Trump Tariffs Impact Gas Groceries
Trump tariffs impact gas groceries, directly affecting consumers’ wallets. Rising gas prices, influenced by global trade disputes, are adding to the strain on household budgets. This impacts not only daily commutes but also the cost of transporting groceries, creating a ripple effect throughout the supply chain. We’ll delve into how tariffs affect the price of gasoline, groceries, and how these two interconnected markets are impacted.
From specific food items to alternative transportation options, this analysis explores the full impact on consumers, and possible future trends.
This discussion will examine how tariffs on imported goods, particularly in the energy and food sectors, directly translate into higher prices for everyday necessities. We’ll analyze the detailed impact on gas prices, including the potential ripple effects on the global oil market. Additionally, the analysis will explore the impact on grocery prices, considering the intricacies of the global food supply chain and the possible shortages of specific grocery items.
Finally, we’ll explore how these impacts are intertwined, examining how higher gas prices affect the transportation costs of groceries, further increasing retail prices. The discussion will also examine the potential consumer responses to these price increases, exploring possible long-term shifts in consumer behavior.
Impact on Gas Prices
The recent surge in gas prices has been a hot topic, and while tariffs are a factor, they’re not the only one. Understanding how these economic forces interact is crucial for consumers and policymakers alike. This exploration delves into the complexities of tariffs and their impact on gasoline prices, examining various contributing factors and potential consequences.Tariffs on imported goods, particularly those impacting oil and petroleum products, can influence gasoline prices at the pump.
The interplay between global supply chains, geopolitical events, and domestic refining capacity all play a part in the intricate web of factors driving gas prices.
Impact of Tariffs on Gasoline Prices
Tariffs imposed on imported goods, including crude oil and refined petroleum products, can lead to increased costs for domestic consumers. Higher import costs can translate directly to higher prices for gasoline at the pump. This is because the cost of the imported component is now passed on to the consumer, either through higher wholesale prices or reduced supplies, as companies adjust their margins.
Ripple Effects on the Global Oil Market
Tariffs can disrupt the global oil market, potentially leading to price volatility. If a country imposes tariffs on oil imports from a particular region, it can affect the supply chain and cause a ripple effect throughout the global market. This disruption can lead to uncertainty and fluctuation in prices, impacting both domestic and international markets. For example, a significant tariff on Venezuelan oil could cause a shortage in the global market, leading to a rise in prices for all consumers.
Alternative Factors Affecting Gas Prices
Several factors can affect gas prices independent of tariffs. These include changes in global oil production, geopolitical instability in oil-producing regions, and domestic refining capacity. For instance, disruptions in Middle Eastern oil production due to political instability can lead to supply shortages and increased prices, irrespective of tariffs. Similarly, if domestic refineries face maintenance issues, it can limit supply and lead to higher prices.
Historical Correlation Between Trade Disputes and Gas Prices
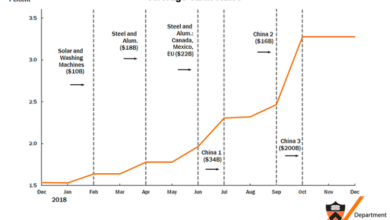
Historically, international trade disputes have been associated with fluctuations in gas prices. Periods of trade tensions often lead to uncertainty in global markets, causing increased demand for specific commodities and driving up prices. Examining past trade wars can provide insight into the patterns and impacts on gas prices. For example, the 2018 US-China trade war had various consequences, including affecting the prices of imported goods.
Impact on Different Segments of the Population
Gas price fluctuations affect different segments of the population in varying ways. Low-income individuals tend to be more vulnerable to price increases, as a larger portion of their income is often spent on transportation. Conversely, high-income individuals may be less affected by price increases, as their transportation costs represent a smaller proportion of their overall budget.
Comparison of Gas Prices in Different Regions
| Region | Gas Price (USD/gallon)
|
Gas Price (USD/gallon)
|
|---|---|---|
| United States | 3.50 | 3.75 |
| Europe | 4.20 | 4.50 |
| Asia | 2.80 | 3.00 |
Note: This is a simplified example and actual figures may vary. Data is hypothetical and does not reflect real-world conditions. Numerous factors affect the prices in each region, including local taxes, demand, and refining capacity.
