Burning Teslas Fried Batteries & Slow ROI
Burning teslas fried battery storage systems slow la return – Burning Teslas: fried battery storage systems slow la return. This article delves into the complexities of Tesla battery degradation, from the common causes of performance decline to the potential financial implications of costly repairs. We’ll explore the role of battery management systems (BMS), analyze the various failure modes of battery cells, and investigate the factors that contribute to slow charging rates.
Finally, we’ll examine Tesla’s response to these issues and assess the long-term return on investment (ROI) of owning a Tesla.
The article will detail the common causes of battery degradation in Tesla vehicles, including thermal management problems and cell-level issues. We’ll discuss the impact of charging cycles, temperature fluctuations, and manufacturing defects on battery performance. Furthermore, the article will explain how battery management system malfunctions can contribute to performance degradation and even catastrophic failure. We will present a table comparing different types of battery failures, highlighting their causes, symptoms, and impact.
Finally, a table will show the potential costs of battery degradation and repair over five years, along with a comparison of the ROI of Teslas versus other EVs.
Tesla Battery Degradation: Burning Teslas Fried Battery Storage Systems Slow La Return
Tesla’s battery technology, while revolutionary, is not immune to degradation over time. Understanding the factors contributing to this decline is crucial for maximizing battery lifespan and range. This knowledge empowers owners to make informed decisions about charging habits and maintenance, ultimately extending the life of their investment.Battery degradation in Tesla vehicles, like in other electric vehicles, stems from a complex interplay of factors.
These range from the inherent limitations of lithium-ion chemistry to environmental influences and even manufacturing inconsistencies. Careful attention to these factors can significantly impact the longevity and performance of the battery pack.
Common Causes of Battery Degradation
Battery degradation in Tesla vehicles isn’t a single issue but a confluence of factors impacting the battery’s overall health. Thermal management and cell-level degradation are prominent contributors. Inefficient or faulty thermal management systems can lead to localized overheating, which accelerates the degradation of individual cells within the battery pack. Also, inconsistencies in cell manufacturing or quality control can result in some cells degrading faster than others, leading to uneven performance and reduced overall capacity.
Factors Contributing to Performance Decline
Several factors contribute to the decline in battery performance over time. Charging cycles, temperature fluctuations, and manufacturing defects all play a role. The number of charge cycles the battery undergoes is a significant factor, with each cycle slightly diminishing the battery’s capacity. Temperature fluctuations also significantly affect the battery’s performance. Extreme temperatures, both high and low, can lead to accelerated degradation and reduced capacity.
Finally, manufacturing defects, while hopefully rare, can lead to inconsistencies in battery performance and lifespan. A faulty cell, for example, can lead to reduced overall capacity and performance.
Strategies to Mitigate Battery Degradation
Optimal charging practices and maintenance procedures can help mitigate the negative effects of battery degradation. Avoiding deep discharges and frequent extreme charging temperatures is essential. Consistent, moderate charging is generally best for battery health. Proper maintenance, including regular inspections and addressing any thermal management concerns, can also help prevent premature degradation.
Impact of Extreme Temperatures
Extreme temperatures, both high and low, have a significant impact on battery performance and lifespan. High temperatures accelerate the chemical reactions within the battery, leading to faster degradation. Conversely, extremely low temperatures can reduce the battery’s capacity and overall efficiency. For example, a battery operating in scorching desert heat will degrade faster than one consistently kept at moderate temperatures.
The recent news about burning Tesla batteries and slow returns on fried battery storage systems in LA is definitely concerning. It’s a big deal for electric vehicle owners, and the issues around these systems are complex. However, this problem is far from the only environmental concern, and the fight for preserving supreme Utah public land is a crucial aspect of the ongoing discussion about responsible environmental management.
supreme utah public land is facing intense pressure, and this highlights the broader need for careful consideration of energy storage solutions and their impact on the environment. Ultimately, we need better solutions to the problems with burning Teslas and fried battery storage systems.
Correlation Between Degradation and Reduced Range
As battery degradation occurs, the usable energy capacity of the battery diminishes, resulting in a reduction in the vehicle’s driving range. The relationship is direct: a lower usable capacity means a shorter driving range. For example, a battery losing 10% of its capacity might result in a noticeable reduction in the vehicle’s range on a typical driving cycle.
This correlation highlights the importance of understanding and managing battery degradation to maintain optimal performance.
