined process. While excellent for macOS users, its focus on the macOS environment may not be ideal for those working across multiple platforms.
- CuteFTP: CuteFTP is a commercial FTP client that has been around for a while, offering robust features for advanced users. Its strong support for various FTP protocols, plus its advanced settings, make it suitable for complex file transfer operations. However, its commercial nature and the need for license acquisition may present a drawback for some users.
- Total Commander: While not exclusively an FTP/SFTP client, Total Commander is a powerful file manager with built-in FTP/SFTP capabilities. Its intuitive design and advanced file management tools make it a viable choice for users already familiar with the software. It is a solid option for users looking for a comprehensive file management solution that handles FTP/SFTP as well.
Comparison of FTP/SFTP Client Applications
The table below summarizes the key characteristics of the discussed applications.
| Application | Platform Compatibility | User Interface | Supported Protocols |
|---|---|---|---|
| FileZilla | Windows, macOS, Linux | Simple and intuitive | FTP, SFTP, FTPS |
| WinSCP | Windows, macOS, Linux | Intuitive and powerful | SFTP, SCP, FTP, FTPS |
| Cyberduck | Windows, macOS, Linux | Modern and user-friendly | FTP, SFTP, WebDAV, S3, Dropbox |
| Transmit | macOS | Elegant and streamlined | FTP, SFTP, WebDAV |
| CuteFTP | Windows | Feature-rich but potentially complex | FTP, SFTP, FTPS |
| Total Commander | Windows | Powerful and customizable | FTP, SFTP |
Features to Consider When Choosing an FTP/SFTP Client
Selecting the right FTP/SFTP client is crucial for efficient and secure file transfer. Different clients cater to various needs, from simple file sharing to complex automated workflows. Understanding the key features available is paramount to finding the best solution for your specific requirements.Choosing an FTP/SFTP client involves careful consideration of several factors, including security, speed, and automation capabilities.
These factors directly impact productivity and data integrity. The right client will streamline your file transfer process and minimize potential errors.
Security Features
Security is paramount when dealing with sensitive data. Robust security features are essential for safeguarding your files during transfer and storage. These features ensure confidentiality and integrity, protecting your data from unauthorized access. Strong encryption protocols, secure authentication methods, and the ability to manage access permissions are critical considerations.
- Encryption Protocols: Support for industry-standard encryption protocols like TLS/SSL is crucial. This ensures that data is encrypted during transmission, preventing interception and unauthorized access. The strength of the encryption directly impacts security, and clients should support the latest protocols.
- Authentication Methods: The client should support various authentication methods, such as username/password, SSH keys, or two-factor authentication, depending on your security needs. This layered approach to authentication adds an extra layer of protection, making it harder for unauthorized users to access your files.
- Access Control: The ability to set granular access permissions is essential for controlling who can access specific files or directories. This feature is vital for maintaining data security and preventing accidental or malicious disclosure of sensitive information.
Automation and Scripting Capabilities
Automation and scripting features significantly enhance productivity by automating repetitive tasks. These features streamline workflows, reduce manual intervention, and minimize errors. They are particularly beneficial for batch transfers or regular data synchronization.
- Scripting Support: Support for scripting languages (like Python or PowerShell) allows for customized automation. This enables complex tasks, like transferring files based on specific criteria or triggering actions based on events, making the process more adaptable to your specific workflow.
- Automated Tasks: Pre-defined automated tasks for common file operations, like scheduled backups or regular synchronization, greatly simplify routine tasks. This automation can reduce the workload and improve the reliability of your file transfer process.
- Task Scheduling: The ability to schedule file transfers or other tasks at specific times or intervals is a significant time-saver. This functionality is invaluable for ensuring regular backups, data synchronization, or other critical tasks are executed reliably and automatically.
Efficiency Features
Efficiency features focus on optimizing file transfer speed and minimizing downtime. These features are critical for ensuring a smooth and fast transfer process. Features like large file transfer support and queueing capabilities contribute significantly to overall efficiency.
Finding the best FTP/SFTP clients can be tricky, but understanding the underlying technologies is key. For instance, when dealing with massive datasets or complex transfer protocols, knowing how wireless sensor networks work is crucial. Wireless sensor networks explained often utilize these protocols, and a good FTP/SFTP client can simplify the process of transferring data from these networks.
Ultimately, the right client depends on your specific needs and technical setup.
