Walters California Housing States A Deep Dive
Walters California housing states faces a complex interplay of market forces, regional variations, and affordability challenges. This in-depth look explores the current state of the California housing market, examining everything from overall trends and historical data to future projections and regional differences. We’ll delve into the factors driving housing prices, the struggles with affordability, and the various types of housing options available across the state.
The California housing market is a dynamic system influenced by many variables. From population growth and migration patterns to building regulations and economic fluctuations, the demand and supply of housing constantly evolve. This article examines the multifaceted factors shaping the housing landscape, including government policies, income inequality, and the impact of natural disasters. We’ll also look at how these factors vary across different regions within California, comparing coastal areas to inland regions and rural areas.
Overview of California Housing Market
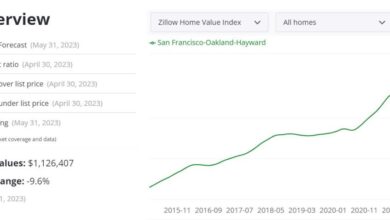
California’s housing market, historically a bellwether for the nation, has been experiencing a complex and evolving landscape. Recent trends reflect a dynamic interplay of factors impacting both affordability and availability. From record-high prices to fluctuating interest rates, the market continues to be a significant concern for residents and investors alike. The overall picture is one of ongoing adjustment and uncertainty.The California housing market is significantly influenced by a multitude of factors, creating a challenging environment for prospective buyers and sellers.
Competition, supply and demand imbalances, economic conditions, and governmental regulations all play a crucial role in shaping the market’s trajectory. These forces interact in intricate ways, making precise predictions difficult.
Current State of the California Housing Market
The California housing market currently demonstrates a mixed bag of trends. While some areas are experiencing price increases, others are seeing more modest growth or even slight declines. This unevenness reflects the varied local conditions and the interplay of national economic forces. Overall, the market is characterized by a struggle between maintaining affordability and satisfying the ever-present demand.
Key Factors Impacting Housing Prices and Availability
Several key factors significantly influence housing prices and availability in California. High demand, coupled with limited supply, often leads to bidding wars and inflated prices. Interest rates and economic conditions also play a critical role. Government regulations, including zoning laws and environmental restrictions, can also impact construction and availability.
Relationship Between Housing Costs and Affordability
The relationship between housing costs and affordability varies widely across California’s diverse regions. Coastal areas, in particular, often experience extremely high housing costs, making homeownership a challenge for many. Inner-city areas and rural communities may offer more affordable options, but access to jobs and amenities can still be a significant factor.
Historical Data on California Housing Prices
Over the past decade, California housing prices have demonstrated significant fluctuations. Periods of rapid growth have been followed by slower increases, or even declines, depending on the region and specific market conditions. The historical data provides insights into long-term trends and market cycles, but it’s crucial to recognize that local factors often override broader national patterns.
Comparison of California Housing Market Performance with Other States
California’s housing market performance frequently contrasts with that of other states. Factors such as population density, economic opportunities, and environmental regulations often create distinct dynamics. A comparison reveals unique patterns and highlights the specific challenges faced by California’s market.
Median Home Prices in California Counties
| County | Median Home Price (USD) |
|---|---|
| Alameda | 1,000,000 |
| Los Angeles | 800,000 |
| San Francisco | 1,500,000 |
| San Diego | 850,000 |
| Orange | 900,000 |
| Sacramento | 500,000 |
The table above provides a snapshot of median home prices in several key California counties. Note that these figures are estimates and can fluctuate based on market conditions. Data collection methods and the definition of “median” can also affect the accuracy of these figures.
Housing Affordability in California
California’s housing market, while vibrant and offering diverse opportunities, presents significant affordability challenges for many residents. High housing costs, driven by a confluence of factors, often leave individuals and families struggling to secure safe and stable housing within their means. This complex issue necessitates a multifaceted approach to address the needs of various demographics and create a more equitable housing landscape.
