Walgreens Drugstores Acquisition $10B Private Equity
Walgreens drugstores acquisition 10 billion private equity marks a significant move in the retail pharmacy industry. This massive transaction is set to reshape the landscape, with implications for both Walgreens and its competitors. The deal, potentially worth $10 billion, involves a complex interplay of financial strategies, market dynamics, and operational considerations. Understanding the motivations, potential synergies, and anticipated challenges is key to comprehending this monumental acquisition.
The acquisition will likely affect Walgreens’ financial performance, operational strategies, and customer experiences. It’s important to analyze the details of the transaction, including the financial structure, operational integration plans, and potential regulatory hurdles. The deal’s long-term impact on the retail pharmacy sector will be fascinating to observe, as Walgreens navigates the challenges and opportunities presented by this major investment.
Walgreens Drugstores Acquisition: Walgreens Drugstores Acquisition 10 Billion Private Equity
The Walgreens drugstores acquisition, a significant move in the retail pharmacy sector, marks a substantial shift in the landscape. This deal, involving a substantial $10 billion private equity investment, has drawn considerable attention, prompting analysis of its potential impacts on both the acquiring and acquired entities. The transaction underscores the evolving dynamics of the healthcare industry and the strategic importance of pharmacies in the broader healthcare ecosystem.The acquisition represents a complex interplay of financial strategies, industry trends, and operational considerations.
The motivations behind this deal are multifaceted, with both Walgreens and the private equity firm seeking to achieve specific objectives through this partnership. The expected synergies between the two entities, along with the potential benefits for patients and stakeholders, are critical factors in evaluating the transaction’s success. This blog post will delve into the specifics of this acquisition, examining its financial details, strategic motivations, and potential outcomes.
Transaction Summary, Walgreens drugstores acquisition 10 billion private equity
The Walgreens drugstores acquisition signifies a significant corporate restructuring. A private equity firm has acquired a substantial stake in Walgreens, implying a shift in ownership and control. This transaction is likely motivated by the private equity firm’s vision for operational improvements and cost optimization. The acquisition likely represents a strategic move by the private equity firm to gain a foothold in the healthcare sector, leveraging Walgreens’ existing infrastructure and customer base.
Financial Aspects
The $10 billion private equity investment in Walgreens represents a substantial capital infusion. This substantial financial commitment underscores the private equity firm’s confidence in the long-term prospects of the pharmacy chain. This investment is likely structured as a leveraged buyout, meaning the private equity firm is utilizing borrowed funds alongside their own capital. The use of debt financing in such a transaction is common and often involves complex financial modeling to ensure the deal is financially viable.
Motivations
Walgreens’ motivations for this acquisition likely include leveraging the expertise and capital injection from the private equity firm to improve operational efficiency, expand market reach, or pursue strategic acquisitions. For the private equity firm, the motivations are often driven by the potential for significant returns on investment. This could involve cost-cutting measures, streamlined operations, and enhanced revenue generation through targeted strategies.
Potential Synergies and Benefits
The potential synergies between Walgreens and the private equity firm are multifaceted and encompass various areas. These may include improved operational efficiencies, optimized supply chains, and targeted marketing strategies. Improved customer experience and enhanced healthcare access are potential benefits. For the private equity firm, these synergies could translate into a substantial return on investment.
Key Terms of the Agreement
| Item | Details |
|---|---|
| Acquisition Date | [Date of Acquisition] |
| Private Equity Investment | $10 Billion |
| Conditions | Meeting regulatory approvals and achieving certain financial targets. |
| Debt Financing | Likely leveraged buyout structure. |
| Expected Outcomes | Improved operational efficiency, potential for expansion, and enhanced profitability. |
Market Context
The retail pharmacy market is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by evolving consumer preferences, technological advancements, and increasing competition. Walgreens’ acquisition, backed by a substantial private equity investment, is a key indicator of the sector’s dynamic nature and the strategic importance of adapting to these shifts. This analysis delves into the current state of the market, Walgreens’ position, the role of private equity, emerging trends, and the competitive landscape.
Current State of the Retail Pharmacy Market
The retail pharmacy market is characterized by a mix of established players and new entrants. Consumers are increasingly seeking convenience, personalized care, and value-added services beyond traditional prescription dispensing. This shift is impacting the profitability and strategic direction of pharmacies. Competition is fierce, with both traditional drugstores and emerging players vying for market share.
