California Insurance Facing a New Bailout?
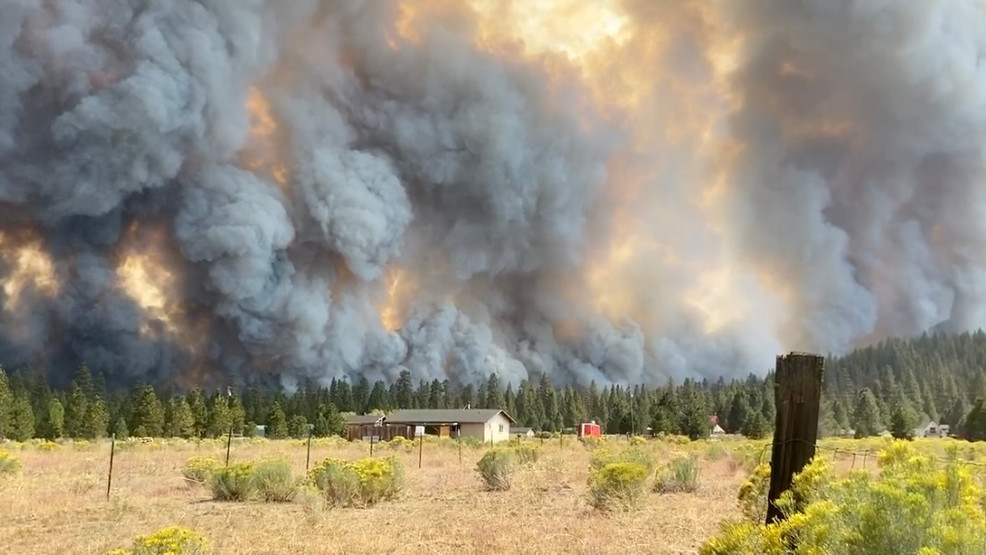
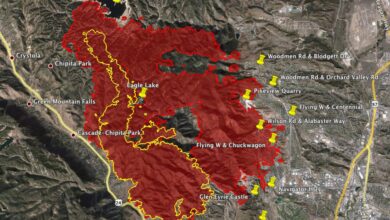
California at risk of new insurance bailout amid fire danger. The state’s escalating wildfire crisis is putting a strain on its insurance industry, potentially leading to another costly bailout. Past bailouts have had significant financial repercussions, impacting insurers and taxpayers. The current wildfire risk assessment paints a concerning picture, highlighting vulnerable regions and the potential for substantial losses.
This analysis explores the historical context, current challenges, potential future instability, alternative solutions, economic impacts, and international comparisons, all aimed at understanding the intricate web of factors driving this looming crisis.
California’s history of wildfire-related insurance bailouts reveals a pattern of increasing frequency and cost. This trend, coupled with the rising threat of climate change and the evolving fire danger, raises critical questions about the state’s long-term financial stability. The current analysis will examine the potential consequences of a new bailout, exploring its effects on insurance rates, consumer access to coverage, and the state’s overall economic health.
The impact on different regions, property types, and businesses will be considered, offering a comprehensive perspective on the challenges ahead.
Historical Context of Insurance Bailouts in California: California At Risk Of New Insurance Bailout Amid Fire Danger
California, a state frequently ravaged by wildfires, has a history of needing insurance bailouts to mitigate the financial fallout from catastrophic events. These bailouts, often triggered by massive fire seasons, highlight the vulnerability of the insurance industry and the state’s infrastructure in the face of intensifying climate change. Understanding these past interventions is crucial for anticipating future needs and developing more resilient systems.The financial strain on insurers and the state budget is significant, often necessitating complex negotiations and government interventions to ensure the continued functioning of the insurance market.
These actions are not merely about financial recovery but about the preservation of a critical service—access to insurance—for California’s residents.
Past Insurance Bailouts: A Summary
California’s history of wildfire-related insurance bailouts demonstrates a growing need for intervention. These bailouts are often prompted by extraordinary events exceeding the capacity of the insurance market to absorb losses. These interventions are critical for maintaining the integrity of the insurance system and ensuring access to insurance for residents and businesses.
Financial Impacts on Insurers and the State
The financial impacts of these bailouts are substantial. Insurers, faced with massive claims exceeding their reserves, can experience significant losses, potentially leading to insolvency. These losses can also lead to rate increases for future policyholders, a phenomenon that impacts homeowners and businesses. State governments, meanwhile, bear the cost of the bailout itself, potentially diverting funds from other crucial areas like infrastructure development or social programs.