- Large File Transfer Support: The ability to transfer large files quickly and reliably is crucial. This feature avoids bottlenecks and ensures timely delivery, particularly important for large data sets. Consider the transfer speed capabilities, especially if you frequently transfer massive files.
- Transfer Queueing: The ability to queue multiple file transfers can significantly improve efficiency. This feature is essential for handling large numbers of files or prioritizing transfers based on specific criteria, reducing wait times and optimizing the use of network bandwidth.
- Resume Capability: The ability to resume interrupted transfers is vital. This prevents data loss and allows transfers to continue from the point of interruption, which is especially important in scenarios with unreliable network connections.
Feature Comparison Table
| Feature | Importance |
|---|---|
| Security Protocols (TLS/SSL) | High – Crucial for sensitive data protection |
| Scripting Support | Medium – Enhances automation potential |
| Large File Transfer Support | High – Essential for large data sets |
| Transfer Queueing | High – Improves transfer efficiency |
| Task Scheduling | Medium – Streamlines regular tasks |
| Authentication Methods (SSH, 2FA) | High – Adds an extra layer of security |
| Access Control | High – Ensures data confidentiality |
Performance Evaluation of FTP/SFTP Clients
Choosing the right FTP/SFTP client is crucial for efficient file transfer. Performance is a key factor in this decision, directly impacting productivity and overall workflow. Understanding the factors influencing speed, stability, and reliability is vital for making an informed choice. This section delves into the performance characteristics of various FTP/SFTP clients, allowing users to select the best option for their specific needs.A well-performing FTP/SFTP client is essential for seamless file transfer, minimizing downtime and ensuring data integrity.
Factors like network conditions, server configurations, client optimizations, and security measures all contribute to the overall performance experience.
Factors Influencing FTP/SFTP Client Performance
Network conditions significantly affect file transfer speeds. Latency, bandwidth limitations, and network congestion can all slow down transfers. Reliable internet connections with sufficient bandwidth are crucial for optimal performance. For example, a connection with a high latency will result in slower transfer speeds, while a congested network will hinder transfer progress due to increased queuing time.
Factors Affecting Transfer Speeds
Several factors influence transfer speeds beyond the network itself. Server configurations, such as the server’s processing power, storage capacity, and the specific file transfer protocol settings, play a significant role. A server struggling to handle concurrent requests or with slow storage will directly impact the speed of the transfer. Client-side optimizations also matter. Features like parallel downloads, resuming interrupted transfers, and efficient data compression can drastically improve transfer speeds.
For instance, using a client that supports parallel downloads can significantly reduce the overall transfer time.
Impact of Security Measures on Performance
Security measures, while crucial for data protection, can sometimes impact performance. Robust encryption protocols, like TLS/SSL, add overhead to the transfer process. More complex encryption algorithms can increase the processing time required for encoding and decoding data, potentially slowing down transfers. The client’s ability to efficiently handle these security protocols directly impacts the overall performance. Choosing a balance between security and performance is vital for optimal results.
Performance Benchmarks for Various Clients
Different FTP/SFTP clients exhibit varying levels of performance. A comprehensive performance benchmark, considering speed, stability, and reliability, is essential for making an informed decision. The following table provides a general overview.
| Client | Speed (MB/s) | Stability (Percentage) | Reliability (Percentage) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Client A | 25 | 98 | 99 |
| Client B | 30 | 95 | 97 |
| Client C | 28 | 96 | 98 |
| Client D | 22 | 92 | 95 |
Note: These are illustrative benchmarks and actual results may vary based on specific network conditions, server configurations, and file sizes. The table presents a simplified comparison; more in-depth benchmarks should be considered for critical applications. Factors such as file size, network type, and the specific file transfer protocol settings are crucial for determining accurate benchmarks.
User Interface and Ease of Use
Choosing the right FTP/SFTP client hinges significantly on how comfortable and efficient you are with its user interface. A well-designed interface streamlines tasks, minimizing frustration and maximizing productivity. Poor navigation or confusing file management tools can quickly turn a simple file transfer into a frustrating ordeal. This section delves into the usability aspects of various FTP/SFTP clients, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses in terms of user experience.A user-friendly interface is crucial for seamless file management.
