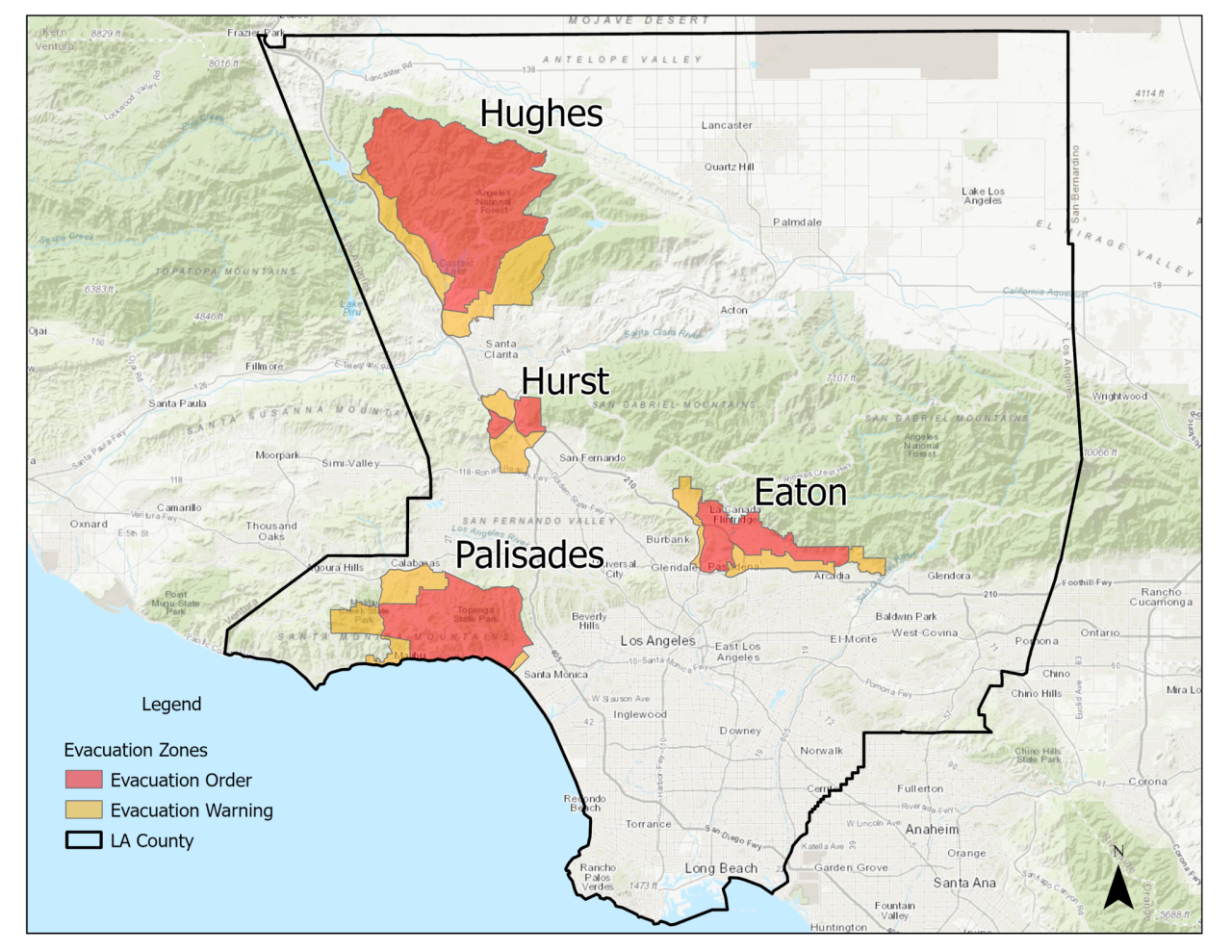
Map Palisades and Eaton Fire Perimeters & Evacuation Zones
Map Palisades and Eaton Fire perimeters and evacuation zones Artikel the affected areas, procedures, and resources for a safe response. This comprehensive guide details the fire’s impact, safety precautions, resource allocation, and communication strategies. Understanding the geographical boundaries and evacuation plans is crucial for residents and emergency personnel. This map will help everyone stay informed and prepared.
