Trump Reciprocal Tariffs Prices A Deep Dive
Trump reciprocal tariffs prices sparked a global trade war, significantly impacting consumer costs and international relations. This exploration delves into the historical context, the Trump administration’s policies, the impact on prices, retaliatory actions, economic effects, long-term implications, and alternative strategies. We’ll examine the timeline of reciprocal tariff policies, focusing on the United States, and detail how tariffs influenced prices for various goods.
Understanding the complex web of tariffs, retaliatory measures, and economic consequences is crucial for analyzing the lasting effects of these trade policies. The Trump administration’s tariffs aimed to protect American industries, but these actions also led to unpredictable ripple effects on global markets. This in-depth analysis will provide a comprehensive understanding of the factors involved.
Historical Context of Reciprocal Tariffs: Trump Reciprocal Tariffs Prices

Reciprocal tariffs, a cornerstone of international trade policy, have a long and complex history, significantly impacting global commerce. Their application, evolution, and economic effects have been shaped by various political and economic factors. This exploration delves into the historical context of reciprocal tariffs, focusing on the United States’ experience.Understanding the interplay between tariffs and trade imbalances is crucial.
These policies often aim to level the playing field, encourage fair competition, and safeguard domestic industries. However, their implementation can also lead to unintended consequences, such as retaliatory measures and reduced global trade.
Timeline of US Reciprocal Tariff Policies
A historical examination reveals a dynamic evolution of US trade policies, where reciprocal tariffs have played a pivotal role. From the early 20th century to the present day, the US has engaged in numerous agreements and unilateral actions concerning tariffs, reflecting shifting economic priorities and geopolitical landscapes.
- Early 20th Century: The Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act of 1930, while intended to protect domestic industries, arguably contributed to the Great Depression by triggering retaliatory tariffs from other countries, illustrating a negative correlation between tariffs and international trade.
- Mid-20th Century: The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) and subsequent World Trade Organization (WTO) agreements sought to reduce tariffs globally. The US participated in these efforts, aiming to promote free trade and reduce trade barriers.
- Late 20th and Early 21st Century: The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), implemented in the 1990s, demonstrated a different approach. NAFTA involved a reduction of tariffs between the US, Canada, and Mexico, aiming to increase trade and economic integration within the region. Subsequently, other bilateral and multilateral trade agreements emerged, reflecting the changing global landscape.
Evolution of Trade Policies
The evolution of trade policies regarding reciprocal tariffs demonstrates a complex relationship between protectionism and free trade. From the protectionist policies of the early 20th century to the more nuanced approaches of the 21st century, the US’s approach to tariffs has reflected a continuous negotiation between the desire to protect domestic industries and the benefits of open trade. This evolution is intrinsically linked to economic growth, global competitiveness, and geopolitical factors.
Different Administrations’ Approaches
Various US administrations have taken differing stances on reciprocal tariffs, reflecting their economic philosophies and geopolitical priorities. Comparing and contrasting these approaches provides valuable insights into the historical context.
- The Trump Administration: The Trump administration adopted a more protectionist stance, imposing tariffs on goods from various countries, particularly China, aiming to reduce trade deficits and promote American manufacturing. This approach sparked retaliatory tariffs and raised concerns about its impact on global trade and the global economy.
- Historical Precedents: Examining previous administrations’ tariff policies offers a framework for evaluating the Trump administration’s approach. Understanding historical precedents allows for a more comprehensive assessment of the impact and potential consequences of such policies.
Tariffs and Trade Imbalances
The relationship between tariffs and trade imbalances is complex. Tariffs can influence trade flows, but they do not necessarily solve underlying trade imbalances. Often, a combination of factors, including exchange rates, labor costs, and domestic policies, contributes to these imbalances. The historical record provides numerous examples of how tariffs have affected trade imbalances.
Examples of Reciprocal Tariff Agreements
Numerous examples exist of reciprocal tariff agreements involving the US and other countries. These agreements demonstrate the complexities and nuances of trade relations. Analyzing these examples provides insights into the historical evolution of reciprocal tariffs.
- US-Canada Trade Agreement: This bilateral agreement exemplifies a reduction in tariffs between the two nations, fostering trade and economic interdependence.