The recent reports on Tesla battery fires and slow returns in the LA area are concerning. To really understand the bigger picture, it’s important to ask critical questions about the information being presented, like those you should be asking yourself about your own website’s performance. For example, are the sources credible? Are there other perspectives being overlooked?
These are the types of questions you should be asking yourself about any news story, especially when it comes to complex issues like the slow return on investments for fried battery storage systems in burning Teslas. This leads to the important questions to ask your homepage, to ensure your site is working as intended. Ultimately, a thorough investigation into these battery issues in LA is crucial to understand the long-term implications for consumers and the automotive industry.
questions to ask your homepage are key to determining credibility and accuracy in any news report.
Battery Management System (BMS) Issues
The Battery Management System (BMS) is the critical brain of an electric vehicle’s battery pack. It monitors and controls every aspect of the battery’s health, from charging and discharging rates to cell temperature and voltage. A malfunctioning BMS can lead to a cascade of problems, impacting battery performance and potentially the vehicle’s overall functionality. Understanding the role and potential pitfalls of BMS systems is crucial for evaluating the long-term reliability of electric vehicles.The BMS acts as a central nervous system for the battery pack, constantly monitoring and regulating the state of each individual cell.
This includes detecting anomalies like overheating, overcharging, or under-voltage conditions. The system’s primary function is to maintain optimal battery health and prevent damage. It ensures the battery operates within safe parameters, extending its lifespan and optimizing performance.
Function of the BMS
The BMS constantly monitors a battery pack’s voltage, current, temperature, and other parameters for each cell. It uses this data to regulate the charging and discharging processes, preventing overcharging or deep discharging that could damage the cells. Furthermore, it actively balances the charge between cells to maintain even performance and prevent the degradation of weaker cells. This crucial balancing action ensures the battery pack functions as a unified unit.
Potential BMS Malfunctions
Several factors can lead to BMS malfunctions. Software glitches, hardware failures, or even external damage to the BMS unit can compromise its ability to monitor and control the battery pack. Poor quality components within the BMS itself, such as faulty sensors or inaccurate data processing, can also lead to faulty readings and improper control actions.
Symptoms of BMS Issues
Symptoms of BMS issues can manifest in various ways, often starting subtly. Reduced range is a common indicator, as the BMS might restrict discharge to protect the battery. Charging problems, like inconsistent charging speeds or premature charging cut-offs, can also be signs of a malfunctioning BMS. An unusual display of error messages or warnings from the vehicle’s instrument panel should also prompt immediate investigation.
Different BMS Designs and Vulnerabilities
Different BMS designs utilize varying levels of redundancy and monitoring. Some systems employ multiple sensors to verify data, while others rely on a single point of failure. Complex designs, while potentially more robust, can also be more susceptible to intricate software glitches. A lack of thorough testing and validation during the BMS development process can also introduce vulnerabilities.
For example, a system relying on a single temperature sensor could misinterpret conditions if that sensor malfunctions.
Impact on Vehicle Operation, Burning teslas fried battery storage systems slow la return
BMS failures can impact the vehicle’s overall operation in significant ways. Reduced performance, as observed through decreased range, is a direct result. Safety features might be compromised, potentially leading to issues with vehicle stability control or regenerative braking. In extreme cases, a malfunctioning BMS could cause the vehicle’s battery to overheat or catch fire. These events emphasize the critical need for a robust and reliable BMS system.
Fried Battery Storage Systems
Electric vehicle (EV) battery packs, while offering significant advantages, are complex systems susceptible to various failure modes. “Fried” battery storage systems, a common concern, describe situations where the battery pack’s performance degrades drastically, often rendering the vehicle undrivable. This degradation can stem from a multitude of issues, including physical damage, chemical reactions, and component failures within the battery cells themselves.
Defining “Fried” Battery Systems
The term “fried” battery system, in the context of EVs, signifies a severe degradation of the battery pack’s functionality. This typically manifests as a significant loss of capacity, leading to reduced driving range and, in extreme cases, complete system failure. The term implies a catastrophic or substantial failure in the battery’s ability to deliver its intended performance, often requiring replacement.
The slow return on investment for burning Tesla’s fried battery storage systems in LA is a real head-scratcher. It’s a complex issue, and like many things these days, it might be a lot more complicated than just the technology itself. The issue reminds me a lot of the complexities in healthcare AI, which, as discussed in health care ai requires expensive humans , often requires significant human oversight and expertise to truly function effectively.
