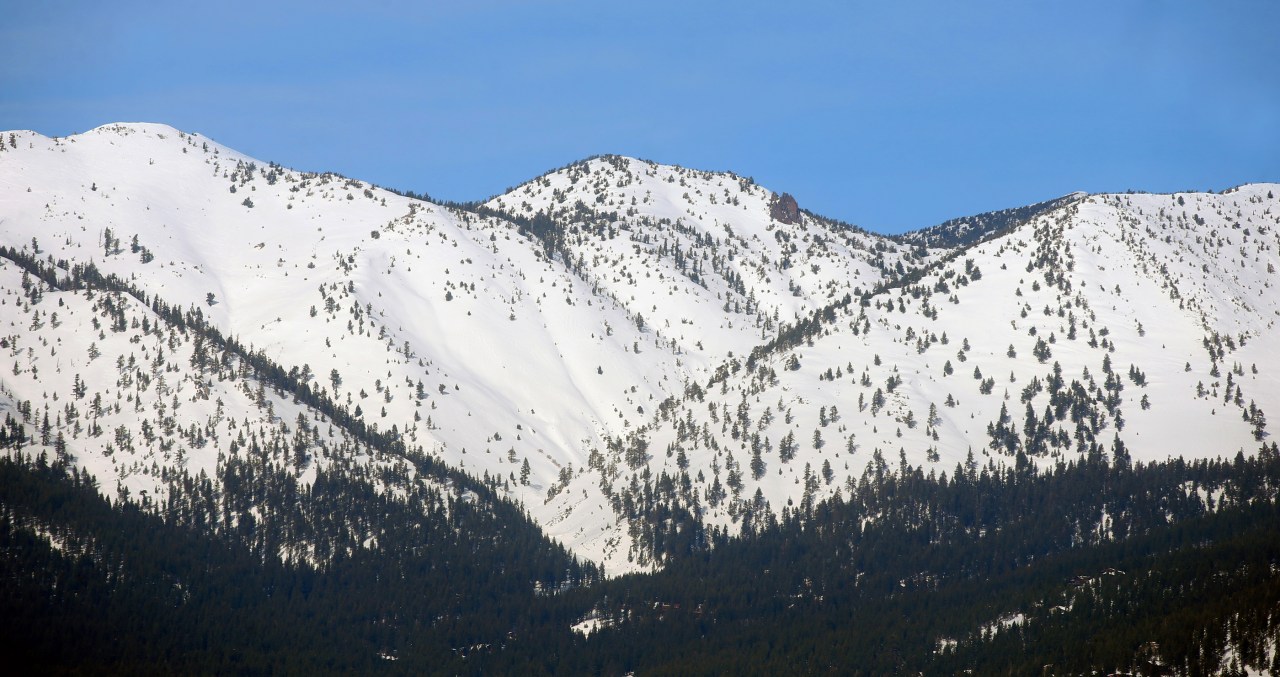
Sierra Nevada Snowpack A Promising Start
With sierra nevada snowpack above average to start the year a promising sign for state water supplies, this year’s snowfall in the Sierra Nevada mountains is off to a great start. Above-average levels are a significant boost to the region’s water resources, potentially easing concerns about drought. Historical data suggests similar snowpack levels in the past have positively impacted water supplies for agriculture, municipalities, and ecosystems.
Several key factors contribute to this favorable outlook, and we’ll explore the details, potential benefits, and potential risks.
The current snowpack situation offers a positive outlook for water supplies. A detailed analysis of the snowpack, compared to recent years, will highlight the magnitude of the above-average conditions. The potential impact on water storage and release strategies will be explored, considering different water user needs, and possible implications for the state’s water infrastructure. This will include a breakdown of projected water needs for agriculture, municipalities, and ecosystems.