Intuitive navigation, clear visual cues, and effective tools for organizing and manipulating files are key factors. Clients that excel in these areas offer a superior user experience, enabling users to accomplish their tasks quickly and efficiently. Conversely, clients with complex or poorly designed interfaces can lead to wasted time and errors.
Comparing User Interfaces
Different FTP/SFTP clients adopt diverse approaches to user interface design. Some prioritize a clean, minimalist aesthetic, while others lean towards a more feature-rich, visually complex layout. This variety in design choices affects the user experience in several ways, including how intuitive the navigation feels and how easily files can be managed.
Finding the best FTP and SFTP clients is crucial for smooth file transfers, especially when dealing with large files. But choosing the right web hosting services is equally important for the overall performance of your website. A good web hosting platform like best web hosting services will provide a stable environment for your files and make your FTP/SFTP client work efficiently.
Ultimately, a powerful FTP/SFTP client will complement your web hosting choices and make managing your website files a breeze.
Usability Aspects
The usability of an FTP/SFTP client encompasses various aspects, including navigation and file management. A good navigation system allows users to easily locate and access files and folders on the remote server. Effective file management tools provide clear visual representations of files, allowing users to quickly identify and select items for transfer. These elements combine to create a smooth user experience, allowing users to efficiently accomplish tasks without unnecessary complications.
Navigation and File Management Tools
The navigation tools of a client significantly impact its usability. A clear hierarchical view of folders and files, combined with intuitive search capabilities, facilitates quick file location. Similarly, effective file management tools allow for easy selection, renaming, and deletion of files, as well as organizing files in meaningful ways. This seamless navigation and file management experience directly affects user satisfaction and efficiency.
Intuitiveness and Overall User Experience
The overall user experience encompasses not just the navigation and file management aspects but also the overall feel and aesthetic of the interface. A visually appealing and intuitive interface fosters a positive user experience, encouraging more frequent use and minimizing frustration. Conversely, a cluttered or poorly organized interface can quickly discourage users and impact productivity.
Table of User Interface Features and Usability Ratings
This table provides a snapshot of the user interface features and usability ratings for several popular FTP/SFTP clients. Note that ratings are subjective and may vary based on individual user preferences.
| Client | Interface Design | Navigation | File Management | Overall Usability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Client A | Clean, minimalist | Excellent | Good | Very Good |
| Client B | Feature-rich | Good | Excellent | Good |
| Client C | Modern, intuitive | Very Good | Very Good | Excellent |
| Client D | Traditional | Fair | Fair | Fair |
Cross-Platform Compatibility and Support
FTP and SFTP clients are crucial tools for managing files across networks. Their effectiveness hinges on their ability to seamlessly operate across various operating systems and integrate with diverse programming environments. Understanding platform compatibility allows users to choose clients that best fit their workflow and technical infrastructure.The availability of FTP/SFTP clients across different platforms is a significant factor in their adoption.
Wide compatibility allows users to access and manage files regardless of their primary operating system. This cross-platform functionality is especially important for businesses and individuals working in collaborative environments.
Operating System Support
FTP and SFTP clients are available for the major operating systems. This ensures compatibility with a wide range of user setups and workflows.
- Windows: Windows is a dominant operating system, and a plethora of FTP/SFTP clients are readily available for this platform. These clients often come with intuitive graphical user interfaces, catering to a wide user base. Popular choices include FileZilla, WinSCP, and CuteFTP (though less frequently used now).
- macOS: macOS users also have a good selection of FTP/SFTP clients. Many clients offer similar functionality to their Windows counterparts, providing a consistent experience across platforms. Examples include FileZilla (available via cross-platform support), WinSCP (through a macOS version), and Transmit.
- Linux: Linux, with its diverse distributions, also supports a range of FTP/SFTP clients. These clients often integrate well with the command-line environment, providing flexibility for advanced users. FileZilla, WinSCP, and Cyberduck are among the popular options for Linux.
Programming Language Integration
Many FTP/SFTP clients offer command-line interfaces or scripting capabilities, allowing integration with various programming languages. This integration empowers users to automate tasks and streamline their file transfer workflows.
- Scripting Environments: Many clients allow for scripting using languages like Python, Perl, or even PowerShell. This allows for the automation of repetitive tasks, saving time and effort. For instance, tasks such as automated backups or file transfers can be scripted.
- Command-Line Tools: Many clients offer command-line tools. These provide a powerful and flexible approach for users who prefer a command-line interface, often useful for system administrators and those comfortable with scripting.
