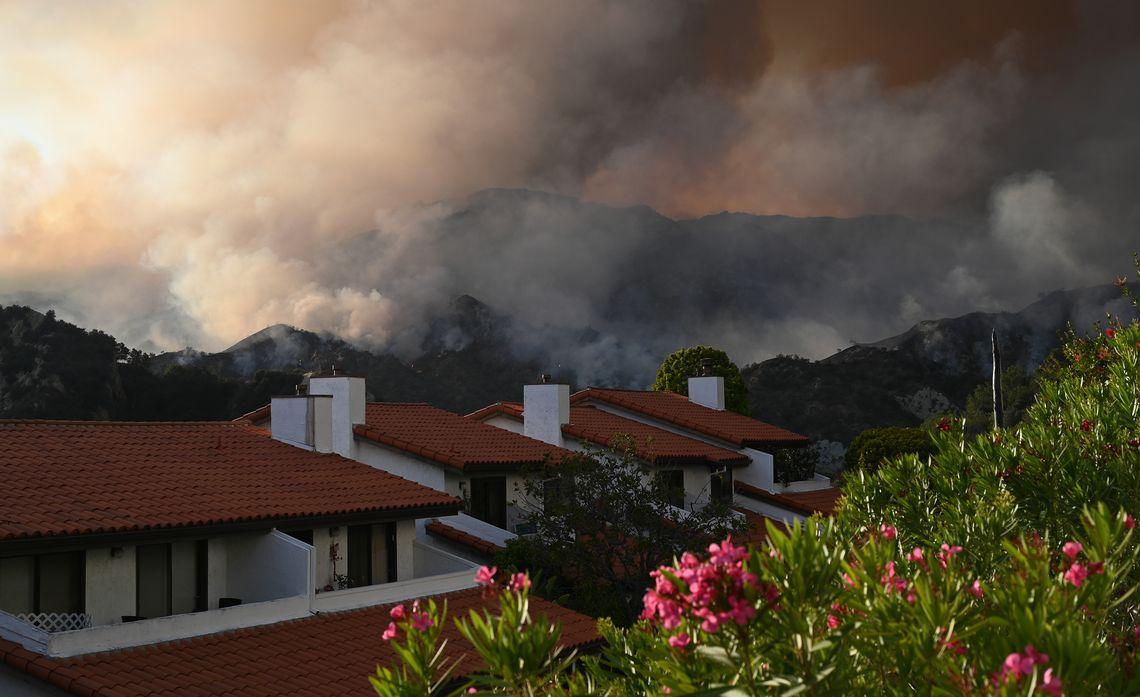
LA Fire Resilience Community & Govt Opinion
Opinion los angeles fire government resilience community is crucial for effective fire prevention and response. This deep dive examines the historical context of fires in Los Angeles, exploring the city’s vulnerabilities, from climate change to urban development. We’ll analyze government responses, community preparedness, and public opinions on fire resilience. Ultimately, we aim to understand how these elements intertwine to shape the future of fire safety in Los Angeles.
The report breaks down the subject into five key areas: the city’s history with fires, the governmental response, community engagement, public sentiment, and the intricate interplay between these factors. A critical component of this analysis involves evaluating different fire prevention strategies and comparing their effectiveness. The report also includes a look at potential future challenges and opportunities for enhanced fire resilience.
Overview of Los Angeles Fire Resilience
Los Angeles, a city renowned for its beauty and vibrant culture, has a long and unfortunately intertwined history with wildfires. The region’s unique climate, coupled with rapid urban growth, has created a complex tapestry of vulnerability and resilience. Understanding this history and the factors that influence fire risk is crucial for developing effective strategies for future protection.The city’s vulnerability to wildfires is not a new phenomenon.
Past devastating fires, such as the 1988 Oakland fire and the 2018 Woolsey Fire, have left indelible marks on the landscape and communities. These events underscore the need for ongoing adaptation and proactive measures to mitigate the risks.
Historical Context of Major Fires in Los Angeles
Los Angeles has experienced numerous significant wildfires throughout its history. These events have often been exacerbated by a combination of factors, including drought conditions, strong winds, and the presence of flammable vegetation. The 1871 Los Angeles fire, for example, caused substantial damage and loss of life, highlighting the city’s vulnerability to fire even in the early years of its development.
