Californias Cost Crunch Progressive Policies vs. High Living
Walters california high living costs conflict progressive policies – California’s high living costs conflict with progressive policies, creating a complex dilemma. From soaring housing prices to inflation impacting all demographics, the state’s economic landscape is strained. Simultaneously, progressive policies like environmental protection and social safety nets aim to improve the lives of Californians. This article explores the tension between these seemingly opposing forces, analyzing the impacts on various groups and suggesting potential solutions.
California’s housing market has experienced significant price increases over recent decades, leading to affordability issues for many residents. This escalating cost of living impacts young professionals, families, and seniors alike, creating financial strain and limiting opportunities. The article will explore the multifaceted causes of these high costs, including limited supply, high demand, and government regulations. A comparative table illustrating California’s cost of living against other states will provide a tangible understanding of the problem.
High Cost of Living in California
California’s allure often masks a harsh reality: the high cost of living. From sprawling coastal cities to inland valleys, the price tag for housing, transportation, and everyday necessities has steadily risen, impacting various demographics in significant ways. This article delves into the historical context, the diverse impacts, and the multifaceted causes behind this persistent issue.California’s housing market has experienced significant inflation over the past few decades.
The price increases have been fueled by a combination of factors, including limited land availability, high demand, and various government regulations. These trends have had a cascading effect on other aspects of life, making it more difficult for residents to maintain a comfortable lifestyle.
Historical Overview of Housing Costs and Inflation
California’s housing market has seen substantial growth and price increases over the years, particularly in recent decades. This upward trend is evident in data from various sources, showing a continuous increase in home values and rental rates. The rate of inflation in California has often outpaced the national average, making housing less affordable compared to other states. This inflationary trend has been driven by factors such as population growth, economic prosperity in specific sectors, and limited construction of new housing units.
Impact on Different Demographics
The escalating cost of living significantly affects various demographic groups. Young professionals, often starting their careers, struggle to afford housing and establish themselves in the state. Families, particularly those with children, face challenges in finding suitable housing options within their budget. The increasing cost of childcare and education further adds to the financial strain, potentially limiting career choices and personal development.
These financial pressures often lead to reduced quality of life and increased stress levels.
Perspectives on the Causes of High Living Costs
Several perspectives contribute to understanding the high cost of living in California. Limited supply of housing due to various factors, including environmental regulations, zoning restrictions, and the inherent scarcity of suitable land, is a crucial element. High demand, fueled by migration and economic opportunities, further exacerbates the problem. Government regulations, while aiming for specific goals like environmental protection or affordability, can inadvertently increase costs by slowing down development.
Comparison of Cost of Living in California to Other States, Walters california high living costs conflict progressive policies
| State | Housing Costs (Median Home Price) | Transportation Costs (Average Gas Price) | Groceries (Average Monthly Expenses) |
|---|---|---|---|
| California | $800,000 (estimated) | $4.50/gallon (estimated) | $1,200 (estimated) |
| Texas | $300,000 (estimated) | $3.50/gallon (estimated) | $900 (estimated) |
| Florida | $350,000 (estimated) | $3.80/gallon (estimated) | $1,000 (estimated) |
| New York | $600,000 (estimated) | $4.20/gallon (estimated) | $1,100 (estimated) |
Note
* These are estimated figures and can vary based on specific locations and individual circumstances. Data is collected from various reliable sources. The table provides a general comparison; further research is needed for precise figures.
Progressive Policies in California
California, often lauded for its innovation and progressive values, has embraced a range of policies aimed at addressing social and environmental challenges. These policies, often reflecting a commitment to social justice and environmental sustainability, have significant implications for the state’s economic trajectory. The implementation of these policies, while aiming for positive societal outcomes, can also present potential economic hurdles.Progressive policies in California often prioritize the well-being of its citizens, including environmental protection and robust social safety nets.
These policies aim to create a more equitable and sustainable future, but their implementation can have both positive and negative economic consequences, which need careful consideration.
Core Tenets of Progressive Policies
Progressive policies in California are fundamentally rooted in the principles of environmental sustainability and social equity. These policies strive to balance economic growth with environmental protection, and aim to create a society where opportunities are available to all. They seek to address systemic inequalities and provide support for vulnerable populations.
Examples of Progressive Policies
California has a history of pioneering progressive legislation. A key example is its stringent environmental regulations, including emission standards for vehicles and renewable energy mandates. These regulations have led to advancements in cleaner technologies and industries. Further, the state’s commitment to affordable housing and its social safety net programs, such as Medi-Cal and CalFresh, aim to ensure basic needs are met for all residents.