- US-Mexico Trade Agreements: NAFTA, and subsequent agreements, highlight the historical progression of trade relationships between the US and Mexico, showcasing the evolving application of reciprocal tariffs.
Impact of Tariffs on US Industries
This table illustrates the potential impact of tariffs on specific US industries, highlighting the complexities and diverse effects of these policies. Analyzing this table underscores the need for careful consideration of the potential consequences of tariff implementation.
| Industry | Potential Impact of Tariffs |
|---|---|
| Automobiles | Increased prices for imported vehicles, potential job losses in related industries, or retaliatory measures |
| Consumer Electronics | Higher costs for electronics, potential impact on consumer spending |
| Agricultural Products | Reduced exports, potential impact on farmers’ incomes |
Trump Administration’s Tariff Policies
The Trump administration’s approach to international trade was significantly marked by the imposition of tariffs on various goods from several countries. These tariffs, often characterized as reciprocal, aimed to protect American industries and jobs, but they also sparked considerable debate and controversy. The policies had wide-reaching consequences, affecting not only the targeted countries but also American consumers and businesses.The rationale behind these tariffs was rooted in the belief that unfair trade practices were hurting American businesses and workers.
Advocates argued that tariffs would level the playing field, encouraging foreign nations to adopt more favorable trade policies. However, critics questioned the effectiveness and potential negative consequences of these measures, including retaliatory tariffs and economic instability.
Specific Tariffs Imposed
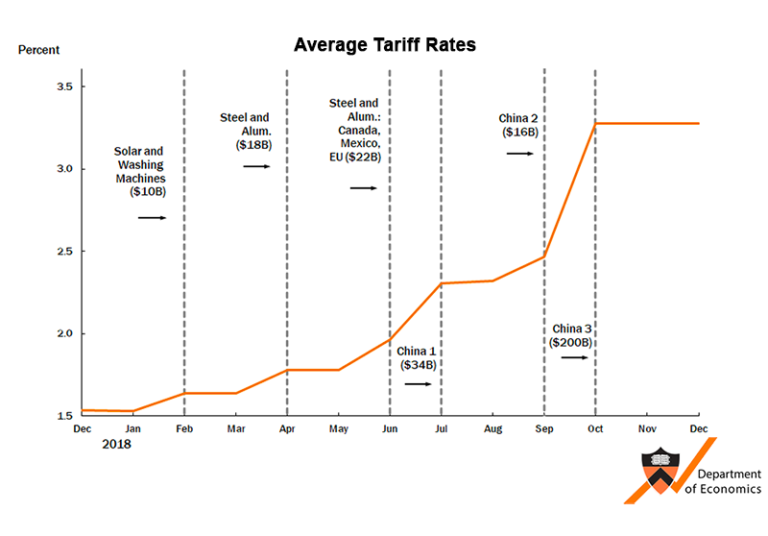
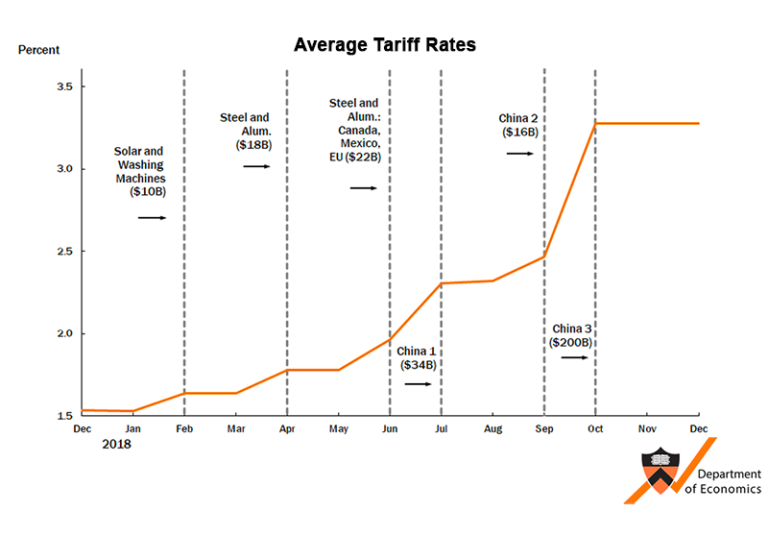
The Trump administration implemented tariffs on a wide range of imported goods, targeting various sectors and countries. These tariffs were often imposed under the guise of national security concerns or allegations of unfair trade practices. The specific tariffs included substantial duties on steel, aluminum, solar panels, washing machines, and numerous other products. This action had a significant impact on global supply chains and trade relationships.