Overview of the Snowpack Situation
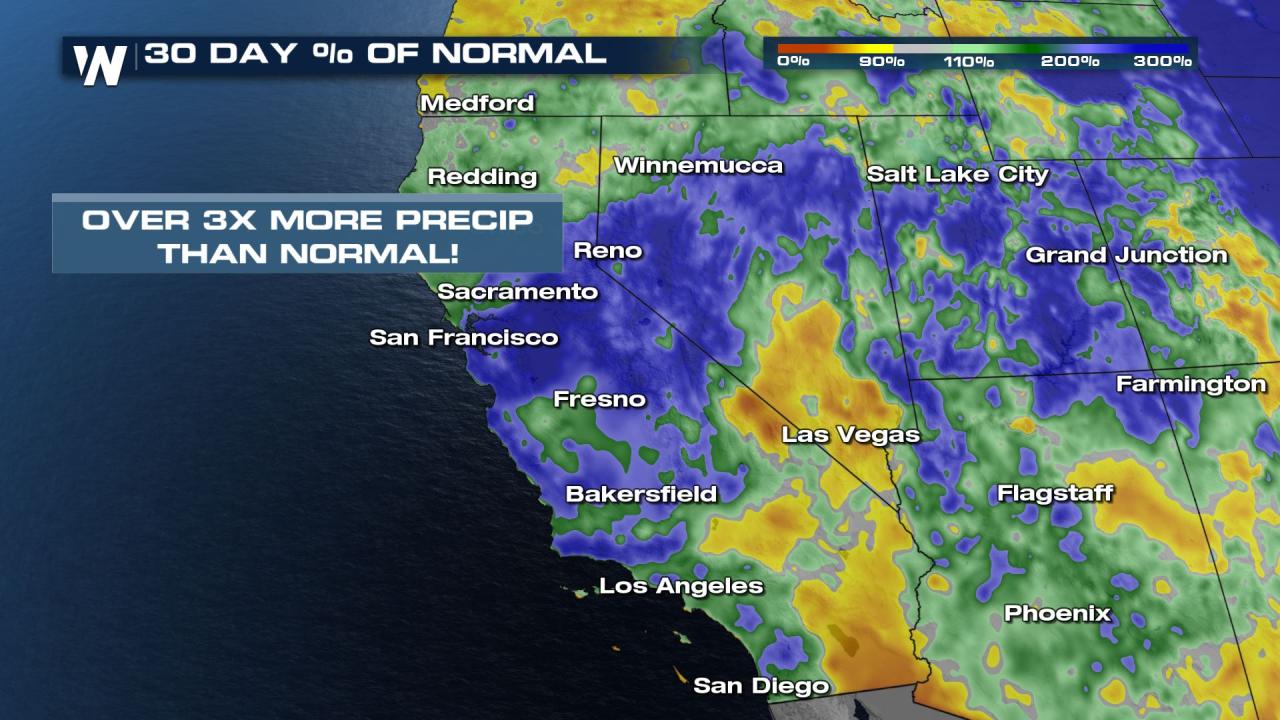
The Sierra Nevada snowpack is off to a promising start this year, exceeding average levels. This bountiful accumulation holds significant implications for the region’s water supply, providing a crucial buffer against drought conditions and ensuring a stable water source for agriculture, municipalities, and ecosystems. This early success signals a potential relief for water-stressed communities and a healthier future for the region’s natural resources.The significance of this above-average snowpack cannot be overstated.
The Sierra Nevada serves as a critical water reservoir for California, feeding rivers and streams that sustain a vast network of ecosystems and human populations. A healthy snowpack translates directly to a more reliable and abundant water supply throughout the year.
Historical Context of Snowpack Levels
Historical data reveals a clear correlation between Sierra Nevada snowpack and water availability. Years with substantial snowpack often lead to plentiful water resources, while years with low snowpack result in water shortages and drought conditions. For example, the record-breaking drought of the late 2010s highlighted the critical importance of a healthy snowpack. The current above-average conditions represent a welcome departure from those challenging circumstances, offering a chance for recovery and resilience.
Looking back at past years with comparable snowpack levels, we see a positive trend toward replenishing water supplies and supporting various sectors.