- Environmental Protection: California’s ambitious renewable energy targets, coupled with its stringent vehicle emission standards, demonstrate a strong commitment to environmental protection. These regulations, while intended to combat climate change and improve public health, can sometimes lead to higher costs for consumers. For example, the transition to electric vehicles, while environmentally beneficial, can be initially more expensive than traditional gasoline vehicles.
- Social Safety Nets: California’s robust social safety net includes programs like Medi-Cal and CalFresh. These programs provide crucial support for low-income individuals and families, helping them meet basic needs. However, the cost of these programs can place a burden on the state’s budget, necessitating ongoing fiscal consideration.
Economic Impacts of Progressive Policies
The economic impacts of California’s progressive policies are multifaceted and often debated. While some policies, like investments in renewable energy, can stimulate job creation and technological advancements, others, such as higher minimum wages, might impact businesses’ ability to compete in the global market. The effect on economic growth and job creation can be seen in various industries, from renewable energy to social services.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Progressive Policies
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
| Enhanced environmental quality, reduced pollution, and improved public health. | Increased costs for businesses and consumers due to stricter regulations. |
| Improved social equity, reduced poverty, and increased access to essential services. | Potential strain on the state budget and increased taxes for some residents. |
| Innovation in renewable energy and sustainable practices. | Potential for job losses in certain industries due to policy changes. |
| Increased access to healthcare and nutrition assistance. | Possible bureaucratic inefficiencies and delays in service delivery. |
Conflict Between High Costs and Progressive Policies: Walters California High Living Costs Conflict Progressive Policies
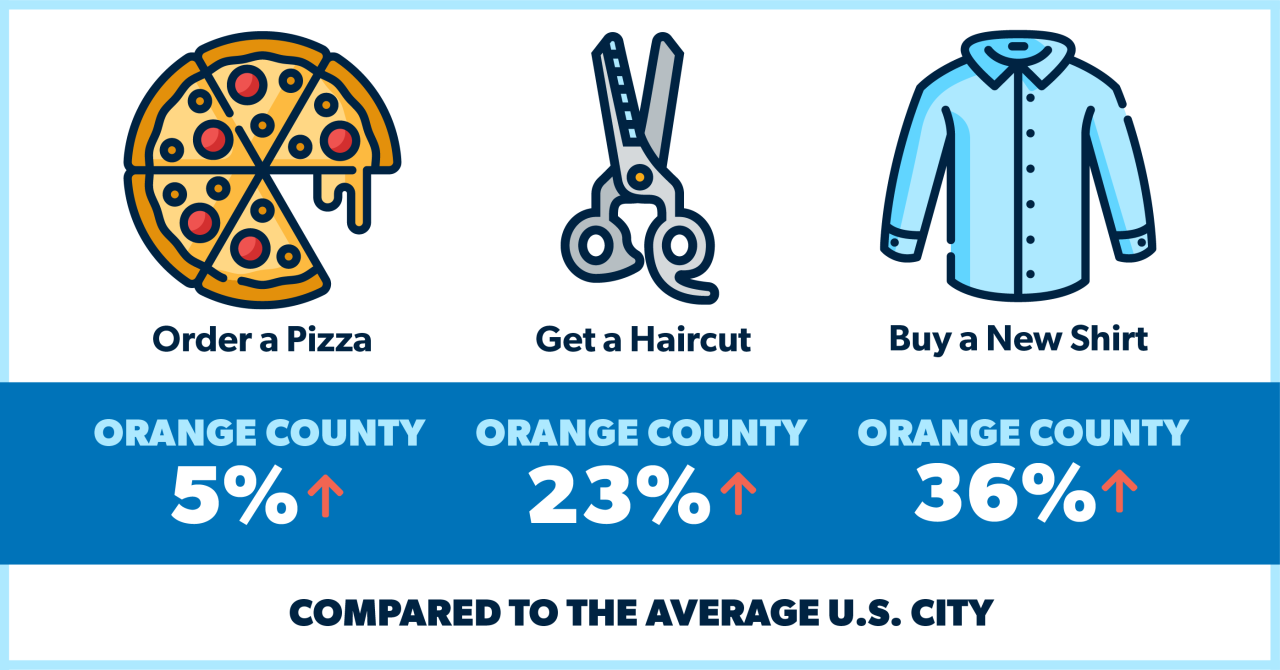
California’s pursuit of progressive policies often clashes with the state’s astronomical housing costs. This tension creates a complex web of challenges, affecting residents’ ability to access essential services and opportunities. The high cost of living in the state necessitates a critical examination of how progressive policies can either exacerbate or mitigate these financial pressures.The very nature of progressive policies, aiming to improve societal well-being, can inadvertently increase the financial burden on residents if not carefully considered.