Rationale Behind the Tariffs
The administration argued that these tariffs were necessary to address trade imbalances and protect American industries. The stated goal was to force other countries to change their trade practices and reduce their trade surpluses with the United States. Advocates claimed that these tariffs would result in job creation and economic growth in the US. The administration believed that the tariffs were a necessary step to level the playing field in international trade.
Products and Countries Targeted
Tariffs were imposed on products originating from countries like China, Canada, Mexico, and the European Union. These tariffs frequently targeted industries such as steel, agricultural products, and consumer goods. The specific products and countries varied depending on the particular policy decisions. These actions significantly altered international trade dynamics.
Stated Goals and Anticipated Outcomes
The stated goals of the tariffs included reducing trade deficits, protecting American industries, and promoting fair trade practices. The anticipated outcomes included a stronger American economy, job creation, and increased domestic production. However, the actual outcomes were more complex and often less favorable than initially projected.
Table: Countries Affected and Goods Impacted
| Country | Goods Impacted |
|---|---|
| China | Technology products, consumer goods, agricultural goods |
| Canada | Steel, aluminum, agricultural products |
| Mexico | Automobiles, agricultural products |
| European Union | Steel, aluminum, agricultural products |
Potential Unintended Consequences
The tariffs imposed by the Trump administration resulted in various unintended consequences. These included retaliatory tariffs from other countries, increased prices for consumers, disruptions to global supply chains, and potential economic instability. The effects were felt globally, as businesses and consumers adjusted to the changing trade landscape. These unforeseen consequences highlighted the complexity and interconnectedness of global trade.
Impact on Prices and Consumer Costs
The Trump administration’s imposition of reciprocal tariffs significantly impacted consumer prices in the United States. These tariffs, intended to protect domestic industries and encourage fair trade practices, ultimately led to a complex interplay of factors affecting the cost of goods for American consumers. The effects were not uniform across all products, and the magnitude of the impact varied depending on the specific good and the degree of its reliance on imported components.The relationship between tariffs and import costs is direct.
Tariffs, essentially taxes on imported goods, increase the price of those goods for domestic consumers. This increased cost is passed on, either fully or partially, to the final consumer. The degree to which this occurs depends on the elasticity of demand for the product and the availability of substitute goods. For example, if the tariffed good has few substitutes, the price increase will likely be greater and more noticeable.
Impact on Import Costs
Tariffs directly increase the cost of imported goods, as the tariff is effectively an additional tax levied on the import. This increase in import cost can be seen in the price paid by domestic importers. The increase in the price of imported inputs directly affects the cost of domestically produced goods that use those inputs. This “ripple effect” can impact various industries, from manufacturing to agriculture, eventually affecting the prices of consumer products.
Price Fluctuations for Specific Products
Analyzing price fluctuations for specific products before and after the tariffs requires examining detailed data sets. Unfortunately, a comprehensive analysis encompassing all products and time periods is not possible within this format. However, available data often shows noticeable price increases for certain goods following the implementation of tariffs, especially those goods with limited domestic alternatives. For instance, certain types of steel and aluminum saw substantial price increases after the imposition of tariffs.
Methods for Calculating Price Impact
Several methods can be used to estimate the impact of tariffs on prices. One approach involves analyzing the difference in prices for a specific product before and after the tariff’s implementation. Another method involves examining the costs of imported components in the production of domestically produced goods. Econometric models can also be used to estimate the overall impact of tariffs on consumer prices, considering various factors like demand elasticity, supply chain disruptions, and substitution effects.
The results of these models should be interpreted cautiously, as they rely on various assumptions and data estimations.