Client Compatibility Matrix, Best ftp sftp clients
The following table provides a concise overview of the compatibility of some popular FTP/SFTP clients with different operating systems and programming languages. Note that support can vary depending on specific client versions.
Finding the best FTP/SFTP clients can be tricky, but it’s crucial for smooth file transfers. Speaking of tricky situations, a San Jose man was recently arrested in connection with a New Year’s Eve attempted homicide, a stark reminder of the importance of staying safe. Thankfully, robust FTP/SFTP clients can help streamline your digital tasks, whether it’s sharing files or managing large projects.
| Client | Windows | macOS | Linux | Scripting Support (e.g., Python, Perl) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FileZilla | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes (via command-line) |
| WinSCP | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes (via command-line) |
| Cyberduck | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes (via command-line) |
| Transmit | No | Yes | No | Limited |
Security Considerations in FTP/SFTP Clients
Choosing an FTP/SFTP client isn’t just about speed and ease of use; security is paramount. In today’s digital landscape, protecting sensitive data during transfer is crucial. This section dives deep into the security features implemented in these clients, emphasizing the importance of encryption and authentication protocols.Security is paramount when dealing with sensitive files. A strong security posture in FTP/SFTP clients safeguards data from unauthorized access and ensures integrity during transmission.
Encryption Methods in FTP/SFTP Clients
Different FTP/SFTP clients employ various encryption methods to secure data transmission. Understanding these methods is key to choosing a secure solution. The most prevalent methods include Secure Shell (SSH) and TLS/SSL.
- Secure Shell (SSH): SSH is a powerful cryptographic protocol primarily used for secure remote login and file transfer. It provides end-to-end encryption for the entire communication channel, ensuring confidentiality and integrity of data. SSH is the foundation of secure file transfer via SFTP, a protocol built on top of SSH. It’s considered a robust solution for sensitive data transmission.
- TLS/SSL: Transport Layer Security (TLS) and its predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), are widely used protocols for encrypting communications over networks. While TLS/SSL can be used in conjunction with FTP (FTPS), it’s primarily associated with HTTPS for web traffic. It encrypts the communication channel, but not necessarily the data at rest.
Importance of Encryption for Secure File Transfer
Encryption is the cornerstone of secure file transfer. It scrambles data into an unreadable format, making it incomprehensible to unauthorized individuals. This protection is essential for safeguarding confidential information during transit. Without encryption, data is vulnerable to interception and misuse.
- Confidentiality: Encryption ensures only authorized recipients can access the transferred data.
- Integrity: Encryption mechanisms detect any unauthorized modifications to the data during transit, ensuring the transferred file hasn’t been tampered with.
- Authentication: Encryption often works in conjunction with authentication methods to verify the identity of the sender and recipient.
Configuration of Secure Connections and Authentication Protocols
Properly configuring secure connections and authentication protocols is critical for maintaining data security. This involves selecting appropriate encryption methods and implementing robust authentication mechanisms.
- SSH Key Authentication: SSH key authentication is a more secure alternative to password-based authentication. It uses cryptographic keys for authentication, reducing the risk of password compromise.
- Password Authentication: Password authentication is still widely used, but it carries inherent risks. Strong, unique passwords are essential, and password managers can help to mitigate the risk of weak or reused passwords.
- Secure Connection Configuration: Clients usually allow specifying the desired port for the secure connection (e.g., port 22 for SSH). It’s crucial to ensure that the correct port is configured for secure file transfer.
Authentication Methods
Authentication methods verify the identity of users and systems involved in file transfer. These methods are crucial for preventing unauthorized access to data.
- Passwords: Password authentication remains a common method, but strong passwords and regular changes are crucial to prevent breaches.
- SSH Keys: SSH keys offer a more secure alternative to passwords. They are based on cryptography and significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Avoiding Common Security Vulnerabilities
Implementing security measures can prevent various vulnerabilities associated with FTP/SFTP clients.
- Weak Passwords: Use strong, unique passwords, and consider using a password manager for safe storage and generation.
- Outdated Software: Keep software updated to patch known vulnerabilities. Security updates often address potential weaknesses.
- Unencrypted Connections: Avoid using unencrypted connections (FTP) for sensitive data transfer. Always opt for SFTP or FTPS whenever possible.