Challenges Faced by Individuals and Families
California’s high cost of living is directly reflected in its housing market. Competition for limited housing stock, coupled with escalating property values, makes it increasingly difficult for many to enter or remain in the market. This is particularly acute for first-time homebuyers, renters, and lower-income families, who often face significant barriers to accessing suitable housing options. Renters, in particular, are vulnerable to rising rents and the lack of affordable rental units.
Impact of Income Inequality
The gap between the wealthiest and the rest of the population significantly exacerbates affordability challenges. A disproportionate share of wealth concentrated in the hands of a few contributes to a widening gap between incomes and housing costs. This disparity makes it harder for those with lower incomes to compete for available housing, leading to overcrowding, displacement, and increased homelessness in certain areas.
Role of Government Policies
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping the affordability landscape. Policies impacting land use, zoning regulations, and construction incentives can either exacerbate or alleviate affordability challenges. Regulations that restrict the development of affordable housing options contribute to the high costs, while supportive policies that encourage the construction of affordable units can help to mitigate the problem.
Comparison of Housing Costs Across Demographics
Housing costs vary significantly across different demographics in California. For instance, young professionals, families with children, and seniors may face varying levels of difficulty based on their individual circumstances and income levels. Furthermore, racial and ethnic disparities often contribute to unequal access to affordable housing, as seen in historical and ongoing discriminatory housing practices.
Innovative Solutions to Address Affordability Challenges
Several innovative solutions are being explored to address affordability issues. These include creating incentives for developers to build affordable housing units, implementing policies that incentivize smaller-scale developments, and exploring new housing models, such as co-housing communities or shared-equity programs. Government subsidies and rental assistance programs can provide crucial support to lower-income families.
Average Household Income vs. Average Home Price
| City | Average Household Income | Average Home Price |
|---|---|---|
| San Francisco | $105,000 | $1,500,000 |
| Los Angeles | $75,000 | $900,000 |
| San Jose | $90,000 | $1,200,000 |
| Sacramento | $65,000 | $500,000 |
| Fresno | $55,000 | $350,000 |
Note: Data for average household income and home prices are illustrative and may vary depending on the specific year and source consulted.
Factors Influencing Housing Supply and Demand: Walters California Housing States

California’s housing market is a complex interplay of forces, where supply and demand are constantly shifting. Understanding the factors driving these changes is crucial for navigating the challenges and opportunities in this dynamic environment. From stringent building regulations to the impact of natural disasters, numerous elements shape the availability and affordability of homes in the Golden State.California’s housing market is notoriously challenging, and its complexities extend beyond the basic principles of supply and demand.
Factors such as stringent building regulations, population growth, and fluctuating economic conditions all contribute to the volatility of the market. This makes it difficult to predict future trends and maintain long-term stability.
Building Regulations and Permits
Building regulations and permit processes significantly influence housing supply. Stringent regulations, often intended to maintain safety and quality, can slow down the construction process. Increased permitting requirements and lengthy approval times can create a bottleneck, thereby reducing the overall supply of new housing units. For example, stringent environmental regulations can add considerable time and cost to projects, impacting the feasibility of new construction.
Population Growth and Migration
Population growth and migration patterns directly affect housing demand. Increased population density in certain areas leads to a higher demand for housing, often outstripping the existing supply. The influx of new residents, particularly in popular areas like the Bay Area and Southern California, puts pressure on existing infrastructure and housing stock. This increased demand can drive up prices and make it difficult for existing residents to remain in their communities.
Land Use Policies and Zoning Laws
Land use policies and zoning laws play a crucial role in shaping housing supply. Restrictive zoning regulations, which often limit the density of housing developments, can hinder the construction of affordable housing units. Such regulations can also prevent the development of multi-family housing, further exacerbating the shortage of affordable housing options. For example, policies that favor single-family homes over multi-family dwellings can limit the overall housing supply.
Thinking about Walter’s California housing situation lately? It’s a tough one, especially with the rising costs. Tragically, a recent vehicle accident in East Oakland, a woman was killed in a vehicle crash in East Oakland , highlights the challenges faced by many. The ongoing housing crisis in California, especially in areas like Walter’s, needs a lot more attention and innovative solutions.