Price Comparison Table (Illustrative Example)
This table presents a hypothetical comparison of prices for a particular consumer good (e.g., washing machines) before and after the implementation of tariffs. Actual data would be necessary for a real-world analysis.
| Time Period | Price per Unit (USD) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Tariff (2018) | 500 | Price of washing machine before the implementation of tariffs. |
| Post-Tariff (2019) | 550 | Price of washing machine after the implementation of tariffs. |
| Post-Tariff (2020) | 580 | Price of washing machine after the implementation of tariffs in a later year. |
Reciprocal Responses from Other Countries
The Trump administration’s imposition of tariffs sparked a wave of retaliatory measures from other countries. These reciprocal actions created a complex web of trade restrictions, significantly impacting global commerce and potentially undermining the intended objectives of the original tariffs. Understanding these responses is crucial for evaluating the broader economic consequences of such trade policies.The retaliatory tariffs imposed by other nations were not simply passive reactions; they were calculated responses designed to counter the perceived negative effects of the American tariffs.
Trump’s reciprocal tariffs on various goods definitely had an impact on prices, but let’s be honest, sometimes a little downtime is needed to decompress after all the economic chatter. If you’re looking for some fun and engaging games to liven up your New Year’s celebrations, check out these top 5 cannabis-inspired games to add some unique flair to your festivities here.
Ultimately, though, the ripple effects of those tariffs are still being felt in the market, and it’s a complex situation.
These actions often targeted specific American industries, aiming to minimize the damage to their own economies while also sending a clear message to the United States.
Retaliatory Tariffs by Other Countries
Various countries responded to the Trump administration’s tariffs with their own retaliatory measures. These responses varied in scope and intensity, depending on the specific industries and the political dynamics between the countries involved.
Specific Examples of Retaliatory Tariffs
China, the European Union, Canada, and Mexico were among the nations that implemented retaliatory tariffs on US goods. These tariffs were often applied to a wide range of products, from agricultural goods to manufactured products. For example, China imposed tariffs on American soybeans, while the EU retaliated with tariffs on American steel and aluminum.
Global Trade Implications of Reciprocal Actions
The global trade implications of these reciprocal actions were far-reaching. The imposition of tariffs led to increased costs for businesses and consumers, potentially hindering economic growth. Furthermore, the uncertainty surrounding these trade policies created a climate of instability, affecting investment decisions and market confidence.
Effects on Various Global Markets
The effects of reciprocal tariffs were not uniform across all global markets. Certain industries, like agriculture and manufacturing, were disproportionately impacted. For instance, the agricultural sector in countries like the US and Canada experienced significant losses due to reduced export markets. In contrast, some industries in other countries might have experienced increased domestic demand, but at the expense of broader economic stability.
Countries Most Affected by Reciprocal Tariffs
The countries most affected by reciprocal tariffs were those heavily reliant on exports to the United States, especially in sectors directly targeted by the US tariffs. For instance, the Canadian agricultural sector, heavily reliant on the US market, faced significant challenges due to the retaliatory tariffs.
Table of Retaliatory Tariffs Imposed by Each Country
| Country | Targeted US Products | Approximate Tariff Rate |
|---|---|---|
| China | Soybeans, agricultural products, manufactured goods | Varying rates, often escalating |
| European Union | Steel, aluminum, agricultural goods | Varying rates, often escalating |
| Canada | Agricultural products, manufactured goods | Varying rates, often escalating |
| Mexico | Agricultural products, manufactured goods | Varying rates, often escalating |
| … | … | … |
Note: This table provides a simplified overview. Actual tariffs and targeted products were more complex and varied depending on the specific trade agreements and political considerations.
Economic Effects of the Tariffs
The Trump administration’s imposition of reciprocal tariffs had profound and multifaceted economic consequences. These tariffs, designed to protect American industries and encourage foreign nations to renegotiate trade deals, significantly impacted various sectors, employment levels, and the overall trajectory of the US economy. The ripple effects were felt not only within the United States but also across global supply chains, reshaping international trade relationships.
Impact on US Industries
The tariffs targeted a broad range of imported goods, affecting numerous industries. These measures aimed to increase domestic production and reduce reliance on foreign imports, but their effectiveness was debated. Industries heavily reliant on imported components or raw materials experienced immediate and substantial disruptions.