The frequency and intensity of these events have increased in recent decades, necessitating a more comprehensive and proactive approach to fire prevention and response.
Factors Contributing to Los Angeles’ Fire Vulnerability
Several factors contribute to Los Angeles’ ongoing fire vulnerability. Climate change is a significant driver, characterized by increasing temperatures, prolonged drought periods, and an elevated frequency of extreme weather events, such as Santa Ana winds. Rapid urban development, often encroaching on natural ecosystems and fire-prone vegetation, further exacerbates the risk. The presence of large swaths of dry brush and other flammable vegetation also significantly increases the potential for wildfires.
Honestly, I’ve been thinking a lot about how the LA fire response could have been improved. Community resilience is key, and the government’s handling of the situation is definitely up for debate. It’s fascinating to consider how much resources are needed to support communities during crises, and it’s a complex topic to fully grasp. In the grand scheme of things, comparing that to Dolly Parton’s impressive net worth, which is reportedly in the hundreds of millions dolly parton net worth , really puts things into perspective about how wealth and resources can be utilized in different ways.
Regardless, the LA fire response needs a lot more attention and resources to ensure better outcomes for the community in the future.
Current State of Fire Preparedness in Los Angeles
Los Angeles County has implemented various strategies to enhance fire preparedness. These include comprehensive fire prevention programs, improved fire suppression capabilities, and community outreach initiatives to educate residents about fire safety. Building codes are designed to limit the spread of fire within structures, and increased investment in fire-fighting resources and personnel reflects a commitment to addressing fire risk.
Moreover, the city has developed detailed evacuation plans and procedures.
Examples of Successful Fire Prevention and Response Strategies
Several successful fire prevention and response strategies have been implemented in Los Angeles. Vegetation management, involving the controlled removal of flammable vegetation, is a crucial element in fire prevention. The proactive approach taken by the city to remove flammable brush from areas surrounding structures has proven effective in limiting the spread of wildfires. Community-based education programs, such as fire safety workshops and presentations, have played a critical role in raising awareness among residents about fire risks and best practices.
Comparison of Fire Prevention Strategies
| Strategy | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Vegetation Management | Controlled burning, clearing, and trimming of flammable vegetation. | High, particularly when implemented in conjunction with other strategies. |
| Building Codes | Regulations requiring fire-resistant materials and features in construction. | High, significantly reducing the spread of fire within structures. |
| Early Warning Systems | Using weather patterns and real-time data to anticipate and respond to fire threats. | Moderate to High, enabling timely evacuation and response. |
| Community Education | Providing information and resources to residents about fire safety. | Moderate, raising awareness and preparedness levels. |
Government Response to Fires
The Los Angeles area’s vulnerability to wildfires underscores the critical role of effective government response. From local fire departments to state agencies and the federal government, a well-coordinated effort is paramount to mitigating the damage and ensuring community safety. This necessitates a robust understanding of funding mechanisms, clear lines of responsibility, and effective communication channels during emergencies. This exploration dives into the intricate web of government action in fire risk management.
Roles of Local, State, and Federal Governments
The management of fire risk is a multi-layered responsibility, spanning local, state, and federal jurisdictions. Local governments, typically represented by fire departments and city councils, are the first responders, responsible for immediate containment and evacuation efforts. State agencies, such as the California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection (Cal Fire), often provide substantial resources and expertise, coordinating large-scale operations.
Honestly, I’m curious about how LA’s government resilience will fare after the recent fires. The community’s spirit is amazing, but how quickly can they bounce back? It’s a tough situation, especially when you consider the current NBA trade deadline drama. For example, check out this article about the Warriors needing GM Dunleavy to let some key players go, moore the warriors need gm dunleavy to let it fly here are their top players to pursue at the trade deadline , which makes me think about how resourcefulness can be key in rebuilding, both on the court and in the community.
Hopefully, LA’s government and people will emerge stronger than ever from this.
Federal agencies, including the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), contribute crucial funding and specialized support during and after catastrophic events, especially when the scale of the disaster transcends local and state capabilities.
Funding Mechanisms and Budgetary Allocations
Fire response and prevention necessitate substantial funding. Local governments rely on property taxes and other local revenue streams. State funding is derived from various sources, including general tax revenue, special assessments, and federal grants. Federal support plays a vital role, particularly in funding research, infrastructure improvements, and long-term recovery efforts. Varied budgetary allocations for fire-related activities reflect the fluctuating risk levels and the needs of different communities.