High living costs in Walter’s California are definitely clashing with progressive policies. It’s a tough spot, and the rising cost of housing in places like Alameda, especially apartments and property, is a huge factor. For instance, exploring the current state of the East Bay real estate market, including the home economy and apartment build scene, is key to understanding the challenges.
alameda home economy apartment east bay real estate property build provides a deeper dive. Ultimately, the struggle remains: how do we balance affordability with the ideals of progressive policies in areas like Walter’s California?
For instance, robust environmental regulations, while crucial for sustainability, can increase construction costs, potentially driving up housing prices. Similarly, policies focused on income redistribution, such as higher minimum wages or stronger worker protections, can lead to increased labor costs for businesses, which could translate into higher prices for goods and services, further impacting affordability.
Potential Conflicts
Progressive policies often aim to address societal inequalities, but the high cost of living can create a significant barrier to their implementation. The rising cost of housing and essential services can disproportionately impact lower-income individuals and families, making it challenging for them to participate in and benefit from these policies. The cost of childcare, education, and healthcare are all major contributors to the overall financial strain, and these are all areas where progressive policies often focus.
Impact on Affordability
Progressive policies can both enhance and hinder affordability. Policies supporting affordable housing, such as stricter regulations on landlord practices, can help maintain housing affordability. However, policies like those supporting increased environmental protections can increase construction costs, thus impacting affordability. Similarly, policies that focus on income redistribution through taxes and subsidies can create a more equitable society but also have the potential to impact business investments, leading to job creation or loss.
The overall impact on affordability is complex and depends on the specific policies and their implementation.
Tension Between Affordability and Social Programs
The tension between affordability and social programs is evident in many areas. For example, robust social safety nets, such as unemployment benefits and food assistance programs, are essential components of progressive policies. However, these programs can strain public resources and potentially impact tax burdens. The need for these programs is often directly related to the affordability crisis. As the cost of living rises, the need for social support also rises, creating a delicate balance.
Potential Solutions
Addressing the conflict between high living costs and progressive policies requires a multifaceted approach.
| Potential Solution | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Targeted Subsidies | Provide financial assistance specifically to those most impacted by high costs. | Targeted housing assistance programs for low-income families. |
| Innovative Housing Solutions | Explore alternative housing models that can reduce costs. | Modular housing, co-housing, or shared housing options. |
| Revenue Generation | Develop strategies to increase revenue without disproportionately affecting lower-income individuals. | Exploring new revenue streams while maintaining tax equity for lower and middle-income individuals. |
| Policy Adjustments | Review and adjust policies to minimize unintended consequences. | Analyzing the impact of environmental regulations on housing costs and adjusting as needed. |
| Community Engagement | Involve local communities in the development and implementation of policies. | Holding town halls and focus groups to gather input and concerns regarding the impact of policies. |
Impact on Different Groups
California’s high cost of living, coupled with progressive policies aimed at social equity, creates a complex interplay affecting various demographics. This tension highlights the need for nuanced solutions that address the specific challenges faced by different groups while maintaining the goals of progressive policy. The conflict necessitates a critical examination of how these policies impact low-income families, seniors, and other vulnerable populations, and how policies can be adjusted to mitigate these impacts.The disparity in access to resources, quality of life, and opportunities created by high living costs often disproportionately affects marginalized groups.
Policies intended to benefit society as a whole can, in some cases, exacerbate existing inequalities if not carefully designed and implemented with these groups’ specific needs in mind. Addressing this requires a thorough understanding of the varied ways these groups are affected.
Impact on Low-Income Families
Low-income families in California face significant challenges navigating the high cost of housing, healthcare, and everyday necessities. Rising rents and home prices often force them to choose between essential needs, like food and utilities, and housing. Progressive policies, such as increased minimum wages and affordable housing initiatives, aim to alleviate these struggles, but the rapid pace of inflation often outpaces these efforts.
High living costs in Walter’s California are definitely a problem, clashing with progressive policies that aim to help lower-income residents. It’s a tough balancing act, and while issues like the city urging residents to report Santa Cruz wharf debris commemorations city urges residents to report Santa Cruz wharf debris commemorations might seem minor, they highlight the broader struggles of affordability and community engagement in the face of rising costs.
The situation in Walter’s highlights the ongoing challenge of making progressive policies work in a high-cost environment.
The gap between policy goals and actual outcomes can be substantial, leading to continued hardship for many low-income families.
Impact on Seniors
Seniors, particularly those on fixed incomes, are particularly vulnerable to the high cost of living. Rising housing costs, healthcare expenses, and transportation costs can strain their budgets significantly. Progressive policies focused on senior care and support can help mitigate some of these pressures, but the overall cost of living often makes it difficult for seniors to maintain their standard of living.