California is facing another potential insurance crisis, with the risk of a new bailout looming amid the ever-present fire danger. It’s a serious situation, but thankfully, amidst all the worry, news of the passing of Broadway star Linda Lavin, Tony Award-winning actress and star of the sitcom Alice, brought a much-needed moment of reflection. Her legacy as a talented performer and a beloved actress will continue to inspire, while California’s insurers still grapple with the devastating consequences of fire seasons.
Linda Lavin ’s impressive career serves as a reminder of the human stories intertwined with the state’s challenges, which unfortunately includes the ongoing risk of costly fire damage.
The state’s role in these bailouts can be seen as a form of financial safety net for both insurers and policyholders, mitigating the catastrophic impacts of widespread damage.
Frequency and Scale of Bailouts Over Time
The frequency and scale of insurance bailouts in California related to wildfires have increased over time, reflecting the intensifying severity and frequency of these events. Historical data suggests a clear correlation between more extreme fire seasons and a higher likelihood of intervention. This trend highlights the urgent need for long-term solutions and proactive measures to mitigate the risks associated with wildfires.
Contributing Factors to Bailouts
Several factors contribute to the need for insurance bailouts in California. Climate change, with its associated increased temperatures and drier conditions, plays a crucial role in fueling more frequent and intense wildfires. Inadequate building codes, especially in high-risk areas, can also increase the vulnerability of properties to fire damage. The density of development in fire-prone areas exacerbates the problem, leading to significant financial consequences for insurers.
Further, a lack of adequate preventative measures, including wildfire mitigation strategies and improved early warning systems, exacerbates the situation.
California’s facing another potential insurance crisis, with the risk of a new bailout looming due to the ever-present fire danger. Meanwhile, a concerning incident unfolded on the Rialto freeway, where a woman was arrested following a suspected road rage shooting. This incident, while tragic, highlights the broader societal issues impacting our communities. With the recent surge in such incidents and the potential for increased insurance costs, the state is already struggling to cope with the ongoing fire threat and its financial implications.
This woman arrested after suspected road rage shooting on the Rialto freeway further underscores the need for increased safety measures and a comprehensive approach to addressing these escalating problems.
Table Summarizing Key Features of Past Insurance Bailouts
| Date | Amount (USD) | Triggering Event(s) | Key Impacts |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | $1 Billion (estimated) | 2020 Northern California wildfires | Significant loss for insurers, rate increases for policyholders, state intervention to provide aid to the insurers. |
| 2018 | $500 Million (estimated) | 2018 Camp Fire, devastating wildfire in Northern California | Large-scale insurance claims, temporary relief for insurers, discussion of policy reforms and preventative measures. |
| 2017 | $200 Million (estimated) | 2017 wildfires across California | Large-scale damage requiring intervention, discussion of wildfire risk management. |
Current Fire Danger and Insurance Market Analysis

California’s persistent drought conditions and heightened temperatures have dramatically increased the risk of devastating wildfires, placing a significant strain on the state’s insurance market. This volatile situation necessitates a thorough examination of the current fire danger, its impact on insurance premiums, and the potential for increased claims. The financial stability of major insurers operating in the state is also crucial to understand.The current wildfire season is already shaping up to be exceptionally dangerous, driven by a confluence of factors including prolonged periods of dry weather, high temperatures, and strong winds.
This combination creates an environment ripe for rapid fire spread, posing significant risks to both human lives and property.
Wildfire Risk Assessment in California
California’s wildfire risk is unevenly distributed, with certain regions facing greater vulnerability than others. Historical data and climate models consistently identify the southern and central parts of the state as particularly susceptible due to their dry, brush-filled landscapes and prolonged drought periods. Furthermore, mountainous regions and areas with high population density often face the highest risk. The impact of these conditions on the insurance industry is substantial.
Impact on Insurance Premiums and Affordability
The escalating wildfire risk directly impacts insurance premiums. As the potential for losses increases, insurers must adjust their pricing models to reflect the elevated risk. This translates into higher premiums for homeowners and businesses in high-risk areas, potentially leading to financial hardship for vulnerable populations. The current market is already experiencing a significant increase in the cost of home and commercial insurance, a trend that is expected to continue if the wildfire season remains active.