Coordination Between Government Agencies
Effective fire response demands seamless coordination among various government agencies. This involves pre-established communication protocols, joint training exercises, and shared resources. Clear lines of authority and responsibility are crucial to avoid duplication of efforts and ensure a unified response. Inter-agency agreements and joint task forces facilitate the efficient allocation of resources and personnel during emergencies.
Comparative Analysis of Fire Resilience Policies
Different government policies demonstrate varying degrees of effectiveness in building fire resilience. Policies emphasizing preventative measures, such as vegetation management and fire safety education, generally yield better long-term outcomes compared to reactive strategies. A robust, proactive approach, incorporating early warning systems, rapid response protocols, and infrastructure improvements, proves more effective than solely relying on emergency response. The effectiveness of specific policies is often evaluated through metrics such as the number of wildfires, the extent of damage, and the speed of recovery.
Key Responsibilities of Each Level of Government in Fire Response
| Level of Government | Key Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Local | Initial response, evacuation, fire suppression, community outreach, and local infrastructure protection. |
| State | Coordination of large-scale operations, provision of specialized resources (e.g., aerial firefighting), and support for local efforts. |
| Federal | Funding for research, long-term recovery, disaster assistance, and support for state and local agencies during major emergencies. |
Community Preparedness and Engagement
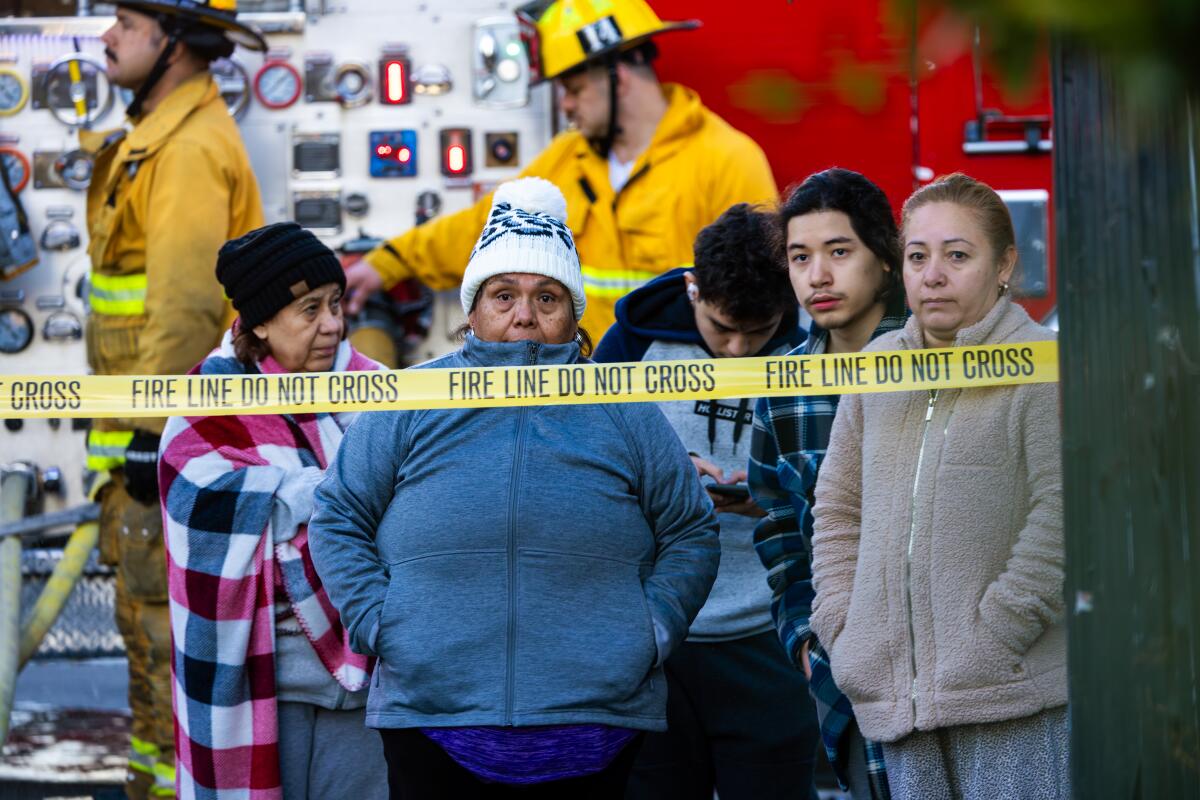

Beyond the infrastructure and government response, the heart of fire resilience lies in the preparedness and engagement of the community. A robust community response system is crucial for minimizing the impact of fires on individuals, businesses, and the overall well-being of the region. Effective community engagement involves proactively educating residents about fire risks and empowering them to take action.The diverse populations of Los Angeles are affected differently by fire events.