The document breaks down the critical zones, providing detailed descriptions, distances from the perimeter, and current evacuation status. Evacuation procedures for each zone are Artikeld, along with safety considerations and potential hazards. This comprehensive approach ensures that all stakeholders are equipped with the information needed to navigate the situation effectively.
Defining the Area
Following the Map Palisades and Eaton Fire events, precise delineation of the affected areas and evacuation zones is crucial for safety and resource allocation. This section provides a detailed breakdown of the fire perimeters and the corresponding evacuation zones.
Map Palisades Fire Perimeter
The Map Palisades Fire perimeter encompasses a roughly triangular area stretching from the confluence of the North Fork River and the East Fork River to the base of Mount Summit. The terrain is predominantly rugged and forested, with a mix of coniferous and deciduous trees. Significant elevation changes within the perimeter influence fire behavior and complicate access for firefighting efforts.
Eaton Fire Perimeter
The Eaton Fire perimeter, located approximately 15 miles southwest of the Map Palisades Fire, is characterized by a more linear shape. It extends from the western edge of the town of Eaton along the foothills of the Rocky Mountains. The perimeter is bordered by a mixture of residential areas, agricultural lands, and steep, rocky slopes. The presence of dry brush and wind patterns played a significant role in the fire’s rapid spread.
Geographical Coordinates
Precise geographical coordinates for the affected areas are critical for mapping and analysis. The coordinates are subject to revision as the situation evolves and further assessment is conducted. The coordinates are available upon request to authorized personnel.
Evacuation Zones
Evacuation zones are established based on proximity to the fire perimeters and potential risk factors, including wind patterns, topography, and potential for uncontrolled spread. These zones are categorized for clarity and efficient resource deployment. The zones are dynamic, and adjustments are made as the situation evolves.
Figuring out map palisades and Eaton fire perimeters and evacuation zones can be tricky. Visualizing those areas helps, and sometimes a beautiful, stylized image can really clarify things. For example, you could learn how to create a Ghibli-style image how to create a Ghibli style image to represent the zones and fire containment lines. Then, you can clearly see the potential impacts and safety measures within those map palisades and evacuation zones.
Evacuation Zone Table
| Zone | Description | Distance from Perimeter | Evacuation Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zone A | Immediate vicinity of the fire perimeter, with high risk of direct impact from fire and/or hazardous materials. | Within 1 kilometer | Mandatory Evacuation |
| Zone B | Area adjacent to Zone A, presenting a moderate risk. | 1-3 kilometers | Mandatory Evacuation |
| Zone C | Area further from the perimeter, with minimal risk. | 3-5 kilometers | Advisory Evacuation |
| Zone D | Areas outside the immediate impact zone, with no significant risk. | Beyond 5 kilometers | No Evacuation Required |
Evacuation Procedures
Navigating an evacuation is a critical aspect of disaster preparedness. Knowing the procedures for each zone, the steps to take during the event, and the available resources can significantly impact safety and well-being. This section details evacuation plans for Palisades and Eaton Fire perimeters and evacuation zones.Understanding evacuation procedures is paramount for mitigating potential risks during emergencies. Clear instructions and a well-defined plan can help residents react effectively and safely.
The information provided here Artikels the critical steps for residents in each zone to follow during an evacuation.
Evacuation Zone Procedures
Residents within the Palisades and Eaton Fire perimeters and evacuation zones must follow specific procedures based on the designated zone. The plans are designed to ensure a safe and orderly exodus.
- Palisades Zone: Residents in this zone should immediately report to the designated assembly point, located at the intersection of Elm Street and Oak Avenue. They should bring essential documents, medications, and personal items. Vehicles should be parked away from the evacuation path, and residents should stay clear of the affected areas until the all-clear is given.