Potential for Increased Claims and Losses
The heightened wildfire risk in California forecasts a significant surge in insurance claims. With the current conditions, the potential for substantial property damage and even loss of life is high. Insurers are bracing for a substantial increase in claims, potentially exceeding those of previous years, and are implementing measures to mitigate the impact on their financial stability.
Financial Stability of Major Insurers
The financial health of major insurers operating in California is a critical factor in the state’s ability to manage the growing wildfire crisis. Companies that maintain robust reserves and demonstrate sound financial practices are better equipped to handle a surge in claims. Insurers with a strong financial position are better positioned to provide coverage during the upcoming wildfire season.
Comparison of Wildfire Risk Across California Regions
| Region | Wildfire Risk Assessment | Key Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Southern California | High | Prolonged drought, dry brush, high temperatures, strong winds |
| Central California | High | Dry grasslands, mountainous terrain, high population density |
| Northern California | Moderate to High | Varying conditions, some areas with abundant rainfall, but others with severe drought and high winds |
The table above provides a simplified comparison. Actual risk assessment factors may vary based on specific locations within each region.
Potential for Future Insurance Instability
California’s precarious fire risk, coupled with the potential for future insurance bailouts, casts a long shadow over the state’s financial future. The delicate balance between affordability and risk mitigation is increasingly strained. A new bailout, while seemingly a short-term solution, could have far-reaching consequences for the insurance industry and its customers.A new insurance bailout, though intended to stabilize the market in the immediate term, risks creating a dangerous precedent.
This can incentivize a culture of dependency, potentially undermining the long-term financial health of the insurance sector and discouraging the development of innovative risk management strategies. The potential for future payouts becomes an ever-present concern, impacting the industry’s ability to accurately assess and price risks.
Potential Consequences of a New Bailout
A new bailout, while seemingly a quick fix, carries significant risks. It could lead to a cycle of dependency, where insurers become reliant on government assistance to handle increasingly frequent and severe natural disasters. This reliance can hinder the industry’s capacity to adapt to future challenges and may ultimately increase the cost of insurance for all. This can impact the ability of insurers to accurately price risks, leading to potential instability in the market.
Long-Term Impacts on Insurance Rates and Availability
The frequency of insurance bailouts directly influences insurance rates. Each bailout effectively raises the cost of insurance for all policyholders, as the risk is spread across a wider pool of customers. Furthermore, insurers may become hesitant to offer coverage in high-risk areas, potentially leading to insurance scarcity in vulnerable communities. This scarcity can significantly affect both businesses and individuals who may find it challenging to secure necessary coverage.
Potential Impacts on Consumers, Businesses, and the State Budget
The consequences of a new bailout ripple through various sectors. Consumers face higher premiums, potentially impacting their budgets and access to essential services. Businesses, particularly those located in high-risk areas, may experience increased operational costs and difficulty in securing necessary insurance coverage. The state budget also faces challenges, as it is expected to absorb the financial burden of the bailout.
The ongoing cost of supporting the insurance industry can create a significant strain on public funds.
Comparison of Scenarios for the Future of Insurance in California
Several scenarios are possible for the future of insurance in California, considering the evolving risk of wildfires. A scenario with continued bailouts could lead to a spiraling cost of insurance, eventually impacting the state’s economy and its ability to attract businesses and residents. A scenario with robust risk management strategies and proactive wildfire mitigation could lead to more stable and affordable insurance rates.
A scenario where the insurance industry adapts to the risks and invests in innovative technologies for risk assessment and prevention is also conceivable.
Potential Increase in Insurance Premiums
The potential increase in insurance premiums will vary based on the type of property. A table illustrating potential increases across different property types demonstrates this variability.
| Property Type | Potential Premium Increase (Estimated Percentage) |
|---|---|
| Residential Homes (Single-family) | 15-25% |
| Residential Homes (Multi-family) | 10-20% |
| Commercial Buildings (Retail) | 20-30% |
| Commercial Buildings (Industrial) | 25-40% |
| Vacant Land | 10-15% |
Note: These figures are estimates and do not reflect specific scenarios. Actual increases may vary based on location-specific factors and the severity of future wildfires.
Alternative Solutions and Mitigation Strategies
California’s escalating wildfire risk necessitates a proactive and multifaceted approach to prevent future insurance bailouts. This involves a shift from reactive firefighting to preventative measures, focusing on reducing the wildfire threat at its source. Comprehensive strategies encompassing building codes, community preparedness, and innovative technologies are crucial. A commitment to fire-resistant construction and proactive land management will be instrumental in safeguarding communities and ensuring the long-term financial stability of the insurance market.