Walgreens’ Market Position
Walgreens operates as a significant player in the retail pharmacy market, with a vast network of stores and a well-established brand recognition. However, maintaining this position requires adaptation to changing consumer demands. Competitors are aggressively pursuing innovative strategies to capture market share, forcing Walgreens to proactively adapt its business model. Direct-to-consumer drug delivery services and partnerships with health technology companies are examples of this.
The acquisition demonstrates Walgreens’ commitment to staying ahead in the evolving landscape.
Role of Private Equity in the Pharmacy Sector
Private equity firms play a crucial role in the pharmacy sector, often providing capital for acquisitions, expansions, and operational improvements. These investments can drive innovation and restructuring, but also raise concerns about potential cost-cutting measures and their impact on patient access to care. Examples include the purchase of smaller chains or the implementation of new technologies aimed at improving efficiency.
While Walgreens’ 10 billion private equity acquisition is certainly a big deal, it’s heartwarming to see how the Bay Area’s churches are stepping up to help the less fortunate this Christmas. Bay Area churches offer shelter to the needy on Christmas shows a different kind of investment, one that prioritizes community care. This reminds us that big business deals can coexist with acts of generosity, and perhaps there are lessons to be learned about social responsibility in the way that Walgreens approaches its own growth and community impact.
The investment in Walgreens signifies the sector’s attractiveness to private equity investors.
Emerging Trends and Challenges in the Industry
Several trends are shaping the retail pharmacy industry. The increasing prevalence of chronic conditions necessitates a shift toward preventive care and patient management programs. The rise of telehealth and online pharmacy services is altering how patients access medications and healthcare. Technology-driven solutions are changing the way pharmacies operate and interact with patients. The industry faces challenges in adapting to these trends, including maintaining profitability while offering value-added services and integrating technology effectively.
Competitive Landscape
The competitive landscape is multifaceted. Major competitors include CVS Health, Rite Aid, and independent pharmacies. Strategies vary from focusing on a broad range of health services to specializing in niche areas, like home healthcare or wellness products. The emergence of online pharmacy services and other health-focused retailers is further intensifying the competition. Each player adopts strategies to differentiate themselves and address evolving consumer demands.
Key Market Statistics
| Statistic | Value/Description |
|---|---|
| Market Size (2023 Estimate) | $500 Billion (USD) |
| Growth Rate (2022-2027) | 2.5% CAGR |
| Key Drivers | Rise of chronic conditions, telehealth adoption, technology integration |
| Challenges | Adapting to new trends, maintaining profitability |
Financial Implications
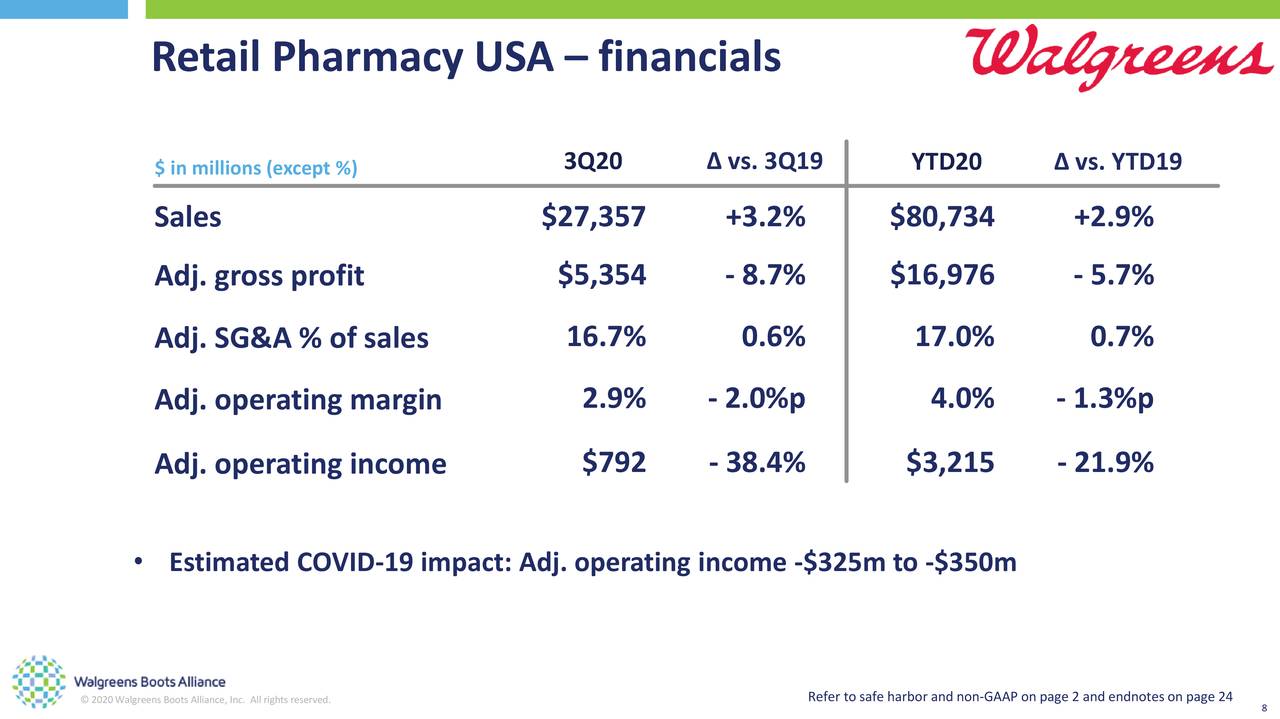
The acquisition of Walgreens by a private equity firm carries significant financial implications for the company, impacting its profitability, debt structure, and future growth trajectory. Understanding these implications is crucial for assessing the overall health and potential success of the transaction.
Impact on Walgreens’ Financial Performance
