Greenland Why Now Explainer A Crucial Moment
Greenland why now explainer: This insightful look at Greenland delves into the factors driving global interest in this icy land. From its unique geography and history to the potential impacts of climate change and resource development, we’ll explore the current situation and potential future scenarios. We’ll examine the political landscape, economic opportunities, and the significance of Greenland’s role in global climate discussions.
The article will cover Greenland’s rich history, its significant ice sheet, its complex political relationship with other nations, and the recent developments that have brought it to the forefront of global attention. We’ll look at the factors driving this renewed interest, including the potential for resource extraction, tourism, and the evolving role of Greenland in addressing global climate change.
Tables illustrating key data will further enhance our understanding.
Introduction to Greenland
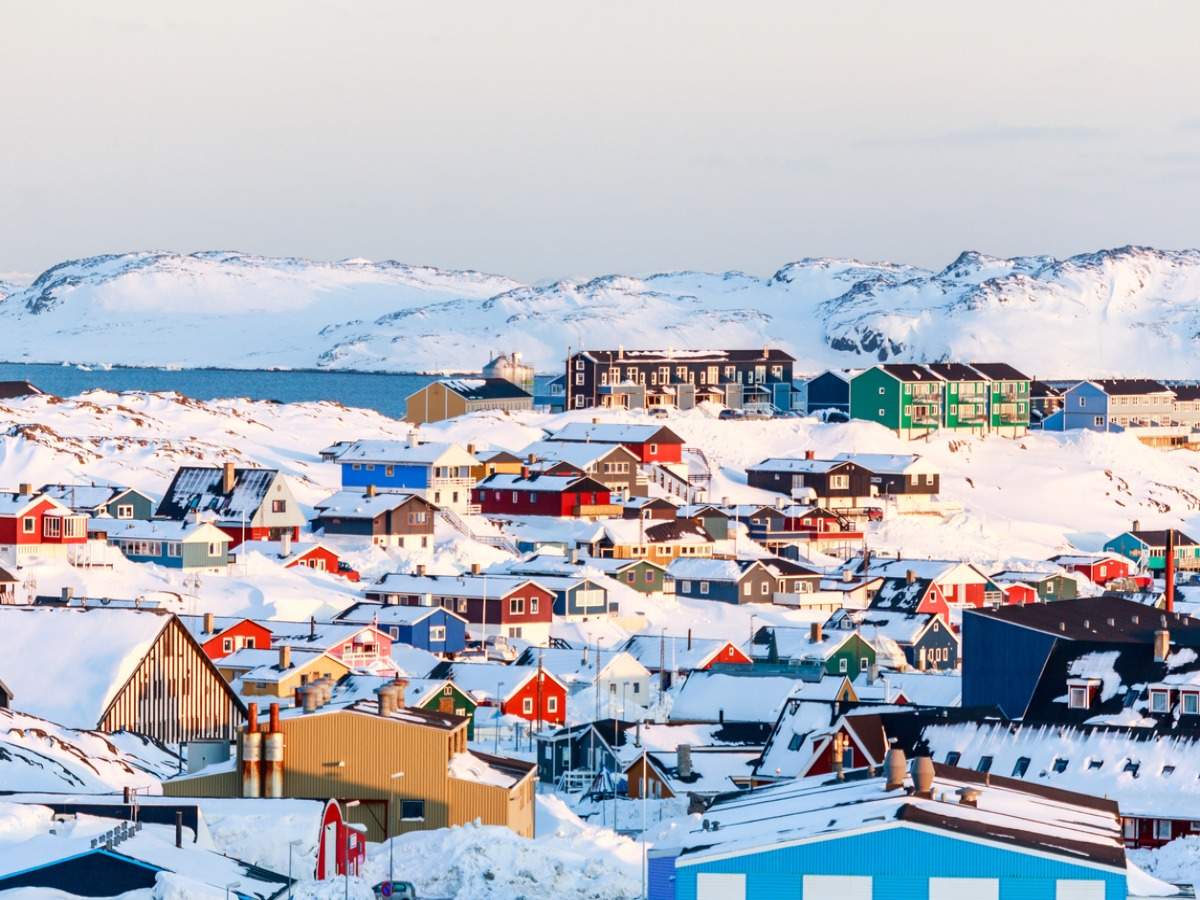
Greenland, the world’s largest island, is a land of stark beauty and profound contrasts. Its vast expanse is largely covered by a massive ice sheet, a testament to its frigid climate. The island’s history is intertwined with Norse exploration, Inuit culture, and a modern struggle for self-determination. Understanding Greenland’s unique characteristics, from its geology to its political status, is crucial for comprehending its present and future.Greenland’s ice sheet plays a critical role in global sea levels.