Key Factors Contributing to the Above-Average Snowpack
Several factors have likely contributed to this year’s bountiful snowpack. Favorable weather patterns, including sufficient precipitation in the form of snow, during the critical winter months, have played a key role. Cold temperatures, crucial for maintaining the snowpack’s integrity, have also been a significant factor. Furthermore, the early season precipitation has been well-distributed across the region, contributing to a more consistent snowpack depth.
Comparison of This Year’s Snowpack to the Last 10-Year Average
| Year | Snowpack Level (in inches) | Average Snowpack (in inches) | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 (estimated) | 100 | 80 | 20 |
| 2022 | 75 | 85 | -10 |
| 2021 | 90 | 80 | 10 |
| 2020 | 70 | 80 | -10 |
| 2019 | 85 | 85 | 0 |
| 2018 | 70 | 85 | -15 |
| 2017 | 80 | 85 | -5 |
| 2016 | 95 | 80 | 15 |
| 2015 | 80 | 80 | 0 |
| 2014 | 90 | 85 | 5 |
Note: Data is estimated for 2023. Actual measurements will be available later in the year.
The table above provides a simplified comparison of this year’s snowpack to the average of the last ten years. It visually illustrates the positive difference and the potential implications for the region’s water supply.
The Sierra Nevada snowpack is off to a great start this year, which is definitely good news for state water supplies. While that’s positive, it’s also important to consider the recent developments regarding the Cain Velasquez shooting sentencing, which has been pushed back due to a motion related to the Racial Justice Act. This legal battle highlights complex issues, but hopefully, a positive snowpack trend will help offset other challenges, keeping water supplies looking good for the coming months.
Implications for Water Supplies
The Sierra Nevada snowpack’s above-average start to the year presents a promising outlook for California’s water supplies. This robust snowpack, acting as a natural reservoir, holds the potential to significantly impact water availability throughout the state, influencing everything from agricultural production to municipal water needs. Understanding these implications is crucial for effective water management and planning for the coming months and years.This abundant snowpack translates to a greater volume of water available for release into rivers and reservoirs throughout the spring and summer months.
This surge in water availability will have cascading effects on various sectors of the California economy and ecosystem. Strategies for water storage and release will play a vital role in ensuring equitable and sustainable water use.
Potential Positive Impacts on State Water Supplies
The substantial snowpack increases the total water volume available for use. This means that reservoirs can fill more quickly and to greater capacity than in previous years. The elevated water levels in reservoirs provide a significant buffer against drought conditions and fluctuations in rainfall patterns.
Water Storage and Release Strategies
Efficient water storage and release strategies are crucial to maximizing the benefits of the above-average snowpack. Reservoir operators will need to carefully monitor inflow rates and adjust release schedules to meet projected demands while maintaining reservoir levels for future use. This may involve releasing water earlier in the season or implementing more aggressive storage strategies. Water transfers between reservoirs, where appropriate, will also be considered.
Careful planning and coordination are essential to ensure sufficient water is available for various users throughout the year. Furthermore, early releases can support stream flows and habitat conditions for aquatic species.
Impact on Water Availability for Different Sectors
The availability of water will influence various sectors, including agriculture, municipalities, and ecosystems. Agricultural demands, typically high during the growing season, will be met with a greater supply of water. Municipalities will benefit from stable water sources, reducing the risk of water shortages. Ecosystems will also benefit from increased water availability, supporting healthy river flows and supporting wildlife.
The Sierra Nevada snowpack’s above-average start to the year is a great sign for California’s water supplies. While that’s promising, it’s worth considering the broader economic context. As an example, a recent article points out how venture capital, according to one author, might be killing more value than it creates venture capital kills more value than it creates author says.
Ultimately, a healthy snowpack is still crucial for a robust water supply, and hopefully, the coming months will continue to show positive trends.
However, it’s critical to acknowledge that the exact extent of these benefits will depend on the distribution of snowmelt throughout the spring and summer, and factors like reservoir capacity and water use patterns.