Residents, businesses, and particularly vulnerable populations like the elderly, low-income families, and individuals with disabilities, face varying degrees of risk and require tailored preparedness strategies. Understanding these distinctions is critical for developing targeted and effective community outreach programs.
Community Groups Affected by Fires
Different community groups experience varying levels of vulnerability during fire events. Residents, especially those living in high-risk areas, face immediate threats to their homes and safety. Businesses, particularly those in vulnerable sectors like tourism or retail, may suffer substantial financial losses due to closures and damage. Vulnerable populations, including the elderly, low-income families, and individuals with disabilities, often lack the resources to adequately prepare for or recover from fires, making them more susceptible to harm.
Specific needs of these groups must be addressed for effective community preparedness.
Strategies for Educating and Engaging Communities
Community education programs play a pivotal role in enhancing fire preparedness. These programs often involve public awareness campaigns, workshops, and community forums to educate residents about fire safety measures. Examples include fire safety demonstrations, home hazard assessments, and providing resources like evacuation plans and emergency contact information. Utilizing community centers, schools, and other gathering places as platforms for education can increase outreach.
Tailored information for different community groups is essential for effective engagement.
Role of Community Organizations in Fire Response and Recovery
Community organizations are essential partners in fire response and recovery. They provide crucial support, including temporary shelter, food, and emotional support to those affected by fires. They can mobilize volunteers, organize fundraising efforts, and advocate for the needs of affected residents. For example, local churches, volunteer fire departments, and social service agencies often play a key role in disaster relief.
Comparison of Community Engagement Models
Different models for community engagement in fire preparedness exist. Some models emphasize individual responsibility, encouraging residents to develop their own preparedness plans. Other models emphasize community-based approaches, creating a collaborative environment where residents, organizations, and government agencies work together. Evaluating the strengths and weaknesses of different models and adapting strategies to the specific needs of the community are crucial.
Community Outreach Programs for Enhancing Fire Resilience
| Program Name | Target Group | Key Activities | Evaluation Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| “Ready, Set, Go!” | Families with young children | Interactive workshops, fire safety demonstrations, home hazard assessments, family evacuation drills. | Workshop attendance, participation in home assessments, adoption of evacuation plans. |
| “Fire Safety for Seniors” | Elderly residents | Tailored workshops on fire safety, home modifications, emergency preparedness, and support networks. | Attendance at workshops, use of provided resources, creation of personal emergency plans. |
| “Business Continuity Plan” | Local businesses | Workshops and resources on developing business continuity plans, including evacuation strategies, communication protocols, and securing critical assets. | Participation in workshops, implementation of plans, and assessment of preparedness. |