So, perhaps the slow return for those fried Tesla batteries isn’t just about the batteries themselves, but also the equally expensive human resources needed to sort out the mess.
Common Failure Modes of Battery Cells
Battery cells, the fundamental building blocks of an EV’s battery pack, can experience several failure modes. These include thermal runaway, where a cell’s temperature rapidly escalates, potentially causing a fire or damaging surrounding cells. Internal short circuits, where the cell’s internal resistance drops to dangerously low levels, can also occur. Cell swelling, often a precursor to more serious issues, arises due to internal gas pressure buildup.
Examples of Catastrophic Battery Pack Failure
Catastrophic battery pack failures can range from localized damage to widespread system failures. One example is a fire in a specific cell that propagates to adjacent cells, leading to a larger-scale thermal event. Another instance is a complete failure of the battery management system (BMS), causing uncontrollable charging or discharging, ultimately damaging the cells beyond repair. Furthermore, mechanical stress on the battery pack, such as a crash, can introduce internal short circuits and cause widespread failure.
Factors Contributing to Rapid Degradation
Several factors contribute to the rapid degradation and failure of battery systems. Overcharging or undercharging can strain the battery cells, accelerating their aging process. Extreme temperatures, whether excessively hot or cold, also negatively impact battery performance and lifespan. Inadequate cooling mechanisms or faulty thermal management systems can lead to localized overheating and accelerate cell degradation. Finally, manufacturing defects in individual cells or the pack assembly can introduce vulnerabilities that lead to premature failure.
Comparison of Battery Failure Types
| Failure Type | Cause | Symptoms | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Runaway | Overheating, internal short circuit, or manufacturing defect | Rapid temperature increase, potential fire, smoke, or structural damage. | Potential for catastrophic cell failure, damage to surrounding components, and significant safety hazards. |
| Internal Short Circuit | Damaged cell components, manufacturing defects, or mechanical stress | Reduced voltage output, rapid discharge, potential overheating. | Reduced driving range, possible battery pack failure, and potential for fire. |
| Cell Swelling | Internal pressure buildup, chemical reactions, or thermal stress | Visual bulging or swelling of the cell, possible deformation of the battery pack. | Potential for internal short circuits, mechanical damage, and overall pack failure. |
Return on Investment (ROI) Concerns
The allure of electric vehicles, particularly Teslas, often overshadows the potential long-term financial implications. While the initial purchase price might be competitive, the ongoing cost of ownership, especially concerning battery health, warrants careful consideration. Understanding the potential for battery degradation and repair costs is crucial for a comprehensive ROI analysis. This analysis will focus on the cost-benefit relationship of owning a Tesla over a five-year period, comparing it to other EV options.The electric vehicle market, while promising, presents a unique challenge regarding long-term ownership costs.
Unlike traditional combustion engine vehicles, the battery pack, a vital component, is subject to degradation over time. This degradation, often influenced by factors like charging habits, temperature fluctuations, and usage patterns, can impact the vehicle’s performance and potentially necessitate costly repairs or replacements. Proactive planning and understanding of these potential costs are paramount for making an informed decision.
Potential Battery Costs and Repairs Over Five Years
Analyzing the potential costs associated with battery degradation and repair over a five-year period allows for a more accurate assessment of the overall ROI. This data is not definitive and should be considered a possible scenario.
| Year | Estimated Battery Costs | Estimated Repairs |
|---|---|---|
| Year 1 | $0 | $0 |
| Year 2 | $0 | $0 |
| Year 3 | $0 – $1,000 | $0 – $500 |
| Year 4 | $1,000 – $2,000 | $500 – $1,500 |
| Year 5 | $2,000 – $4,000 | $1,500 – $3,000 |
These figures represent potential costs. Several factors influence these estimates, including driving habits, charging patterns, and environmental conditions. For example, a driver who frequently drives long distances at high speeds or in extreme temperatures might experience more rapid battery degradation compared to a driver who primarily uses shorter trips in moderate conditions.
Comparison with Other Electric Vehicle Options
The cost of battery replacement or repair varies significantly between different EV models. While Tesla is a leading brand, it’s not immune to the inherent risks associated with battery technology. Other EV manufacturers might offer different warranty structures or battery management systems that could lead to lower long-term costs. Comparing potential costs across different brands is essential for a complete evaluation.