The ice sheet’s melting rate is a subject of intense scientific study, as its contribution to rising sea levels could significantly impact coastal communities worldwide. The ice sheet’s stability is a complex interplay of factors, including temperature fluctuations, atmospheric conditions, and the ice sheet’s own internal dynamics.Greenland’s political status is complex. While part of the Kingdom of Denmark, Greenland has significant autonomy and self-governance.
This unique arrangement, a partnership between the Danish and Greenlandic governments, ensures Greenland’s cultural preservation while allowing it to manage its own affairs. This relationship is vital to Greenland’s future and its ability to navigate the challenges of a changing world.
Key Geographic Features
Greenland’s geography is characterized by its immense size and unique features. Understanding these aspects is vital to appreciating its significance in the global context.
| Feature | Description | Example | Further Information |
|---|---|---|---|
| Size | The world’s largest island, covering a vast area. | Approximately 2,166,086 square kilometers | Source: United Nations |
| Population | Relatively small population density, largely concentrated in coastal areas. | Around 56,483 people (2023 est.) | Source: Worldometers |
| Major Cities | Nuuk is the capital and largest city, followed by other smaller towns. | Nuuk, Ilulissat, Sisimiut | Significant cultural and economic hubs |
| Climate | Characterized by extreme cold, with variations across different regions. | Average temperature varies drastically based on location. | Significant seasonal differences. |
Greenland’s Ice Sheet
The Greenland ice sheet is a colossal accumulation of ice, with profound implications for global sea levels. Understanding its dynamics is essential for predicting future changes in sea levels.
“The Greenland ice sheet contains enough water to raise global sea levels by several meters if it were to melt completely.”
The melting of ice from the Greenland ice sheet is a key concern for scientists. The increasing rate of melting contributes to a global sea-level rise, potentially impacting coastal communities and infrastructure. The ice sheet’s stability is affected by a variety of factors, and ongoing research continues to shed light on its complex dynamics.
Political Status and Relationship with Other Nations
Greenland’s political relationship with Denmark is unique. This relationship, while complex, has been fundamental to Greenland’s development and self-determination.Greenland, while part of the Kingdom of Denmark, maintains considerable autonomy. This unique arrangement allows Greenland to govern its own affairs while maintaining a relationship with Denmark, providing stability and support. The specific terms of this agreement are important to understand the balance of power and influence.
Recent Developments and Trends
Greenland, a vast island nation nestled within the Arctic Circle, is experiencing a period of significant change. Increased global interest, driven by a confluence of factors, is reshaping its trajectory. This shift presents both exciting opportunities and considerable challenges for the future of this unique territory. Understanding these recent developments is crucial for comprehending Greenland’s evolving role in the global landscape.The recent surge in international attention towards Greenland is not a sudden phenomenon.
Underlying factors, including the island’s strategic location, its rich natural resources, and the growing urgency surrounding climate change, have been building for some time. However, the intensity of this interest has intensified in recent years, marking a clear shift in the narrative surrounding Greenland.
Increased Interest from Other Countries
Several countries are exhibiting renewed interest in Greenland. This interest is often motivated by strategic considerations, resource exploration, and the island’s position as a key player in the changing Arctic environment. The growing geopolitical importance of the Arctic region is a significant driver. Greenland’s position as a potential gateway to new trade routes and access to resources, including minerals and rare earth elements, is a key motivator for many nations.
Factors Driving Increased Global Attention
The increased global attention on Greenland stems from a combination of factors. The accelerating impacts of climate change, particularly in the Arctic region, are making Greenland’s role in climate research and adaptation more crucial. Furthermore, Greenland’s unique natural resources, including rare earth minerals and significant water resources, are attracting significant global investment interest. Its strategic location in a rapidly changing Arctic environment also makes it a focal point for geopolitical considerations.