| “Community Resource Directory” | All residents | Creating a comprehensive online and print directory of local resources, including fire departments, hospitals, shelters, and community organizations. | Number of resources listed, accessibility of the directory, and usage by community members. |
Public Opinion on Fire Resilience
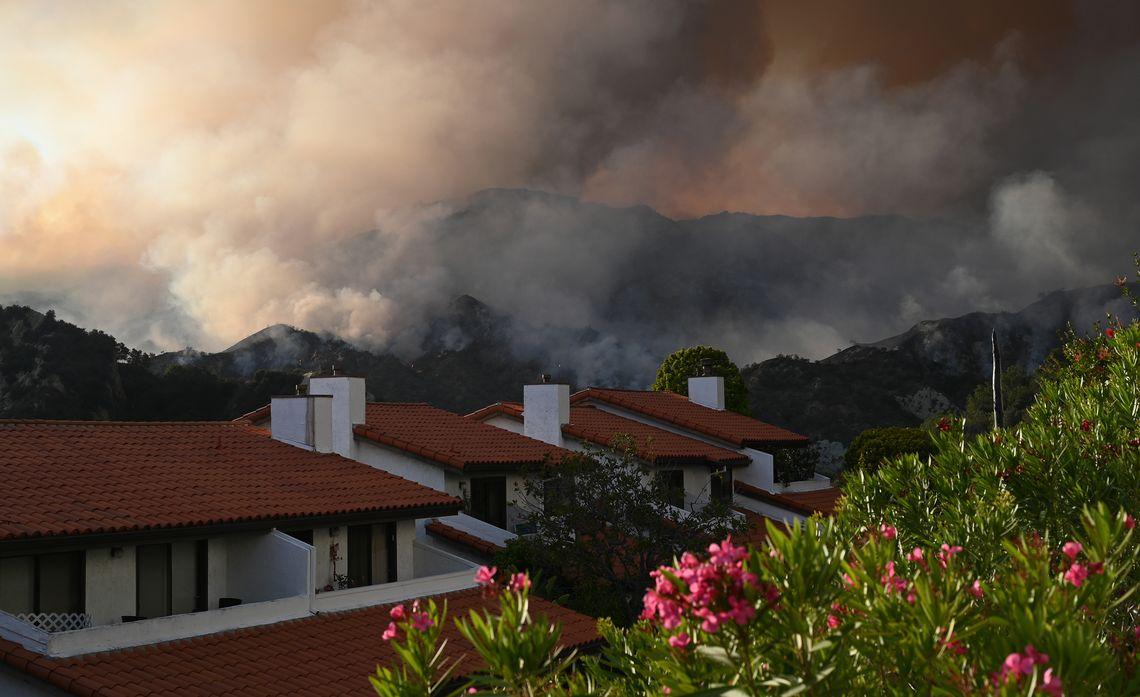

Public opinion on the effectiveness of fire resilience strategies in Los Angeles is a complex and multifaceted issue. While there’s a general recognition of the severity of the fire risk, public perception of government response and individual preparedness varies significantly. This dynamic landscape is shaped by a range of factors, including past experiences, media portrayals, and the perceived effectiveness of preventative measures.
Analyzing these varying perspectives provides valuable insight into fostering greater community engagement and building a more resilient Los Angeles.Public sentiment towards government response to fire emergencies often hinges on the perceived speed and adequacy of aid provided during crisis situations. Public trust in the effectiveness of evacuation plans and communication systems plays a crucial role in shaping overall opinions.
Factors like perceived preparedness of first responders, timely provision of information to the public, and efficient coordination between various agencies all contribute to public perceptions of government effectiveness.
Government Response to Fire Emergencies
Public opinion regarding the effectiveness of government response varies greatly. Some residents feel that the government’s response is swift and comprehensive, praising the coordination between different agencies and the provision of crucial resources. Conversely, others criticize delays in response, communication breakdowns, or insufficient support for impacted communities. These contrasting views often stem from personal experiences during past fire emergencies, shaping the perception of preparedness and responsiveness.
Public Sentiment Regarding Fire Prevention Measures
Public sentiment regarding the effectiveness of fire prevention measures is mixed. Some residents feel that current prevention efforts are adequate and that the implementation of fire-resistant building codes and increased vegetation management are crucial steps toward mitigation. Others, however, believe that these measures are insufficient or that they are not consistently enforced. The public’s perception is influenced by factors such as the perceived success of past initiatives and the degree to which preventative measures are perceived to address specific concerns.
Factors Influencing Public Opinions About Fire Resilience
Public opinion on fire resilience is influenced by a variety of factors. Personal experiences with past fires, the perception of risk, and media portrayals significantly shape public sentiment. Additionally, socioeconomic factors such as access to resources and community involvement also play a role. Understanding these factors is vital to tailoring fire resilience strategies to effectively address diverse community needs.
For example, residents in low-income neighborhoods might perceive a lack of resources or support, leading to different perspectives on fire resilience than those in more affluent areas.
Importance of Transparent Communication
Transparent communication between the government and the community during fire emergencies is crucial for building trust and fostering resilience. Effective communication channels, including clear and concise information dissemination, public forums, and readily accessible resources, are vital for ensuring that residents are informed and prepared. Lack of transparency can lead to misinformation, anxiety, and a decrease in public trust, hindering overall community resilience.