Furthermore, considering factors like the resale value of each EV model is crucial for a comprehensive ROI analysis.
Slow Charging Rates
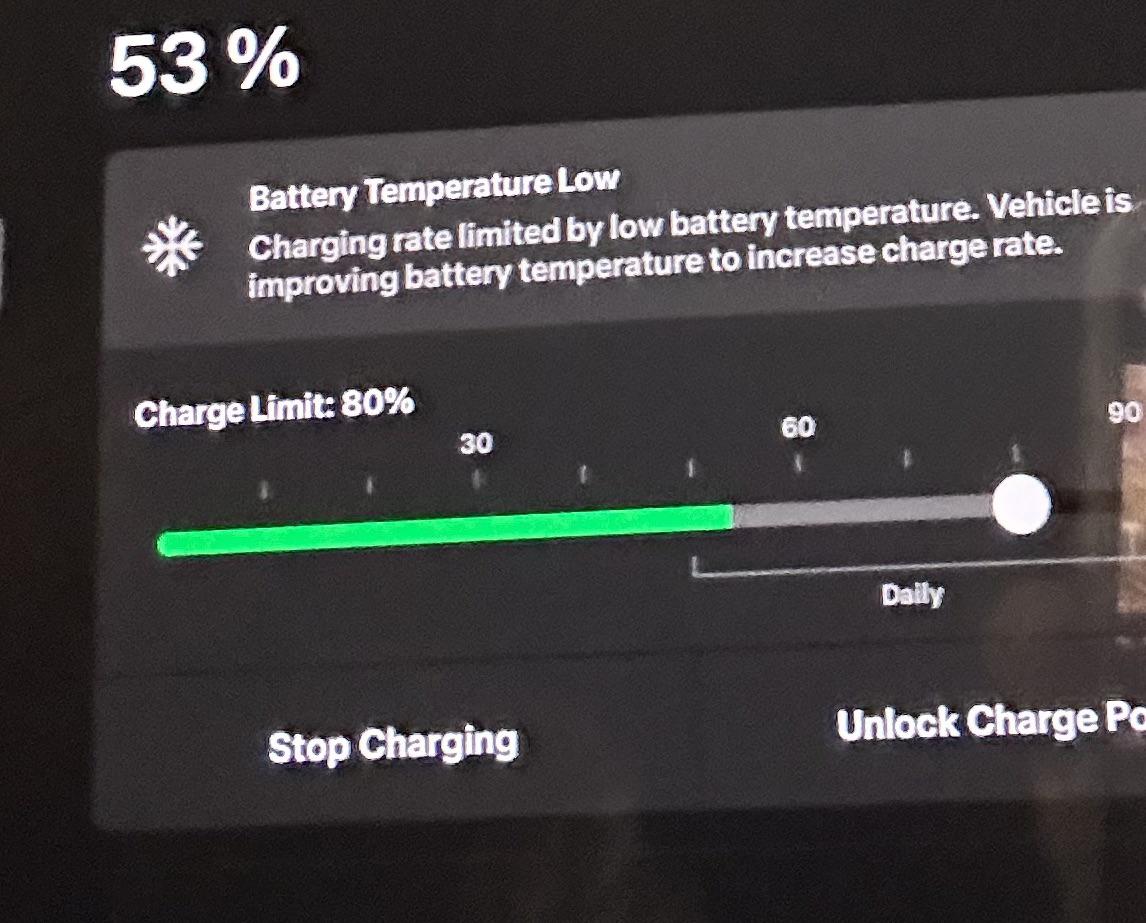
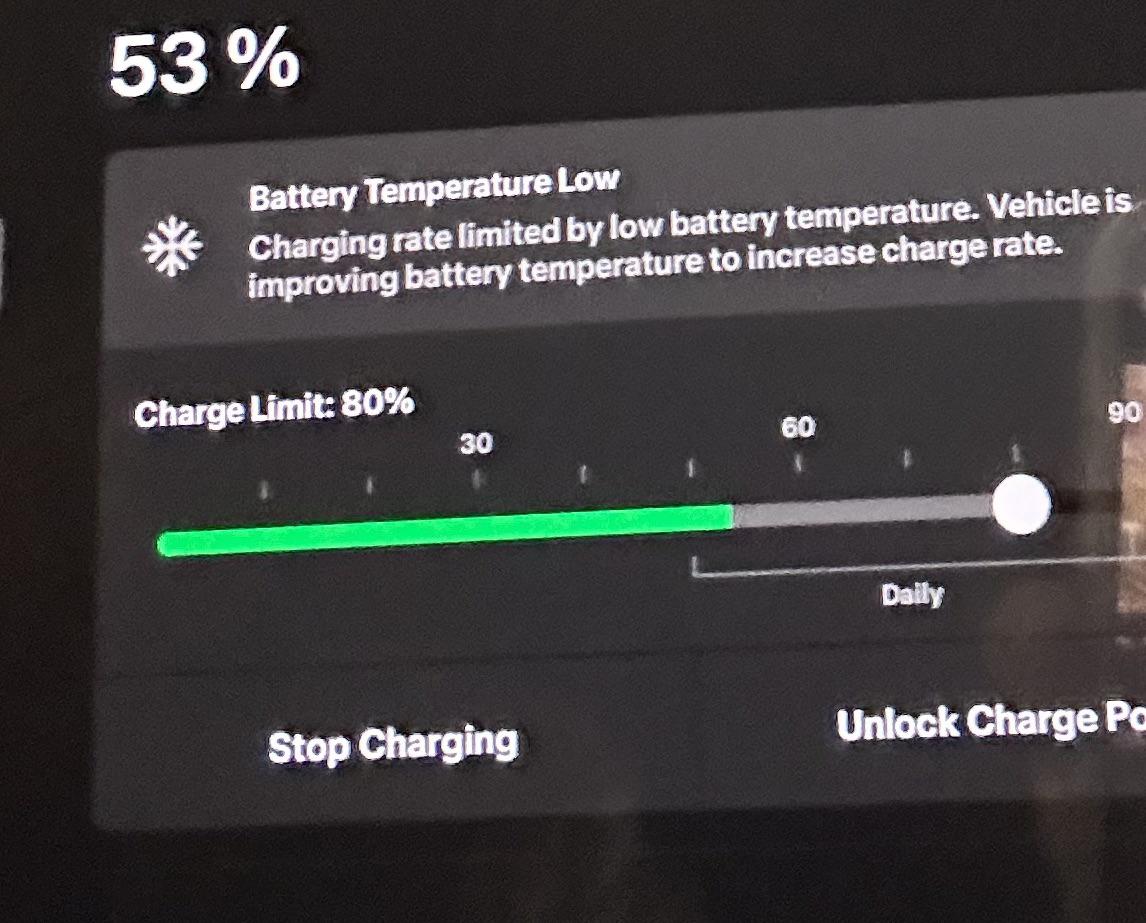
Tesla owners frequently encounter slow charging rates, impacting the overall experience and potentially affecting the return on investment. This issue stems from a combination of factors, including the limitations of the charging infrastructure and the vehicle’s battery management system. Understanding these causes is crucial for evaluating the practicality and efficiency of Tesla ownership.Slow charging rates, while sometimes frustrating, can be directly tied to the performance and financial viability of Tesla ownership.
The time spent charging directly translates to the time owners are unable to utilize their vehicles, impacting their overall usability. This impact extends beyond mere inconvenience and influences the return on investment (ROI) calculation. A thorough understanding of the causes, impacts, and potential solutions is key to maximizing the benefits of Tesla ownership.
Common Causes of Slow Charging Rates
Several factors contribute to slower-than-expected charging speeds for Tesla vehicles. These include the charging station’s power output, the vehicle’s battery temperature, and the compatibility of the charging connector with the charging station. The charging station’s infrastructure and available power capacity are significant determinants. A station with lower power output will naturally result in a slower charging rate.
Impact on Range and Usability
Slow charging rates directly affect the overall range and usability of a Tesla vehicle. Longer charging times mean less time for travel, potentially necessitating alternative transportation or planning around charging availability. The practical impact is significant, particularly during longer trips or when charging is necessary between destinations. Users need to plan charging stops accordingly, impacting the flexibility of their travel plans.
Impact on ROI Calculations
Charging times are a critical element in calculating the return on investment (ROI) for Tesla ownership. The time spent charging reduces the effective use of the vehicle, impacting its daily usability. This needs to be factored into the cost-benefit analysis of Tesla ownership, as longer charging times translate into decreased operational efficiency and increased charging costs, thus potentially affecting the ROI negatively.
An example would be comparing the time spent charging with a conventional vehicle with a similar range, highlighting the difference in usability.