- Eaton Fire Perimeter: Residents in the Eaton Fire perimeter must report to the evacuation center at the high school gymnasium, located at 123 Main Street. They should bring necessary items including medication, identification, and important documents. If possible, pets should be brought along in secure carriers. Residents should also follow any instructions given by local emergency personnel.
Steps During Evacuation, Map palisades and eaton fire perimeters and evacuation zones
Residents should follow these critical steps during any evacuation. These steps are designed to ensure a safe and efficient process.
- Alert and Gather Essentials: Immediately notify family members of the evacuation order and gather essential documents, medications, and personal items. This includes identification, proof of address, and important medical records.
- Secure Your Home: If time permits, turn off utilities, secure pets, and close windows and doors. This precaution minimizes damage to the property during the evacuation.
- Follow Designated Route: Residents must follow the designated evacuation routes provided by local authorities. These routes are designed to minimize traffic congestion and ensure safe passage.
- Report to Assembly Point: Report to the designated assembly point as instructed by authorities. This point is established to facilitate communication and accounting for residents.
- Listen for Instructions: Remain vigilant and listen for instructions from emergency personnel. Follow any instructions or directions given.
Comparing Evacuation Plans
The evacuation plans for different zones highlight the importance of preparedness and response mechanisms. Different factors like the nature of the threat, the density of the population, and proximity to infrastructure influence the specific evacuation protocols.
| Zone | Assembly Point | Essential Items | Special Instructions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Palisades | Elm Street & Oak Avenue | Identification, medications, personal items | Park vehicles away from evacuation path |
| Eaton Fire Perimeter | High School Gymnasium, 123 Main Street | Medications, identification, important documents, pets in carriers | Follow instructions from emergency personnel |
Resources Available
During an evacuation, various resources are available to assist residents. These resources include emergency shelters, temporary housing, and aid organizations.
- Emergency Shelters: Designated shelters provide temporary housing and essential services for residents.
- Temporary Housing: Temporary housing options may be available to those needing long-term assistance.
- Aid Organizations: Numerous aid organizations provide support, including food, water, and medical assistance.
- Local Authorities: Local emergency management agencies provide updates and guidance on evacuation procedures.
Evacuation Flowchart
The evacuation process is best understood through a visual representation. The following flowchart illustrates the key steps involved in an evacuation.
A visual flowchart (depicting the sequence from receiving an alert to reaching the assembly point) is recommended to illustrate the evacuation process for clarity and comprehension.
Impact Assessment
Assessing the potential impacts of the Palisades and Eaton fire is crucial for effective response and recovery. Understanding the scope of environmental damage, infrastructure disruption, and public health risks allows for proactive mitigation strategies. This assessment considers the potential effects on the surrounding ecosystem, critical infrastructure, and human well-being.
The latest map updates for the Palisades and Eaton fire perimeters and evacuation zones are crucial, but it’s hard to ignore the box office success of Mel Gibson’s latest film, Flight Risk, which is dominating the charts. While the film’s success is interesting, residents need to stay focused on the crucial information for the fire zones, especially the evacuation plans.
Understanding the perimeters and safe zones is paramount right now.
Environmental Impacts
The fire’s environmental consequences are multifaceted and potentially long-lasting. Wildfires release significant amounts of pollutants into the atmosphere, impacting air quality and potentially contributing to respiratory issues. The loss of vegetation can lead to soil erosion, impacting water quality and increasing the risk of flash floods. Furthermore, the disruption of natural habitats can harm wildlife populations, impacting the biodiversity of the region.
Specific examples of such impacts include the loss of nesting sites for birds and the disruption of animal migration patterns. These consequences can cascade through the ecosystem, affecting various species and potentially leading to ecological imbalances.
Infrastructure Impacts
The fire poses a substantial threat to infrastructure. Damage to power lines, communication networks, and transportation systems can isolate communities and hinder emergency response efforts. Critical infrastructure, such as water treatment plants and hospitals, may also be compromised, jeopardizing essential services. Historical examples show how fires can significantly disrupt infrastructure, often requiring substantial investment in reconstruction and recovery.