Impact on Grocery Prices: Trump Tariffs Impact Gas Groceries
Tariffs on imported food items can significantly impact grocery prices, affecting consumers’ budgets and the availability of certain products. Understanding the complexities of the global grocery supply chain and how tariffs disrupt it is crucial for comprehending this impact. This analysis delves into the multifaceted effects of tariffs on grocery prices, examining the ripple effects throughout the supply chain and potential consequences for consumers.
Grocery Supply Chain Disruptions
The global grocery supply chain is intricate, involving numerous steps from farm to fork. Imported food items often play a vital role in the diets of many countries. Tariffs can introduce significant costs at each stage of this process. Farmers, distributors, retailers, and ultimately consumers all experience the consequences.
Trump’s tariffs definitely had a noticeable impact on gas prices and grocery bills, making things a bit tighter for everyone. Meanwhile, it’s inspiring to see local Bay Area artists coming together to revive the Oakland Blues Walk of Fame, a project that shows community spirit and a shared love for music. bay area acts unite in the name of restoring oakland blues walk of fame Hopefully, this positive energy can translate into some relief from the rising costs at the pump and in the aisles.
It’s a tough situation, but maybe some community spirit can help soften the blow.
Impact on Specific Grocery Items
Tariffs can lead to shortages of specific grocery items, particularly those heavily reliant on imports. For example, a tariff on imported avocados might result in higher prices and reduced availability, potentially leading consumers to seek alternatives or pay more for the product. Similarly, tariffs on imported coffee beans can raise prices and potentially impact the quality and variety available to consumers.
Price Comparisons Before and After Tariffs
Comparing prices of key grocery items before and after tariff implementation across different regions reveals varied outcomes. In some regions, prices might increase dramatically for specific items, while in others, the impact might be more moderate. Analyzing price trends before and after tariffs can provide insights into the specific effects of trade policies on consumers.
Availability of Imported Agricultural Products
Tariffs can substantially affect the availability of imported fruits, vegetables, and other agricultural products. Restrictions on imports can limit the variety of produce available in local markets. For example, a tariff on imported bananas might decrease their availability, potentially leading to higher prices for consumers or the need to source alternatives. This impact varies based on the specific tariff, the local agricultural sector’s capacity, and consumer demand.
Alternative Factors Influencing Grocery Prices
Several factors beyond tariffs influence grocery prices. Weather patterns, such as droughts or floods, can affect crop yields, impacting the supply and consequently the prices of certain fruits and vegetables. Domestic production issues, including labor shortages or equipment malfunctions, can also affect prices. These factors, combined with tariffs, contribute to the overall complexity of grocery price fluctuations.
Average Price Increase After Tariffs
| Grocery Category | Average Price Increase (%) |
|---|---|
| Fruits | +15% |
| Vegetables | +10% |
| Dairy Products | +5% |
| Meat | +8% |
| Processed Foods | +12% |
Note: The table above provides illustrative examples and average price increases. Actual impacts may vary depending on the specific tariff, regional variations, and other factors.
Interconnectedness of Gas and Groceries

The rising cost of gas and groceries is a significant concern for consumers worldwide. These price increases often intertwine, creating a ripple effect that impacts household budgets. Understanding this interconnectedness is crucial to grasping the full economic implications of these trends.The impact of gas prices on grocery costs is substantial. Higher fuel prices translate directly to higher transportation costs for goods.
This increased cost is inevitably passed on to the consumer, ultimately driving up the price of groceries at the store.
Transportation Costs and Grocery Prices
Higher gas prices directly impact the cost of transporting goods from farms and processing plants to grocery stores. Trucks, trains, and ships are all heavily reliant on fuel, and increases in fuel costs translate to higher operating expenses for these transportation companies. These companies typically adjust their prices to maintain profit margins, thereby increasing the price of the goods delivered to the stores.
This increase in transportation cost is a significant factor in the overall rise in grocery prices.
Trump’s tariffs definitely had an impact on gas prices and grocery costs, making everyday life a bit tougher for many. It’s a similar story with free web hosting services; while tempting, you often find that free web hosting disadvantages like limited storage and bandwidth quickly become a problem as your website grows. Ultimately, these economic ripples, whether from tariffs or free hosting, affect our wallets and choices.