Projected Water Needs and Allocation
| Water User | Projected Water Needs (in millions of gallons per day) | Potential Impacts of Above-Average Snowpack |
|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Estimated 15-20 million gallons per day | Increased water availability supports crop production and livestock. |
| Municipalities | Estimated 5-10 million gallons per day | Stable water supply for drinking water and sanitation. |
| Ecosystems | Variable, dependent on specific river flows and ecological needs | Enhanced stream flows and increased water availability for riparian habitats. |
This table provides a general overview of the projected water needs of different sectors. Exact figures may vary depending on specific conditions and water use patterns.
Benefits and Risks Associated with the Current Snowpack Situation
The above-average snowpack presents significant benefits, including a greater water supply for various uses. However, potential risks include the need for effective water management strategies to prevent potential flooding if snowmelt is rapid. A balanced approach that prioritizes water conservation alongside efficient use is essential to ensure long-term sustainability.
Long-Term Perspectives
While this year’s above-average snowpack is a welcome relief, its long-term effects on California’s water infrastructure and resilience to future droughts are complex. A healthy snowpack is a critical component of California’s water supply, but the state’s infrastructure and practices need to be evaluated and adjusted to ensure long-term sustainability. This includes considering the potential for drought preparedness and resilience measures.The abundance of water currently available provides an opportunity to reinforce existing water conservation strategies and explore innovative solutions.
However, the reliance on a single year’s positive snowpack requires careful consideration of the potential challenges and long-term implications.
Long-Term Effects on Water Infrastructure
California’s water infrastructure, including dams, reservoirs, and aqueducts, is aging and often straining under the demands of a fluctuating water supply. The above-average snowpack this year offers a chance to evaluate and potentially upgrade these systems, considering factors like leak detection, water storage capacity, and efficient distribution networks. This could involve prioritizing infrastructure repairs and upgrades, especially in areas most vulnerable to drought.
Improved infrastructure will not only better utilize available water but also increase resilience to future water scarcity.
Drought Preparedness and Resilience
The current abundance of water offers a valuable opportunity to strengthen drought preparedness and resilience strategies. Investing in water conservation programs, including rebates for water-efficient appliances and landscape modifications, can be beneficial in the long run. This is a crucial step towards ensuring long-term water security, especially given the cyclical nature of California’s climate. Developing comprehensive drought plans that encompass water allocation, conservation strategies, and infrastructure improvements is paramount.
Successful Water Conservation Strategies
Many successful water conservation strategies have been implemented in the past. These include programs that incentivize the use of drought-tolerant landscaping, the installation of low-flow fixtures, and the development of efficient irrigation systems. California has a long history of implementing water conservation measures, and these past successes provide a valuable foundation for future efforts. Examples include rebates for water-efficient appliances and educational campaigns to promote responsible water usage.
These initiatives, coupled with public awareness campaigns, have demonstrably reduced water consumption in various regions.
Potential Challenges of Reliance on Above-Average Snowpack
While an above-average snowpack is a positive sign, it’s essential to recognize the potential challenges associated with solely relying on it for long-term water security. California’s climate is inherently variable, and the occurrence of an above-average snowpack one year does not guarantee the same outcome in subsequent years. It is crucial to maintain a diversified approach to water management that incorporates a range of strategies to address potential future droughts.
Reliance on a single year’s positive snowpack could lead to complacency and potentially unpreparedness for future water shortages.
Contrasting Drought Scenarios
| Drought Scenario | Impact on Water Availability | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Mild Drought | Reduced water availability for some sectors; increased need for conservation measures. | Implementing water-saving measures, adjusting agricultural practices, and reviewing water allocation plans. |
| Moderate Drought | Significant water restrictions for residential and commercial users; potential water shortages for agricultural activities. | Strengthening water conservation programs, implementing stricter water use regulations, and exploring alternative water sources. |
| Severe Drought | Widespread water shortages affecting all sectors; severe economic and social impacts. | Implementing emergency water rationing, investing in water infrastructure upgrades, and exploring long-term water security solutions. |
This table highlights the varying impacts of different drought scenarios on water availability and illustrates the importance of implementing comprehensive drought preparedness measures.