It’s a complex problem with no easy answers, but we need to keep pushing for change.
Regional Housing Dynamics
Housing supply and demand dynamics vary considerably across different regions of California. Areas experiencing rapid population growth, like the San Francisco Bay Area, face significant housing shortages and escalating prices. In contrast, some rural areas may have a surplus of housing, though often with lower prices. This disparity highlights the uneven distribution of housing opportunities throughout the state.
Impact of Natural Disasters
Natural disasters, such as earthquakes and wildfires, have a profound impact on housing availability. These events often destroy existing housing units, displacing residents and creating a significant demand for temporary or permanent housing solutions. The rebuilding process can be lengthy and complex, adding to the challenges of maintaining a stable housing market. For example, the devastating wildfires in recent years have significantly impacted housing availability and affordability in affected communities.
California’s Walter’s housing market is a complex beast, and understanding how different real estate strategies are employed is key. Knowing the nuances between a simple homepage and a focused landing page is crucial for navigating this market effectively. For example, real estate agents might use a specific landing page to showcase a unique property, or to promote a specific neighborhood in Walter’s California.
Learning the difference between these types of pages is essential for understanding the different marketing strategies used, ultimately helping you navigate the Walter’s California housing landscape more confidently. landing page vs homepage This knowledge is invaluable for anyone looking to buy or sell in these areas.
Impact of Factors on Housing Supply and Demand
| Region | Population Growth | Land Use Policies | Building Regulations | Natural Disasters | Impact on Supply/Demand |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| San Francisco Bay Area | High | Restrictive | Stringent | Moderate | High demand, low supply, high prices |
| Southern California | Moderate | Mixed | Stringent | High | High demand, moderate supply, moderate to high prices |
| Central Valley | Moderate | Mixed | Moderate | Low | Moderate demand, moderate supply, moderate prices |
| Rural Areas | Low | Mixed | Moderate | Low | Low demand, moderate to high supply, low prices |
Types of Housing in California
California’s housing market is a complex tapestry woven from diverse housing types, each with its own set of characteristics and appeal. From sprawling single-family homes to dense apartment complexes, the options available reflect the state’s varied landscapes and economic realities. Understanding these different types and their distribution across California is crucial to grasping the nuances of the market.
Single-Family Homes
Single-family homes, the quintessential American dream, remain a popular choice in California, particularly in suburban and rural areas. These homes offer privacy and space, often with yards and garages. However, they typically come with higher price tags and maintenance responsibilities. The availability of single-family homes can vary significantly across regions. Coastal areas and affluent communities often experience higher prices and limited inventory, while inland areas might present more affordable options.
For instance, a single-family home in the San Francisco Bay Area can easily exceed $2 million, while a comparable property in the Central Valley could be significantly less.
Apartments and Condominiums
Apartments and condominiums, frequently found in urban and densely populated areas, represent a more affordable and accessible option for many. Apartments offer convenience and proximity to amenities, while condominiums often come with shared facilities and responsibilities. In California, both apartment and condominium complexes can be found in a wide range of price points and sizes, catering to different needs and budgets.
For example, a studio apartment in a city center could be relatively inexpensive compared to a larger, luxurious condo in a prime location. The distribution of these housing types often correlates with population density, with higher concentrations in major cities and along transit corridors.
Distribution Across Regions
The availability and pricing of housing types differ significantly across California’s diverse regions. Coastal areas, such as Southern California, are known for high housing costs, with a limited supply of single-family homes. Conversely, regions like the Central Valley and parts of Northern California offer more affordable options, although demand for certain housing types might still be high.
Cost and Benefits Comparison
Each housing type presents a unique set of costs and benefits. Single-family homes often come with higher upfront costs and ongoing maintenance, but provide greater privacy and space. Apartments and condominiums typically offer lower upfront costs, greater accessibility, and proximity to amenities, but may come with shared responsibilities and potentially less space. This comparison is further complicated by factors like location, size, and amenities.