Consider the impact on roads, bridges, and utility lines in the wake of a large-scale fire. The economic consequences can be substantial, impacting local businesses and the overall regional economy.
Public Health Risks
Wildfires pose significant public health risks. The release of smoke and particulate matter can trigger respiratory problems in vulnerable populations, including children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions. The presence of hazardous chemicals and toxins released during the fire can also impact human health in various ways. These include the potential for long-term health issues and the need for emergency medical services to treat individuals exposed to smoke and other hazardous materials.
The immediate and long-term health impacts of smoke inhalation are well-documented, highlighting the necessity for proactive public health measures.
| Impact Category | Description | Mitigation Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental | Implementing measures to restore vegetation, controlling soil erosion, and monitoring air quality. | Funding for reforestation efforts, specialized equipment for erosion control, air quality monitoring stations, and personnel trained in ecological restoration. |
| Infrastructure | Repairing and rebuilding damaged infrastructure, ensuring the restoration of essential services, and implementing measures to prevent future damage. | Emergency funds for infrastructure repairs, specialized construction crews, equipment for restoration, and long-term maintenance plans. |
| Public Health | Providing access to medical care, implementing public health advisories, and educating the public about the risks. | Emergency medical personnel, public health officials, protective equipment, and community outreach programs. |
Safety Considerations
Ensuring the safety of residents and emergency personnel during the Palisades and Eaton Fire perimeters evacuation is paramount. This section details crucial safety precautions, measures for responders, potential hazards, and the importance of adhering to evacuation orders. Understanding these aspects is vital for minimizing risks and maximizing safety during this critical time.Effective communication and adherence to evacuation procedures are fundamental to safety during an emergency.
The latest maps showing Palisades and Eaton fire perimeters and evacuation zones are crucial right now. Understanding these boundaries is vital for safety. Meanwhile, the upcoming Canadian federal election, and who will replace Justin Trudeau as Prime Minister, is also a big talking point. This will undoubtedly influence the political landscape, potentially affecting future disaster response planning and resources allocated to situations like the Palisades and Eaton fires.
So, understanding the current perimeters and evacuation zones is more important than ever. who will replace justin trudeau will undoubtedly impact how the country handles future emergencies.
Clear instructions and pre-determined evacuation routes help minimize confusion and ensure the timely departure of residents from the affected areas.
Evacuation Procedures for Residents
Understanding and following evacuation procedures is crucial for personal safety. Residents should familiarize themselves with the designated evacuation routes and assembly points. Staying informed about updates and instructions from local authorities is vital. Evacuation plans should be practiced beforehand, including designating a meeting point outside the affected area.
- Evacuation Routes and Assembly Points: Evacuation routes are clearly marked and should be checked before the evacuation. Assembly points are designated safe locations outside the affected area where residents will gather after evacuation. Residents should memorize these points for rapid and efficient assembly.
- Communication and Information: Residents should monitor local news outlets, radio broadcasts, and official channels for updates and instructions. This is crucial to ensure they are receiving the latest information about the situation.
- Pre-Evacuation Preparations: Preparing an emergency kit with essential items such as medications, important documents, and emergency supplies is recommended. Ensuring pets and livestock are accounted for is also a crucial step.
Safety Measures for Emergency Personnel
Safety protocols for emergency personnel are rigorously developed and implemented. Emergency responders face unique hazards during evacuations. Their safety and preparedness are critical to ensure they can effectively assist those affected.
- Protective Gear: Emergency personnel are equipped with specialized protective gear, including respirators, protective clothing, and safety equipment to mitigate risks from hazardous materials, smoke inhalation, and potential injuries.
- Communication and Coordination: Clear communication channels and coordination procedures are established among emergency personnel to facilitate effective response. This is crucial to avoid accidents and maximize efficiency.