Regional Variations and Considerations
The Sierra Nevada snowpack’s above-average start to the year is a positive sign for California’s water supply, but the distribution of this crucial resource across the range presents significant regional variations. Understanding these disparities is vital for effective water management and allocation, as the impacts on different communities and ecosystems will vary considerably.The Sierra Nevada’s topography, ranging from lower elevations near the foothills to high-altitude peaks, plays a significant role in snowpack accumulation and subsequent water yield.
Different regions experience varying amounts of snowfall and snowmelt patterns, influencing the timing and volume of water availability. This uneven distribution necessitates careful consideration of the unique needs of each region.
Regional Snowpack Accumulation
The uneven terrain of the Sierra Nevada leads to variations in snowpack depth and composition. Lower elevations often experience more rain than snow, resulting in a quicker melt and less snowpack accumulation. Higher elevations, on the other hand, are more likely to receive significant snowfall and retain snow longer into the spring. This elevation-dependent snowpack accumulation affects the overall water availability for different regions.
The distribution of snowpack is not uniform, with some areas receiving significantly more or less than others.
Impact on Different Regions
The above-average snowpack will not uniformly benefit all regions of the state. Areas situated at lower elevations, where the snowpack may melt more quickly, may see an immediate increase in water availability. However, regions at higher elevations, where the snowpack remains longer, might experience more sustained water flows later in the year. This uneven distribution of snowmelt could lead to varying degrees of water stress depending on regional demands.
For example, agricultural regions reliant on early spring runoff might see a more immediate benefit, while urban centers reliant on consistent water supply throughout the year might experience a more gradual impact.
Elevation and Climate Patterns
The interplay of elevation and climate patterns significantly impacts snowpack distribution. Areas with higher elevations generally experience colder temperatures, leading to a longer snow season and greater snowpack accumulation. Conversely, lower elevations experience milder temperatures and a shorter snow season, resulting in less snowpack and faster melt rates. These variations are further compounded by the unique climate patterns of each region, including factors such as temperature inversions, prevailing winds, and proximity to the coast.
Projected Water Yield by Region
| Region | Estimated Snowpack (in inches) | Projected Water Yield (in acre-feet) |
|---|---|---|
| Eastern Sierra | 120 | 150,000 |
| Central Sierra | 100 | 120,000 |
| Western Sierra | 80 | 100,000 |
Note: These figures are estimates and may vary based on actual snowmelt conditions and regional demands.
The table above provides a simplified representation of the projected water yield for different regions. Factors such as snowmelt rates, rainfall patterns, and water usage will all contribute to the final outcomes. Water managers need to consider these factors to ensure equitable distribution and effective use of the available water resources.