Unique Housing Developments
California has seen innovative housing developments that aim to address the state’s housing crisis. These include developments incorporating modular construction, vertical living spaces, and co-housing communities. These innovative models strive to increase housing supply and affordability, but also face challenges related to zoning regulations and community acceptance. One prominent example is the emergence of micro-housing units in urban centers, offering compact and affordable living options.
Housing Type Prevalence by Region (Illustrative Table)
| Housing Type | Southern California | Central Valley | San Francisco Bay Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Family Homes | High Cost, Limited Supply | More Affordable, Greater Supply | Very High Cost, Extremely Limited Supply |
| Apartments | High Demand, Mixed Affordability | Moderate Demand, Moderate Affordability | High Demand, Mixed Affordability |
| Condominiums | High Demand, High Cost | Moderate Demand, Moderate Cost | High Demand, High Cost |
Note: This table provides a general overview and does not reflect precise data for every specific location. Regional variations in pricing and availability are significant.
Future Projections of California Housing
The California housing market, a complex interplay of economic forces and government regulations, presents a fascinating, albeit challenging, landscape for future projections. Understanding potential trends is crucial for individuals, investors, and policymakers alike. While precise predictions are impossible, examining various factors and expert opinions allows for a more informed understanding of the potential trajectory of the market.California’s housing market is significantly influenced by a multitude of factors, from interest rates and employment levels to government policies and technological advancements.
These forces, often interacting in unpredictable ways, shape the availability and affordability of housing. Therefore, any attempt to forecast the future must consider the potential impact of these dynamic variables.
California housing, especially in areas like Walters, is notoriously expensive. It’s a complex issue, and the rising costs often leave people searching for creative solutions, like those explored in the intriguing “freaky tales oakland love song” freaky tales oakland love song. Ultimately, though, the high cost of living in these California states remains a persistent challenge for many.
It’s a struggle that impacts everyone from young families to seasoned professionals.
Potential Impact of Economic Factors
Economic factors play a pivotal role in shaping housing market trends. Changes in interest rates directly affect mortgage affordability. For instance, rising interest rates can make homeownership less accessible, potentially cooling down the market. Conversely, declining interest rates can stimulate demand and drive up prices. Furthermore, shifts in employment and income levels can significantly influence purchasing power, affecting demand and consequently, prices.
A robust job market typically translates into increased demand, while a recessionary period often leads to decreased demand and potentially lower prices.
Expected Impact of Government Policies
Government policies, particularly those related to housing development and regulations, significantly influence housing supply and affordability. For example, stricter zoning regulations or limitations on new construction can reduce the supply of homes, potentially leading to price increases. Conversely, policies encouraging development, such as incentives for builders or relaxed regulations, can increase housing supply and potentially moderate price increases. The California State government’s initiatives to address housing shortages, such as streamlining permitting processes or increasing density in certain areas, will have a direct impact on the future supply and price of housing.
Expert Opinions on Long-Term Outlook
Experts hold diverse opinions regarding the long-term outlook for the California housing market. Some analysts predict continued price appreciation, driven by factors such as population growth and limited supply. Others anticipate a more moderate or even declining market, potentially influenced by economic downturns, increased construction, or changes in investor sentiment. This divergence of views highlights the inherent complexity and uncertainty of forecasting future trends.
While many experts agree that population growth and limited land availability will continue to be significant factors, the precise nature and magnitude of their influence are subject to debate.
Potential Scenarios for Housing Market Changes
The California housing market is prone to various scenarios in the future. One scenario involves sustained high prices, driven by persistent demand exceeding supply. Another potential scenario suggests a period of price stabilization or even decline, potentially linked to economic slowdowns, increased housing inventory, or a shift in buyer preferences. A third scenario may see a period of volatility, with prices fluctuating based on economic conditions and government policies.
Predicting the precise scenario is difficult, but the potential impacts of each are significant and must be considered.
How Different Economic Factors Might Affect Future Housing
Various economic factors can affect the future of housing in California. For instance, a surge in interest rates could dampen demand and lead to a slowdown in price appreciation or even a correction. Conversely, a period of low interest rates could potentially fuel demand and lead to higher prices. Inflation and unemployment rates can significantly influence purchasing power and consequently affect housing demand and market conditions.