- Manufacturing: Sectors like automotive, electronics, and machinery, which rely heavily on imported parts and materials, faced significant cost increases due to tariffs. Higher input costs translated into increased production costs, potentially impacting profitability and competitiveness. The loss of economies of scale resulting from reduced imports also led to a decline in production output and efficiency. For example, the increased cost of steel imports affected the construction industry, impacting housing and infrastructure projects.
- Agriculture: Farmers faced challenges from retaliatory tariffs imposed by other countries on American agricultural products. The loss of export markets for agricultural commodities like soybeans and pork had a direct impact on farm incomes and profitability. The price fluctuations caused by the tariffs created uncertainty and made long-term planning difficult for farmers. The resulting instability also negatively impacted farm employment and overall agricultural production.
- Consumer Goods: Consumers bore the brunt of increased prices for goods affected by tariffs. The cost of imported consumer goods, ranging from clothing to electronics, rose, reducing consumer purchasing power. This ultimately impacted overall consumer spending and economic growth.
Impact on Employment
The economic effects of tariffs on employment were complex and varied across different sectors. While some industries experienced job losses due to reduced production and competitiveness, others saw limited or no impact. The overall impact on employment was a subject of debate and analysis.
- Manufacturing Jobs: The rise in production costs in manufacturing industries led to job losses in some factories as companies sought to minimize costs. The impact was more pronounced in industries heavily reliant on imported inputs. For instance, auto parts manufacturers faced reduced output and job losses due to tariffs on imported steel and aluminum.
- Agricultural Employment: Retaliatory tariffs from other countries decreased demand for American agricultural products, impacting farm incomes and leading to potential job losses in rural communities. The decline in agricultural exports resulted in reduced farm income and potential job losses in related industries.
Impact on Supply Chains and Global Trade Flows, Trump reciprocal tariffs prices
The tariffs significantly disrupted global supply chains. The imposition of tariffs made it more costly and complex to source materials and goods internationally, impacting businesses’ ability to optimize production and logistics.
- Disruptions in Global Trade: Tariffs created uncertainty and increased transaction costs in international trade. Businesses had to adapt to new trade regulations and find alternative suppliers, which caused delays and increased costs. This ultimately affected the flow of goods and services across borders.
- Shifting Trade Patterns: Companies sought to diversify their supply chains to avoid tariffs and minimize costs. This resulted in shifting trade patterns and potentially increased reliance on non-tariffed countries. The tariffs may have also incentivized companies to invest more in domestic production to reduce their dependence on foreign imports.
Impact on Competitiveness of US Businesses
The tariffs affected the competitiveness of US businesses in both domestic and international markets. The increased costs of imported inputs and the retaliatory tariffs imposed by other countries reduced the competitiveness of American companies.
- Reduced Profit Margins: The increased costs associated with tariffs reduced the profit margins for businesses in affected sectors. Higher input costs translated directly into higher prices for consumers, potentially reducing demand and impacting sales. Reduced exports to other countries also lowered revenues.
- Loss of Export Markets: The retaliatory tariffs imposed by other countries on US goods reduced the demand for American exports in those markets. This resulted in decreased sales and revenues for US companies, impacting their ability to compete in global markets.
Specific Industries Affected
The tariffs had a substantial impact on several specific industries. The industries most directly affected were those heavily reliant on imported inputs or those targeting export markets.
| Industry | Impact |
|---|---|
| Automotive | Increased production costs, reduced profitability, potential job losses. |
| Agriculture | Decreased export markets, reduced farm incomes, potential job losses. |
| Electronics | Increased input costs, reduced competitiveness, potential job losses. |
| Machinery | Increased production costs, reduced profitability, potential job losses. |
Analysis of Long-Term Implications
Reciprocal tariffs, while intended to level the playing field, have profound and far-reaching consequences that extend beyond the immediate economic impact. Understanding these long-term implications is crucial for predicting the future of global trade relations and navigating the potential risks and opportunities. The ripple effects of these policies can reshape international trade patterns and alter the economic landscape for decades to come.The potential for escalating trade conflicts is significant.