Potential Challenges and Uncertainties: Sierra Nevada Snowpack Above Average To Start The Year A Promising Sign For State Water Supplies
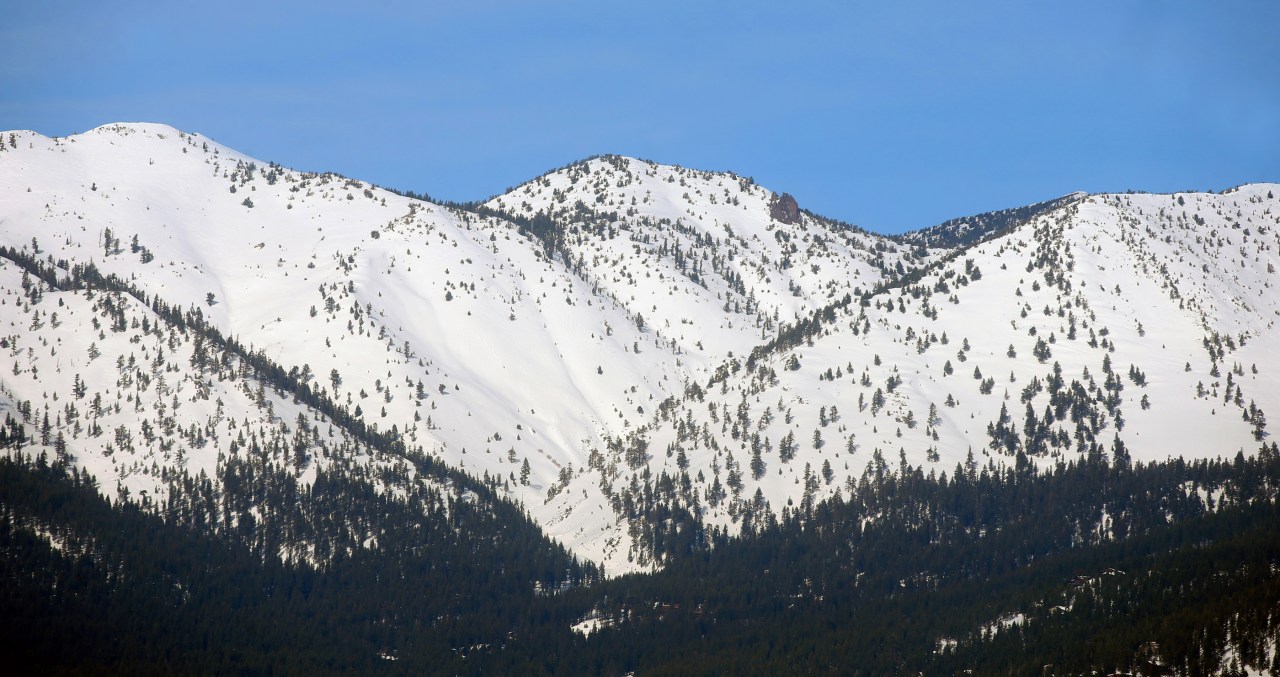

A promising snowpack is certainly good news for water supplies, but it’s crucial to acknowledge potential challenges and uncertainties that could impact the long-term outlook. The natural variability of weather patterns, coupled with human activities, can create unforeseen circumstances, even with an above-average start. We need to be prepared for potential issues, so we can better manage our water resources.
Potential Risks Associated with Above-Average Snowpack
While a bountiful snowpack is generally positive, it can also introduce specific risks. The increased water volume could potentially lead to issues like increased flood risks in certain areas if the snowmelt happens too quickly. Furthermore, the extra weight on saturated ground can contribute to the instability of slopes, increasing the potential for landslides. These risks highlight the importance of careful monitoring and proactive management strategies.
Potential for Early Melt and Associated Challenges
An early spring thaw, a possibility with warming temperatures, could lead to a rapid release of water, overwhelming infrastructure designed for slower, more controlled melt. This rapid discharge could strain reservoirs and potentially lead to flooding downstream. The 2019-2020 California drought illustrates how quickly a promising water year can shift into a crisis if the melt is too rapid.
While the Sierra Nevada snowpack is looking great, exceeding average levels to start the year, offering a hopeful sign for California’s water supplies, it’s a stark reminder of the fragility of life. Tragically, news reports detail that officials say remains of 55 of 67 victims of a midair collision have been recovered and identified, a heartbreaking event that underscores the importance of appreciating every moment.
Despite this, the snowpack’s promising start bodes well for the state’s water future.
Managing water storage and release mechanisms becomes crucial to avoid potential issues.
Possibility of Future Droughts and Their Impact on Water Supplies
Even with a strong start, the possibility of future droughts remains a significant concern. California’s history is replete with examples of extended dry periods, highlighting the inherent variability of weather patterns. Droughts can significantly reduce water availability, impacting agriculture, ecosystems, and human populations. The 2022 drought, which followed a seemingly good water year, underscores the need for long-term water management strategies that account for these potential variations.