Wildfire Prevention Strategies
Addressing the root causes of wildfires is paramount. Strategies to prevent future blazes should prioritize proactive land management. This includes controlled burns, forest thinning, and the responsible use of prescribed fire. Early detection and rapid response systems are also vital to mitigating the impacts of wildfires.
- Controlled Burns: Controlled burns, when conducted properly under expert supervision, can reduce the accumulation of dry brush and undergrowth, thereby decreasing the intensity and spread of wildfires. Examples in similar ecosystems demonstrate how controlled burns can significantly reduce the risk of catastrophic fires.
- Forest Thinning: Selective removal of trees, under the guidance of forestry experts, can reduce the overall fuel load in forests, limiting the potential for intense fire behavior. This approach, coupled with careful monitoring, can prevent widespread damage and promote healthier forest ecosystems.
- Prescribed Fire Practices: The responsible application of prescribed burns is essential for maintaining a healthy forest ecosystem. Careful planning, adherence to safety protocols, and collaboration with local authorities are critical elements in successful prescribed fire programs.
- Early Detection and Rapid Response Systems: Improved early warning systems, coupled with rapid response teams, are crucial for mitigating the impact of wildfires. Utilizing advanced technologies such as drone surveillance and real-time data analysis can enhance detection and response capabilities. This approach can minimize property damage and save lives.
Building Codes and Wildfire Mitigation
Implementing stricter building codes that incorporate fire resistance is essential. This includes incentivizing the use of fire-resistant materials in construction and encouraging fire-safe landscaping practices. Regulations focused on defensible space around homes can dramatically reduce the risk of fire spreading to structures.
- Enhanced Building Codes: Enacting stricter building codes that mandate fire-resistant materials and construction techniques in high-risk areas is crucial. This will necessitate ongoing research and development of innovative fire-resistant building materials and strategies.
- Defensible Space Regulations: Implementing regulations that mandate defensible space around homes and structures will be instrumental in reducing the risk of wildfire damage. These regulations will need to specify clear guidelines on vegetation management and appropriate landscaping choices.
- Incentivizing Fire-Resistant Construction: Incentivizing fire-resistant construction through tax breaks, grants, or other financial incentives can encourage homeowners and developers to adopt safer building practices. These incentives should be targeted towards high-risk areas to maximize their impact.
Innovative Solutions
New technologies and approaches are crucial to improving wildfire prevention and response. This includes exploring the use of innovative technologies, such as fire-resistant coatings for vegetation, or aerial drones for enhanced surveillance.
- Fire-Resistant Coatings for Vegetation: Research and development of fire-resistant coatings for vegetation could potentially reduce the flammability of brush and undergrowth. This approach, coupled with other prevention strategies, could reduce the likelihood of wildfires spreading.
- Advanced Surveillance Systems: Implementing advanced surveillance systems, such as high-resolution cameras and drones, could improve early detection of wildfires. This approach could be particularly valuable in remote areas where traditional monitoring systems are less effective.
Mitigation Strategies Cost-Benefit Analysis
| Mitigation Strategy | Estimated Costs | Estimated Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Controlled Burns | Variable (depending on scale and complexity) | Reduced fuel load, decreased fire intensity, improved forest health |
| Forest Thinning | Variable (depending on scale and complexity) | Reduced fuel load, decreased fire intensity, improved forest health |
| Prescribed Fire Practices | Variable (depending on scale and complexity) | Reduced fuel load, decreased fire intensity, improved forest health |
| Improved Building Codes | Variable (depending on specific regulations) | Reduced property damage, increased fire safety |
| Defensible Space Regulations | Variable (depending on specific regulations) | Reduced property damage, increased fire safety |
Note: Costs and benefits are estimates and may vary depending on the specific implementation and local conditions.
Impact on the California Economy
A potential insurance bailout in California, triggered by escalating wildfire risks, carries significant economic implications. The financial burden, while aimed at stabilizing the insurance market, could ripple through various sectors, impacting job creation, investments, and the state’s overall fiscal health. Understanding these potential consequences is crucial for policymakers and stakeholders alike.
California’s facing another potential insurance bailout due to escalating wildfire risks. It’s a serious situation, but isn’t this just a symptom of deeper problems? Maybe we should look at how Republican tax policies, like those from the Trump administration, are impacting the financial burden on the poor, like in this insightful article about how opinion republicans want the poor to pay for trumps tax cuts.