Potential Solutions to Address Slow Charging Issues
Several solutions can mitigate slow charging rates, improving the overall experience. Using higher-powered charging stations is a primary solution. These stations deliver a greater charging rate, reducing the time required to reach full capacity. Optimizing charging times by scheduling charging sessions during off-peak hours can also contribute to faster charging.
Comparison of Charging Infrastructure Types
Different charging infrastructure types offer varying charging speeds. Supercharger stations are generally known for their high power output and fast charging capabilities. Level 2 charging stations, on the other hand, offer a slower charging rate but are more accessible. Public charging infrastructure availability also significantly impacts charging rates. The availability of various charging options directly influences the user experience and the return on investment.
A table comparing charging infrastructure types, power output, and typical charging times can provide a clearer overview.
| Charging Infrastructure Type | Typical Power Output (kW) | Typical Charging Time (estimated) | Accessibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supercharger | >150 kW | 30-60 minutes | Relatively widespread |
| Level 2 | 7-22 kW | 4-8 hours | Common at home and some public locations |
| Destination Chargers | 22-100 kW | 2-6 hours | Varying, often specific to locations |
Tesla’s Response to Battery Issues
Tesla’s battery technology, while revolutionary, has faced scrutiny regarding degradation, potential repairs, and customer experiences. This section delves into Tesla’s official stance, service procedures, customer feedback, warranty policies, and avenues for addressing battery concerns. Understanding these aspects is crucial for potential Tesla owners and current ones facing battery-related issues.Tesla’s official stance on battery degradation is largely centered around a product lifecycle perspective.
They acknowledge that battery performance naturally diminishes over time, often attributed to factors like temperature fluctuations, charging cycles, and usage patterns. However, Tesla aims to manage this degradation through various strategies, including advanced battery management systems (BMS) and proactive maintenance.
Tesla’s Official Stance on Battery Degradation and Repairs
Tesla acknowledges battery degradation as a natural consequence of extended use. Their official position highlights the factors contributing to this decline, such as temperature variations, charging patterns, and usage frequency. Tesla emphasizes that its BMS plays a crucial role in mitigating performance loss and maximizing battery lifespan. They maintain that the degradation process is part of the overall product lifecycle and is not necessarily indicative of a defect.
Tesla’s Service Procedures for Battery Replacement or Repair
Tesla’s service procedures for battery issues vary based on the nature of the problem and the vehicle’s age. For minor performance concerns, Tesla often employs software updates or BMS adjustments to optimize battery management. In cases requiring a replacement, Tesla typically follows a structured process involving diagnostics, evaluation of the battery’s condition, and a replacement procedure. The specific process can be found on Tesla’s official website or by contacting a service center directly.
Customer Reviews and Experiences Regarding Tesla’s Response
Customer experiences with Tesla’s battery response vary. Some report positive experiences with prompt and effective repairs or replacements under warranty. Others cite instances of prolonged wait times, difficulty in navigating the service process, or dissatisfaction with the solutions offered. Customer reviews on various online forums provide a diverse range of opinions, showcasing the complexity of individual experiences.
It’s essential to note that experiences can vary widely, highlighting the importance of individual cases.
Warranty Policies Surrounding Battery Performance and Replacement
Tesla’s warranty policies for battery performance and replacement vary based on the specific model, purchase date, and usage history. Warranty details are usually clearly Artikeld in the vehicle purchase agreement and online resources. The warranty typically covers specific performance criteria, such as charging capacity, range, and cycle life, for a defined period. It’s crucial for owners to thoroughly understand the warranty terms and conditions.
Procedures for Addressing Concerns and Seeking Service Regarding Battery Problems
Tesla provides several channels for addressing battery-related concerns and seeking service. Owners can contact Tesla customer support through various channels, including phone, email, or online portals. Tesla service centers offer in-person diagnostics and repair options. Documentation, such as maintenance records and charging history, is often requested to facilitate a thorough assessment. Proactive communication and thorough record-keeping are crucial to navigating the service process effectively.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, burning Teslas: fried battery storage systems slow la return presents a complex picture of potential issues with Tesla vehicles. From battery degradation and BMS malfunctions to slow charging and costly repairs, the article highlights the factors that can impact the long-term value and usability of Tesla vehicles. Understanding these issues is crucial for potential buyers and existing owners alike, allowing them to make informed decisions about their investment and future maintenance plans.