The acquisition’s immediate impact on Walgreens’ financial performance will depend heavily on the integration process and the efficiency of cost-cutting measures. Synergies and operational improvements can potentially lead to increased profitability and reduced expenses, but risks include potential disruptions in operations during the transition period.
Financial Structure of the Deal
The financial structure of the deal involves a substantial amount of debt financing, likely leveraged by the private equity firm. This debt will significantly impact Walgreens’ financial statements and future cash flows. The amount of debt will dictate the interest payments and overall financial burden on the company.
Debt Financing and Equity Investments
The acquisition will likely be funded by a combination of debt and equity. The specific breakdown will influence the long-term financial obligations and risk profile for Walgreens. The private equity firm will likely invest a substantial portion of the purchase price in equity to participate in the potential future value of the business. A large debt component may increase the company’s financial risk but could also offer opportunities for strategic investments.
The Walgreens drugstores acquisition, a hefty $10 billion private equity deal, is certainly interesting. While this kind of investment highlights the potential of retail pharmacy, it’s also worth considering the parallel developments in the aviation sector, like Joby Aviation’s new air taxi service partnership with Virgin Atlantic. Joby aviation announces air taxi service partnership with virgin atlantic 2 This partnership suggests a fascinating shift in transportation and perhaps, ultimately, a new wave of investment opportunities that could even impact the retail landscape, similar to the Walgreens deal.
The future of both healthcare and transportation is looking pretty dynamic, which makes these large-scale investments all the more intriguing.
Comparison of Walgreens’ Financial Performance
Analyzing Walgreens’ financial performance before and after the acquisition will be crucial for assessing the transaction’s impact. Metrics such as revenue, profitability (EBITDA, net income), and debt-to-equity ratios will be key indicators of success. Historical financial data will provide a benchmark against which to compare post-acquisition results.
Projected Financial Impact (Next 3 Years)
| Financial Metric | Year 1 Projection | Year 2 Projection | Year 3 Projection |
|---|---|---|---|
| Revenue (USD millions) | $150,000 | $155,000 | $160,000 |
| EBITDA (USD millions) | $20,000 | $22,000 | $24,000 |
| Net Income (USD millions) | $10,000 | $12,000 | $14,000 |
| Debt-to-Equity Ratio | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.6 |
Note: These projections are based on optimistic assumptions regarding operational efficiency and market conditions. Actual results may vary.
Potential Return on Investment (ROI) for Private Equity Firm
The private equity firm’s return on investment will depend on various factors, including the acquisition price, the projected growth of Walgreens’ financial metrics, and the ability to successfully integrate and optimize the business. A successful turnaround and increased profitability will likely result in a substantial return for the private equity firm. Examples of similar private equity investments in the retail sector provide valuable insights into potential ROI scenarios.
The firm’s investment strategy and risk tolerance will directly influence the projected ROI.