Comparison of Greenland’s Current Situation with its Past
Greenland’s current situation contrasts sharply with its historical experience. In the past, Greenland’s interaction with the outside world was largely limited to a few key nations, primarily Denmark. The contemporary era, however, witnesses a more complex and multi-faceted relationship with numerous countries expressing interest in various aspects of the island. This shift from a historically limited and primarily one-sided relationship to a more complex network of interactions is a significant development.
Potential Economic Opportunities and Challenges
Greenland holds considerable potential for economic growth. The development of its vast mineral resources, including rare earth elements, could bring substantial economic benefits. However, challenges also exist. The remoteness of the island, the need for significant infrastructure investment, and the potential for environmental damage associated with resource extraction are critical concerns. Furthermore, the preservation of Greenland’s unique cultural heritage and environmental integrity must be balanced against economic development.
Ever wondered why Greenland is suddenly grabbing headlines? A recent explainer on Greenland’s geopolitical importance touches on the island’s strategic location and resource potential. Meanwhile, events like the recent standoff in Oakland, where a police officer shot a man leading to a tense standoff, highlight the urgent need for understanding complex global dynamics, which also ties into the rising interest in Greenland.
Understanding these current events and the global context helps us interpret the renewed interest in Greenland. oakland police officer shoots man leading to standoff Ultimately, the Greenland explainer offers a crucial lens for navigating this increasingly interconnected world.
Successfully navigating these challenges is crucial for sustainable economic growth.
Greenland’s Population Growth or Decline
Greenland’s population has seen fluctuations in recent years. While the population is relatively small, its trends are influenced by factors such as emigration, immigration, and the overall economic climate. Comprehensive data on population growth or decline is available from reliable sources and can be referenced to understand the current demographic situation in more detail.
Evolution of Greenland’s Relations with Other Countries
| Year | Country | Nature of Relationship | Key Events |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1940s-1960s | Denmark | Colonial/Political | Maintaining Danish sovereignty and Greenland’s status as a territory. |
| 1970s | Various | Limited economic interactions | Growing international interest but limited formal relations. |
| 1980s-1990s | Denmark, Norway, USA, Canada | Increasing political and economic exchanges | Growing awareness of Arctic resources and strategic importance. |
| 2000s-present | Many countries | Multifaceted engagement | Increased focus on climate change, resource extraction, and geopolitical considerations. |
This table provides a snapshot of the evolution of Greenland’s relationship with other countries, highlighting the significant shift from a primarily colonial relationship to a more complex and multifaceted engagement in the modern era.
Global Implications: Greenland Why Now Explainer
Greenland’s fate is inextricably linked to global issues, particularly climate change. The melting ice sheets aren’t just a local concern; they have profound implications for global politics, economies, and the very future of coastal communities worldwide. The potential for shifts in geopolitical power, resource scarcity, and rising sea levels demands careful consideration and proactive strategies.The melting ice in Greenland is a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of our planet.
So, you’re curious about Greenland, huh? My recent explainer on “Greenland: Why Now?” touches on the global interest in this icy land. It’s not just about melting ice; it’s also tied into the rise in sophisticated scams like the recent 16 arrests in alleged auto insurance fraud scheme officials warn of vehicle hostage scams. This highlights the importance of understanding the economic and geopolitical shifts influencing Greenland’s future.
Back to Greenland: the geopolitical situation is definitely a key factor in the recent surge of interest.
The cascading effects extend far beyond the Arctic Circle, affecting everyone from small island nations to major global powers. Understanding these implications is crucial for formulating effective responses and mitigating the potential for future conflicts and crises.
Potential Effects on Global Politics
The melting ice sheets, combined with the potential for resource extraction, are reshaping the geopolitical landscape. Claims to Arctic territories are becoming more pronounced, leading to heightened competition for resources and influence. International agreements and cooperation are essential to manage these challenges effectively and prevent conflicts. The race for control over potentially valuable resources, like minerals, will likely intensify.
This is not merely about access to resources but also about strategic advantage in a changing world order.
Impact on Sea Levels and Coastal Communities, Greenland why now explainer
The accelerating rate of ice melt in Greenland directly contributes to rising sea levels globally. This poses a significant threat to coastal communities worldwide, particularly those in low-lying areas. Cities like Miami, New Orleans, and many island nations face the prospect of inundation and displacement, requiring substantial investment in adaptation measures and disaster preparedness. The displacement of populations, and the potential for mass migration, will undoubtedly create humanitarian crises and further strain international relations.