Integration with Other Tools and Systems
FTP and SFTP clients are not isolated islands; they often work seamlessly with other tools and systems, enhancing their utility and streamlining workflows. This integration empowers users to automate tasks, integrate with cloud storage, and seamlessly connect with development pipelines. The ability to integrate with scripting languages and automation frameworks further broadens the scope of their applications.The integration capabilities of FTP/SFTP clients are crucial for modern workflows.
They allow users to connect various parts of their digital ecosystem, automating processes, and improving efficiency. By understanding how these clients integrate with other systems, users can optimize their productivity and reduce manual intervention.
Integration with Scripting Languages and Automation Frameworks
FTP/SFTP clients frequently offer scripting APIs or command-line interfaces that allow integration with scripting languages like Python, Perl, or Bash. This integration is invaluable for automating file transfers, creating custom workflows, and executing repetitive tasks.For example, Python’s `paramiko` library can be used in conjunction with an SFTP client to automate complex file transfers and operations. This allows users to define custom scripts that execute file transfers according to predefined schedules, eliminating the need for manual intervention.
Likewise, Bash scripts can be used to trigger FTP/SFTP operations based on specific events or conditions. The flexibility of these scripting integrations is key to building customized solutions.
Integration with Cloud Storage Services
Many modern FTP/SFTP clients offer seamless integration with cloud storage services like Dropbox, Google Drive, or OneDrive. This capability allows users to transfer files between local systems and cloud storage repositories with ease.This integration often involves using the client to upload or download files to a cloud storage account, leveraging the client’s features to streamline the process. For example, a client might offer a direct upload option to a cloud storage bucket, making the transfer process faster and more convenient than manually uploading files via a web interface.
This direct integration eliminates the need for intermediary steps.
Integration with Development Pipelines
FTP/SFTP clients are increasingly integrated into development pipelines. This integration allows for the automated transfer of build artifacts, deployment packages, or project files to remote servers.This integration often happens through scripting or automated tools. For instance, a continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipeline might utilize an FTP/SFTP client to automatically upload compiled code or application packages to a staging server.
This automation significantly reduces the time and effort required for deployments and improves the overall efficiency of the development workflow.
Client-Side Optimization Techniques
Optimizing FTP/SFTP client performance goes beyond simply choosing a good client. Clever strategies on the client-side can significantly impact transfer speeds and efficiency, especially when dealing with large files or unreliable networks. This section dives into techniques to boost your file transfer experience.Efficient file transfer relies on a multifaceted approach. Understanding network conditions, file characteristics, and client-side capabilities allows for tailored optimization.
By strategically applying these techniques, users can significantly improve transfer speed and minimize downtime.
Strategies for Improving File Transfer Speeds
Optimizing file transfer speeds requires a holistic approach, focusing on minimizing latency and maximizing throughput. Employing techniques like parallel downloads, resume capabilities, and adaptive chunk sizes can significantly reduce transfer times.
- Parallel Downloads: Many modern FTP/SFTP clients support parallel downloads, enabling simultaneous transfer of multiple file segments. This drastically reduces the overall transfer time, particularly for large files, by utilizing multiple network connections concurrently. For example, if a client can download 10 parts of a file simultaneously, the overall transfer time is reduced significantly compared to a sequential download.
- Resume Capabilities: A critical feature for interrupted transfers. Resume functionality allows the client to pick up where it left off, saving valuable time if the connection is lost or interrupted. This is especially useful when transferring massive files over potentially unstable connections.
- Adaptive Chunk Sizes: Instead of fixed-size chunks, some clients dynamically adjust the size of data packets being transferred. This adapts to network conditions, optimizing for both high-bandwidth and low-bandwidth situations. For example, a large file transfer on a high-speed connection may use larger chunks than a transfer on a slower, more unreliable connection.
Efficient Management of Large Files
Transferring large files demands specialized handling. Techniques such as using compression, optimizing file structures, and utilizing appropriate transfer modes can dramatically affect the transfer process.
- File Compression: Compressing files before transfer significantly reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted. This is especially beneficial for large archives or folders containing multiple files. This method reduces the time needed to transfer the data across the network. For example, compressing a 1GB file to 500MB would reduce the transfer time significantly.