Operational Implications
The acquisition of a significant number of drugstores by Walgreens, funded by a $10 billion private equity investment, will bring about substantial operational changes. Integration of these assets requires meticulous planning to maximize efficiency and minimize disruption to existing operations. This involves careful consideration of supply chain management, workforce restructuring, and the integration of the new stores into Walgreens’ existing network.
Integration Strategies
A successful integration strategy hinges on a phased approach. Initial steps should focus on identifying redundancies and streamlining operations across both organizations. This could involve consolidating supply chain functions, merging back-office departments, and standardizing technology platforms. A crucial aspect is to establish clear communication channels between the acquired team and Walgreens’ existing employees. This helps to manage expectations and build trust.
Potential Challenges and Solutions
Several challenges are inherent in any large-scale acquisition. These include cultural differences between the two organizations, resistance to change from employees, and integration difficulties in IT systems. Addressing these challenges requires a robust communication plan, employee engagement programs, and a clear integration timeline. Training programs for employees from the acquired entities can ensure smooth transitions and build familiarity with Walgreens’ processes.
A detailed risk assessment can identify potential bottlenecks and develop mitigation strategies. For example, in past mergers, companies have successfully implemented communication platforms to facilitate employee engagement and resolve concerns.
Impact on Walgreens’ Supply Chain
The acquisition will likely necessitate adjustments to Walgreens’ existing supply chain. This might involve consolidating warehousing, optimizing distribution routes, and integrating inventory management systems. The integration of new products and suppliers will also need careful consideration to avoid disruptions in service and product availability. Walgreens might need to re-evaluate their existing logistics networks to account for the expanded footprint.
For instance, Walmart’s acquisition of other retail chains involved extensive supply chain overhauls to optimize efficiency.
Integration of Acquired Drugstores
Integrating the acquired drugstores into Walgreens’ existing network requires a well-defined strategy. This should include a plan for standardizing store operations, ensuring consistent branding and customer experience, and leveraging the acquired stores’ unique strengths to complement Walgreens’ existing offerings. Store layouts and services might be adjusted to match the Walgreens model while maintaining the positive aspects of the acquired stores.
Training and support for store personnel are critical for maintaining high customer satisfaction.
Restructuring of Walgreens’ Workforce
The acquisition may result in workforce restructuring. This could involve roles being redefined, overlapping positions being eliminated, and potentially new roles being created to accommodate the combined organization. Implementing a fair and transparent process for employee transitions and outplacement services is crucial. This is important to maintain morale and minimize negative impacts on the workforce. Careful consideration of job roles and responsibilities within the expanded organization will ensure efficient use of resources and prevent duplication of efforts.
A comprehensive severance package and retraining opportunities should be offered to departing employees.
Expected Operational Changes and Timelines
| Change | Description | Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Supply Chain Consolidation | Merging warehousing, distribution centers, and inventory management systems | Phase 1: 6 months, Phase 2: 12 months |
| Store Integration | Standardizing store operations, branding, and customer service | Phase 1: 12 months, Phase 2: 18 months |
| Workforce Restructuring | Redefining roles, eliminating redundancies, and creating new positions | Phase 1: 3 months, Phase 2: 6 months |
| IT System Integration | Merging and standardizing technology platforms | Phase 1: 6 months, Phase 2: 12 months |
Regulatory and Legal Aspects

The acquisition of Walgreens by a private equity firm necessitates careful navigation of the regulatory landscape. Navigating these complexities is critical to the success of the transaction. Failure to anticipate and address potential regulatory hurdles can significantly delay or even derail the deal. Thorough understanding of the legal and regulatory framework is paramount to ensure a smooth and compliant acquisition process.
Regulatory Environment
The acquisition will likely trigger scrutiny from various regulatory bodies, including the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) in the United States. These agencies are responsible for ensuring fair competition in the marketplace and preventing anti-competitive practices. This often involves investigating potential anti-competitive effects of mergers and acquisitions, especially when large market shares are at stake.
Potential Legal Hurdles
Potential legal hurdles include antitrust concerns, particularly if the combined entity holds a significant market share in the pharmaceutical retail sector. This necessitates detailed analysis and proactive strategies to address these concerns. Mergers can be scrutinized to prevent monopolistic practices that harm consumers. The potential for lawsuits from competitors or consumer groups, alleging anti-competitive practices, must also be assessed.