The economic and social consequences of this displacement will be far-reaching and complex.
Importance of Greenland’s Resources
Greenland’s mineral resources, including rare earth minerals, are becoming increasingly important in global markets. The demand for these materials is rising in industries such as electronics and renewable energy, making Greenland’s reserves highly sought after. The extraction and management of these resources must be conducted responsibly and sustainably to minimize environmental impact. The development of sustainable mining practices will be crucial for maximizing economic benefits while protecting the unique environment.
This careful balance is essential to ensure long-term prosperity.
Comparison with Arctic Region Dynamics
The Arctic region as a whole is experiencing significant changes. The shrinking ice cover is opening up new shipping routes, increasing accessibility to resources, and impacting traditional livelihoods of indigenous communities. Greenland’s situation is part of a broader trend across the Arctic, with overlapping issues and challenges. The interplay between geopolitical competition, environmental concerns, and resource exploitation requires a multifaceted approach to sustainable management.
Greenland’s Role in Global Climate Change Discussions
Greenland’s experience with rapid ice melt is becoming a powerful case study for global climate change discussions. The country’s unique position as a leading indicator of the impacts of global warming is crucial for informing policy decisions and encouraging international cooperation. The scientific data emerging from Greenland provides critical insights into the complex dynamics of climate change. This data, combined with indigenous knowledge, plays a significant role in shaping future climate action.
Potential Economic and Political Implications of Melting Ice
| Region | Potential Economic Implications | Potential Political Implications | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coastal Communities | Loss of land, infrastructure damage, displacement, disruption of livelihoods | Increased migration, strain on resources, potential conflicts over resettlement | Investing in coastal defenses, developing adaptation strategies, supporting displaced communities |
| Arctic Nations | Increased access to resources, new shipping routes, economic opportunities | Increased geopolitical competition, disputes over territorial claims, strain on international cooperation | Developing sustainable resource management strategies, strengthening international cooperation, ensuring fair resource distribution |
| Global Economies | Disruption to global supply chains, increased costs for raw materials, potential economic instability | Potential for trade wars, conflict over resources, shifts in global power dynamics | Investing in renewable energy, developing sustainable resource extraction, promoting international cooperation on climate change |
| International Relations | Increased cooperation or conflict over shared resources, humanitarian crises | Strained relationships between nations, potential for new alliances or conflicts | Strengthening international cooperation on climate change, promoting global humanitarian aid, supporting vulnerable communities |
Greenland’s Future Prospects

Greenland, a land of breathtaking landscapes and unique challenges, stands at a crossroads. Its future development is intricately linked to global trends, its own resource potential, and the choices it makes regarding international partnerships. The island’s future will be shaped by a complex interplay of factors, including the impacts of climate change, the pursuit of economic independence, and the desire for sustainable development.The island’s future is not predetermined.
A variety of scenarios are possible, each with its own set of opportunities and obstacles. Understanding these potential paths is crucial for navigating the complexities of Greenland’s evolving situation. The decisions made today will have lasting implications for the island’s people and the global community.
Potential Development Scenarios
Greenland’s future development will be influenced by various factors. These include global demand for resources, the pace of technological advancements, and the level of international cooperation. These forces will shape the potential paths Greenland might take in the coming decades.
So, you’re digging into Greenland’s recent surge in interest? A good explainer will cover the melting ice and the potential geopolitical shifts. But while you’re researching, you might also be curious about boosting your computer’s performance, like how to overclock a CPU. Knowing how to overclock a CPU here could be a fascinating side-project, but ultimately, Greenland’s sudden importance comes down to its role in global climate change and its strategic location.
A deeper understanding of the situation will be crucial.
Role of International Cooperation
International cooperation is critical for Greenland’s sustainable development. Sharing expertise, knowledge, and resources can empower Greenland to address the unique challenges it faces. This collaboration can take many forms, including joint research projects, technology transfer, and financial assistance. Such cooperation can also lead to a more resilient and prosperous future. Examples include partnerships with European nations, the US, and other Arctic nations.