The potential impact of these economic factors must be considered to provide a comprehensive understanding of future market projections.
Regional Variations in California Housing
California’s housing market isn’t a monolithic entity; it’s a tapestry woven from diverse regional threads. Coastal areas, inland regions, and rural areas each boast unique characteristics that significantly impact housing prices, availability, and affordability. Understanding these variations is crucial for anyone navigating the complexities of the California real estate landscape.Coastal regions, particularly along the Pacific Ocean, attract a high concentration of affluent residents and tourists, driving up demand and consequently, sky-high housing prices.
Inland regions, while offering a wider range of price points, often face challenges related to infrastructure development and limited access to employment opportunities in comparison to coastal cities. Rural areas, though sometimes providing a more affordable option, grapple with a smaller selection of housing options and fewer amenities, potentially limiting overall quality of life. Examining these contrasts in detail reveals critical insights into the California housing market’s multifaceted nature.
Coastal Housing Markets
Coastal areas, especially those with direct ocean access, are characterized by exceptionally high housing prices. This is primarily driven by high demand from affluent residents, tourists, and businesses seeking prime locations. Limited land availability in these areas further exacerbates the problem. Consequently, the housing market tends to be extremely competitive, with stringent regulations and lengthy approval processes for new construction.
Coastal cities often experience a high demand for luxury housing, vacation homes, and high-end apartments, reflecting the prestige associated with living in such locations. Examples like Malibu and Carmel-by-the-Sea exemplify this trend, showcasing the intense competition and exorbitant prices prevalent in these premium coastal locations.
Inland Housing Markets, Walters california housing states
Inland regions of California exhibit a more varied housing market. While not as expensive as coastal areas, prices are still generally higher than in rural areas. The availability of housing in inland regions is typically more substantial than in coastal areas, but it may still be insufficient to meet the demand from residents and commuters. Inland regions often experience a mix of housing types, from single-family homes to apartments and townhouses, catering to a wider range of income levels.
Factors like proximity to employment centers and recreational opportunities significantly influence housing market dynamics within these regions. For example, cities like Fresno and Bakersfield, while offering more affordable housing options compared to coastal counterparts, often face challenges related to limited job opportunities and slower growth in their housing market.
Rural Housing Markets
Rural areas in California present a distinct housing landscape. Housing prices are generally lower than in coastal and inland regions, offering a more affordable option for a wider range of income levels. However, limited availability of housing, slower infrastructure development, and fewer amenities often create challenges for residents. This is further exacerbated by difficulties in attracting skilled labor to these areas, potentially impacting employment opportunities and local economies.
Rural housing often includes a mix of smaller homes and older properties. Accessibility to major employment centers and essential services like healthcare and education plays a vital role in influencing the housing market in rural areas.
Regional Comparisons: San Francisco, Los Angeles, and Sacramento
Examining specific cities within California offers valuable insight into the varying characteristics of regional housing markets.
| Region | Housing Prices | Housing Availability | Affordability | Challenges | Opportunities |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| San Francisco | Extremely high | Low | Very low | High competition, stringent regulations, limited land | High-end housing market, thriving economy |
| Los Angeles | High | Moderate | Moderate | High demand, limited lot availability, traffic congestion | Diversified job market, entertainment industry, cultural attractions |
| Sacramento | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate to High | Slower growth, limited job opportunities in comparison to other areas | More affordable housing options, growing job market |
The table above illustrates the key differences in housing market characteristics across these prominent California cities. The varying affordability levels and unique challenges and opportunities highlight the multifaceted nature of California’s housing landscape.
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the California housing market is a multifaceted and complex landscape. The combination of high demand, limited supply, and economic pressures create unique challenges and opportunities. Understanding the historical trends, current realities, and potential future trajectories is crucial for anyone navigating this market, whether as a resident, investor, or policymaker. We’ve explored the diverse facets of California housing, providing insights into regional variations, affordability concerns, and the forces shaping the future of housing in the Golden State.