Evolution of Public Opinion on Fire Safety
Public opinion on fire safety has evolved significantly over the past decade. Increased media coverage of wildfires and the rising frequency of large-scale fires have heightened public awareness of the risk. This has led to a growing demand for more proactive fire prevention strategies and greater community engagement in fire safety initiatives. Public discourse on fire safety has become more nuanced and critical, with a growing emphasis on addressing the underlying causes of increased fire risk.
The Interplay of Government, Community, and Opinion: Opinion Los Angeles Fire Government Resilience Community
The interplay between public opinion, community involvement, and government policies is crucial for effective fire resilience strategies in Los Angeles. Understanding how these elements interact allows for a more nuanced and proactive approach to mitigating fire risks. A strong community response, informed by public sentiment, can bolster government efforts, while government initiatives can, in turn, shape public perception and engagement.Public opinion often acts as a catalyst for policy changes.
When residents express concerns about fire safety measures, or lack thereof, it pressures local governments to implement more comprehensive strategies. For instance, if residents feel inadequately informed about evacuation procedures, the government might prioritize community outreach and education programs to enhance preparedness.
Public Opinion Shaping Government Policies
Public opinion plays a significant role in influencing government policies related to fire resilience. When residents express concerns or anxieties about fire safety, the government is prompted to implement or adjust fire prevention and mitigation strategies. This is often observed through public forums, surveys, and social media discussions. The government, recognizing the power of public opinion, often incorporates feedback into their decision-making process.
This may involve adjusting building codes, increasing funding for fire departments, or enhancing community preparedness programs.
Community Involvement in Fire Preparedness, Opinion los angeles fire government resilience community
Community involvement is paramount in fostering fire resilience. Active participation in community-based fire safety programs, such as volunteer fire brigades, wildfire preparedness workshops, and evacuation drills, demonstrates a proactive stance against fire risks. This translates into a greater sense of responsibility and collective effort in protecting the community. Residents who actively participate in these initiatives often develop a deeper understanding of fire risks and the importance of preparedness.
This active participation, in turn, shapes the community’s overall response to fire threats.
Media and Communication in Shaping Public Perception
The media, including local news outlets, social media, and community forums, significantly influences public perception of fire resilience. Effective communication strategies from the government, local fire departments, and community organizations are vital in conveying accurate information and fostering a sense of preparedness. Clear, concise, and easily accessible information about fire risks, prevention measures, and evacuation procedures empowers residents.
Conversely, misinformation or inadequate communication can exacerbate public anxieties and hinder effective responses to fire events. Credible and consistent messaging from all parties involved is crucial.
Thinking about the LA fire and how the government and community responded, it got me pondering broader resilience issues. Recent events like the Gaza conflict, highlighted in a powerful piece on kristof gaza war proves a tragedy and failure for all , really make you question the effectiveness of our systems in handling crises. Ultimately, though, the crucial thing about the LA fire is how the community and government work together to build stronger systems for future emergencies.
Differing Opinions on Fire Management Strategies
Differing opinions on fire management strategies often lead to diverse community responses. Some communities may favor aggressive fire suppression tactics, while others might advocate for controlled burns or other mitigation methods. Understanding these diverse viewpoints is essential for developing comprehensive fire resilience plans. The government should strive to engage with all stakeholders and consider diverse perspectives in their decision-making process.
This ensures a more inclusive and effective approach.
Comparison of Community Responses to Fire Risks
Different communities exhibit diverse responses to fire risks and concerns, influenced by factors such as socioeconomic status, historical experiences with wildfires, and levels of community engagement. Wealthier communities, for example, may have better access to resources and infrastructure, enabling them to implement more sophisticated fire prevention measures. Conversely, lower-income communities might face challenges in accessing these resources, requiring targeted interventions from the government and community organizations.
The analysis of community-specific responses should focus on these factors to understand the root causes of disparities in fire preparedness and response.