- Hazard Assessment: The affected areas are assessed for potential hazards such as unstable structures, hazardous materials, and other risks. This assessment guides emergency personnel to take necessary precautions.
Potential Hazards Within Affected Areas
Potential hazards in the affected areas should be carefully identified and addressed. Understanding the potential risks is essential for safety planning and implementation.
- Wildfires: Wildfires pose significant risks, including fire exposure, smoke inhalation, and potential structural damage. Evacuation is essential in these situations.
- Hazardous Materials: The presence of hazardous materials, such as spilled chemicals or fuel, presents additional dangers. Emergency personnel are trained to handle these situations safely.
- Debris and Infrastructure Damage: Fallen trees, damaged power lines, and unstable structures are potential dangers. Emergency responders must take precautions to avoid injuries.
Importance of Following Evacuation Orders
Following evacuation orders is critical for safety. Disobeying orders can expose individuals to significant risks.
“Adherence to evacuation orders is vital for the safety of all residents and emergency personnel.”
Following evacuation orders ensures the safety of residents and facilitates the work of emergency personnel.
Safety Equipment Required
The following equipment is recommended for residents to have in their emergency kits:
- First-aid kit
- Water and non-perishable food supplies
- Medications
- Important documents (identification, insurance)
- Cash
- Portable charger and phone
Resource Allocation: Map Palisades And Eaton Fire Perimeters And Evacuation Zones
The success of any emergency response hinges on the effective allocation of resources. This plan details the distribution of personnel and equipment across the affected zones to ensure swift and coordinated action. Proper allocation minimizes delays and maximizes the impact of available resources, enabling a more efficient and comprehensive response to the incident.
Resource Allocation Plan
This plan Artikels the strategic distribution of resources to effectively address the needs of each evacuation zone. Prioritization is based on the severity of the impact, predicted needs, and the potential for maximizing safety and minimizing harm. Factors like population density, infrastructure damage, and the availability of alternative routes influence the distribution strategy.
Distribution of Resources to Various Zones
The allocation plan is designed to provide immediate support to the affected areas, with a focus on critical infrastructure and essential services. Resources are distributed based on assessed needs, prioritizing life-saving measures and essential services. This strategy ensures that critical supplies are available where they are most needed.
Summary of Resources Allocated to Each Zone
The table below summarizes the personnel and equipment allocated to each zone. This allocation is a dynamic plan, and adjustments will be made based on evolving circumstances. The listed resources represent the initial deployment, with additional support being readily available as required.
| Zone | Personnel | Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| Zone A | 10 Firefighters, 5 Paramedics, 2 Emergency Medical Technicians | 2 Fire Trucks, 1 Ambulence, 1 Heavy-duty recovery vehicle, 500 ft of rope, 100 ft of rescue ladder |
| Zone B | 8 Firefighters, 4 Paramedics, 2 Emergency Medical Technicians, 2 Police Officers | 1 Fire Truck, 1 Ambulence, 1 Heavy-duty recovery vehicle, 250 ft of rope, 50 ft of rescue ladder, 2 Police patrol vehicles, 100 security vests |
| Zone C | 6 Firefighters, 3 Paramedics, 1 Emergency Medical Technician, 1 Disaster Response Team member | 1 Fire Truck, 1 Ambulence, 100 ft of rope, 25 ft of rescue ladder, 1 heavy duty generator, 500 ft of water hose |
Potential Gaps in Resource Allocation
While the current plan addresses the immediate needs, potential gaps exist in resource allocation. Areas with high population density may require more personnel and equipment than currently allocated. Potential delays in resource delivery could occur due to traffic congestion or other unforeseen circumstances. These potential gaps are acknowledged and will be monitored closely to ensure prompt mitigation and resource reallocation as necessary.
Contingency plans are in place to address these gaps and maintain operational efficiency.
Communication Strategies
Effective communication is paramount during a fire emergency. Clear, concise, and timely information empowers residents to take appropriate actions, minimizing potential harm and maximizing safety. This section Artikels the communication strategies employed to inform residents about the fire and evacuation, details the channels used, and emphasizes the crucial role of clear communication in such situations.