Solutions must consider their specific needs, like accessible housing options and affordable healthcare.
Impact on Vulnerable Populations
Beyond low-income families and seniors, other vulnerable populations like single parents, immigrants, and people with disabilities also face unique challenges. The rising cost of living can exacerbate existing disparities, impacting their ability to access education, employment opportunities, and essential services. Progressive policies aimed at reducing inequality need to account for these specific needs to ensure equitable outcomes.
Disproportionate Impact of Cost of Living Crisis
| Demographic Group | Specific Impact | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Low-income families | Limited access to affordable housing, food insecurity, and difficulty affording necessities. | Families may have to choose between paying rent and buying groceries, leading to malnutrition and health issues. |
| Seniors | Strain on fixed incomes due to rising housing costs, healthcare expenses, and transportation costs. | Seniors may have to choose between paying for medications and other essential needs. |
| Single parents | Difficulty balancing work and childcare responsibilities with rising living expenses. | Single parents may have to take on multiple jobs to make ends meet, impacting their ability to provide adequate childcare. |
| Immigrants | Difficulty integrating into the community due to high housing costs and language barriers. | Immigrants may struggle to find affordable housing, which can affect their ability to find employment and access resources. |
| People with disabilities | Increased costs of specialized care and support services. | The cost of assistive technology, therapy, and other necessary services can place a significant burden on individuals with disabilities and their families. |
Alternative Perspectives and Solutions
California’s high cost of living, intertwined with progressive policies, presents a complex challenge. Finding solutions requires a nuanced understanding of the interplay between economic realities and social ideals. Simply increasing taxes or decreasing social programs isn’t a sustainable or equitable solution. Innovative approaches, addressing both affordability and social justice, are essential for a thriving future.Addressing the high cost of living necessitates a multi-faceted approach, considering various factors like housing, transportation, and the overall economic climate.
Progressive policies, while aiming for social good, must be examined for their potential impact on affordability and their unintended consequences. Finding the right balance between these competing priorities is crucial for long-term prosperity.
Potential Solutions to Mitigate High Cost of Living
California’s high cost of living is a multifaceted problem, requiring a comprehensive solution. Addressing affordability demands considering multiple levers of influence, from regulatory changes to economic incentives. Innovative solutions might include exploring zoning regulations, increasing housing supply, and investing in public transportation.
- Expanding Housing Supply: Increasing the supply of affordable housing is paramount. This can be achieved through various means, including streamlining permitting processes, incentivizing developers to build affordable units, and exploring innovative housing models like tiny homes or co-housing. Regulations can be adjusted to promote density in appropriate areas, while still considering community needs and environmental impact.
- Improving Transportation Infrastructure: A robust public transportation system can reduce reliance on cars, easing traffic congestion and lowering transportation costs. Increased investment in light rail, bus rapid transit, and bike lanes can make commuting more affordable and environmentally friendly. Dedicated funding for these projects and incentives for using public transit could be implemented.
- Controlling Housing Speculation: Speculative buying of properties, particularly in high-demand areas, often contributes to inflated housing prices. Regulations to curb this practice, such as limits on investment properties or higher taxes on vacant properties, could help stabilize the market. Monitoring housing transactions and applying stricter regulations to prevent artificial price hikes is essential.
Adjusting Progressive Policies for Affordability
Progressive policies are designed to address societal inequities, but their implementation can sometimes have unforeseen economic consequences. Examining these policies through the lens of affordability can lead to necessary adjustments.
Walter’s California is facing a tough dilemma: high living costs clashing with progressive policies. Figuring out how to balance these competing forces is a real challenge. Luckily, there are tools like the best AI presentation makers, like these , that can help policymakers visualize and communicate complex solutions to the public. Ultimately, finding affordable housing solutions while upholding progressive ideals will be key to a better future for all residents.
- Targeted Financial Assistance: Instead of broad-based tax increases, targeted financial assistance programs could help low- and moderate-income families cope with rising costs. These programs could include direct subsidies for housing, transportation, or childcare, or tax credits specifically for lower-income households. The focus should be on providing relief without creating dependency or creating disincentives to work.
- Incentivizing Affordable Housing Development: Tax breaks or subsidies for developers who construct affordable housing units can encourage a greater supply. These incentives can be designed to target specific housing types and locations where the need is greatest, maximizing their effectiveness. Careful planning and community engagement are key to ensure these incentives benefit the community as a whole.