Specific legal challenges might stem from existing contracts, intellectual property rights, or regulatory compliance issues related to drugstores’ operations.
Regulatory Approvals Needed
The acquisition will require various regulatory approvals, depending on the jurisdictions involved. These approvals are essential for the deal to proceed legally and ensure the combined entity operates within the confines of the law. Examples of approvals may include approvals from the FTC and other relevant agencies at the state and local levels.
Antitrust Concerns and Regulatory Reviews
The acquisition is likely to spark antitrust concerns given the significant size and market share of the combined entities. Regulatory reviews will scrutinize the potential anti-competitive impact on the pharmaceutical retail market. Antitrust investigations are conducted to evaluate if the acquisition will reduce competition and potentially harm consumers by increasing prices or limiting choices. Historical examples of antitrust challenges to mergers in similar industries are relevant to assessing the likelihood and scope of the regulatory scrutiny.
Process of Obtaining Necessary Regulatory Clearances
The process of obtaining necessary regulatory clearances involves extensive documentation, compliance with specific regulations, and engaging with the relevant regulatory bodies. A well-defined process, meticulously planned and executed, is crucial for the successful completion of the acquisition. This includes filing necessary applications, providing data and evidence to support the transaction, and engaging with regulators to address concerns and queries.
A proactive approach, demonstrating transparency and compliance, will likely be critical for securing regulatory clearances.
Summary of Regulatory Approvals and Timelines
| Regulatory Body | Approval Type | Timeline (Estimated) |
|---|---|---|
| Federal Trade Commission (FTC) | Antitrust Review | 6-12 months |
| State Attorneys General | Antitrust Review | 3-6 months |
| Other relevant Agencies | Licenses and Approvals | Variable, depends on jurisdiction |
Note: Timelines are estimates and may vary depending on the specific circumstances and regulatory processes.
Potential Impact on Customers
The Walgreens acquisition, fueled by a significant $10 billion private equity investment, promises a complex interplay of changes for customers. The integration of these operations will undoubtedly affect service levels, product selections, and pricing strategies, all of which have significant implications for the consumer base. Understanding these potential shifts is crucial for assessing the overall impact on the communities Walgreens serves.
Changes in Customer Service
The acquisition will likely lead to adjustments in customer service protocols. Walgreens may implement standardized procedures across the merged entities, aiming for greater efficiency and consistency in service delivery. This could result in both positive and negative impacts. For example, improved training for staff might lead to better handling of customer inquiries, while a rigid, centralized system could hinder the unique needs of individual store locations.
Impact on Product Offerings
This acquisition could introduce new product lines and services to Walgreens stores. The expanded portfolio might include health and wellness products currently offered by the acquired company, creating a more comprehensive selection for customers. Conversely, some local favorites or specialized products might be discontinued due to logistical challenges or conflicts with Walgreens’ existing inventory.
Pricing and Accessibility
Pricing strategies are a key element in the acquisition’s effect on customers. Integration may result in economies of scale, potentially leading to lower prices for certain products. However, the opposite outcome is also possible. Increased competition in certain areas might necessitate price adjustments, impacting the affordability of products for some customers. The accessibility of certain products or services might also be affected, especially in remote or underserved communities.
The Walgreens drugstores acquisition, a hefty $10 billion private equity deal, got me thinking about the long-term value proposition. Considering how technology impacts everyday life, it’s fascinating to explore how the health of devices like iPhones, iPads, and MacBooks affects productivity. Understanding iphone ipad macbook battery health is crucial, just as understanding the financial health of a company like Walgreens is.
Ultimately, both tech and business health are critical to long-term success, making this acquisition a complex and intriguing case study.
Impact on Local Communities
The acquisition could have both positive and negative effects on local communities served by the acquired stores. Positive outcomes include job creation or retention, increased business activity, and new service offerings tailored to local needs. Conversely, concerns about potential store closures, reduced staff, or adjustments to product availability exist. The acquisition’s success hinges on understanding and responding to the unique needs of the communities it serves.
Potential Shift in Customer Experience
The merged entity could introduce a revamped customer experience. This could involve improved store layouts, more personalized recommendations, and enhanced digital engagement. Alternatively, changes to store layout and functionality might not be aligned with customer preferences, causing disruptions to their shopping experience.