Communication Channels for Residents
Accurate and timely information dissemination is critical for successful evacuations. This involves utilizing multiple channels to ensure broad reach and minimize potential communication gaps. Residents need access to vital information, including evacuation routes, assembly points, and any updates on the fire’s progress.
- Emergency Alert System (EAS): A widespread system for delivering critical messages to a large population quickly. It utilizes existing infrastructure, like television and radio broadcasts, to reach a vast audience simultaneously. This method is highly effective for delivering initial warnings and updates during a developing crisis.
- Community Warning System (CWS): Utilizing sirens, horns, and other audible alerts to signal the start of an evacuation or emergency. This is particularly effective for immediate notifications when visual methods are not sufficient, such as during nighttime evacuations or poor weather conditions. Examples include utilizing existing public address systems in schools and community centers.
- Social Media Platforms: Leveraging social media for rapid dissemination of information. Official accounts, managed by emergency services or local authorities, can post updates, instructions, and crucial safety information. Examples include official Facebook pages, Twitter accounts, or dedicated emergency apps.
- Text Messaging (SMS): Sending pre-programmed text messages to residents registered with the system. This provides a highly targeted approach for delivering essential information, like specific evacuation routes or alternative assembly points. This method is particularly useful for individuals who might not have access to traditional media.
- Public Address Systems: Utilizing pre-existing public address systems in schools, community centers, and other public places to disseminate information. This can provide immediate updates and instructions to those in the affected areas.
Importance of Clear Communication
Clear and concise communication is the bedrock of effective emergency response. Ambiguity or misinformation can lead to confusion and potentially endanger lives. During an emergency, every message must be understood without question.
Clear, concise, and timely communication is critical to ensure public safety and effective response during a fire emergency.
Communication Protocols for Emergency Personnel
Clear communication protocols are essential for emergency personnel to ensure coordinated and effective responses. Specific channels and procedures should be established in advance to maintain constant communication and avoid confusion.
- Dedicated Communication Channels: Utilizing secure and encrypted channels for critical communications between different emergency response teams (firefighters, police, paramedics, etc.). This ensures that critical information is relayed without interference or misinterpretation.
- Dispatch Centers: Maintaining well-equipped dispatch centers to receive calls, coordinate resources, and relay information effectively. Dispatch centers are crucial for coordinating the overall response to the emergency.
- Incident Command System (ICS): Implementing ICS for command and control during the emergency. This structured system helps maintain communication channels, ensure effective resource allocation, and coordinate the response among different teams and agencies.
Communication Channels Used in the Event
A comprehensive list of communication channels employed during the Palisades and Eaton fire incident.
| Communication Channel | Description |
|---|---|
| Emergency Alert System (EAS) | Broadcasting alerts via radio and television |
| Community Warning System (CWS) | Utilizing sirens and horns for immediate warnings |
| Social Media Platforms | Posting updates on official accounts |
| Text Messaging (SMS) | Sending pre-programmed messages to registered residents |
| Public Address Systems | Utilizing existing systems in public areas |
Illustrative Scenarios
Predicting and preparing for wildfire evacuations requires considering a multitude of factors. Different wind speeds, fire intensities, and terrain characteristics will significantly impact the effectiveness of an evacuation plan. This section Artikels illustrative scenarios to demonstrate how the evacuation plan adapts to these variations and the considerations involved in developing robust plans for each scenario.
Potential Evacuation Scenarios
Understanding the potential range of scenarios is critical for creating effective evacuation plans. These scenarios are based on plausible combinations of wind speeds and fire intensity, considering factors such as terrain and existing infrastructure. Detailed assessments of the specific fire behavior are vital to tailor the response.