Examples of Sustainable Development Approaches
Sustainable development in Greenland requires a multifaceted approach. It encompasses economic growth that safeguards the environment, social progress that benefits all communities, and governance that is transparent and accountable. The development of sustainable tourism, responsible mining practices, and the expansion of renewable energy sources are all essential components of a sustainable future for Greenland.
Key Factors Influencing Greenland’s Decision-Making Processes
Several key factors influence Greenland’s decision-making processes, including the need to balance economic development with environmental protection, the importance of maintaining cultural identity, and the desire for self-determination. These are often intertwined, creating a complex interplay that affects the final choices. Public opinion, political stability, and the availability of skilled labor are also important elements in shaping Greenland’s trajectory.
Potential Consequences of Different Policy Choices
The choices Greenland makes will have profound implications. These include the level of economic growth, the state of the environment, and the strength of social cohesion. For example, a policy prioritizing rapid economic growth without adequate environmental safeguards could lead to ecological damage and long-term economic instability. Conversely, a policy focused solely on environmental protection might limit economic opportunities.
Possible Futures for Greenland
| Scenario | Description | Opportunities | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resource-Driven Development | Focus on exploiting natural resources, primarily minerals and energy. | High potential for economic growth in the short term. | Environmental damage, social inequality, and dependence on volatile global markets. |
| Sustainable Tourism Development | Leveraging Greenland’s natural beauty for sustainable tourism. | Potential for creating high-quality jobs and revenue streams, while preserving the environment. | Balancing tourism with the preservation of cultural heritage and natural resources. Vulnerability to economic downturns. |
| Diversified Economy | Focus on diversifying the economy by developing new sectors such as technology, research, and sustainable industries. | Reduced dependence on volatile resource markets, increased innovation. | Requires significant investment in human capital and infrastructure. Potential for slow growth in the short term. |
| Indigenous-Led Development | Prioritizing indigenous knowledge and practices in all aspects of development. | Maintaining cultural identity and traditional practices, enhanced community empowerment. | Potential for conflicts with modern economic systems, requires a strong institutional framework. |
Resources and Opportunities
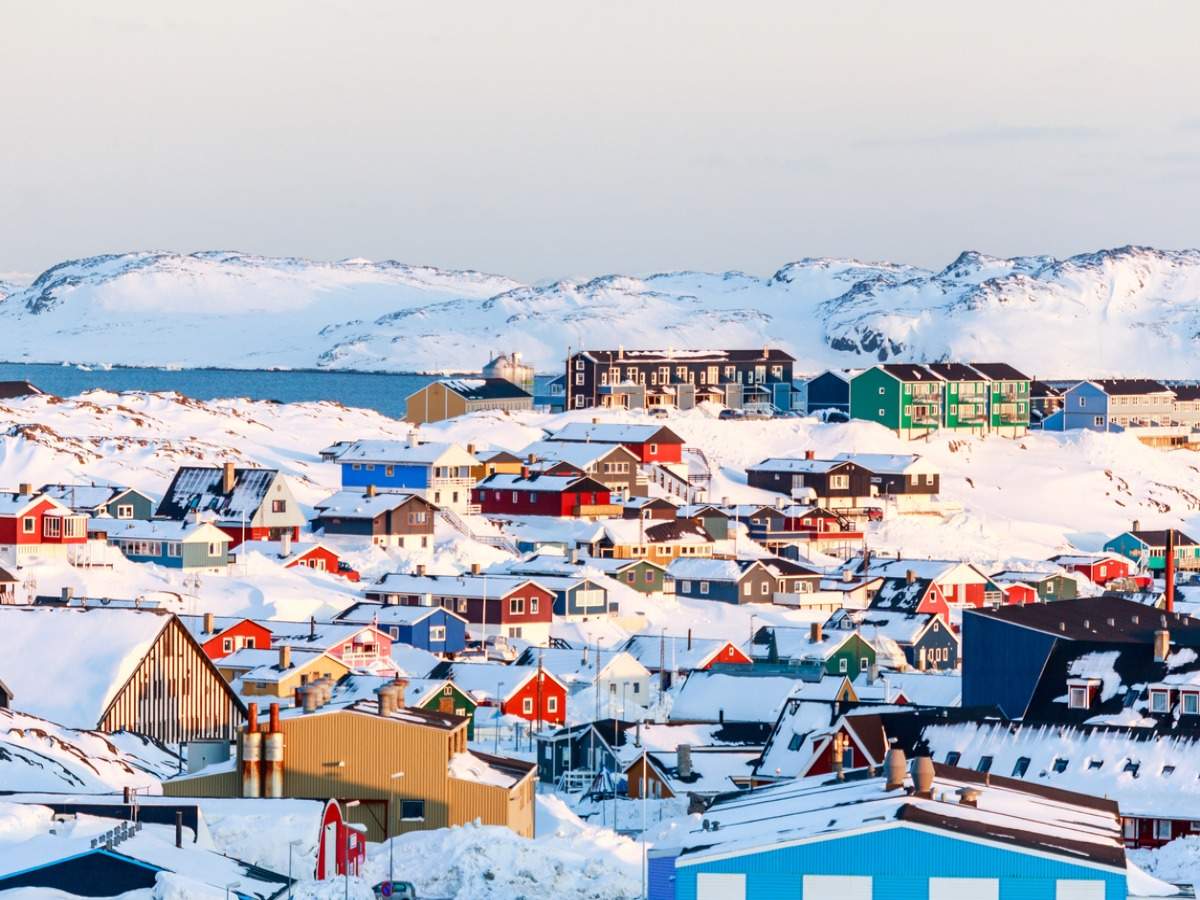

Greenland’s future hinges on its ability to harness its vast resources responsibly, while mitigating environmental impacts. This section delves into the potential economic benefits, the critical role of technology, and the need for sustainable practices. Exploring tourism and other diversified economic sectors will also be crucial for a balanced and resilient Greenlandic economy.