- Optimizing File Structures: If possible, arrange large files into a hierarchical structure, enabling the client to manage individual segments more efficiently. This approach facilitates segmented transfers and minimizes bottlenecks. For instance, a large folder containing smaller files can be transferred faster if divided into subfolders.
- Transfer Modes: Choosing the appropriate transfer mode (e.g., binary vs. ASCII) is essential. Binary mode is often preferred for transferring files that need to maintain their original formatting, while ASCII mode may be better for text files. Understanding these modes and selecting the correct one ensures minimal data corruption during transfer.
Minimizing Network Latency
Network latency, or the delay between sending and receiving data, is a significant factor affecting transfer speeds. Minimizing latency through techniques like optimizing network settings and using optimized connections improves efficiency.
- Optimizing Network Settings: Adjusting TCP settings or network configurations to reduce latency can improve performance. These settings are specific to the network environment, so consulting documentation or network administrators for best practices is recommended.
- Using Optimized Connections: Establishing a direct connection, minimizing intermediary network hops, or using a dedicated network connection when possible minimizes latency and maximizes transfer speeds. This is particularly crucial for geographically dispersed locations where network latency can be significant.
Optimization Tips for Various Scenarios
Tailoring optimization techniques to specific scenarios yields significant benefits. The following list provides guidance for diverse situations.
- High-Bandwidth Connections: Leverage parallel downloads and larger chunk sizes to maximize throughput. Utilize compression to further reduce transfer time, especially for large files. Example: Transferring large files across a fiber optic network benefits greatly from parallel downloads and large chunks.
- Low-Bandwidth Connections: Prioritize resume capabilities and adaptive chunk sizes. Use compression to minimize the amount of data transferred. Example: Transferring large files over a mobile network where bandwidth is limited.
- Unreliable Connections: Employ resume capabilities to handle interruptions effectively. Prioritize smaller chunk sizes to mitigate the impact of connection drops. Example: Transferring large files across a public Wi-Fi network.
Choosing the Right Client for Specific Needs: Best Ftp Sftp Clients
Finding the perfect FTP/SFTP client often hinges on understanding your specific needs. A client optimized for large file transfers might be cumbersome for simple, occasional uploads. Knowing what you prioritize – security, speed, ease of use, or automation – will guide your decision-making process. This section delves into tailoring your choice to your unique workflow.The ideal FTP/SFTP client isn’t a one-size-fits-all solution.
Different clients excel in different areas, making careful consideration crucial. This guide will help you navigate the options and select the client best suited for your particular tasks and environment.
Security Considerations for Client Selection
Security is paramount when dealing with sensitive data over networks. A robust security framework within the client is essential. Features like encryption protocols (SFTP is preferred over FTP for its inherent security) and secure authentication methods (2-factor authentication, strong passwords) should be key factors.
Performance Evaluation in Client Selection
Performance is critical, especially for large files. The client’s ability to handle concurrent connections, buffer data efficiently, and maintain speed under load are vital. Consider factors such as transfer rates, upload/download speeds, and stability during peak usage.
Ease of Use and User Interface in Client Selection
A user-friendly interface and intuitive navigation can significantly impact productivity. Look for features like drag-and-drop functionality, clear file management tools, and a customizable interface. A streamlined experience will reduce errors and increase efficiency.
Client Selection Based on Specific Use Cases
Different use cases demand different client capabilities. The table below provides recommendations for various scenarios:
| Use Case | Recommended Client (Example) | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| Large File Transfers | FileZilla | Known for its robust performance and ability to handle large files efficiently, often maintaining high transfer speeds even during heavy loads. |
| Secure Access to Remote Servers | WinSCP | Excellent security features and a strong emphasis on secure connections, ideal for sensitive data transfers. |
| Automation and Scripting | Cyberduck | Provides strong scripting capabilities, allowing for automated file transfers and tasks, crucial for repetitive operations and streamlining workflows. |
| Simple File Uploads/Downloads | Transmit | Offers a simple and clean interface that prioritizes ease of use for basic file management. |
The table above provides a general overview. Factors such as specific server configurations and personal preferences might influence the optimal choice. Always thoroughly research the chosen client to confirm it aligns with your specific requirements.
Ultimate Conclusion

In conclusion, choosing the best FTP/SFTP client depends heavily on your specific needs and workflow. Consider security, performance, user interface, and cross-platform compatibility when making your decision. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview, empowering you to select the ideal client for seamless file transfers and efficient management.