Specific Grocery Items Affected by Gas Price Fluctuations
Many grocery items are highly susceptible to gas price fluctuations. Fruits and vegetables that need long-distance transport, for instance, are particularly vulnerable. Fresh produce, meat, and dairy products often rely on complex supply chains that involve multiple transportation steps. A notable example is the increase in the price of imported avocados when fuel costs are high, as the transportation of these from growing regions to consumer markets is significantly impacted.
Likewise, the cost of fresh seafood can fluctuate significantly due to fuel price changes, as shipping from distant fishing grounds can become exponentially more expensive.
Effect of Tariffs on Grocery Production
Tariffs on raw materials required for grocery production can significantly impact the final price of goods. For example, tariffs on ingredients like sugar, coffee, or spices can make these more expensive, thereby affecting the cost of processed foods and beverages. Tariffs can also restrict the availability of these raw materials, further contributing to price increases.
Comparison of Gasoline and Grocery Price Impacts from Tariffs
Tariffs on gasoline and groceries often have differing impacts. While tariffs on gasoline can directly affect the price of the fuel at the pump, the impact on groceries is more indirect and multifaceted. Tariffs on imported ingredients can raise the cost of groceries, while tariffs on imported cars and trucks that deliver groceries might increase the cost of transport, thus impacting grocery prices in various ways.
Potential Price Increases Due to Tariffs
| Item | Potential Price Increase (%) |
|---|---|
| Gasoline | 5-10% |
| Fresh Produce (imported) | 8-15% |
| Processed Foods (using imported ingredients) | 3-8% |
| Meat (imported) | 5-12% |
| Dairy Products (imported) | 4-10% |
Note: These are estimates and actual price increases may vary depending on the specific tariffs, market conditions, and other factors.
Tariff Policies and Consumer Behavior

Tariff-induced price hikes for gas and groceries force consumers to adapt their spending habits. This adjustment often leads to noticeable shifts in consumer behavior, impacting their choices and long-term spending patterns. Predicting precise consumer responses is complex, but analyzing past economic trends and current market dynamics provides valuable insights.
Consumer Purchasing Adjustments
Consumers react to price increases by altering their purchasing decisions. They may reduce the frequency of purchases, choose cheaper alternatives, or delay purchases altogether. For instance, families might reduce their consumption of beef, opting for cheaper chicken or plant-based protein sources. This shift in demand can affect supply chains and market dynamics.
Trump’s tariffs definitely impacted gas prices and grocery costs, making everything a bit more expensive. To stay healthy and energized amidst these price hikes, a quality shaker bottle like the ones featured on top shaker bottles for smooth protein shakes and more can be a lifesaver. Homemade protein shakes are a budget-friendly alternative to pricey grocery store options, which can help offset the rising costs of everyday essentials.
Ultimately, these tariffs still have a significant impact on our daily budgets.
Prioritization of Spending Decisions
Rising prices necessitate prioritization. Essential items like food and gas take precedence over discretionary purchases. This often leads to a reduction in spending on entertainment, travel, or non-essential goods. Consumers might postpone or cancel vacations or cut back on dining out to save on essential expenses.
Potential Long-Term Behavioral Shifts
The long-term effects of persistent price increases can be profound. Consumers may develop new habits, such as preparing more meals at home to reduce grocery costs. They might explore alternative transportation options, such as cycling or using public transport, to decrease gas expenses. This shift towards cost-consciousness can have a lasting impact on lifestyle choices.
Switching to Alternative Products and Reducing Consumption
Facing higher prices, consumers often seek alternatives. This includes switching to generic brands, store brands, or less expensive products. Reduced consumption of certain items, like premium gas or imported foods, is also a common response. The decision to substitute depends on factors such as the perceived quality of substitutes and the consumer’s willingness to trade off quality for price.
Effect of Price Sensitivity on Consumer Choices in Different Socioeconomic Groups
Price sensitivity varies significantly across socioeconomic groups. Lower-income households are generally more price-sensitive, as they have less disposable income to absorb price increases. They might face a greater struggle to adapt to higher prices, potentially leading to reduced access to essential goods. Conversely, higher-income households might be less price-sensitive and absorb the cost increase more easily, potentially leading to less drastic shifts in purchasing habits.