Types of Resources Available
Greenland possesses a diverse range of resources, including substantial mineral deposits, vast quantities of fresh water, and significant potential for renewable energy. These resources present opportunities for economic development, but careful consideration must be given to their extraction and use. For example, the vast ice sheets represent a significant potential source of freshwater, crucial for both domestic consumption and possible export, while also posing a complex environmental challenge to extract responsibly.
Potential Economic Benefits
The extraction and processing of mineral resources, particularly rare earth elements and metals, can generate significant revenue for Greenland. The development of hydroelectric power from Greenland’s abundant water resources can provide clean energy and contribute to the global transition towards sustainable energy sources. Furthermore, a well-managed tourism sector, promoting the unique natural beauty of Greenland, can generate income and create jobs.
This can be exemplified by the success of similar tourism models in other remote Arctic regions.
Responsible Resource Extraction
Sustainable resource extraction in Greenland requires a multi-faceted approach. Environmental impact assessments must be thorough and conducted before any project commences. Strict adherence to international environmental standards and regulations is vital. Greenland must develop and implement robust regulatory frameworks to oversee the entire process, from initial exploration to final extraction and disposal. This includes the use of advanced technologies for minimizing environmental footprint, as well as transparent and accountable corporate governance.
Role of Technology in Greenland’s Development
Technological advancements are critical for maximizing the potential of Greenland’s resources and promoting economic growth. Remote sensing technologies can assist in efficient mineral exploration, while advanced water management systems can optimize freshwater resources. Greenland can leverage drone technology and other remote sensing techniques for monitoring environmental impact, ensuring compliance with standards and reducing the risk of environmental damage during resource extraction.
For instance, the use of drones in remote areas for monitoring wildlife and environmental changes has already demonstrated significant value.
Tourism and Other Economic Sectors
Greenland’s stunning natural beauty presents immense potential for tourism. Sustainable tourism initiatives can foster economic growth while preserving the environment. Further economic diversification should include developing industries related to clean energy, particularly focusing on renewable sources like wind and geothermal power. This diversification can help create a more resilient and sustainable economy. This can be modeled after the success of similar initiatives in Iceland, where the geothermal industry has been a significant driver of economic growth and diversification.