- Re-evaluating Property Tax Policies: Re-evaluating property tax policies to account for the increased cost of living is crucial. Adjustments could include implementing tiered tax rates or reducing the burden on lower-income homeowners. The goal should be to maintain the revenue needed for essential services while easing the burden on those most affected by rising costs.
Incentives and Disincentives to Address Affordability
Incentives and disincentives play a vital role in shaping behavior and encouraging the desired outcomes.
- Incentivizing Workforce Housing: Incentivizing employers to provide workforce housing or contribute to employee housing costs can help employees stay in the area and avoid displacement. Subsidized housing or employer-sponsored housing programs can reduce employee housing costs.
- Disincentivizing Speculative Investment: Disincentivizing speculative investment in housing markets through increased taxes on vacant properties or limitations on investment purchases can help stabilize prices and encourage development of housing for residents, rather than investors. Effective regulations can significantly impact price fluctuations and create more stability in the market.
Effectiveness of Proposed Solutions
| Solution | Potential Effectiveness | Potential Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Expanding Housing Supply | High potential for lowering housing costs, increasing supply | Potential for environmental concerns, community opposition, and slow implementation |
| Improving Transportation Infrastructure | High potential for lowering transportation costs, improving accessibility | High upfront costs, potential for NIMBYism (Not In My Backyard), and political opposition |
| Controlling Housing Speculation | Potential for stabilizing housing prices | Potential for legal challenges, difficulty in enforcement, and impact on investment |
| Targeted Financial Assistance | High potential for direct impact on affordability for lower-income families | Potential for administrative complexities, concerns about misuse of funds, and long-term sustainability |
Illustrative Examples

California’s high cost of living presents a unique challenge when juxtaposed with progressive policies aimed at social equity and environmental sustainability. This tension highlights a broader issue: how to balance ambitious societal goals with economic realities. Examining successful strategies employed elsewhere offers valuable insights into potential solutions for California.Looking beyond state lines, we find that various regions have tackled similar conflicts.
Understanding their approaches provides a framework for adapting effective strategies to the California context. It’s important to acknowledge that each situation is unique, requiring tailored solutions rather than simple replication.
Successful Policies in Other Regions
Successful policies often address the cost of living by focusing on affordable housing initiatives and robust job creation strategies. Some regions have implemented policies like rent control, which, while controversial, aims to mitigate rising housing costs. Others have focused on incentivizing affordable housing developments through tax breaks or subsidies. This approach often involves a collaborative effort between government, developers, and community organizations.
Case Studies: Successful and Unsuccessful Policies
| Policy Area | Successful Example (Region) | Unsuccessful Example (Region) | Key Factors for Success/Failure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Affordable Housing | Denmark (focus on public housing and rental subsidies) | Some US cities with overly restrictive zoning regulations (hindering development) | Denmark’s success stemmed from government support and incentives, unlike some US cities where regulations stifled supply. |
| Job Creation | Germany (strong vocational training and emphasis on skilled labor) | Some US states with inadequate workforce development programs (failing to address specific labor demands) | Germany’s focus on vocational training and skilled labor development created a robust job market, while some US states lacked the necessary programs. |
| Environmental Regulations | Norway (taxing carbon emissions and investing in renewable energy) | Some US states with conflicting regulations and inadequate infrastructure for green technologies | Norway’s comprehensive approach to environmental policy, including carbon taxation, led to successful transitions, contrasting with some US states where policies lacked cohesion or infrastructure support. |
The table above highlights varying approaches to similar challenges. Note that the success or failure of a policy often hinges on the specific context, including local demographics, economic conditions, and political will. There’s no one-size-fits-all solution.
Adapting Successful Solutions
California can adapt successful policies from other regions by considering their specific strengths and tailoring them to its unique circumstances. For instance, Denmark’s focus on affordable housing and rental subsidies could be adapted to create a mix of public and private housing initiatives in California. Furthermore, the German model of robust vocational training can inform California’s efforts to address skills gaps in high-demand industries.
Careful consideration of the historical and cultural contexts is critical. This involves understanding the complexities of California’s political and economic landscapes, considering how policies are received by various stakeholders, and acknowledging the potential for unintended consequences.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, California’s struggle with balancing high living costs against progressive policies highlights a significant challenge. The tension between affordability and social programs necessitates innovative solutions. The article has explored various aspects of this complex issue, from historical context to the disproportionate impact on different demographics. The potential solutions range from adjusting existing policies to adopting alternative approaches, and case studies from other regions will be examined to glean valuable insights.
Ultimately, finding a sustainable path forward requires thoughtful consideration of all perspectives and a willingness to adapt existing policies to ensure that California’s progressive ideals are attainable for all its residents.