Countries may retaliate with further tariffs, leading to a trade war with unpredictable outcomes. The 2009-2016 trade war between the United States and China serves as a cautionary example. Such conflicts can disrupt supply chains, harm businesses, and ultimately reduce global economic output.
Potential for Trade Wars and Their Implications
Trade wars, characterized by escalating tariffs and retaliatory measures, create significant uncertainty and instability in global markets. This uncertainty hinders investment, discourages innovation, and reduces economic growth. Businesses face difficulties in planning and executing long-term strategies, as the shifting trade landscape creates unpredictable conditions. The potential for trade wars is a major concern for economists and policymakers, as it can trigger a domino effect across multiple industries and economies.
Trump’s reciprocal tariffs, while aiming to level the playing field, often resulted in higher prices for consumers. This economic ripple effect, however, is now playing out in unexpected ways, like the recent sale of a single family residence in Oakland for a staggering $1.5 million. This high-priced home sale in Oakland could be a symptom of the broader economic shifts caused by those tariffs, ultimately highlighting the complex interplay between international trade policies and local real estate markets.
The long-term impact of Trump’s reciprocal tariffs prices remains a subject of debate.
The unpredictability of such conflicts and their lasting impact makes them a significant threat to global economic stability.
Comparison of Different Scenarios for Future Trade Relations
Different scenarios for future trade relations offer varied implications. A scenario of increased cooperation and reduced tariffs could lead to a more integrated global economy, fostering greater economic growth and prosperity. Conversely, a scenario of heightened protectionism and continued trade wars could result in fragmented trade blocs and slower global economic growth. The path taken will depend on the actions of individual countries and their willingness to engage in constructive dialogue and negotiation.
Comprehensive Overview of Effects on the World Economy
Tariffs impose significant costs on consumers through higher prices and reduced availability of goods. This can impact industries reliant on imported components or raw materials, leading to higher production costs and potentially reduced competitiveness. The economic consequences of tariffs can vary significantly across different countries and industries. Some sectors might experience a decline in output, while others might experience temporary gains due to reduced competition from imports.
The overall impact on the global economy depends on the extent of the tariff implementation and the reactions of other countries.
Trump’s reciprocal tariffs on various goods definitely had a ripple effect. Now, with Biden’s final full day in office, Biden’s final full day is certainly a historical moment, but it’s worth remembering the lingering impacts of those trade policies. Looking back, the effect on consumer prices from those tariffs remains a significant talking point.
Potential Risks and Opportunities Arising from the Policies
The implementation of reciprocal tariffs presents both risks and opportunities. The risk of trade wars, reduced global trade, and economic instability is significant. However, the opportunity for countries to strengthen their domestic industries and reduce reliance on imports exists. This opportunity often comes at the cost of increased consumer prices and reduced access to a wider range of goods.
The balance between these competing forces needs careful consideration.
Summary of Potential Outcomes
| Scenario | Global Trade Relations | Economic Impact | Consumer Costs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Increased Cooperation | Harmonized trade rules, reduced tariffs | Higher global economic growth, increased trade | Lower prices, increased choice |
| Heightened Protectionism | Fragmented trade blocs, escalating tariffs | Slower global economic growth, reduced trade | Higher prices, reduced choice |
| Unpredictable Trade Wars | Escalating tariffs, retaliatory measures | Significant economic uncertainty, reduced investment | Higher prices, reduced availability of goods |
Alternative Trade Strategies
Navigating the complexities of international trade requires more than just imposing tariffs. Alternative strategies offer a nuanced approach, focusing on fostering cooperation, fairness, and mutually beneficial outcomes. These strategies aim to address the negative impacts of protectionist policies while promoting long-term economic growth and stability. By prioritizing trade agreements and fair practices, we can create a more predictable and prosperous global economy.
Examples of Alternative Trade Strategies
Alternative trade strategies offer a range of approaches beyond tariffs. They aim to mitigate negative effects and foster a more balanced global trade system. These strategies include pursuing reciprocal trade agreements, emphasizing transparency and fair competition, and exploring dispute resolution mechanisms.