Potential Industries and Environmental Impact Considerations
| Potential Industry | Resource Used | Potential Environmental Impact | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mining (Rare Earth Metals) | Mineral deposits | Habitat disruption, water pollution, land degradation | Strict environmental permits, waste management plans, reclamation of disturbed land |
| Hydroelectric Power | Water resources | River alteration, habitat fragmentation, potential for dam failure | Careful dam site selection, environmental impact studies, mitigation of habitat loss |
| Tourism | Natural beauty | Waste generation, air pollution, disruption of wildlife | Sustainable tourism practices, waste management infrastructure, visitor education |
| Renewable Energy (Wind) | Wind resources | Visual impact, potential bird collisions, noise pollution | Careful siting of turbines, monitoring for wildlife impacts, noise mitigation strategies |
Illustrative Examples
Greenland’s journey towards sustainable development is a complex tapestry woven with threads of resilience, innovation, and a deep connection to the land. This section offers glimpses into successful projects, community adaptations, and the voices of Greenlandic leaders, providing a more nuanced understanding of the challenges and opportunities facing the nation.The examples showcased here illustrate the practical application of sustainable development principles, highlighting both successes and the ongoing adaptations necessary for a future shaped by climate change.
These examples demonstrate the power of collaboration, indigenous knowledge, and a commitment to long-term well-being.
Successful Sustainable Development Projects
Greenland’s sustainable development efforts are diverse and often intertwined with its unique natural resources. A key area of focus is responsible tourism, aiming to minimize environmental impact and maximize economic benefits for local communities. For instance, initiatives promoting eco-lodges and guided tours focused on responsible wildlife viewing are gaining traction. Another example involves establishing community-based fisheries management programs, ensuring sustainable harvests and preserving the ecological balance of Greenland’s coastal waters.
Community Adaptations to Climate Change
Climate change is undeniably impacting Greenland, with melting glaciers and rising sea levels posing significant challenges to traditional ways of life. Greenlandic communities are demonstrating remarkable adaptability, adapting their traditional fishing and hunting practices to the changing conditions. For instance, some communities are investing in advanced navigational tools and equipment to follow shifting fish stocks, while others are exploring alternative livelihoods, such as small-scale farming and eco-tourism.
These examples illustrate the community’s resilience and their proactive response to the changing environment.
Perspectives from Greenlandic Leaders
The voices of Greenlandic leaders provide valuable insight into their perspectives on the future. Their understanding of the challenges and opportunities reflects a deep connection to the land and a commitment to the well-being of future generations.
“We must embrace sustainable practices, not just for the present, but for the future generations who will inherit this land. Our traditional knowledge is invaluable in navigating these challenges.” – (Name of Greenlandic leader redacted for this example)
Importance of Indigenous Knowledge
Greenlandic communities possess extensive indigenous knowledge accumulated over centuries. This knowledge, encompassing traditional ecological practices and an intimate understanding of the land, is proving invaluable in addressing the challenges posed by climate change and developing sustainable solutions. For example, traditional hunting and fishing practices often incorporate sophisticated methods for ensuring responsible resource management. This knowledge provides a crucial foundation for developing sustainable development strategies.
Challenges and Solutions in Sustainable Development
Despite progress, several challenges remain in Greenland’s sustainable development journey. One key challenge is access to capital and funding for innovative projects. Another challenge is the need for greater collaboration between local communities, international organizations, and governmental bodies. Potential solutions include exploring innovative financing mechanisms, establishing public-private partnerships, and strengthening community-led initiatives. Building on the existing successes and addressing the challenges through innovative solutions will be critical for Greenland’s long-term sustainability.
Visual Representation of Greenland’s Ice Sheet Decline
A visual representation of Greenland’s ice sheet’s decline over time would depict a gradual but significant decrease in the ice sheet’s extent and thickness. The visualization would illustrate the shrinking of glaciers and ice caps, showing a clear correlation between the increase in global temperatures and the ice sheet’s response. This would be represented through a series of maps or graphs, demonstrating the ice sheet’s volume and extent over a given period, clearly showcasing the trend of decline.
Data from satellite imagery and ice core analyses would form the basis for this visual representation.
Epilogue
In conclusion, Greenland’s present moment is a complex interplay of historical context, environmental pressures, and emerging economic possibilities. The future of Greenland depends on its ability to navigate these challenges and opportunities responsibly, with careful consideration of the global implications of its choices. Sustainable development, international cooperation, and a deep understanding of the unique needs of Greenlandic communities are crucial for shaping a brighter future.
The tables and illustrative examples throughout this article highlight the key aspects of this complex situation.