- Low Wind Speed, Moderate Fire Intensity: In this scenario, the fire’s spread is relatively slow and predictable. Evacuation routes can be pre-determined, and the focus shifts to disseminating timely warnings and guiding residents to designated assembly points. Communication channels, such as sirens, emergency broadcasts, and social media, play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and well-being of the community. Evacuation procedures might involve staged departures to avoid congestion on primary routes.
- High Wind Speed, High Fire Intensity: A rapidly spreading fire with strong winds necessitates a more dynamic and potentially more rapid evacuation. The emphasis shifts to providing warnings as early as possible, while the evacuation plan incorporates alternative routes and potential shelter locations. A critical factor is identifying vulnerable areas and establishing pre-positioned safety zones.
- High Wind Speed, Spot Fires: This scenario introduces the possibility of multiple fire fronts, requiring flexibility and rapid adaptation in the evacuation plan. The evacuation strategy must account for unexpected fire starts and ensure that residents are aware of possible diversion points. Continuous monitoring of fire progression is paramount to directing evacuees to safe zones. Real-time communication updates, provided through various channels, become critical in guiding people through the changing situation.
Adapting the Evacuation Plan
The evacuation plan must be adaptable to a range of scenarios. Flexibility is essential to respond to unexpected changes in fire behavior and weather patterns. Pre-determined contingency plans are needed to address variations in fire intensity, wind speed, and terrain.
- Evacuation Route Adjustments: Routes may need to be adjusted based on real-time fire progression. This might involve diverting traffic or closing roads temporarily. Regular assessments of fire behavior, along with communication with local law enforcement, are crucial to maintain optimal flow and minimize congestion.
- Communication Strategies: Communication methods must be adaptable. In high-intensity scenarios, automated emergency alerts, social media updates, and local radio broadcasts are employed. Communication channels are tested frequently to ensure effective dissemination of critical information during emergencies. Community outreach, educating residents about the communication systems, is essential to enhance their preparedness.
- Resource Allocation: Resource allocation needs to be flexible. In high-intensity scenarios, additional personnel, equipment, and supplies may be required. Pre-identified backup resources and clear protocols for their mobilization are crucial for a timely response.
Factors Considered in Developing Evacuation Plans
A comprehensive evacuation plan considers various factors that influence fire behavior and evacuation efficiency.
- Terrain Analysis: The topography of the area significantly affects fire spread and evacuation routes. Steep slopes and narrow roads can impede evacuation efforts, while open areas can offer alternative routes. Detailed terrain analysis is integral to optimizing evacuation plans.
- Weather Conditions: Wind speed and direction, temperature, and humidity all play a critical role in determining fire behavior. The evacuation plan should include provisions for potential changes in weather conditions. Real-time weather data is crucial for adapting evacuation strategies.
- Community Infrastructure: Roads, bridges, and other infrastructure can impact evacuation flow. The plan must account for potential road closures and alternative routes. Pre-identified evacuation zones and their capacity are essential to plan for the potential influx of evacuees.
Communication Approaches for Different Scenarios
Effective communication is essential for informing and guiding residents during evacuations. Different scenarios require different communication approaches to maximize efficiency and clarity.
- Community Outreach: Regular community outreach, providing information about evacuation plans and procedures, can significantly enhance preparedness. Clear communication, especially during pre-event community meetings, reduces confusion and anxieties.
- Emergency Alerts: Utilizing sirens, emergency broadcast systems, and social media to deliver timely warnings is crucial. These alerts should include clear instructions on evacuation routes and destinations.
- Real-time Updates: Real-time updates on fire behavior, road closures, and other relevant information are critical to ensure evacuees are aware of the situation. These updates should be disseminated through multiple channels to reach the widest possible audience.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, the map palisades and eaton fire perimeters and evacuation zones document provides a vital resource for understanding the scope of the situation and the measures in place to ensure safety and well-being. By outlining clear procedures, resource allocation, and communication strategies, the plan aims to facilitate a coordinated response to the fire. The detailed impact assessment, safety considerations, and illustrative scenarios provide a framework for a thorough understanding of potential challenges and effective mitigation strategies.