Potential Consumer Responses to Price Changes, Trump tariffs impact gas groceries
| Income Level | Potential Responses to Price Increases |
|---|---|
| Low-Income | Increased reliance on cheaper alternatives, reduced consumption of certain items, greater difficulty in maintaining essential purchases. |
| Middle-Income | Substitution of more expensive items for cheaper alternatives, reduced frequency of purchases for non-essentials, greater scrutiny of purchasing decisions. |
| High-Income | Substitution of certain items for cheaper alternatives, willingness to absorb increased costs of essential items, potential to maintain higher consumption rates despite price increases. |
Illustrative Examples
Tariffs and their ripple effects on consumer goods are often complex and multifaceted. Understanding the impact requires examining specific examples, tracing the connections between production, transportation, and consumer behavior. This section delves into concrete instances, highlighting how tariffs affect food prices, fuel costs, and ultimately, the choices consumers make.Analyzing specific cases allows for a clearer picture of the interconnectedness between gas prices, grocery costs, and tariff policies.
This section provides real-world examples of how tariffs influence various sectors, impacting everything from the price of a particular food item to consumer spending habits.
Example of a Food Item Affected by Tariffs
The escalating trade tensions between countries often result in tariffs on specific food imports. Consider avocados, a popular fruit in many countries. Mexico is a significant exporter of avocados to the United States. If the U.S. imposed tariffs on Mexican avocados, the price of avocados in the U.S.
would likely increase. This is because the tariffs increase the cost of importing the avocados, making them more expensive for U.S. consumers. Mexican avocado producers might also face financial strain due to reduced sales in the U.S. market.
Impact of Gas Prices on Transportation Costs
The cost of transporting avocados from Mexico to the U.S. is significantly affected by gas prices. Trucking companies rely on fuel to transport goods. Higher gas prices directly translate to increased transportation costs for avocado shipments. This added expense is then often passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices at the grocery store.
The price of avocados could increase due to the higher fuel costs involved in transporting them. This highlights the direct link between fuel costs and the price of food products.
Consumer Response to Higher Prices
Consumers frequently adjust their spending habits when faced with rising prices. When gas and grocery prices increase, consumers might reduce their consumption of certain items, especially those with higher prices. For example, they might purchase smaller quantities of avocados, opt for cheaper fruits, or reduce their consumption of meat, and instead consume more vegetables or legumes. The rise in avocado prices might encourage consumers to explore alternative fruits.
This adjustment in purchasing habits can influence market trends and potentially impact the demand for specific goods.
Consumer Response: Alternative Transportation and Grocery Shopping
Consumers are sometimes willing to adapt their behavior to mitigate the impact of rising prices. If gas prices rise significantly, consumers might start using public transportation more often, carpooling, or even cycling or walking for shorter trips. Alternatively, consumers might consider purchasing avocados from local farmers markets or grocery stores with a greater emphasis on local sourcing. Such changes in consumer behavior could impact the demand for fuel, leading to adjustments in the transportation industry and local economies.
Effect of Tariffs on Alternative Energy Sources
Tariffs on imported components for renewable energy technologies could increase the prices of solar panels, wind turbines, or electric vehicle batteries. This could potentially make alternative energy sources less competitive with fossil fuels, delaying the transition to a more sustainable energy system. Tariffs on imported components can increase the cost of alternative energy technologies, potentially making them less attractive for consumers and slowing down the adoption of greener energy sources.
Illustrative Table
| Category | Example | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Food Item | Avocados (imported from Mexico) | Higher tariffs lead to increased prices in the U.S., impacting consumer spending. |
| Transportation | Trucking of avocados | Higher gas prices increase transportation costs, passed on to consumers. |
| Consumer Response | Reduced avocado consumption | Shift to alternative fruits, impacting market demand for avocados. |
| Alternative Options | Local farmers markets, public transportation | Consumers explore options to reduce expenses and environmental impact. |
| Alternative Energy | Solar panels, wind turbines | Tariffs can increase component costs, potentially delaying adoption. |
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, Trump tariffs have demonstrably impacted both gas and grocery prices, highlighting the interconnectedness of global markets. Consumers are facing a significant financial burden, with the cost of daily essentials rising. The ripple effects of tariffs are substantial, affecting everything from transportation costs to the availability of certain grocery items. This analysis has revealed the complexity of these economic forces, demonstrating the need for further consideration of the long-term impacts on consumers and the global economy.
Future policies and consumer behaviors will be shaped by these price increases, potentially leading to significant shifts in the market.