Ultimately, these interconnected issues raise critical questions about how we manage disaster preparedness and long-term economic fairness, and how that ultimately impacts the insurance costs in California.
Broad Economic Implications, California at risk of new insurance bailout amid fire danger
The economic consequences of an insurance bailout extend far beyond the insurance industry. Direct financial support for insurers could stimulate short-term economic activity, as the bailout funds are likely to be invested and circulated throughout the economy. However, the long-term effects on job creation and investment are more complex and uncertain. While some new jobs might be created in the insurance sector and related industries, potential job losses in other sectors, such as tourism, could offset these gains.
Impact on Tourism and Related Industries
Wildfires and their aftermath often cause significant disruptions to tourism, a vital part of California’s economy. High insurance premiums, a consequence of increased wildfire risk, might deter tourists and reduce visitor spending. Businesses reliant on tourism, such as hotels, restaurants, and attractions, could experience substantial revenue declines. The bailout, while aimed at protecting the insurance market, may have unintended consequences for the state’s tourism sector.
Potential Impact on State’s Fiscal Health and Budget
The cost of an insurance bailout will undoubtedly strain the state’s budget. The financial commitment required for such an intervention could divert resources from other essential services, potentially impacting education, infrastructure, and public safety. The state may need to increase taxes, cut spending in other areas, or borrow money to cover the costs, which in turn could have further economic repercussions.
Comparison of Potential Economic Outcomes
The economic impacts of a bailout are likely to be different from those in a scenario without one. Without a bailout, the insurance market might collapse, leading to widespread economic disruptions. The insurance industry would be significantly affected, potentially resulting in the collapse of insurance companies, and causing the loss of jobs in that industry and related industries. The loss of confidence in the insurance market could also negatively impact other sectors, such as real estate, as it would make obtaining insurance more difficult and expensive.
Conversely, a bailout could mitigate the immediate economic fallout, but could lead to future instability and possibly larger costs in the long run. The potential for a future, more substantial bailout would also need to be considered.
Projected Economic Impact of a Bailout
The following table provides a projected overview of the economic impact of a bailout on various sectors. It’s important to note that these are estimates and the actual impact could vary.
| Sector | Potential Positive Impact | Potential Negative Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Insurance | Stabilization of the market, preservation of jobs | Increased state debt, potential for future instability |
| Tourism | Short-term stability in visitor spending | Deterrence of tourists due to high premiums, possible loss of revenue |
| Real Estate | Reduced impact of potential market collapse | Potential for long-term instability due to high premiums |
| State Budget | Avoidance of significant short-term economic disruption | Increased state debt, potential need for future bailouts |
International Comparisons of Wildfire Insurance
California’s wildfire crisis isn’t unique. Many regions globally face similar challenges, from the Mediterranean to Australia. Understanding how other countries manage wildfire insurance risk offers valuable insights for California’s evolving situation. Examining international approaches can illuminate potential solutions and strategies for mitigating future instability.Examining international strategies for wildfire insurance allows California to identify effective models and avoid repeating past mistakes.
Comparing risk management strategies and regulatory frameworks provides a broader perspective, enabling the state to adapt and improve its own wildfire insurance system. This comparison highlights successful mitigation techniques, effective risk transfer mechanisms, and the role of government regulation in creating a stable insurance market.
International Strategies for Managing Wildfire Insurance Risk
Comparing California’s experience with other regions facing similar wildfire risks reveals diverse approaches to managing insurance risk. Several international regions, including the Mediterranean, Australia, and parts of Canada, have faced escalating wildfire activity and its impact on insurance markets. Examining their strategies and regulatory frameworks provides valuable lessons.
- Australia’s experience with large-scale wildfires has led to the development of sophisticated risk assessment models, which incorporate factors such as vegetation density, proximity to urban areas, and historical fire patterns. These models are used to determine appropriate premiums and coverage limits for different properties.
- In the Mediterranean, where drought and high temperatures frequently contribute to severe wildfires, insurance policies often include provisions for catastrophic events. These provisions can trigger increased coverage or government assistance in the case of extensive damage.
- Some regions use a combination of government subsidies, risk-sharing mechanisms, and public awareness campaigns to encourage residents to implement preventative measures, reducing the overall risk of wildfire damage.