Future of Fire Resilience in Los Angeles
The recent history of devastating wildfires in Los Angeles underscores the urgent need for proactive strategies to enhance fire resilience. Moving forward, a multifaceted approach encompassing technological advancements, community engagement, and long-term planning is critical for mitigating future risks. This necessitates a comprehensive understanding of potential challenges and opportunities, as well as a commitment to sustainable practices.The future of fire resilience in Los Angeles hinges on a nuanced understanding of the interplay between human activity, climate change, and the natural environment.
We need to anticipate and prepare for increasingly extreme fire conditions, while also recognizing the importance of maintaining a healthy and vibrant urban landscape. Adapting to the changing climate will be a constant process of learning and refinement.
Potential Challenges and Opportunities
The growing population density in Los Angeles, coupled with the increasing risk of extreme weather events, presents significant challenges for fire resilience. Maintaining adequate access for emergency vehicles, ensuring the effectiveness of early warning systems, and adapting to altered fire behavior are key considerations. Conversely, opportunities exist in harnessing technological advancements to enhance fire response and in fostering a stronger sense of community responsibility.
Potential Technological Advancements
Advanced fire detection systems, incorporating real-time data analysis and predictive modeling, can provide earlier warnings and more targeted responses. Drone technology offers a novel approach to aerial surveillance and fire mapping, allowing for rapid assessment of affected areas. Improved communication technologies, such as secure, wide-area networks, are vital for facilitating rapid information exchange among firefighters, emergency responders, and the public.
The integration of these technologies into a comprehensive system will improve situational awareness and optimize response times.
Long-Term Strategies for Sustainable Fire Prevention and Management
Long-term strategies for sustainable fire prevention and management must address the underlying causes of wildfire risk. Implementing vegetation management plans that account for climate change impacts is crucial. This includes controlled burns, selective thinning, and the introduction of fire-resistant vegetation. Education programs focused on fire safety and responsible land use practices are essential for fostering community engagement.
Investing in robust infrastructure, including fire-resistant building codes and improved fire hydrant networks, will enhance protection of structures.
Recommendations for Improving Fire Resilience
Recommendations for Government Agencies
- Prioritize funding for research and development in fire-resistant materials and advanced fire suppression technologies.
- Implement stricter building codes and land-use regulations that minimize wildfire risks in high-risk areas.
- Develop comprehensive, community-based fire safety plans, encompassing education and evacuation strategies.
These measures are crucial for safeguarding lives and property.
Recommendations for Community Organizations
- Engage in community outreach programs to educate residents on fire safety practices and evacuation procedures.
- Establish neighborhood watch programs and promote community vigilance in detecting potential fire hazards.
- Encourage the adoption of fire-resistant landscaping techniques to reduce the risk of ignition sources.
Community participation is essential for a robust fire resilience strategy.
Recommendations for Residents
- Develop and maintain an emergency preparedness plan, including evacuation routes and communication strategies.
- Regularly inspect homes and property for potential fire hazards, and take necessary preventative measures.
- Participate in fire safety education programs and workshops offered by local authorities.
Individual responsibility plays a vital role in mitigating fire risk.
Potential Future Scenarios for Fire Risk in Los Angeles
| Scenario | Description | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1: Increased Frequency of High-Intensity Fires | Prolonged periods of drought, coupled with higher temperatures, lead to more frequent and intense wildfires, potentially impacting larger areas. | Invest in advanced fire detection and suppression technologies. Implement stricter land management practices. |
| Scenario 2: Rapid Spread of Wildfires | Strong winds and dry conditions facilitate the rapid spread of wildfires, causing extensive damage and requiring rapid response. | Improve early warning systems and enhance communication protocols. Strengthen infrastructure, including roads and evacuation routes. |
| Scenario 3: Urban Wildland Interface Fires | Increased wildfire activity in urban areas results in significant property damage and potential loss of life. | Enforce stricter building codes in urban-wildland interface zones. Develop and implement robust fire-resistant building materials and landscaping strategies. |
A thorough understanding of potential future fire risk scenarios is essential for proactive planning and mitigation.
Last Point
In conclusion, opinion los angeles fire government resilience community is multifaceted and dynamic. The analysis highlights the critical role of government policies, community engagement, and public opinion in shaping fire resilience. The interplay of these elements is essential to a successful approach. The discussion underscores the need for continued dialogue, collaboration, and innovative solutions to address the evolving fire risks in Los Angeles.
Ultimately, a holistic approach is necessary to achieve sustainable fire prevention and management.