- Reciprocal Trade Agreements: Agreements that establish common ground for trade between countries, with mutual benefits. They often include reduced tariffs, quotas, or other trade barriers. These agreements can foster greater trade volumes and lower costs for consumers. For example, the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) aimed to lower trade barriers and promote economic growth among member nations.
- Emphasis on Transparency and Fair Competition: Establishing clear and transparent rules and regulations for trade promotes a level playing field for all participants. This approach minimizes unfair trade practices, like subsidies or dumping, that can distort markets. Stronger enforcement mechanisms are needed to ensure compliance and address concerns.
- Trade Negotiations for Dispute Resolution: A critical element in mitigating trade conflicts is establishing effective mechanisms for resolving disputes. These mechanisms include international organizations like the World Trade Organization (WTO), which provide platforms for dialogue and arbitration. Using these forums can prevent escalating trade wars and promote stability.
- Fair Trade Practices: Ensuring fair treatment of workers and producers in the supply chain is a vital aspect of sustainable trade. Fair trade practices promote ethical labor standards, environmental protection, and the livelihoods of producers, especially in developing countries. These principles promote social responsibility in global commerce. For example, fair trade certifications for coffee and other agricultural products help guarantee fairer prices and working conditions for farmers.
Potential Benefits of International Trade Agreements
International trade agreements offer significant benefits to participating nations. These agreements establish clear rules and regulations, promoting predictability and transparency in trade relations.
- Reduced Trade Barriers: Agreements often reduce tariffs, quotas, and other trade barriers, making it easier and more affordable for businesses to import and export goods and services. This increased access to markets expands opportunities for economic growth and development.
- Increased Market Access: Agreements create access to larger markets for participating countries, potentially boosting economic activity and employment opportunities. Access to new consumers and buyers is a key benefit.
- Investment Promotion: Agreements can attract foreign investment by establishing a stable and predictable regulatory environment. Foreign investment often leads to economic growth and job creation.
The Role of Trade Negotiations in Resolving Trade Disputes
Trade negotiations are essential for resolving trade disputes and preventing escalations. They provide a platform for dialogue and compromise.
- Facilitating Dialogue and Compromise: Negotiations provide a structured environment for parties to discuss their concerns and explore mutually acceptable solutions. This can lead to the de-escalation of trade tensions and the restoration of positive trade relations.
- Addressing Concerns and Interests: Negotiations allow parties to address specific concerns and interests regarding trade practices. They can lead to adjustments in policies and regulations that address imbalances or unfair trade practices.
Importance of Fair Trade Practices
Fair trade practices ensure ethical treatment of workers and producers in the global supply chain. These practices contribute to a more equitable and sustainable global economy.
- Ethical Labor Standards: Fair trade practices promote fair wages, safe working conditions, and freedom of association for workers. These practices often benefit workers and promote social responsibility.
- Environmental Protection: Fair trade emphasizes environmentally sound practices, including sustainable resource management and reducing environmental damage. These measures can promote sustainability and minimize harm to the environment.
- Livelihoods of Producers: Fair trade initiatives ensure fair prices and terms for producers, particularly in developing countries. These measures help sustain livelihoods and support local economies.
Benefits of Alternative Trade Strategies
The table below summarizes the potential benefits of alternative trade strategies.
| Strategy | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|
| Reciprocal Trade Agreements | Reduced trade barriers, increased market access, investment promotion |
| Transparency and Fair Competition | Level playing field, reduced unfair trade practices, greater predictability |
| Trade Negotiations for Dispute Resolution | Dialogue and compromise, de-escalation of trade tensions, restoration of positive trade relations |
| Fair Trade Practices | Ethical labor standards, environmental protection, sustainable livelihoods |
Closing Summary
In conclusion, the Trump reciprocal tariffs prices policy proved to be a complex and multifaceted event with far-reaching consequences. The analysis reveals the significant impact on consumer prices, global trade relations, and the US economy. While the initial goals may have been to protect domestic industries, the unintended consequences and reciprocal responses from other nations created a global trade war with long-term implications.
Alternative trade strategies are crucial to mitigating future conflicts and ensuring a more stable and prosperous global economy.