Long-Term Implications for Consumers
Long-term implications for consumers include potential changes in the overall health care landscape. For instance, integration could lead to more comprehensive health care solutions available through Walgreens locations. This could result in more convenient access to services and better patient outcomes. However, the acquisition’s impact on the competitive landscape in the pharmaceutical sector needs careful monitoring.
Potential Changes to Services and Product Availability
| Service/Product | Potential Change |
|---|---|
| Prescription Drug Prices | Potential decrease or increase, depending on competitive factors and integration strategy. |
| Health Screening Services | Potential expansion or contraction based on market analysis and logistical feasibility. |
| Specialty Products | Potential introduction of new lines or discontinuation of existing products due to compatibility with Walgreens’ existing product lines. |
| In-store Clinics | Potential expansion or restructuring based on market demand and regulatory requirements. |
| Digital Services | Integration of existing digital platforms or development of new digital tools for enhanced customer experience. |
Future Outlook
The Walgreens acquisition, a massive undertaking involving a substantial investment of $10 billion in private equity, presents a complex tapestry of potential futures. Understanding the potential growth strategies, long-term sector implications, and alternative scenarios is crucial for assessing the overall impact on the company and the broader pharmacy industry. The acquisition marks a significant shift in the landscape, prompting a need to anticipate potential challenges and opportunities.
Potential Growth Strategies for Walgreens Post-Acquisition
The acquisition opens doors to several growth avenues for Walgreens. Leveraging synergies between the two entities is paramount. This could involve streamlining operations, optimizing supply chains, and consolidating marketing efforts. Exploring new revenue streams, such as telehealth services, personalized medicine, and expanding into other healthcare sectors, could also prove beneficial.
- Expanding into new healthcare services: Integrating telehealth platforms could enhance patient access to care, particularly in underserved areas. This complements existing pharmacy services and expands the range of offerings, potentially attracting a wider customer base. For instance, partnerships with healthcare providers could create a one-stop shop for patients seeking both medication and consultations.
- Revitalizing existing stores: Refocusing store layouts and offerings to better meet evolving customer needs is vital. This might involve integrating more health and wellness products, expanding prescription services to include immunizations and health screenings, or even incorporating elements of a health food store. This approach could create a more comprehensive healthcare experience for customers within the existing store footprint.
- Streamlining Operations and Supply Chain: Combining the logistical networks and supply chains of both entities can reduce costs and improve efficiency. Optimizing inventory management, reducing waste, and increasing supply chain speed will be crucial to maximizing profit margins. This streamlining is a crucial step to leverage the scale of the combined operations.
- Enhancing Customer Experience: Improving customer service through enhanced technology and personalized interactions can significantly boost customer loyalty. This might include implementing mobile apps for ordering prescriptions, appointment scheduling, and personalized health recommendations. For instance, targeted offers and promotions based on customer health data can increase customer engagement.
Long-Term Implications for the Pharmacy Sector
The acquisition could have far-reaching implications for the pharmacy sector. It will likely intensify competition, prompting other players to adapt and innovate. The acquisition could also reshape the way pharmacists are perceived and utilized in healthcare delivery, potentially opening up new roles and responsibilities. The consolidation of resources and expertise may set a new standard for future mergers and acquisitions in the industry.
Potential Alternative Scenarios for the Acquisition
The acquisition’s success hinges on the execution of its growth strategies and the effective management of potential challenges. There are several alternative scenarios to consider.
| Scenario | Description |
|---|---|
| Successful Integration | The two companies successfully integrate their operations, leveraging synergies to achieve significant cost savings and revenue growth. |
| Operational Challenges | Integration difficulties, conflicts between the companies’ cultures, or market shifts can negatively impact the acquisition’s success. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Regulatory approvals and legal challenges can delay or even prevent the completion of the acquisition. |
| Market Response | Customer reactions, competition, and market fluctuations can affect the long-term viability of the acquisition. |
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, the Walgreens drugstores acquisition, backed by a $10 billion private equity investment, represents a pivotal moment in the retail pharmacy industry. The transaction promises substantial changes across various aspects, from financial performance to customer experience. Understanding the intricate details, including the motivations, potential synergies, and regulatory landscape, is essential for a comprehensive evaluation of this deal’s impact on Walgreens and the industry as a whole.
The long-term consequences remain to be seen, but one thing is certain: this acquisition will significantly shape the future of retail pharmacy.