Lessons Learned from Similar Situations
Examining historical wildfire events in other regions highlights common threads. Understanding the interplay between environmental factors, land-use policies, and insurance market dynamics is crucial.
- The importance of early warning systems and evacuation procedures cannot be overstated. Early warning systems and evacuation procedures play a critical role in mitigating losses during wildfires. These systems are vital for minimizing property damage and human casualties.
- Effective land-use planning, including firebreaks and controlled burns, is critical for preventing the spread of wildfires and mitigating damage. Strategies like controlled burns can reduce the risk of intense, uncontrolled wildfires.
- Government regulation and financial incentives are often employed to encourage the adoption of fire-resistant building materials and practices. These incentives can be implemented to support the adoption of fire-resistant materials and construction practices.
Regulatory Frameworks for Wildfire Insurance
Different countries and regions have different regulatory frameworks to manage wildfire insurance. Understanding these differences is essential to developing suitable policies for California.
- Australia has implemented strict building codes for wildfire-prone areas, requiring the use of fire-resistant materials and construction techniques. This approach emphasizes the need for proactive measures to reduce the risk of wildfires.
- The Mediterranean region often incorporates subsidies or incentives for residents to install fire-resistant roofing and other protective measures. This strategy promotes preventative actions by residents.
- Many regions implement mandatory insurance policies for properties in high-risk areas. Mandatory insurance policies in high-risk zones are frequently implemented.
Comparison of Wildfire Insurance Policies and Strategies
The table below illustrates a comparison of wildfire insurance policies and strategies across different countries. Note that this is a simplified comparison and specific policies and strategies can vary significantly within each region.
| Country/Region | Risk Assessment Models | Insurance Policy Provisions | Regulatory Frameworks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | Sophisticated, incorporating vegetation, proximity, and historical data | Catastrophic event provisions, increased coverage | Strict building codes, fire-resistant materials |
| Mediterranean | Based on drought, temperature, and historical fire data | Increased coverage during high-risk periods | Subsidies for fire-resistant measures |
| Canada | Varied, often region-specific | Government assistance programs | Regional variations in building codes |
Ending Remarks
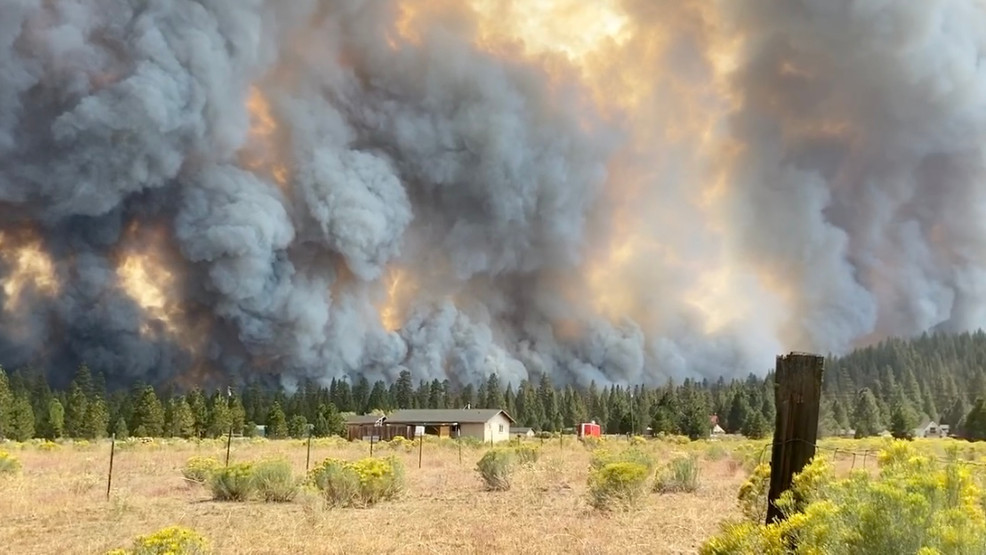

California’s wildfire crisis poses a significant threat to its insurance industry and the state’s economy. The potential for a new bailout, while perhaps a necessary short-term solution, carries long-term implications for insurance rates, affordability, and the overall fiscal health of the state. Examining alternative solutions, mitigation strategies, and international best practices is crucial for finding sustainable and long-term solutions.
Ultimately, this analysis highlights the urgent need for comprehensive wildfire prevention and preparedness efforts to mitigate future crises and protect California’s residents and businesses.