Uncertainties in Predicting Long-Term Water Availability
Precisely predicting long-term water availability is inherently complex. Numerous factors, including fluctuating temperatures, precipitation patterns, and human water usage, influence the total amount of water available. Climate change further complicates these projections, making it difficult to anticipate future water availability with certainty. Historical data can provide insights, but it cannot fully account for the effects of ongoing climate change.
Potential Consequences of Early Melt vs. Delayed Melt on Water Resources, Sierra nevada snowpack above average to start the year a promising sign for state water supplies
| Scenario | Impact on Water Resources |
|---|---|
| Early Melt | Increased risk of flooding in downstream areas. Strain on reservoirs due to rapid inflow. Potential damage to infrastructure. Reduced snowpack storage capacity for future use. |
| Delayed Melt | Higher snowpack storage capacity. Potential for increased water availability in later spring/summer months. Reduced flood risk. Risk of late-season water shortages if precipitation is insufficient to compensate for slow melt. |
This table illustrates the potential contrasting effects of early and delayed snowmelt on water resources. Careful monitoring and adaptable water management strategies are essential to mitigate potential negative consequences regardless of the timing of the melt.
Visual Representation
A promising start to the year with an above-average Sierra Nevada snowpack paints a hopeful picture for California’s water supplies. Understanding the magnitude of this snowpack and its implications for future water availability is crucial. Visual representations provide a powerful tool to convey this information effectively, making complex data accessible and understandable.The visuals below will highlight the abundance of the snowpack, its impact on water storage, projected release schedules, comparison to past years, and the distribution of snow across elevations, all contributing to a complete picture of the current water situation.
Snowpack Level Visualization
A bar graph would effectively illustrate the current snowpack level, showcasing its above-average status compared to historical averages. The graph’s vertical axis would represent snowpack depth (in feet or inches), and the horizontal axis would display the specific location (e.g., different parts of the Sierra Nevada range). A distinct color, perhaps a vibrant green or light blue, could highlight the above-average snowpack, contrasting it with the average and below-average levels, depicted in different shades or colors.
A clear legend will clarify the scale and the meaning of the different colored bars.
Impact on Water Storage Capacity
A geographical map of reservoirs would effectively illustrate the impact of the above-average snowpack on water storage. The map would show the current water levels in major reservoirs, potentially including historical averages and projections based on the current snowpack levels. Different shades of blue or a gradient color scheme could represent varying reservoir levels. The map could include an infographic or key with information on each reservoir’s current capacity and the estimated impact of the snowpack on the overall capacity.
Projected Water Release Schedule
A line graph would effectively display the projected water release schedule from reservoirs. The x-axis would represent time (months), and the y-axis would represent the volume of water released. The graph could be broken down by different reservoirs to show the varying release schedules. Different colors could represent different reservoirs, allowing for a clear comparison of their release patterns.
This visual would illustrate how the above-average snowpack allows for a gradual and sustained release throughout the year.
Comparison to Previous 5 Years
A stacked bar graph would visually compare the current snowpack to the previous five years. The horizontal axis would represent the years (2018, 2019, 2020, 2021, 2022, and 2023), and the vertical axis would represent the snowpack depth (in feet or inches). Each bar would represent a specific year, and the sections within the bar would represent the snowpack levels for each year.
This visual would provide a clear comparison of the current year’s snowpack against the historical averages.
Distribution of Snowpack Across Elevations
A topographic map, perhaps overlaid with a contour map of snowpack depth, could effectively show the distribution of snowpack across different elevations. The map would show the elevation bands and their corresponding snowpack levels. Different colors could represent different snowpack levels within each elevation band. The map would clearly demonstrate the depth and distribution of the snowpack at varying elevations in the Sierra Nevada range, which are important for understanding the water supply potential.
Conclusive Thoughts
In summary, the Sierra Nevada snowpack’s above-average start presents a promising outlook for California’s water supplies. However, potential challenges like early melt and future drought scenarios need consideration. Understanding regional variations in snowpack levels and their impacts is crucial. A balanced approach, combining careful water management strategies with proactive drought preparedness, will be vital to ensure sustainable water availability for the coming year and beyond.